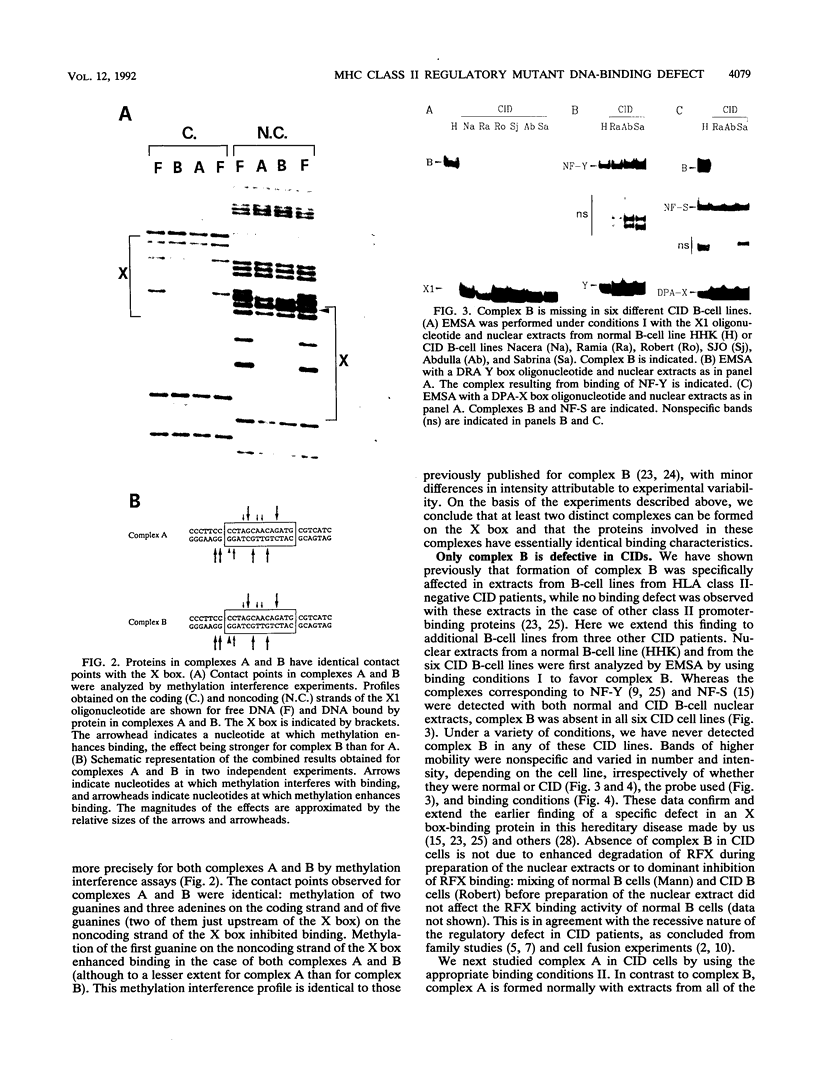
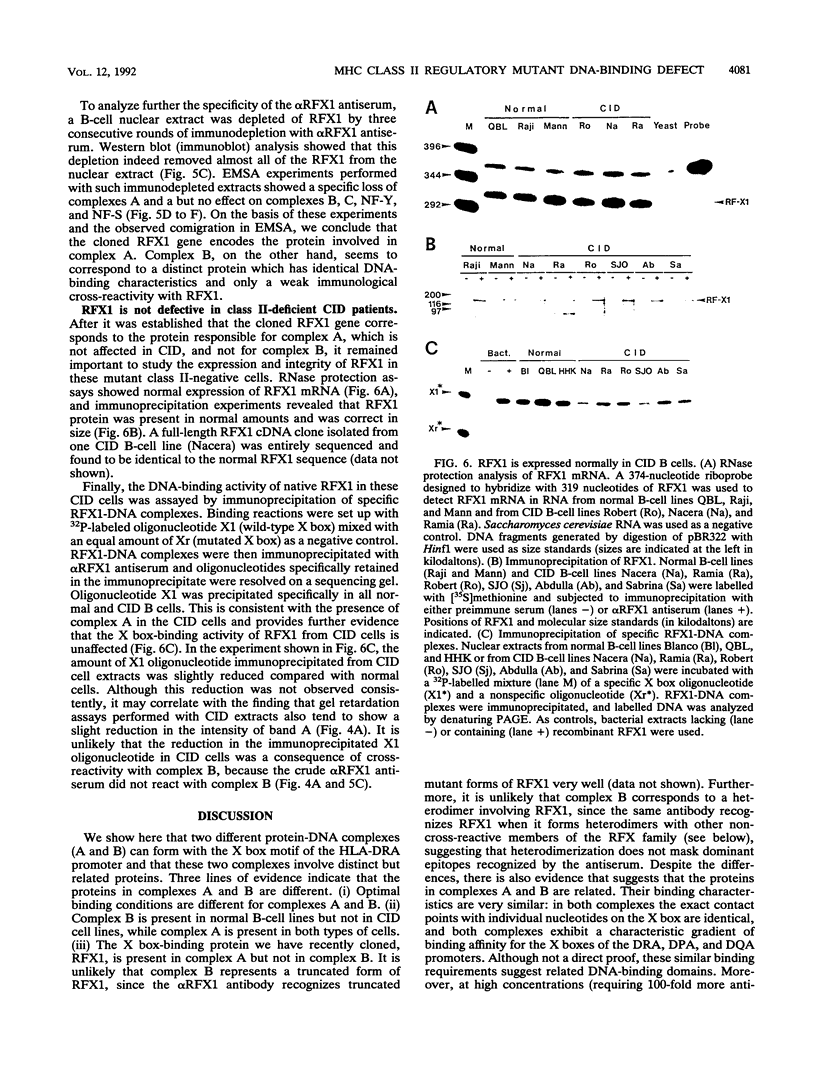
Abstract
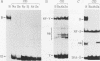
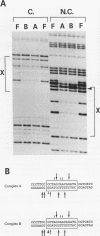
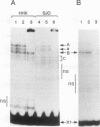
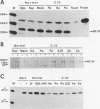
The X box of major histocompatibility complex class II promoters is essential for proper expression of class II genes. Here we show that two distinct protein-DNA complexes (A and B), which exhibit similar binding characteristics and identical contact points on the X box, can be formed. This suggests the existence of a family of related X box-binding factors. Complex B (and not complex A) is specifically affected in primary combined immunodeficiency, a congenital defect in class II gene regulation. RFX1, the first X box-binding protein cloned, encodes a functionally relevant factor present in complex A and not in complex B as originally suspected. This report also illustrates the need for caution in correlating specific cloned proteins with nuclear factors identified by DNA-binding assays, particularly when dealing with families of related proteins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson G., Peterlin B. M. NF-X2 that binds to the DRA X2-box is activator protein 1. Expression cloning of c-Jun. J Immunol. 1990 Nov 15;145(10):3456–3462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benoist C., Mathis D. Regulation of major histocompatibility complex class-II genes: X, Y and other letters of the alphabet. Annu Rev Immunol. 1990;8:681–715. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.08.040190.003341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bénichou B., Strominger J. L. Class II-antigen-negative patient and mutant B-cell lines represent at least three, and probably four, distinct genetic defects defined by complementation analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4285–4288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran J., Kolakofsky D. Scanning independent ribosomal initiation of the Sendai virus X protein. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2869–2874. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03143.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehling H. J., Viville S., van Ewijk W., Benoist C., Mathis D. Fine-tuning of MHC class II gene expression in defined microenvironments. Trends Genet. 1989 Oct;5(10):342–347. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90140-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griscelli C., Lisowska-Grospierre B., Mach B. Combined immunodeficiency with defective expression in MHC class II genes. Immunodefic Rev. 1989;1(2):135–153. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Levine M. Divergent homeo box proteins recognize similar DNA sequences in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):858–861. doi: 10.1038/332858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hooft van Huijsduijnen R., Li X. Y., Black D., Matthes H., Benoist C., Mathis D. Co-evolution from yeast to mouse: cDNA cloning of the two NF-Y (CP-1/CBF) subunits. EMBO J. 1990 Oct;9(10):3119–3127. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07509.