Abstract
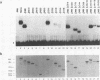
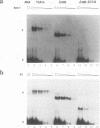
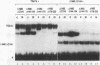
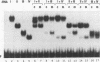
We have carried out deletion analyses of a tobacco transcription activator, TGA1a, in order to define its functional domains. TGA1a belongs to the basic-region-leucine zipper (bZIP) class of DNA-binding proteins. Like other proteins of this class, it binds to its target DNA as a dimer, and its bZIP domain is necessary and sufficient for specific DNA binding. A mutant polypeptide containing the bZIP domain alone, however, shows a lower DNA-binding affinity than the full-length TGA1a. The C-terminal portion of TGA1a, which is essential for the higher DNA-binding affinity, contains a polypeptide region that can stabilize dimeric forms of the protein. This polypeptide region is designated the dimer stabilization (DS) region. Under our in vitro conditions, TGA1a derivatives with the DS region and those without the region do not form a detectable mixed dimer. This result indicates that in addition to the leucine zipper, the DS region can serve as another determinant of the dimerization specificity of TGA1a. In fact, the DS region, when fused to another bZIP protein, C/EBP, can inhibit dimer formation between the fusion protein and native C/EBP, whereas each of these can form homodimers. Such a portable determinant of dimerization specificity has potential application in studies of DNA-binding proteins as well as in biotechnology.
Full text
PDF

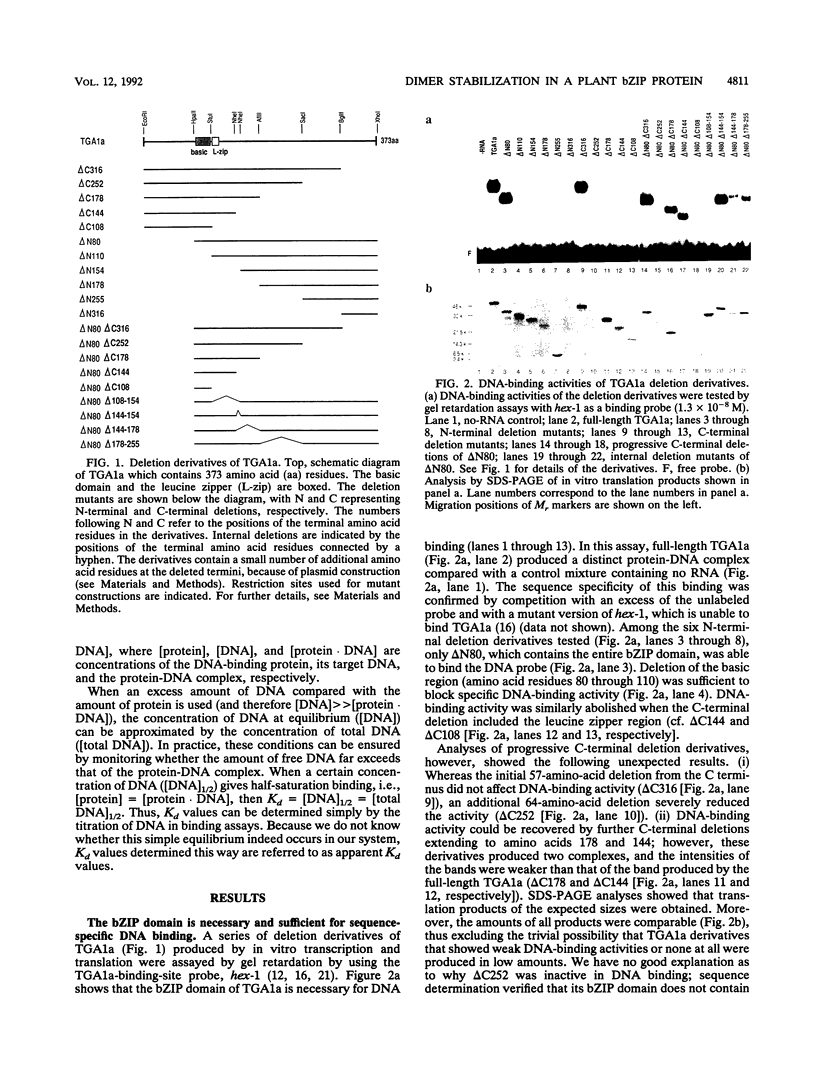





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beckmann H., Kadesch T. The leucine zipper of TFE3 dictates helix-loop-helix dimerization specificity. Genes Dev. 1991 Jun;5(6):1057–1066. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.6.1057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beckmann H., Su L. K., Kadesch T. TFE3: a helix-loop-helix protein that activates transcription through the immunoglobulin enhancer muE3 motif. Genes Dev. 1990 Feb;4(2):167–179. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blackwood E. M., Eisenman R. N. Max: a helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991 Mar 8;251(4998):1211–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.2006410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman A. D., Landschulz W. H., McKnight S. L. CCAAT/enhancer binding protein activates the promoter of the serum albumin gene in cultured hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1989 Sep;3(9):1314–1322. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.9.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fromm H., Katagiri F., Chua N. H. The tobacco transcription activator TGA1a binds to a sequence in the 5' upstream region of a gene encoding a TGA1a-related protein. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Oct;229(2):181–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00272154. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gentz R., Rauscher F. J., 3rd, Abate C., Curran T. Parallel association of Fos and Jun leucine zippers juxtaposes DNA binding domains. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1695–1699. doi: 10.1126/science.2494702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilbert W. Why genes in pieces? Nature. 1978 Feb 9;271(5645):501–501. doi: 10.1038/271501a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gregor P. D., Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. The adenovirus major late transcription factor USF is a member of the helix-loop-helix group of regulatory proteins and binds to DNA as a dimer. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1730–1740. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. GCN4, a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, binds as a dimer to target DNA. EMBO J. 1987 Sep;6(9):2781–2784. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02573.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu Y. F., Lüscher B., Admon A., Mermod N., Tjian R. Transcription factor AP-4 contains multiple dimerization domains that regulate dimer specificity. Genes Dev. 1990 Oct;4(10):1741–1752. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.10.1741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri F., Lam E., Chua N. H. Two tobacco DNA-binding proteins with homology to the nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1989 Aug 31;340(6236):727–730. doi: 10.1038/340727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katagiri F., Yamazaki K., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G., Chua N. H. A plant DNA-binding protein increases the number of active preinitiation complexes in a human in vitro transcription system. Genes Dev. 1990 Nov;4(11):1899–1909. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.11.1899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. An analysis of 5'-noncoding sequences from 699 vertebrate messenger RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8125–8148. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E., Benfey P. N., Gilmartin P. M., Fang R. X., Chua N. H. Site-specific mutations alter in vitro factor binding and change promoter expression pattern in transgenic plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7890–7894. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam E., Katagiri F., Chua N. H. Plant nuclear factor ASF-1 binds to an essential region of the nopaline synthase promoter. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9909–9913. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The DNA binding domain of the rat liver nuclear protein C/EBP is bipartite. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1681–1688. doi: 10.1126/science.2494700. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lüscher B., Eisenman R. N. New light on Myc and Myb. Part I. Myc. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2025–2035. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikami K., Tabata T., Kawata T., Nakayama T., Iwabuchi M. Nuclear protein(s) binding to the conserved DNA hexameric sequence postulated to regulate transcription of wheat histone genes. FEBS Lett. 1987 Nov 2;223(2):273–278. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80303-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murre C., McCaw P. S., Baltimore D. A new DNA binding and dimerization motif in immunoglobulin enhancer binding, daughterless, MyoD, and myc proteins. Cell. 1989 Mar 10;56(5):777–783. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90682-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norman C., Runswick M., Pollock R., Treisman R. Isolation and properties of cDNA clones encoding SRF, a transcription factor that binds to the c-fos serum response element. Cell. 1988 Dec 23;55(6):989–1003. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90244-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Shea E. K., Rutkowski R., Kim P. S. Evidence that the leucine zipper is a coiled coil. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):538–542. doi: 10.1126/science.2911757. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabata T., Nakayama T., Mikami K., Iwabuchi M. HBP-1a and HBP-1b: leucine zipper-type transcription factors of wheat. EMBO J. 1991 Jun;10(6):1459–1467. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb07666.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Talanian R. V., McKnight C. J., Kim P. S. Sequence-specific DNA binding by a short peptide dimer. Science. 1990 Aug 17;249(4970):769–771. doi: 10.1126/science.2389142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Turner R., Tjian R. Leucine repeats and an adjacent DNA binding domain mediate the formation of functional cFos-cJun heterodimers. Science. 1989 Mar 31;243(4899):1689–1694. doi: 10.1126/science.2494701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson C. R., Sigler P. B., McKnight S. L. Scissors-grip model for DNA recognition by a family of leucine zipper proteins. Science. 1989 Nov 17;246(4932):911–916. doi: 10.1126/science.2683088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamazaki K., Katagiri F., Imaseki H., Chua N. H. TGA1a, a tobacco DNA-binding protein, increases the rate of preinitiation complex formation in a plant in vitro transcription system [corrected]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Sep;87(18):7035–7039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]