Abstract
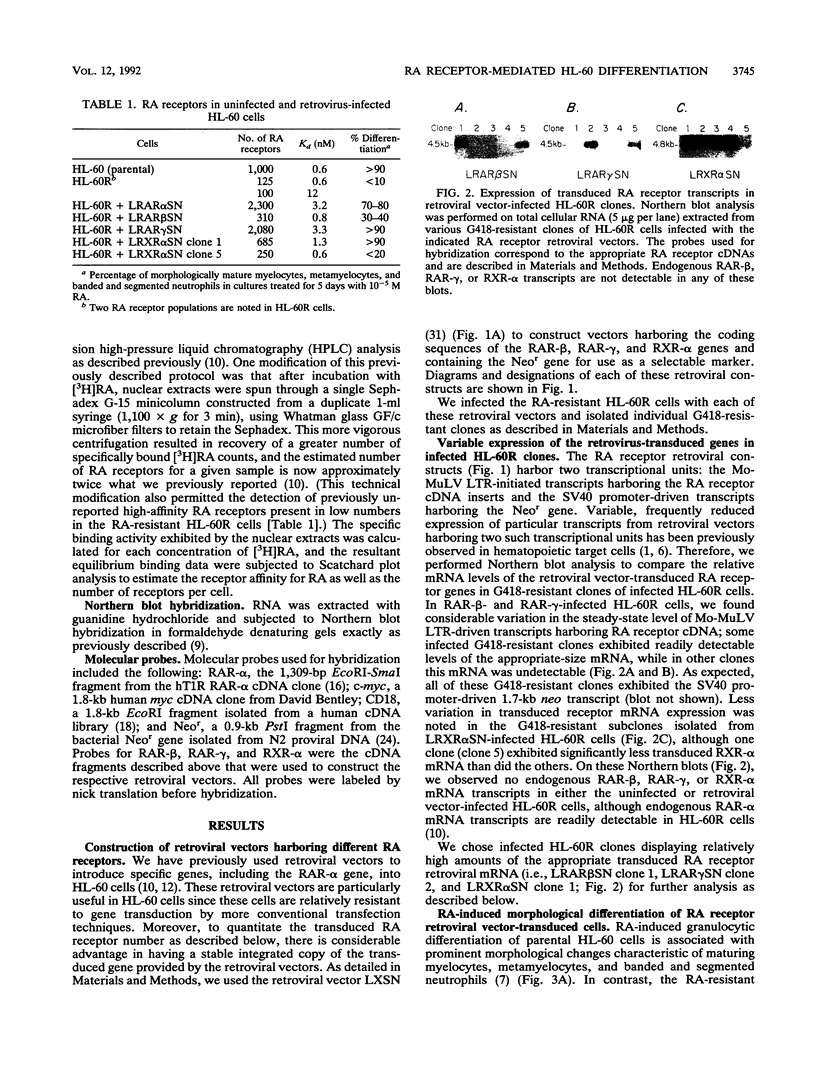
The complex and diverse biological effects of retinoic acid (RA) are mediated through specific receptors that are members of the steroid hormone family of nuclear transcription factors. The RA receptor family consists of multiple structurally distinct RA receptors, which diverge primarily at the NH2-terminal domain. The evolutionary conservation of this divergent region in individual RA receptors among different species together with their tissue-specific patterns of expression suggest that the biological function and activity of the individual RA receptors may be confined to specific tissues. To test this hypothesis in hematopoietic cells, we used retrovirus-mediated gene transduction to introduce the RA receptors RAR-alpha, RAR-beta, and RAR-gamma as well as RXR-alpha into a mutant subclone of the HL-60 promyelocytic leukemia cell line (designated HL-60R) that is relatively resistant to RA-induced granulocytic differentiation. We found that each of these structurally distinct RA receptors could restore sensitivity of the HL-60R cells to RA. A critical threshold number of transduced receptors per cell appears to be necessary to restore this functional activity. Thus, the capability to mediate granulocytic differentiation of HL-60 cells is shared among distinctly different RA receptors.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Apperley J. F., Luskey B. D., Williams D. A. Retroviral gene transfer of human adenosine deaminase in murine hematopoietic cells: effect of selectable marker sequences on long-term expression. Blood. 1991 Jul 15;78(2):310–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balling R., Mutter G., Gruss P., Kessel M. Craniofacial abnormalities induced by ectopic expression of the homeobox gene Hox-1.1 in transgenic mice. Cell. 1989 Jul 28;58(2):337–347. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90848-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook D., Lernhardt E., Pfahl M. A new retinoic acid receptor identified from a hepatocellular carcinoma. Nature. 1988 Jun 16;333(6174):669–672. doi: 10.1038/333669a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag W. Prophylaxis of chemically induced benign and malignant epithelial tumors by vitamin A acid (retinoic acid). Eur J Cancer. 1972 Dec;8(6):689–693. doi: 10.1016/0014-2964(72)90153-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowtell D. D., Cory S., Johnson G. R., Gonda T. J. Comparison of expression in hemopoietic cells by retroviral vectors carrying two genes. J Virol. 1988 Jul;62(7):2464–2473. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.7.2464-2473.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitman T. R., Selonick S. E., Collins S. J. Induction of differentiation of the human promyelocytic leukemia cell line (HL-60) by retinoic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2936–2940. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2936. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaigne S., Chomienne C., Daniel M. T., Ballerini P., Berger R., Fenaux P., Degos L. All-trans retinoic acid as a differentiation therapy for acute promyelocytic leukemia. I. Clinical results. Blood. 1990 Nov 1;76(9):1704–1709. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J. Different mechanisms account for the relative resistance of KG-1 and HL-60 cell lines to retrovirus infection. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4346–4348. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4346-4348.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Robertson K. A., Mueller L. Retinoic acid-induced granulocytic differentiation of HL-60 myeloid leukemia cells is mediated directly through the retinoic acid receptor (RAR-alpha). Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2154–2163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2154. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Ruscetti F. W., Gallagher R. E., Gallo R. C. Terminal differentiation of human promyelocytic leukemia cells induced by dimethyl sulfoxide and other polar compounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 May;75(5):2458–2462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.5.2458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S., Coleman H., Groudine M. Expression of bcr and bcr-abl fusion transcripts in normal and leukemic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2870–2876. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desbois C., Aubert D., Legrand C., Pain B., Samarut J. A novel mechanism of action for v-ErbA: abrogation of the inactivation of transcription factor AP-1 by retinoic acid and thyroid hormone receptors. Cell. 1991 Nov 15;67(4):731–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90068-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Shago M., Zirngibl R., Tate P., Rossant J., Varmuza S. Identification of a novel isoform of the retinoic acid receptor gamma expressed in the mouse embryo. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2335–2340. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickstein D. D., Hickey M. J., Collins S. J. Transcriptional regulation of the leukocyte adherence protein beta subunit during human myeloid cell differentiation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13863–13867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hock R. A., Miller A. D., Osborne W. R. Expression of human adenosine deaminase from various strong promoters after gene transfer into human hematopoietic cell lines. Blood. 1989 Aug 1;74(2):876–881. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
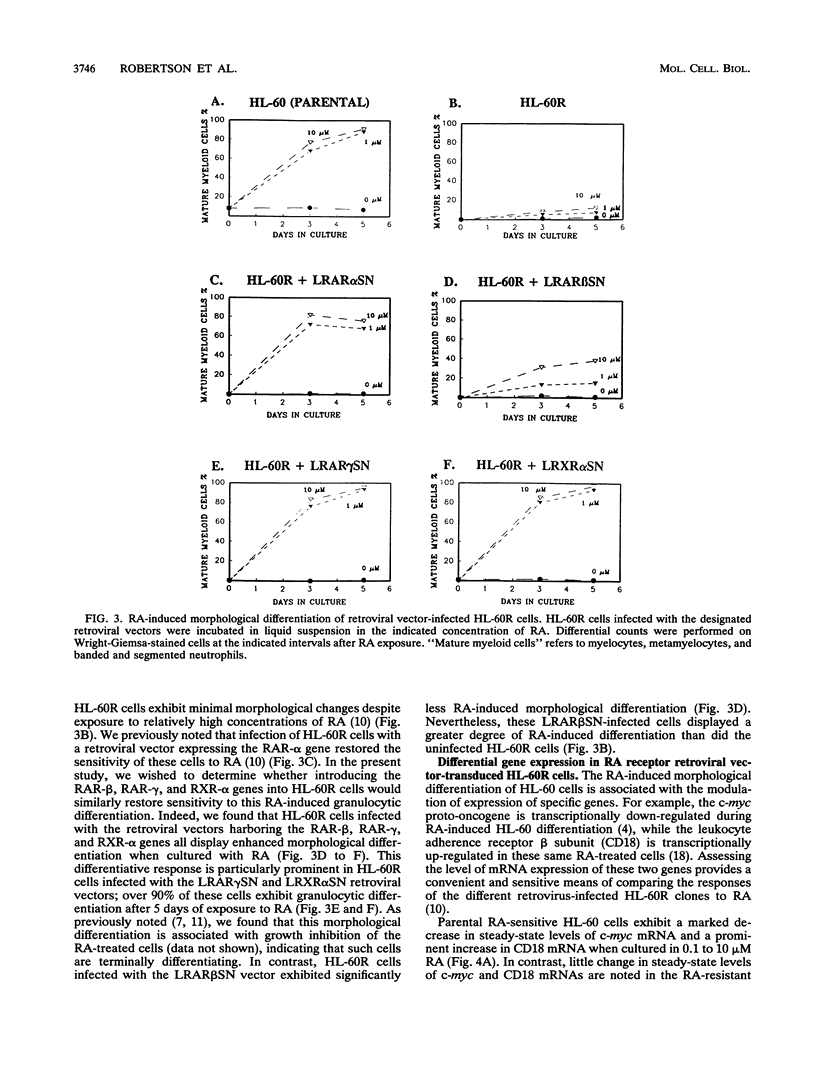
- Hong W. K., Lippman S. M., Itri L. M., Karp D. D., Lee J. S., Byers R. M., Schantz S. P., Kramer A. M., Lotan R., Peters L. J. Prevention of second primary tumors with isotretinoin in squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 1990 Sep 20;323(12):795–801. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199009203231205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang M. E., Ye Y. C., Chen S. R., Chai J. R., Lu J. X., Zhoa L., Gu L. J., Wang Z. Y. Use of all-trans retinoic acid in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 1988 Aug;72(2):567–572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishikawa T., Umesono K., Mangelsdorf D. J., Aburatani H., Stanger B. Z., Shibasaki Y., Imawari M., Evans R. M., Takaku F. A functional retinoic acid receptor encoded by the gene on human chromosome 12. Mol Endocrinol. 1990 Jun;4(6):837–844. doi: 10.1210/mend-4-6-837. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kastner P., Krust A., Mendelsohn C., Garnier J. M., Zelent A., Leroy P., Staub A., Chambon P. Murine isoforms of retinoic acid receptor gamma with specific patterns of expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2700–2704. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller G., Paige C., Gilboa E., Wagner E. F. Expression of a foreign gene in myeloid and lymphoid cells derived from multipotent haematopoietic precursors. Nature. 1985 Nov 14;318(6042):149–154. doi: 10.1038/318149a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Kastner P., Petkovich M., Zelent A., Chambon P. A third human retinoic acid receptor, hRAR-gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5310–5314. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leroy P., Krust A., Zelent A., Mendelsohn C., Garnier J. M., Kastner P., Dierich A., Chambon P. Multiple isoforms of the mouse retinoic acid receptor alpha are generated by alternative splicing and differential induction by retinoic acid. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):59–69. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07921.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotan R. Effects of vitamin A and its analogs (retinoids) on normal and neoplastic cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Mar 12;605(1):33–91. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(80)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangelsdorf D. J., Ong E. S., Dyck J. A., Evans R. M. Nuclear receptor that identifies a novel retinoic acid response pathway. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):224–229. doi: 10.1038/345224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merriman R. L., Bertram J. S. Reversible inhibition by retinoids of 3-methylcholanthrene-induced neoplastic transformation in C3H/10T1/2 clone 8 cells. Cancer Res. 1979 May;39(5):1661–1666. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Buttimore C. Redesign of retrovirus packaging cell lines to avoid recombination leading to helper virus production. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2895–2902. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Rosman G. J. Improved retroviral vectors for gene transfer and expression. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):980-2, 984-6, 989-90. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottman J. N., Widom R. L., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V., Karathanasis S. K. A retinoic acid-responsive element in the apolipoprotein AI gene distinguishes between two different retinoic acid response pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3814–3820. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüle R., Rangarajan P., Yang N., Kliewer S., Ransone L. J., Bolado J., Verma I. M., Evans R. M. Retinoic acid is a negative regulator of AP-1-responsive genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jul 15;88(14):6092–6096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.14.6092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thaller C., Eichele G. Isolation of 3,4-didehydroretinoic acid, a novel morphogenetic signal in the chick wing bud. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):815–819. doi: 10.1038/345815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tora L., Gronemeyer H., Turcotte B., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. The N-terminal region of the chicken progesterone receptor specifies target gene activation. Nature. 1988 May 12;333(6169):185–188. doi: 10.1038/333185a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrell R. P., Jr, Frankel S. R., Miller W. H., Jr, Scheinberg D. A., Itri L. M., Hittelman W. N., Vyas R., Andreeff M., Tafuri A., Jakubowski A. Differentiation therapy of acute promyelocytic leukemia with tretinoin (all-trans-retinoic acid). N Engl J Med. 1991 May 16;324(20):1385–1393. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199105163242002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelent A., Mendelsohn C., Kastner P., Krust A., Garnier J. M., Ruffenach F., Leroy P., Chambon P. Differentially expressed isoforms of the mouse retinoic acid receptor beta generated by usage of two promoters and alternative splicing. EMBO J. 1991 Jan;10(1):71–81. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07922.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de The H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. Differential expression and ligand regulation of the retinoic acid receptor alpha and beta genes. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):429–433. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03394.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]