Abstract
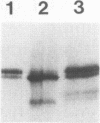
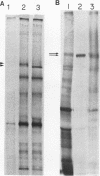
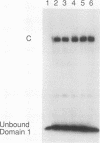
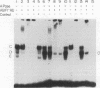
Previously, we have shown that the Saccharomyces cerevisiae DNA-binding protein ABF1 exists in at least two different electrophoretic forms (K. S. Sweder, P. R. Rhode, and J. L. Campbell, J. Biol. Chem. 263: 17270-17277, 1988). In this report, we show that these forms represent different states of phosphorylation of ABF1 and that at least four different phosphorylation states can be resolved electrophoretically. The ratios of these states to one another differ according to growth conditions and carbon source. Phosphorylation of ABF1 is therefore a regulated process. In nitrogen-starved cells or in cells grown on nonfermentable carbon sources (e.g., lactate), phosphorylated forms predominate, while in cells grown on fermentable carbon sources (e.g., glucose), dephosphorylated forms are enriched. The phosphorylation pattern is affected by mutations in the SNF1-SSN6 pathway, which is involved in glucose repression-depression. Whereas a functional SNF1 gene, which encodes a protein kinase, is not required for the phosphorylation of ABF1, a functional SSN6 gene is required for itsd ephosphorylation. The phosphorylation patterns that we have observed correlate with the regulation of a specific target gene, COX6, which encodes subunit VI of cytochrome c oxidase. Transcription of COX6 is repressed by growth in medium containing a fermentable carbon source and is derepressed by growth in medium containing a nonfermentable carbon source. COX6 repression-derepression is under the control of the SNF1-SSN6 pathway. This carbon source regulation is exerted through domain 1, a region of the upstream activation sequence UAS6 that binds ABF1 (J. D. Trawick, N. Kraut, F. Simon, and R. O. Poyton, Mol. Cell Biol. 12:2302-2314, 1992). We show that the greater the phosphorylation of ABF1, the greater the transcription of COX6. Furthermore, the ABF1-containing protein-DNA complexes formed at domain 1 differ according to the phosphorylation state of ABF1 and the carbon source on which the cells were grown. From these findings, we propose that the phosphorylation of ABF1 is involved in glucose repression-derepression of COX6 transcription.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcangioli B., Lescure B. Identification of proteins involved in the regulation of yeast iso- 1-cytochrome C expression by oxygen. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2627–2633. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03980.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Micklem G., Nasmyth K. A yeast silencer contains sequences that can promote autonomous plasmid replication and transcriptional activation. Cell. 1987 Dec 4;51(5):709–719. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90094-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brindle P. K., Holland J. P., Willett C. E., Innis M. A., Holland M. J. Multiple factors bind the upstream activation sites of the yeast enolase genes ENO1 and ENO2: ABFI protein, like repressor activator protein RAP1, binds cis-acting sequences which modulate repression or activation of transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4872–4885. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kimmerly W. J., Rine J., Kornberg R. D. Two DNA-binding factors recognize specific sequences at silencers, upstream activating sequences, autonomously replicating sequences, and telomeres in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):210–225. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman A. R., Kornberg R. D. A yeast ARS-binding protein activates transcription synergistically in combination with other weak activating factors. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):887–897. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Osmond B. C., Neigeborn L., Botstein D. A suppressor of SNF1 mutations causes constitutive high-level invertase synthesis in yeast. Genetics. 1984 May;107(1):19–32. doi: 10.1093/genetics/107.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celenza J. L., Carlson M. A yeast gene that is essential for release from glucose repression encodes a protein kinase. Science. 1986 Sep 12;233(4769):1175–1180. doi: 10.1126/science.3526554. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celenza J. L., Carlson M. Mutational analysis of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae SNF1 protein kinase and evidence for functional interaction with the SNF4 protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5034–5044. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5034. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cherry J. R., Johnson T. R., Dollard C., Shuster J. R., Denis C. L. Cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase phosphorylates and inactivates the yeast transcriptional activator ADR1. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):409–419. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90244-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R., Holland J. P., Yokoi T., Holland M. J. Identification of a regulatory region that mediates glucose-dependent induction of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae enolase gene ENO2. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2287–2297. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumsky M. G., Ko C., Trueblood C. E., Poyton R. O. Two nonidentical forms of subunit V are functional in yeast cytochrome c oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2235–2239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Seta F., Ciafré S. A., Marck C., Santoro B., Presutti C., Sentenac A., Bozzoni I. The ABF1 factor is the transcriptional activator of the L2 ribosomal protein genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2437–2441. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Della Seta F., Treich I., Buhler J. M., Sentenac A. ABF1 binding sites in yeast RNA polymerase genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 5;265(25):15168–15175. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. Purification of a yeast protein that binds to origins of DNA replication and a transcriptional silencer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2120–2124. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2120. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. Similarity between the transcriptional silencer binding proteins ABF1 and RAP1. Science. 1989 Nov 24;246(4933):1034–1038. doi: 10.1126/science.2511628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsman J. C., Doorenbosch M. M., Maurer C. T., de Winde J. H., Mager W. H., Planta R. J., Grivell L. A. An ARS/silencer binding factor also activates two ribosomal protein genes in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):4917–4923. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.4917. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dorsman J. C., van Heeswijk W. C., Grivell L. A. Identification of two factors which bind to the upstream sequences of a number of nuclear genes coding for mitochondrial proteins and to genetic elements important for cell division in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Aug 11;16(15):7287–7301. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.15.7287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman A. M., Blumenthal D. K., Krebs E. G. Protein serine/threonine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:567–613. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiechter A., Fuhrmann G. F., Käppeli O. Regulation of glucose metabolism in growing yeast cells. Adv Microb Physiol. 1981;22:123–183. