Abstract
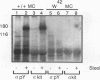
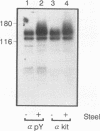
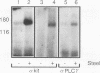
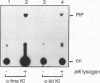
The W/c-kit and Steel loci respectively encode a receptor tyrosine kinase (Kit) and its extracellular ligand, Steel factor, which are essential for the development of hematopoietic, melanocyte, and germ cell lineages in the mouse. To determine the biochemical basis of the Steel/W developmental pathway, we have investigated the response of the Kit tyrosine kinase and several potential cytoplasmic targets to stimulation with Steel in mast cells derived from normal and mutant W mice. In normal mast cells, Steel induces Kit to autophosphorylate on tyrosine and bind to phosphatidylinositol 3'-kinase (PI3K) and phospholipase C-gamma 1 but not detectably to Ras GTPase-activating protein. Additionally, we present evidence that Kit tyrosine phosphorylation acts as a switch to promote complex formation with PI3K. In mast cells from mice homozygous for the W42 mutant allele, Kit is not tyrosine phosphorylated and fails to bind PI3K following Steel stimulation. In contrast, in the transformed mast cell line P815, Kit is constitutively phosphorylated and binds to PI3K in the absence of ligand. These results suggest that Kit autophosphorylation and its physical association with a unique subset of cytoplasmic signaling proteins are critical for mammalian development.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D., Koch C. A., Grey L., Ellis C., Moran M. F., Pawson T. Binding of SH2 domains of phospholipase C gamma 1, GAP, and Src to activated growth factor receptors. Science. 1990 Nov 16;250(4983):979–982. doi: 10.1126/science.2173144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aroian R. V., Koga M., Mendel J. E., Ohshima Y., Sternberg P. W. The let-23 gene necessary for Caenorhabditis elegans vulval induction encodes a tyrosine kinase of the EGF receptor subfamily. Nature. 1990 Dec 20;348(6303):693–699. doi: 10.1038/348693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein A., Chabot B., Dubreuil P., Reith A., Nocka K., Majumder S., Ray P., Besmer P. The mouse W/c-kit locus. Ciba Found Symp. 1990;148:158–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bjorge J. D., Chan T. O., Antczak M., Kung H. J., Fujita D. J. Activated type I phosphatidylinositol kinase is associated with the epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor following EGF stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 May;87(10):3816–3820. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.10.3816. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boswell H. S., Mochizuki D. Y., Burgess G. S., Gillis S., Walker E. B., Anderson D., Williams D. E. A novel mast cell growth factor (MCGF-3) produced by marrow-adherent cells that synergizes with interleukin 3 and interleukin 4. Exp Hematol. 1990 Aug;18(7):794–800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böni-Schnetzler M., Pilch P. F. Mechanism of epidermal growth factor receptor autophosphorylation and high-affinity binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):7832–7836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.7832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter C. L., Duckworth B. C., Auger K. R., Cohen B., Schaffhausen B. S., Cantley L. C. Purification and characterization of phosphoinositide 3-kinase from rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 15;265(32):19704–19711. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chabot B., Stephenson D. A., Chapman V. M., Besmer P., Bernstein A. The proto-oncogene c-kit encoding a transmembrane tyrosine kinase receptor maps to the mouse W locus. Nature. 1988 Sep 1;335(6185):88–89. doi: 10.1038/335088a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland N. G., Gilbert D. J., Cho B. C., Donovan P. J., Jenkins N. A., Cosman D., Anderson D., Lyman S. D., Williams D. E. Mast cell growth factor maps near the steel locus on mouse chromosome 10 and is deleted in a number of steel alleles. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90298-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coughlin S. R., Escobedo J. A., Williams L. T. Role of phosphatidylinositol kinase in PDGF receptor signal transduction. Science. 1989 Mar 3;243(4895):1191–1194. doi: 10.1126/science.2466336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A., Heber A. An 81 kd protein complexed with middle T antigen and pp60c-src: a possible phosphatidylinositol kinase. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1031–1037. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Decker S. J., Ellis C., Pawson T., Velu T. Effects of substitution of threonine 654 of the epidermal growth factor receptor on epidermal growth factor-mediated activation of phospholipase C. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):7009–7015. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downing J. R., Margolis B. L., Zilberstein A., Ashmun R. A., Ullrich A., Sherr C. J., Schlessinger J. Phospholipase C-gamma, a substrate for PDGF receptor kinase, is not phosphorylated on tyrosine during the mitogenic response to CSF-1. EMBO J. 1989 Nov;8(11):3345–3350. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08496.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubreuil P., Forrester L., Rottapel R., Reedijk M., Fujita J., Bernstein A. The c-fms gene complements the mitogenic defect in mast cells derived from mutant W mice but not mi (microphthalmia) mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 15;88(6):2341–2345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.6.2341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebi Y., Kasugai T., Seino Y., Onoue H., Kanemoto T., Kitamura Y. Mechanism of mast cell deficiency in mutant mice of mi/mi genotype: an analysis by co-culture of mast cells and fibroblasts. Blood. 1990 Mar 15;75(6):1247–1251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis C., Moran M., McCormick F., Pawson T. Phosphorylation of GAP and GAP-associated proteins by transforming and mitogenic tyrosine kinases. Nature. 1990 Jan 25;343(6256):377–381. doi: 10.1038/343377a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita J., Onoue H., Ebi Y., Nakayama H., Kanakura Y. In vitro duplication and in vivo cure of mast-cell deficiency of Sl/Sld mutant mice by cloned 3T3 fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2888–2891. