Abstract
Success in constructing a physical map of the human genome will depend on two capabilities: rapid resolution of very large DNA and identification of migration anomalies. To address these issues, a systematic exploration of pulsed-field electrophoresis conditions for separating multimegabase-sized DNA was undertaken. Conditions were found for first liberating and then separating DNA up to 6 megabases at higher field strengths and more rapidly than previously reported. In addition, some conditions for transversely pulsed fields produced mobility inversion, in which increased size was accompanied by faster rather than slower migration. Importantly, anomalous migration could be identified by the presence of lateral band spreading, in which the DNA band remained sharply defined but spread laterally while moving down the gel. These results have implications for both practical applications and theoretical models of pulsed-field electrophoresis.
Full text
PDF

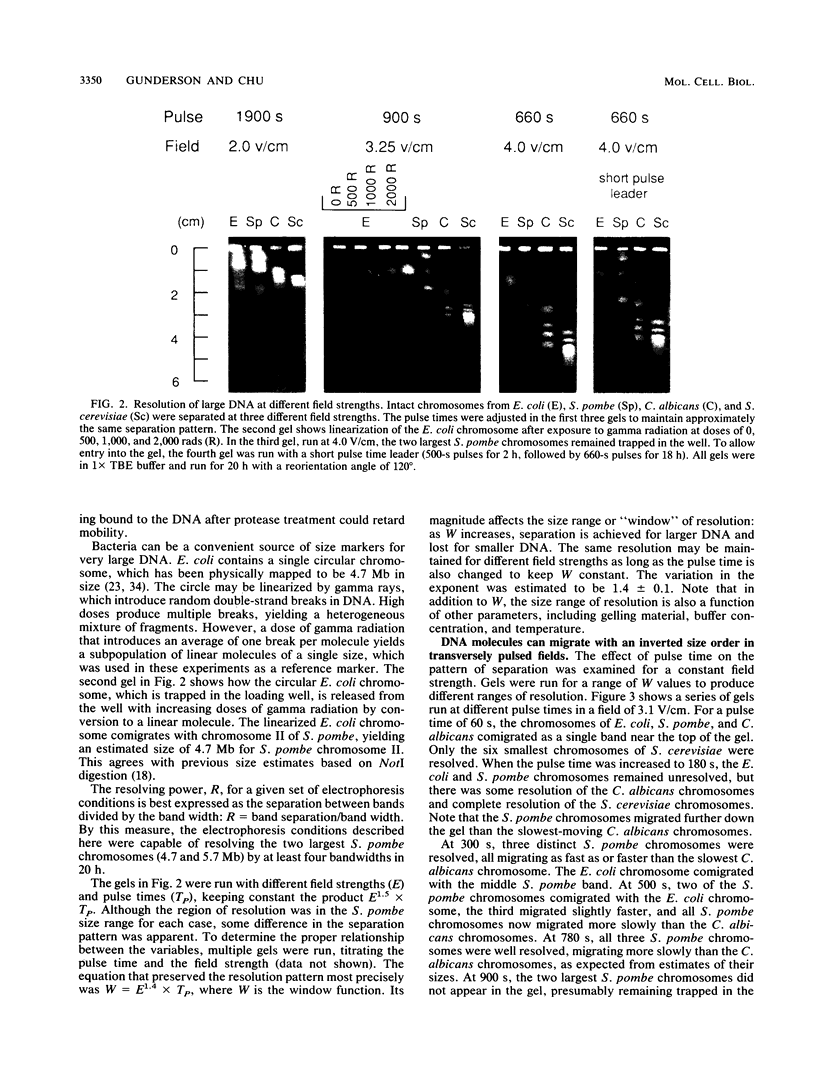
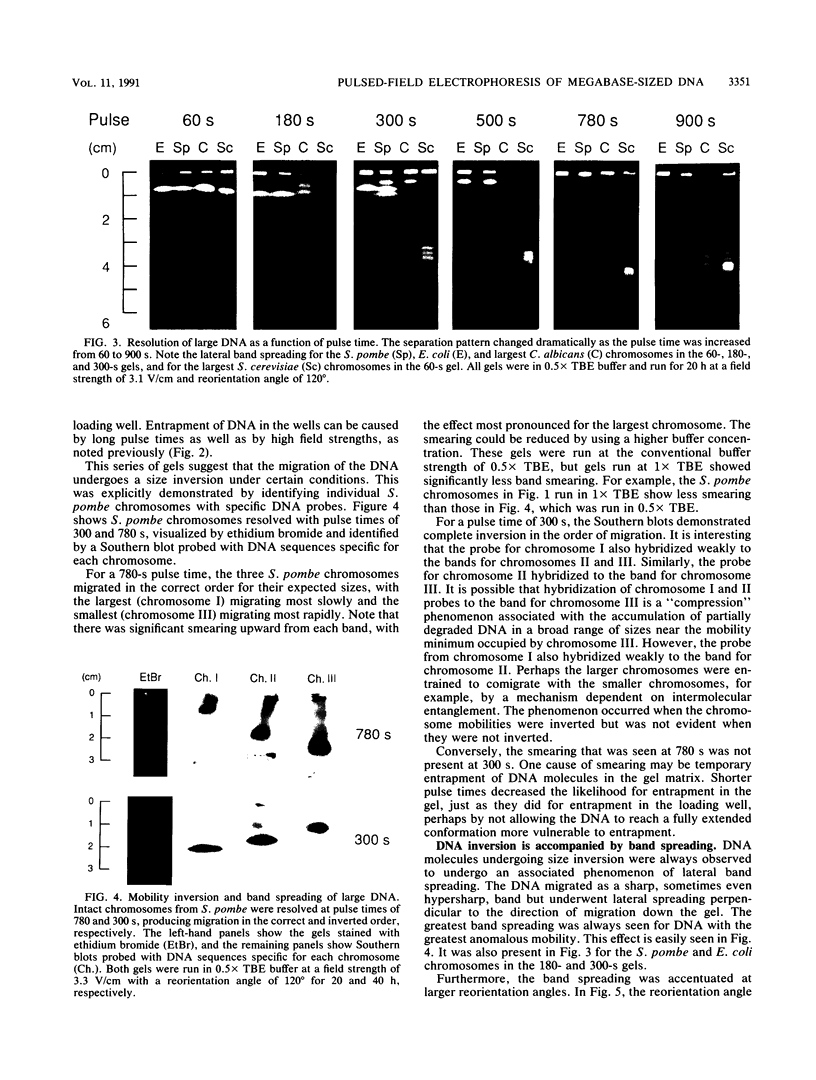



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beach D., Rodgers L., Gould J. ran1+ controls the transition from mitotic division to meiosis in fission yeast. Curr Genet. 1985;10(4):297–311. doi: 10.1007/BF00365626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beverley S. M. Estimation of circular DNA size using gamma-irradiation and pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1989 Feb 15;177(1):110–114. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90023-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birren B. W., Lai E., Clark S. M., Hood L., Simon M. I. Optimized conditions for pulsed field gel electrophoretic separations of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7563–7582. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Frank M., Olson M. V. Electrophoretic separations of large DNA molecules by periodic inversion of the electric field. Science. 1986 Apr 4;232(4746):65–68. doi: 10.1126/science.3952500. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. An electrophoretic karyotype for yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3756–3760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carle G. F., Olson M. V. Orthogonal-field-alternation gel electrophoresis. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:468–482. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G. Pulsed field electrophoresis in contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields for the resolution of DNA by size or topology. Electrophoresis. 1989 May-Jun;10(5-6):290–295. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150100504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu G., Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Separation of large DNA molecules by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Science. 1986 Dec 19;234(4783):1582–1585. doi: 10.1126/science.3538420. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deutsch J. M. Theoretical studies of DNA during gel electrophoresis. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):922–924. doi: 10.1126/science.3363374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan J. B., Chikashige Y., Smith C. L., Niwa O., Yanagida M., Cantor C. R. Construction of a Not I restriction map of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2801–2818. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardiner K., Laas W., Patterson D. Fractionation of large mammalian DNA restriction fragments using vertical pulsed-field gradient gel electrophoresis. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1986 Mar;12(2):185–195. doi: 10.1007/BF01560665. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurrieri S., Rizzarelli E., Beach D., Bustamante C. Imaging of kinked configurations of DNA molecules undergoing orthogonal field alternating gel electrophoresis by fluorescence microscopy. Biochemistry. 1990 Apr 3;29(13):3396–3401. doi: 10.1021/bi00465a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall J. L., Ramanis Z., Luck D. J. Basal body/centriolar DNA: molecular genetic studies in Chlamydomonas. Cell. 1989 Oct 6;59(1):121–132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90875-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Birren B. W., Clark S. M., Simon M. I., Hood L. Pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Biotechniques. 1989 Jan;7(1):34–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerman L. S., Frisch H. L. Why does the electrophoretic mobility of DNA in gels vary with the length of the molecule? Biopolymers. 1982 May;21(5):995–997. doi: 10.1002/bip.360210511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumpkin O. J., Déjardin P., Zimm B. H. Theory of gel electrophoresis of DNA. Biopolymers. 1985 Aug;24(8):1573–1593. doi: 10.1002/bip.360240812. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLeod M., Stein M., Beach D. The product of the mei3+ gene, expressed under control of the mating-type locus, induces meiosis and sporulation in fission yeast. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):729–736. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04814.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olvera de la Cruz M, Gersappe D, Shaffer EO. Dynamics of DNA during pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Phys Rev Lett. 1990 May 7;64(19):2324–2327. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.64.2324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orbach M. J., Vollrath D., Davis R. W., Yanofsky C. An electrophoretic karyotype of Neurospora crassa. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1469–1473. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philippsen P., Thomas M., Kramer R. A., Davis R. W. Unique arrangement of coding sequences for 5 S, 5.8 S, 18 S and 25 S ribosomal RNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae as determined by R-loop and hybridization analysis. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 15;123(3):387–404. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90086-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Cantor C. R. Separation of yeast chromosome-sized DNAs by pulsed field gradient gel electrophoresis. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):67–75. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90301-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. C., Koval M. Conformational dynamics of individual DNA molecules during gel electrophoresis. Nature. 1989 Apr 6;338(6215):520–522. doi: 10.1038/338520a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater G. W., Noolandi J. Effect of nonparallel alternating fields on the mobility of DNA in the biased reptation model of gel electrophoresis. Electrophoresis. 1989 May-Jun;10(5-6):413–428. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150100520. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Econome J. G., Schutt A., Klco S., Cantor C. R. A physical map of the Escherichia coli K12 genome. Science. 1987 Jun 12;236(4807):1448–1453. doi: 10.1126/science.3296194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Matsumoto T., Niwa O., Klco S., Fan J. B., Yanagida M., Cantor C. R. An electrophoretic karyotype for Schizosaccharomyces pombe by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 11;15(11):4481–4489. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.11.4481. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. B., Aldridge P. K., Callis J. B. Observation of individual DNA molecules undergoing gel electrophoresis. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):203–206. doi: 10.1126/science.2911733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith S. S., Gilroy T. E., Ferrari F. A. The influence of agarose--DNA affinity on the electrophoretic separation of DNA fragments in agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jan;128(1):138–151. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90354-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M., Anand R., Brown W. R., Fletcher D. S. A model for the separation of large DNA molecules by crossed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):5925–5943. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.5925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viovy J. L. Reptation-breathing theory of pulsed electrophoresis: dynamic regimes, antiresonance and symmetry breakdown effects. Electrophoresis. 1989 May-Jun;10(5-6):429–441. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150100521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vollrath D., Davis R. W. Resolution of DNA molecules greater than 5 megabases by contour-clamped homogeneous electric fields. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 12;15(19):7865–7876. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.19.7865. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]