Abstract
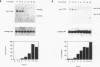
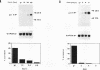
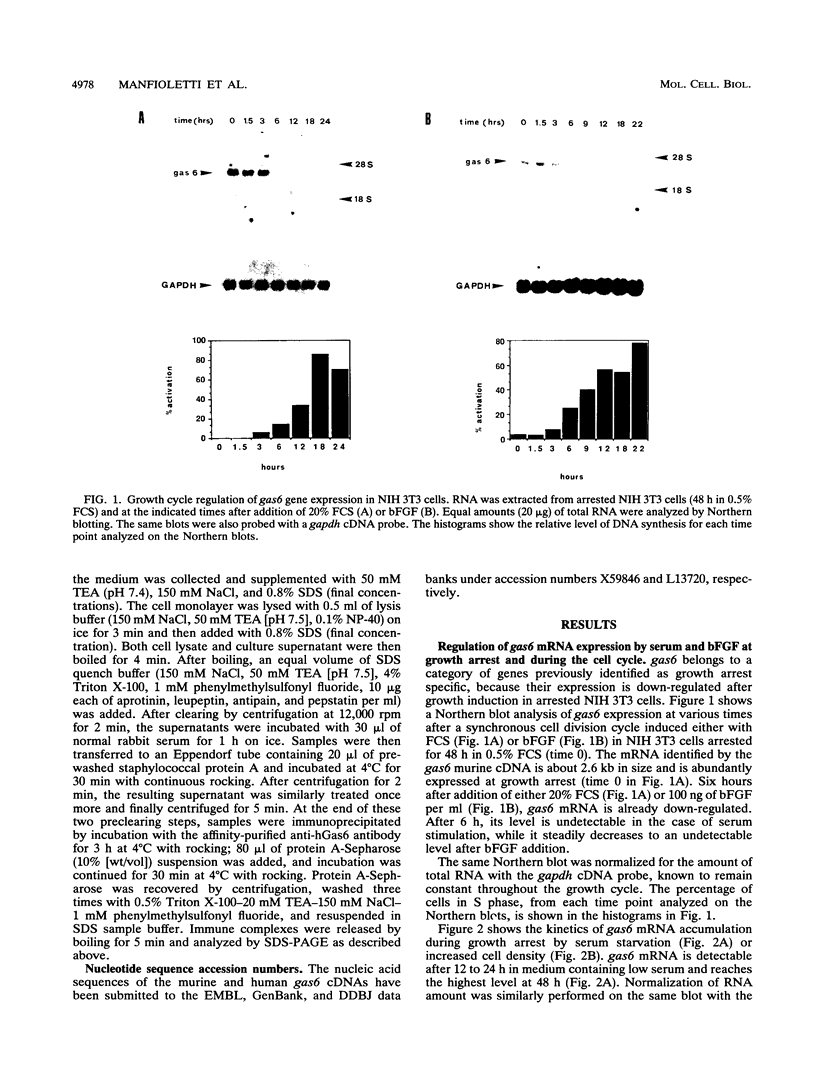
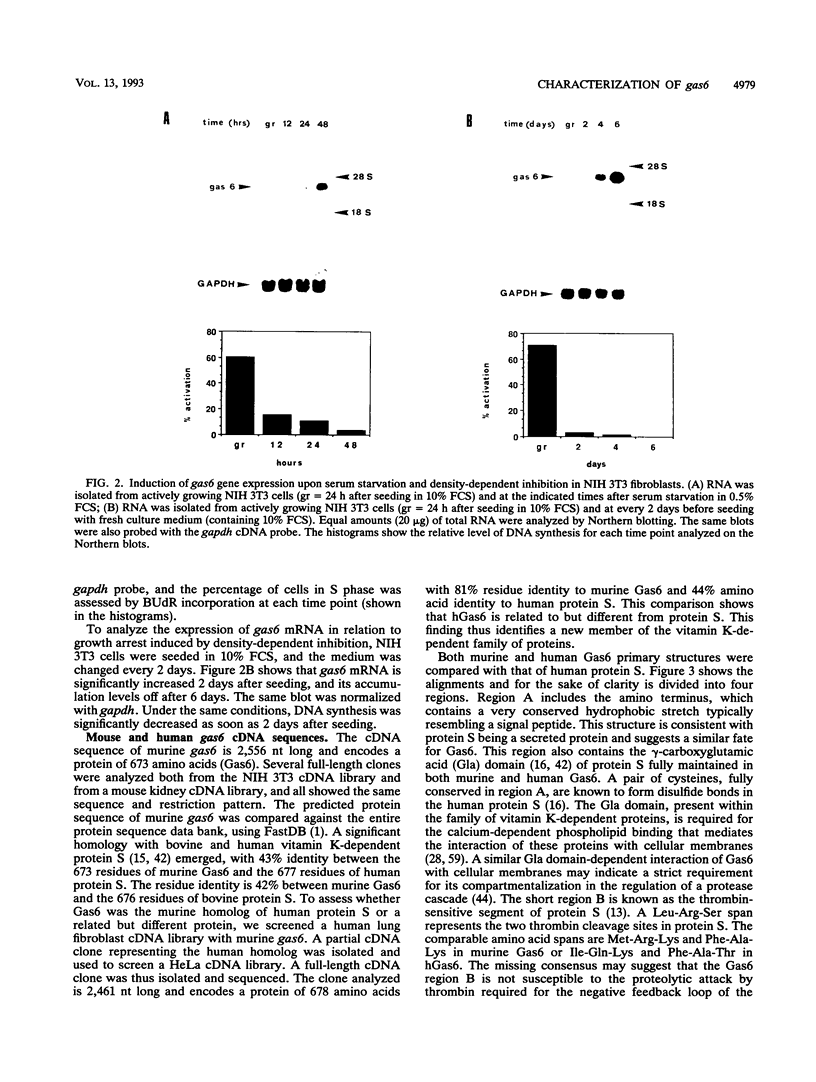
A set of growth arrest-specific genes (gas) whose expression is negatively regulated after serum induction has previously been described (C. Schneider, R. M. King, and L. Philipson, Cell 54:787-793, 1988). The detailed analysis of one of them, gas6, is reported here, gas6 mRNA (2.6 kb) is abundantly expressed in serum-starved (48 h in 0.5% fetal calf serum) NIH 3T3 cells but decreases dramatically after fetal calf serum or basic fibroblast growth factor stimulation. The human homolog of gas6 was also cloned and sequenced, revealing a high degree of homology and a similar pattern of expression in IMR90 human fibroblasts. Computer analysis of the protein encoded by murine and human gas6 cDNAs showed significant homology (43 and 44% amino acid identity, respectively) to human protein S, a negative coregulator in the blood coagulation pathway. By using an anti-human Gas6 monospecific affinity-purified antibody, we show that the biosynthetic level of human Gas6 fully reflects mRNA expression in IMR90 human fibroblasts. This finding thus defines a new member of vitamin K-dependent proteins that is expressed in many human and mouse tissues and may be involved in the regulation of a protease cascade relevant in growth regulation.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aukland K., Reed R. K. Interstitial-lymphatic mechanisms in the control of extracellular fluid volume. Physiol Rev. 1993 Jan;73(1):1–78. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1993.73.1.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker M. E., French F. S., Joseph D. R. Vitamin K-dependent protein S is similar to rat androgen-binding protein. Biochem J. 1987 Apr 1;243(1):293–296. doi: 10.1042/bj2430293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barr P. J. Mammalian subtilisins: the long-sought dibasic processing endoproteases. Cell. 1991 Jul 12;66(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90129-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beck K., Hunter I., Engel J. Structure and function of laminin: anatomy of a multidomain glycoprotein. FASEB J. 1990 Feb 1;4(2):148–160. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.2.2404817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binge D. Molecular matchmakers. Curr Biol. 1992 Oct;2(10):545–547. doi: 10.1016/0960-9822(92)90028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bottaro D. P., Rubin J. S., Faletto D. L., Chan A. M., Kmiecik T. E., Vande Woude G. F., Aaronson S. A. Identification of the hepatocyte growth factor receptor as the c-met proto-oncogene product. Science. 1991 Feb 15;251(4995):802–804. doi: 10.1126/science.1846706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brancolini C., Bottega S., Schneider C. Gas2, a growth arrest-specific protein, is a component of the microfilament network system. J Cell Biol. 1992 Jun;117(6):1251–1261. doi: 10.1083/jcb.117.6.1251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasan R., Anderson K. V. The role of easter, an apparent serine protease, in organizing the dorsal-ventral pattern of the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90242-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. B., Buchanan J. M. Mitogenic activity of blood components. I. Thrombin and prothrombin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):131–135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L. B., Teng N. N., Buchanan J. M. Mitogenicity of thrombin and surface alterations on mouse splenocytes. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Aug;101(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W. T. Membrane proteases: roles in tissue remodeling and tumour invasion. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1992 Oct;4(5):802–809. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(92)90103-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung L. P., Gagnon J., Reid K. B. Amino acid sequence studies of human C4b-binding protein: N-terminal sequence analysis and alignment of the fragments produced by limited proteolysis with chymotrypsin and the peptides produced by cyanogen bromide treatment. Mol Immunol. 1985 Apr;22(4):427–435. