Abstract
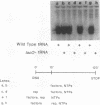
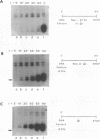
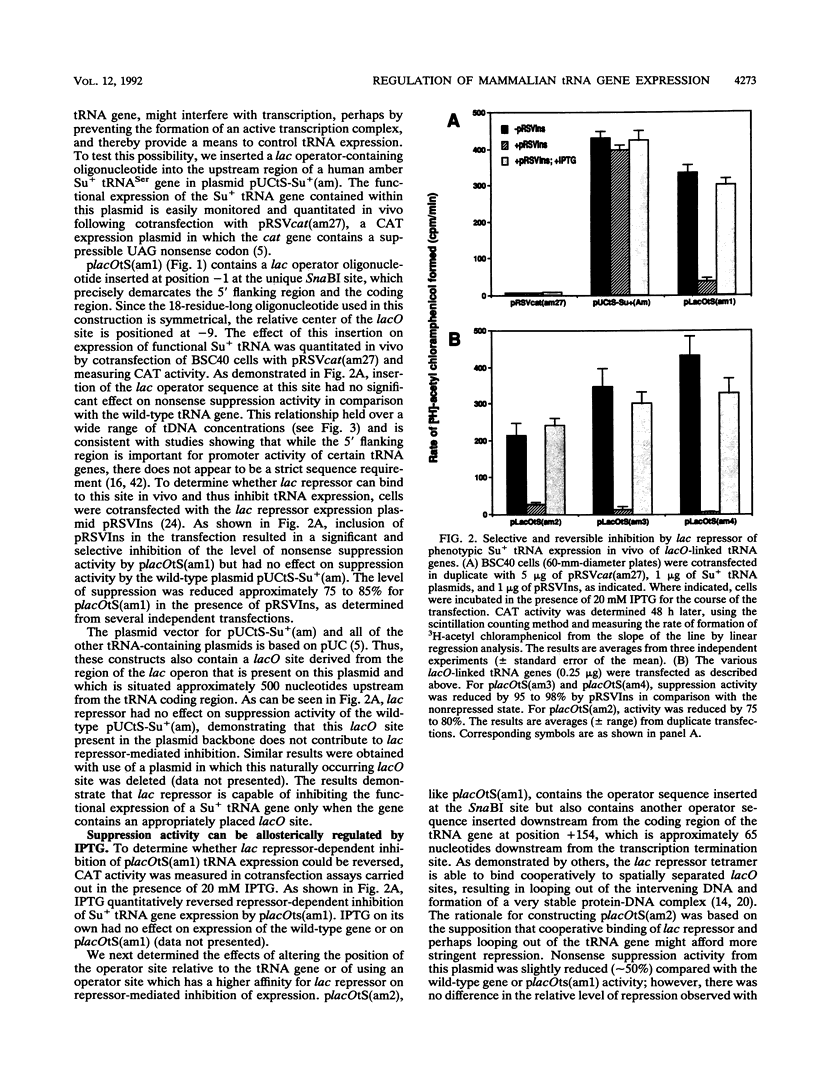
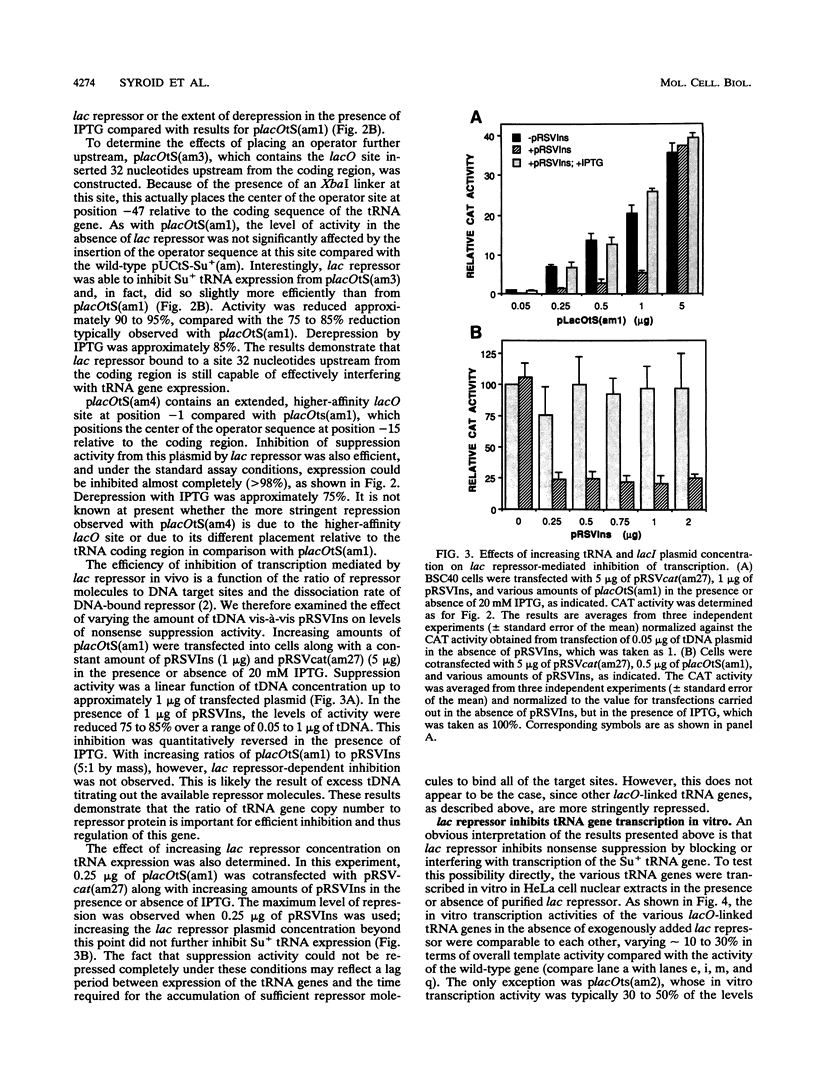
We have exploited the Escherichia coli lac operator/repressor system as a means to regulate the expression of a mammalian tRNA gene in vivo and in vitro. An oligonucleotide containing a lac operator (lacO) site was cloned immediately upstream of a human serine amber suppressor (Su+) tRNA gene. Insertion of a single lac repressor binding site at position -1 or -32 relative to the coding region had no effect on the amount of functional tRNA made in vivo, as measured by suppression of a nonsense mutation in the E. coli chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene following cotransfection of mammalian cells. Inclusion of a plasmid expressing the lac repressor in the transfections resulted in 75 to 98% inhibition of suppression activity of lac operator-linked tRNA genes but had no effect on expression of the wild-type gene. Inhibition could be quantitatively relieved with the allosteric inducer isopropylthio-beta-D-galactoside (IPTG). Similarly, transcription in vitro of lac operator-linked tRNA genes in HeLa cell extracts was repressed in the presence of lac repressor, and this inhibition was reversible with IPTG. These results demonstrate that the bacterial lac operator/repressor system can be used to reversibly control the expression of mammalian genes that are transcribed by RNA polymerase III.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison L. A., Moyle M., Shales M., Ingles C. J. Extensive homology among the largest subunits of eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartholomew B., Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Two components of Saccharomyces cerevisiae transcription factor IIIB (TFIIIB) are stereospecifically located upstream of a tRNA gene and interact with the second-largest subunit of TFIIIC. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Oct;11(10):5181–5189. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.10.5181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown M., Figge J., Hansen U., Wright C., Jeang K. T., Khoury G., Livingston D. M., Roberts T. M. lac repressor can regulate expression from a hybrid SV40 early promoter containing a lac operator in animal cells. Cell. 1987 Jun 5;49(5):603–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90536-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capone J. P., Sedivy J. M., Sharp P. A., RajBhandary U. L. Introduction of UAG, UAA, and UGA nonsense mutations at a specific site in the Escherichia coli chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene: use in measurement of amber, ochre, and opal suppression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;6(9):3059–3067. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.9.3059. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Capone J. P., Sharp P. A., RajBhandary U. L. Amber, ochre and opal suppressor tRNA genes derived from a human serine tRNA gene. EMBO J. 1985 Jan;4(1):213–221. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb02338.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco D., Sharp S., Söll D. Identification of regulatory sequences contained in the 5'-flanking region of Drosophila lysine tRNA2 genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12424–12429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deuschle U., Hipskind R. A., Bujard H. RNA polymerase II transcription blocked by Escherichia coli lac repressor. Science. 1990 Apr 27;248(4954):480–483. doi: 10.1126/science.2158670. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dingermann T., Frank-Stoll U., Werner H., Wissmann A., Hillen W., Jacquet M., Marschalek R. RNA polymerase III catalysed transcription can be regulated in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by the bacterial tetracycline repressor-operator system. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1487–1492. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05193.