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hume C. R., Lee J. S. Congenital immunodeficiencies associated with absence of HLA class II antigens on lymphocytes result from distinct mutations in trans-acting factors. Hum Immunol. 1989 Dec;26(4):288–309. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(89)90007-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivashkiv L. B., Liou H. C., Kara C. J., Lamph W. W., Verma I. M., Glimcher L. H. mXBP/CRE-BP2 and c-Jun form a complex which binds to the cyclic AMP, but not to the 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate, response element. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1609–1621. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes J. B., O'Farrell P. H. Activation and repression of transcription by homoeodomain-containing proteins that bind a common site. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):744–749. doi: 10.1038/336744a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kara C. J., Glimcher L. H. In vivo footprinting of MHC class II genes: bare promoters in the bare lymphocyte syndrome. Science. 1991 May 3;252(5006):709–712. doi: 10.1126/science.1902592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kara C. J., Glimcher L. H. Regulation of MHC class II gene transcription. Curr Opin Immunol. 1991 Feb;3(1):16–21. doi: 10.1016/0952-7915(91)90070-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobr M., Reith W., Herrero-Sanchez C., Mach B. Two DNA-binding proteins discriminate between the promoters of different members of the major histocompatibility complex class II multigene family. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):965–971. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouskoff V., Mantovani R. M., Candéias S. M., Dorn A., Staub A., Lisowska-Grospierre B., Griscelli C., Benoist C. O., Mathis D. J. NF-X, a transcription factor implicated in MHC class II gene regulation. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):3197–3204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kouzarides T., Ziff E. Leucine zippers of fos, jun and GCN4 dictate dimerization specificity and thereby control DNA binding. Nature. 1989 Aug 17;340(6234):568–571. doi: 10.1038/340568a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liou H. C., Boothby M. R., Finn P. W., Davidon R., Nabavi N., Zeleznik-Le N. J., Ting J. P., Glimcher L. H. A new member of the leucine zipper class of proteins that binds to the HLA DR alpha promoter. Science. 1990 Mar 30;247(4950):1581–1584. doi: 10.1126/science.2321018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matis L. A., Glimcher L. H., Paul W. E., Schwartz R. H. Magnitude of response of histocompatibility-restricted T-cell clones is a function of the product of the concentrations of antigen and Ia molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):6019–6023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.6019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Vaessin H., Caudy M., Jan L. Y., Jan Y. N., Cabrera C. V., Buskin J. N., Hauschka S. D., Lassar A. B. Interactions between heterologous helix-loop-helix proteins generate complexes that bind specifically to a common DNA sequence. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):537–544. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90434-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono S. J., Bazil V., Levi B. Z., Ozato K., Strominger J. L. Transcription of a subset of human class II major histocompatibility complex genes is regulated by a nucleoprotein complex that contains c-fos or an antigenically related protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4304–4308. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4304. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono S. J., Liou H. C., Davidon R., Strominger J. L., Glimcher L. H. Human X-box-binding protein 1 is required for the transcription of a subset of human class II major histocompatibility genes and forms a heterodimer with c-fos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4309–4312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith W., Barras E., Satola S., Kobr M., Reinhart D., Sanchez C. H., Mach B. Cloning of the major histocompatibility complex class II promoter binding protein affected in a hereditary defect in class II gene regulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4200–4204. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith W., Herrero-Sanchez C., Kobr M., Silacci P., Berte C., Barras E., Fey S., Mach B. MHC class II regulatory factor RFX has a novel DNA-binding domain and a functionally independent dimerization domain. Genes Dev. 1990 Sep;4(9):1528–1540. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.9.1528. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reith W., Satola S., Sanchez C. H., Amaldi I., Lisowska-Grospierre B., Griscelli C., Hadam M. R., Mach B. Congenital immunodeficiency with a regulatory defect in MHC class II gene expression lacks a specific HLA-DR promoter binding protein, RF-X. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):897–906. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90389-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffner W. How do different transcription factors binding the same DNA sequence sort out their jobs? Trends Genet. 1989 Feb;5(2):37–39. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(89)90017-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro D. J., Sharp P. A., Wahli W. W., Keller M. J. A high-efficiency HeLa cell nuclear transcription extract. DNA. 1988 Jan-Feb;7(1):47–55. doi: 10.1089/dna.1988.7.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stimac E., Urieli-Shoval S., Kempin S., Pious D. Defective HLA DRA X box binding in the class II transactive transcription factor mutant 6.1.6 and in cell lines from class II immunodeficient patients. J Immunol. 1991 Jun 15;146(12):4398–4405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Préval C., Lisowska-Grospierre B., Loche M., Griscelli C., Mach B. A trans-acting class II regulatory gene unlinked to the MHC controls expression of HLA class II genes. Nature. 1985 Nov 21;318(6043):291–293. doi: 10.1038/318291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]