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90127-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Hildebrand B., Malm J. Characterization of functionally important domains in human vitamin K-dependent protein S using monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8127–8135. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Lundwall A., Stenflo J. Localization of thrombin cleavage sites in the amino-terminal region of bovine protein S. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5111–5115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Lundwall A., Stenflo J. Primary structure of bovine vitamin K-dependent protein S. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4199–4203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B. Purification of human vitamin K-dependent protein S and its limited proteolysis by thrombin. Biochem J. 1983 Mar 1;209(3):837–846. doi: 10.1042/bj2090837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlbäck B., Stenflo J. High molecular weight complex in human plasma between vitamin K-dependent protein S and complement component C4b-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2512–2516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Sal G., Manfioletti G., Schneider C. The CTAB-DNA precipitation method: a common mini-scale preparation of template DNA from phagemids, phages or plasmids suitable for sequencing. Biotechniques. 1989 May;7(5):514–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Del Sal G., Ruaro M. E., Philipson L., Schneider C. The growth arrest-specific gene, gas1, is involved in growth suppression. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):595–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90429-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Renzo M. F., Narsimhan R. P., Olivero M., Bretti S., Giordano S., Medico E., Gaglia P., Zara P., Comoglio P. M. Expression of the Met/HGF receptor in normal and neoplastic human tissues. Oncogene. 1991 Nov;6(11):1997–2003. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Feng D. F., Johnson M. S. Computer-based characterization of epidermal growth factor precursor. Nature. 1984 Feb 9;307(5951):558–560. doi: 10.1038/307558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorssers L., Postmes A. M. A simplified, orientation-specific cDNA cloning strategy. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3629–3629. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The regulation of natural anticoagulant pathways. Science. 1987 Mar 13;235(4794):1348–1352. doi: 10.1126/science.3029867. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esmon C. T. The roles of protein C and thrombomodulin in the regulation of blood coagulation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4743–4746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaumenhaft R., Abe M., Mignatti P., Rifkin D. B. Basic fibroblast growth factor-induced activation of latent transforming growth factor beta in endothelial cells: regulation of plasminogen activator activity. J Cell Biol. 1992 Aug;118(4):901–909. doi: 10.1083/jcb.118.4.901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flaumenhaft R., Rifkin D. B. Extracellular matrix regulation of growth factor and protease activity. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;3(5):817–823. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(91)90055-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita T., Gigli I., Nussenzweig V. Human C4-binding protein. II. Role in proteolysis of C4b by C3b-inactivator. J Exp Med. 1978 Oct 1;148(4):1044–1051. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.4.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furie B., Furie B. C. The molecular basis of blood coagulation. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90567-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasic G. P., Arenas C. P., Gasic T. B., Gasic G. J. Coagulation factors X, Xa, and protein S as potent mitogens of cultured aortic smooth muscle cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 15;89(6):2317–2320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.6.2317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershagen S., Fernlund P., Lundwall A. A cDNA coding for human sex hormone binding globulin. Homology to vitamin K-dependent protein S. FEBS Lett. 1987 Aug 10;220(1):129–135. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80890-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gherardi E., Stoker M. Hepatocytes and scatter factor. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):228–228. doi: 10.1038/346228b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gigli I., Fujita T., Nussenzweig V. Modulation of the classical pathway C3 convertase by plasma proteins C4 binding protein and C3b inactivator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6596–6600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimaldi G., Manfioletti G., Schneider C. A lambda vector for directional cDNA cloning and in vitro transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Nov 25;15(22):9608–9608. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.22.9608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handford P. A., Baron M., Mayhew M., Willis A., Beesley T., Brownlee G. G., Campbell I. D. The first EGF-like domain from human factor IX contains a high-affinity calcium binding site. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):475–480. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08133.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht P. M., Anderson K. V. Extracellular proteases and embryonic pattern formation. Trends Cell Biol. 1992 Jul;2(7):197–202. doi: 10.1016/0962-8924(92)90246-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessing M., Kanters D., Hackeng T. M., Bouma B. N. Identification of different forms of human C4b-binding protein lacking beta-chain and protein S binding ability. Thromb Haemost. 1990 Oct 22;64(2):245–250. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hessing M. The interaction between complement component C4b-binding protein and the vitamin K-dependent protein S forms a link between blood coagulation and the complement system. Biochem J. 1991 Aug 1;277(Pt 3):581–592. doi: 10.1042/bj2770581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillarp A., Hessing M., Dahlbäck B. Protein S binding in relation to the subunit composition of human C4b-binding protein. FEBS Lett. 1989 Dec 18;259(1):53–56. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)81492-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liotta L. A., Steeg P. S., Stetler-Stevenson W. G. Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):327–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90642-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundwall A., Dackowski W., Cohen E., Shaffer M., Mahr A., Dahlbäck B., Stenflo J., Wydro R. Isolation and sequence of the cDNA for human protein S, a regulator of blood coagulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6716–6720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manfioletti G., Ruaro M. E., Del Sal G., Philipson L., Schneider C. A growth arrest-specific (gas) gene codes for a membrane protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jun;10(6):2924–2930. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.6.2924. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann K. G., Jenny R. J., Krishnaswamy S. Cofactor proteins in the assembly and expression of blood clotting enzyme complexes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:915–956. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matrisian L. M. The matrix-degrading metalloproteinases. Bioessays. 1992 Jul;14(7):455–463. doi: 10.1002/bies.950140705. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montesano R., Matsumoto K., Nakamura T., Orci L. Identification of a fibroblast-derived epithelial morphogen as hepatocyte growth factor. Cell. 1991 Nov 29;67(5):901–908. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90363-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Nishizawa T., Hagiya M., Seki T., Shimonishi M., Sugimura A., Tashiro K., Shimizu S. Molecular cloning and expression of human hepatocyte growth factor. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):440–443. doi: 10.1038/342440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naldini L., Vigna E., Narsimhan R. P., Gaudino G., Zarnegar R., Michalopoulos G. K., Comoglio P. M. Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) stimulates the tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor encoded by the proto-oncogene c-MET. Oncogene. 