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Figge J., Wright C., Collins C. J., Roberts T. M., Livingston D. M. Stringent regulation of stably integrated chloramphenicol acetyl transferase genes by E. coli lac repressor in monkey cells. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):713–722. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90409-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flashner Y., Gralla J. D. Dual mechanism of repression at a distance in the lac operon. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8968–8972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrman S. A., Engelke D. R., Geiduschek E. P. HeLa cell RNA polymerase III transcription factors. Functional characterization of a fraction identified by its activity in a second template rescue assay. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1934–1943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P., Tocchini-Valentini G. P. Transcription by RNA polymerase III. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:873–914. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.004301. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hipskind R. A., Clarkson S. G. 5'-flanking sequences that inhibit in vitro transcription of a xenopus laevis tRNA gene. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90545-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsieh W. T., Whitson P. A., Matthews K. S., Wells R. D. Influence of sequence and distance between two operators on interaction with the lac repressor. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 25;262(30):14583–14591. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M. C., Davidson N. A combination of derepression of the lac operator-repressor system with positive induction by glucocorticoid and metal ions provides a high-level-inducible gene expression system based on the human metallothionein-IIA promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Dec;10(12):6141–6151. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.12.6141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M. C., Davidson N. Targeting the Escherichia coli lac repressor to the mammalian cell nucleus. Gene. 1991 Mar 15;99(2):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90120-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M. C., Davidson N. The inducible lac operator-repressor system is functional for control of expression of injected DNA in Xenopus oocytes. Gene. 1988;62(2):301–313. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90567-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu M. C., Davidson N. The inducible lac operator-repressor system is functional in mammalian cells. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):555–566. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90234-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hudziak R. M., Laski F. A., RajBhandary U. L., Sharp P. A., Capecchi M. R. Establishment of mammalian cell lines containing multiple nonsense mutations and functional suppressor tRNA genes. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90413-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes N. E., Kennedy N., Rahmsdorf U., Groner B. Hormone-responsive expression of an endogenous proviral gene of mouse mammary tumor virus after molecular cloning and gene transfer into cultured cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2038–2042. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2038. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbra R. J., Karin M. Metallothionein gene expression is regulated by serum factors and activators of protein kinase C. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1358–1363. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1358. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Heguy A., Dietlin T., Cooke T. Metal-responsive elements act as positive modulators of human metallothionein-IIA enhancer activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):606–613. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Cathala G., Slater E., Baxter J. D. Activation of a heterologous promoter in response to dexamethasone and cadmium by metallothionein gene 5'-flanking DNA. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):371–379. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90230-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Holtgreve H., Richards R. I., Krauter P., Westphal H. M., Beato M. Characterization of DNA sequences through which cadmium and glucocorticoid hormones induce human metallothionein-IIA gene. Nature. 1984 Apr 5;308(5959):513–519. doi: 10.1038/308513a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Braun B. R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. S. cerevisiae TFIIIB is the transcription initiation factor proper of RNA polymerase III, while TFIIIA and TFIIIC are assembly factors. Cell. 1990 Jan 26;60(2):235–245. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90739-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Riggs D. L., Negri R., Nguyen L. H., Geiduschek E. P. Transcription factor IIIB generates extended DNA interactions in RNA polymerase III transcription complexes on tRNA genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2551–2566. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovelman R., Roeder R. G. Sarkosyl defines three intermediate steps in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase III: application to stimulation of transcription by E1A. Genes Dev. 1990 Apr;4(4):646–658. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.4.646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labow M. A., Baim S. B., Shenk T., Levine A. J. Conversion of the lac repressor into an allosterically regulated transcriptional activator for mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jul;10(7):3343–3356. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.7.3343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laski F. A., Belagaje R., Hudziak R. M., Capecchi M. R., Norton G. P., Palese P., RajBhandary U. L., Sharp P. A. Synthesis of an ochre suppressor tRNA gene and expression in mammalian cells. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2445–2452. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02154.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laski F. A., Belagaje R., RajBhandary U. L., Sharp P. A. An amber suppressor tRNA gene derived by site-specific mutagenesis: cloning and function in mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5813–5817. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lassar A. B., Martin P. L., Roeder R. G. Transcription of class III genes: formation of preinitiation complexes. Science. 1983 Nov 18;222(4625):740–748. doi: 10.1126/science.6356356. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J., Goldfarb A. lac repressor acts by modifying the initial transcribing complex so that it cannot leave the promoter. Cell. 1991 Aug 23;66(4):793–798. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90122-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadler J. R., Sasmor H., Betz J. L. A perfectly symmetric lac operator binds the lac repressor very tightly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Nov;80(22):6785–6789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.22.6785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sedivy J. M., Capone J. P., RajBhandary U. L., Sharp P. A. An inducible mammalian amber suppressor: propagation of a poliovirus mutant. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90492-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp S. J., Schaack J., Cooley L., Burke D. J., Söll D. Structure and transcription of eukaryotic tRNA genes. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;19(2):107–144. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temple G. F., Dozy A. M., Roy K. L., Kan Y. W. Construction of a functional human suppressor tRNA gene: an approach to gene therapy for beta-thalassaemia. Nature. 1982 Apr 8;296(5857):537–540. doi: 10.1038/296537a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S., Takahashi N., Sprague K. U. Upstream sequences confer distinctive transcriptional properties on genes encoding silkgland-specific tRNAAla. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jan;83(2):374–378. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.2.374. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]