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Hanafusa H. Phosphatidylinositol kinase activity associates with viral p60src protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1651–1658. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Kornbluth S., Jong S. M., Wang L. H., Hanafusa H. Phosphatidylinositol kinase type I activity associates with various oncogene products. Oncogene Res. 1989;4(4):283–292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geissler E. N., Ryan M. A., Housman D. E. The dominant-white spotting (W) locus of the mouse encodes the c-kit proto-oncogene. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):185–192. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90020-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heldin C. H., Ernlund A., Rorsman C., Rönnstrand L. Dimerization of B-type platelet-derived growth factor receptors occurs after ligand binding and is closely associated with receptor kinase activation. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 25;264(15):8905–8912. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann F. M. Roles of Drosophila proto-oncogene and growth factor homologs during development of the fly. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;147:1–29. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74697-0_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang E., Nocka K., Beier D. R., Chu T. Y., Buck J., Lahm H. W., Wellner D., Leder P., Besmer P. The hematopoietic growth factor KL is encoded by the Sl locus and is the ligand of the c-kit receptor, the gene product of the W locus. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):225–233. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90303-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Keller J., Oroszlan S., Henderson L. E., Copeland T. D., Fitch F., Prystowsky M. B., Goldwasser E., Schrader J. W., Palaszynski E. Biologic properties of homogeneous interleukin 3. I. Demonstration of WEHI-3 growth factor activity, mast cell growth factor activity, p cell-stimulating factor activity, colony-stimulating factor activity, and histamine-producing cell-stimulating factor activity. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Morrison D. K., Wong G., McCormick F., Williams L. T. PDGF beta-receptor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of GAP and association of GAP with a signaling complex. Cell. 1990 Apr 6;61(1):125–133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90220-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan D. R., Whitman M., Schaffhausen B., Pallas D. C., White M., Cantley L., Roberts T. M. Common elements in growth factor stimulation and oncogenic transformation: 85 kd phosphoprotein and phosphatidylinositol kinase activity. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1021–1029. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90168-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karasuyama H., Melchers F. Establishment of mouse cell lines which constitutively secrete large quantities of interleukin 2, 3, 4 or 5, using modified cDNA expression vectors. Eur J Immunol. 1988 Jan;18(1):97–104. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830180115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A. Autophosphorylation of the PDGF receptor in the kinase insert region regulates interactions with cell proteins. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1121–1133. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90510-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Cooper J. A. Phosphorylation of the PDGF receptor beta subunit creates a tight binding site for phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3279–3286. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07527.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kazlauskas A., Ellis C., Pawson T., Cooper J. A. Binding of GAP to activated PDGF receptors. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1578–1581. doi: 10.1126/science.2157284. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumjian D. A., Wahl M. I., Rhee S. G., Daniel T. O. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) binding promotes physical association of PDGF receptor with phospholipase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8232–8236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kypta R. M., Goldberg Y., Ulug E. T., Courtneidge S. A. Association between the PDGF receptor and members of the src family of tyrosine kinases. Cell. 1990 Aug 10;62(3):481–492. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90013-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Letwin K., Yee S. P., Pawson T. Novel protein-tyrosine kinase cDNAs related to fps/fes and eph cloned using anti-phosphotyrosine antibody. Oncogene. 1988 Dec;3(6):621–627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Margolis B., Rhee S. G., Felder S., Mervic M., Lyall R., Levitzki A., Ullrich A., Zilberstein A., Schlessinger J. EGF induces tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1101–1107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisenhelder J., Suh P. G., Rhee S. G., Hunter T. Phospholipase C-gamma is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein-tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1109–1122. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90048-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molloy C. J., Bottaro D. P., Fleming T. P., Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Aaronson S. A. PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase activating protein. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):711–714. doi: 10.1038/342711a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Koch C. A., Anderson D., Ellis C., England L., Martin G. S., Pawson T. Src homology region 2 domains direct protein-protein interactions in signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(21):8622–8626. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.21.8622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran M. F., Koch C. A., Sadowski I., Pawson T. Mutational analysis of a phosphotransfer motif essential for v-fps tyrosine kinase activity. Oncogene. 1988 Dec;3(6):665–672. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. K., Kaplan D. R., Escobedo J. A., Rapp U. R., Roberts T. M., Williams L. T. Direct activation of the serine/threonine kinase activity of Raf-1 through tyrosine phosphorylation by the PDGF beta-receptor. Cell. 1989 Aug 25;58(4):649–657. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishibe S., Wahl M. I., Hernández-Sotomayor S. M., Tonks N. K., Rhee S. G., Carpenter G. Increase of the catalytic activity of phospholipase C-gamma 1 by tyrosine phosphorylation. Science. 1990 Nov 30;250(4985):1253–1256. doi: 10.1126/science.1700866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocka K., Buck J., Levi E., Besmer P. Candidate ligand for the c-kit transmembrane kinase receptor: KL, a fibroblast derived growth factor stimulates mast cells and erythroid progenitors. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3287–3294. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocka K., Majumder S., Chabot B., Ray P., Cervone M., Bernstein A., Besmer P. Expression of c-kit gene products in known cellular targets of W mutations in normal and W mutant mice--evidence for an impaired c-kit kinase in mutant mice. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):816–826. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nocka K., Tan J. C., Chiu E., Chu T. Y., Ray P., Traktman P., Besmer P. Molecular bases of dominant negative and loss of function mutations at the murine c-kit/white spotting locus: W37, Wv, W41 and W. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1805–1813. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08305.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Bernstein A. Receptor tyrosine kinases: genetic evidence for their role in Drosophila and mouse development. Trends Genet. 1990 Nov;6(11):350–356. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(90)90276-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reedijk M., Liu X. Q., Pawson T. Interactions of phosphatidylinositol kinase, GTPase-activating protein (GAP), and GAP-associated proteins with the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5601–5608. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith A. D., Rottapel R., Giddens E., Brady C., Forrester L., Bernstein A. W mutant mice with mild or severe developmental defects contain distinct point mutations in the kinase domain of the c-kit receptor. Genes Dev. 1990 Mar;4(3):390–400. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.3.390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell E. S. Hereditary anemias of the mouse: a review for geneticists. Adv Genet. 1979;20:357–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrader J. W. The panspecific hemopoietin of activated T lymphocytes (interleukin-3). Annu Rev Immunol. 1986;4:205–230. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.04.040186.001225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shurtleff S. A., Downing J. R., Rock C. O., Hawkins S. A., Roussel M. F., Sherr C. J. Structural features of the colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor that affect its association with phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2415–2421. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07417.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugimoto Y., Whitman M., Cantley L. C., Erikson R. L. Evidence that the Rous sarcoma virus transforming gene product phosphorylates phosphatidylinositol and diacylglycerol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2117–2121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan J. C., Nocka K., Ray P., Traktman P., Besmer P. The dominant W42 spotting phenotype results from a missense mutation in the c-kit receptor kinase. Science. 1990 Jan 12;247(4939):209–212. doi: 10.1126/science.1688471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuji K., Nakahata T., Takagi M., Kobayashi T., Ishiguro A., Kikuchi T., Naganuma K., Koike K., Miyajima A., Arai K. Effects of interleukin-3 and interleukin-4 on the development of "connective tissue-type" mast cells: interleukin-3 supports their survival and interleukin-4 triggers and supports their proliferation synergistically with interleukin-3. Blood. 1990 Jan 15;75(2):421–427. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Schlessinger J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell. 1990 Apr 20;61(2):203–212. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90801-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varticovski L., Druker B., Morrison D., Cantley L., Roberts T. The colony stimulating factor-1 receptor associates with and activates phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):699–702. doi: 10.1038/342699a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitman M., Kaplan D., Roberts T., Cantley L. Evidence for two distinct phosphatidylinositol kinases in fibroblasts. Implications for cellular regulation. Biochem J. 1987 Oct 1;247(1):165–174. doi: 10.1042/bj2470165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiktor-Jedrzejczak W., Bartocci A., Ferrante A. W., Jr, Ahmed-Ansari A., Sell K. W., Pollard J. W., Stanley E. R. Total absence of colony-stimulating factor 1 in the macrophage-deficient osteopetrotic (op/op) mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4828–4832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Kuang W. J., Yang-Feng T., Coussens L., Munemitsu S., Dull T. J., Chen E., Schlessinger J., Francke U., Ullrich A. Human proto-oncogene c-kit: a new cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase for an unidentified ligand. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3341–3351. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02655.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yarden Y., Ullrich A. Growth factor receptor tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:443–478. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Hayashi S., Kunisada T., Ogawa M., Nishikawa S., Okamura H., Sudo T., Shultz L. D., Nishikawa S. The murine mutation osteopetrosis is in the coding region of the macrophage colony stimulating factor gene. Nature. 1990 May 31;345(6274):442–444. doi: 10.1038/345442a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yung Y. P., Eger R., Tertian G., Moore M. A. Long-term in vitro culture of murine mast cells. II. Purification of a mast cell growth factor and its dissociation from TCGF. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):794–799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zsebo K. M., Williams D. A., Geissler E. N., Broudy V. C., Martin F. H., Atkins H. L., Hsu R. Y., Birkett N. C., Okino K. H., Murdock D. C. Stem cell factor is encoded at the Sl locus of the mouse and is the ligand for the c-kit tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90302-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]