1991 Apr;6(4):501–504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rebay I., Fleming R. J., Fehon R. G., Cherbas L., Cherbas P., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Specific EGF repeats of Notch mediate interactions with Delta and Serrate: implications for Notch as a multifunctional receptor. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):687–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90064-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin J. S., Chan A. M., Bottaro D. P., Burgess W. H., Taylor W. G., Cech A. C., Hirschfield D. W., Wong J., Miki T., Finch P. W. A broad-spectrum human lung fibroblast-derived mitogen is a variant of hepatocyte growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):415–419. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C., King R. M., Philipson L. Genes specifically expressed at growth arrest of mammalian cells. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):787–793. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimell M. J., Ferguson E. L., Childs S. R., O'Connor M. B. The Drosophila dorsal-ventral patterning gene tolloid is related to human bone morphogenetic protein 1. Cell. 1991 Nov 1;67(3):469–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90522-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stenflo J., Lundwall A., Dahlbäck B. beta-Hydroxyasparagine in domains homologous to the epidermal growth factor precursor in vitamin K-dependent protein S. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):368–372. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.368. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoolman L. M. Adhesion molecules controlling lymphocyte migration. Cell. 1989 Mar 24;56(6):907–910. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90620-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugo T., Dahlbäck B., Holmgren A., Stenflo J. Calcium binding of bovine protein S. Effect of thrombin cleavage and removal of the gamma-carboxyglutamic acid-containing region. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5116–5120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki K., Nishioka J., Hashimoto S. Regulation of activated protein C by thrombin-modified protein S. J Biochem. 1983 Sep;94(3):699–705. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vu T. K., Hung D. T., Wheaton V. I., Coughlin S. R. Molecular cloning of a functional thrombin receptor reveals a novel proteolytic mechanism of receptor activation. Cell. 1991 Mar 22;64(6):1057–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90261-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Characterization of a synthetic peptide that inhibits the interaction between protein S and C4b-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17645–17648. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J., Chavin S. I., Fay P. J. Inactivation of factor VIII by activated protein C and protein S. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Jan;252(1):322–328. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90037-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Regulation of activated protein C by a new protein. A possible function for bovine protein S. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 25;255(12):5521–5524. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker F. J. Regulation of activated protein C by protein S. The role of phospholipid in factor Va inactivation. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 10;256(21):11128–11131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberg R. A. Tumor suppressor genes. Science. 1991 Nov 22;254(5035):1138–1146. doi: 10.1126/science.1659741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wharton K. A., Johansen K. M., Xu T., Artavanis-Tsakonas S. Nucleotide sequence from the neurogenic locus notch implies a gene product that shares homology with proteins containing EGF-like repeats. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):567–581. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90229-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmermann D. R., Ruoslahti E. Multiple domains of the large fibroblast proteoglycan, versican. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2975–2981. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]