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60327-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francesconi S. C., Eisenberg S. The multifunctional protein OBF1 is phosphorylated at serine and threonine residues in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 May 15;88(10):4089–4093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.10.4089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halfter H., Müller U., Winnacker E. L., Gallwitz D. Isolation and DNA-binding characteristics of a protein involved in transcription activation of two divergently transcribed, essential yeast genes. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):3029–3037. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08453.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamil K. G., Nam H. G., Fried H. M. Constitutive transcription of yeast ribosomal protein gene TCM1 is promoted by uncommon cis- and trans-acting elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4328–4341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4328. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herruer M. H., Mager W. H., Doorenbosch T. M., Wessels P. L., Wassenaar T. M., Planta R. J. The extended promoter of the gene encoding ribosomal protein S33 in yeast consists of multiple protein binding elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Sep 25;17(18):7427–7439. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.18.7427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holland J. P., Brindle P. K., Holland M. J. Sequences within an upstream activation site in the yeast enolase gene ENO2 modulate repression of ENO2 expression in strains carrying a null mutation in the positive regulatory gene GCR1. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4863–4871. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson S. P., MacDonald J. J., Lees-Miller S., Tjian R. GC box binding induces phosphorylation of Sp1 by a DNA-dependent protein kinase. Cell. 1990 Oct 5;63(1):155–165. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90296-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmerly W., Buchman A., Kornberg R., Rine J. Roles of two DNA-binding factors in replication, segregation and transcriptional repression mediated by a yeast silencer. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2241–2253. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03064.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moreno S., Nurse P. Substrates for p34cdc2: in vivo veritas? Cell. 1990 May 18;61(4):549–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90463-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mylin L. M., Bhat J. P., Hopper J. E. Regulated phosphorylation and dephosphorylation of GAL4, a transcriptional activator. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1157–1165. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mylin L. M., Johnston M., Hopper J. E. Phosphorylated forms of GAL4 are correlated with ability to activate transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4623–4629. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K., Adolf G., Lydall D., Seddon A. The identification of a second cell cycle control on the HO promoter in yeast: cell cycle regulation of SW15 nuclear entry. Cell. 1990 Aug 24;62(4):631–647. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90110-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poyton R. O., Trueblood C. E., Wright R. M., Farrell L. E. Expression and function of cytochrome c oxidase subunit isologues. Modulators of cellular energy production? Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1988;550:289–307. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1988.tb35344.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhode P. R., Sweder K. S., Oegema K. F., Campbell J. L. The gene encoding ARS-binding factor I is essential for the viability of yeast. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12A):1926–1939. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12a.1926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach P. J. Multisite and hierarchal protein phosphorylation. J Biol Chem. 1991 Aug 5;266(22):14139–14142. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rocha V., Ringo D. L., Read D. B. Casein production during differentiation of mammary epithelial cells in collagen gel culture. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Jul;159(1):201–210. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(85)80049-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz J., Marshall-Carlson L., Carlson M. The N-terminal TPR region is the functional domain of SSN6, a nuclear phosphoprotein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;10(9):4744–4756. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.9.4744. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shore D., Stillman D. J., Brand A. H., Nasmyth K. A. Identification of silencer binding proteins from yeast: possible roles in SIR control and DNA replication. EMBO J. 1987 Feb;6(2):461–467. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04776.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silve S., Monod M., Hinnen A., Haguenauer-Tsapis R. The yeast acid phosphatase can enter the secretory pathway without its N-terminal signal sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3306–3314. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Yeast heat shock factor is an essential DNA-binding protein that exhibits temperature-dependent phosphorylation. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):855–864. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweder K. S., Rhode P. R., Campbell J. L. Purification and characterization of proteins that bind to yeast ARSs. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17270–17277. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trawick J. D., Kraut N., Simon F. R., Poyton R. O. Regulation of yeast COX6 by the general transcription factor ABF1 and separate HAP2- and heme-responsive elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 May;12(5):2302–2314. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.5.2302. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trawick J. D., Rogness C., Poyton R. O. Identification of an upstream activation sequence and other cis-acting elements required for transcription of COX6 from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;9(12):5350–5358. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trawick J. D., Wright R. M., Poyton R. O. Transcription of yeast COX6, the gene for cytochrome c oxidase subunit VI, is dependent on heme and on the HAP2 gene. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 25;264(12):7005–7008. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trueblood C. E., Wright R. M., Poyton R. O. Differential regulation of the two genes encoding Saccharomyces cerevisiae cytochrome c oxidase subunit V by heme and the HAP2 and REO1 genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4537–4540. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams F. E., Varanasi U., Trumbly R. J. The CYC8 and TUP1 proteins involved in glucose repression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae are associated in a protein complex. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3307–3316. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R. M., Ko C., Cumsky M. G., Poyton R. O. Isolation and sequence of the structural gene for cytochrome c oxidase subunit VI from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15401–15407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright R. M., Poyton R. O. Release of two Saccharomyces cerevisiae cytochrome genes, COX6 and CYC1, from glucose repression requires the SNF1 and SSN6 gene products. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1297–1300. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1297. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe M. P., Schatz G. Two nuclear mutations that block mitochondrial protein import in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4819–4823. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4819. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]