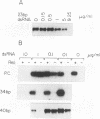
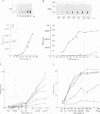
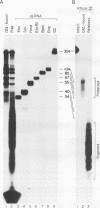
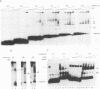
Abstract
The interferon-induced protein kinase DAI, the double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-activated inhibitor of translation, plays a key role in regulating protein synthesis in higher cells. Once activated, in a process that involves autophosphorylation, it phosphorylates the initiation factor eIF-2, leading to inhibition of polypeptide chain initiation. The activity of DAI is controlled by RNA regulators, including dsRNA activators and highly structured single-stranded RNAs which block activation by dsRNA. To elucidate the mechanism of activation, we studied the interaction of DAI with RNA duplexes of discrete sizes. Molecules shorter than 30 bp fail to bind stably and do not activate the enzyme, but at high concentrations they prevent activation by long dsRNA. Molecules longer than 30 bp bind and activate the enzyme, with an efficiency that increases with increasing chain length, reaching a maximum at about 85 bp. These dsRNAs fail to activate at high concentrations and also prevent activation by long dsRNA. Analysis of complexes between dsRNA and DAI suggests that at maximal packing the enzyme interacts with as little as a single helical turn of dsRNA (11 bp) but under conditions that allow activation the binding site protects about 80 bp of duplex. When the RNA-binding site is fully occupied with an RNA activator, the complex appears to undergo a conformational change.
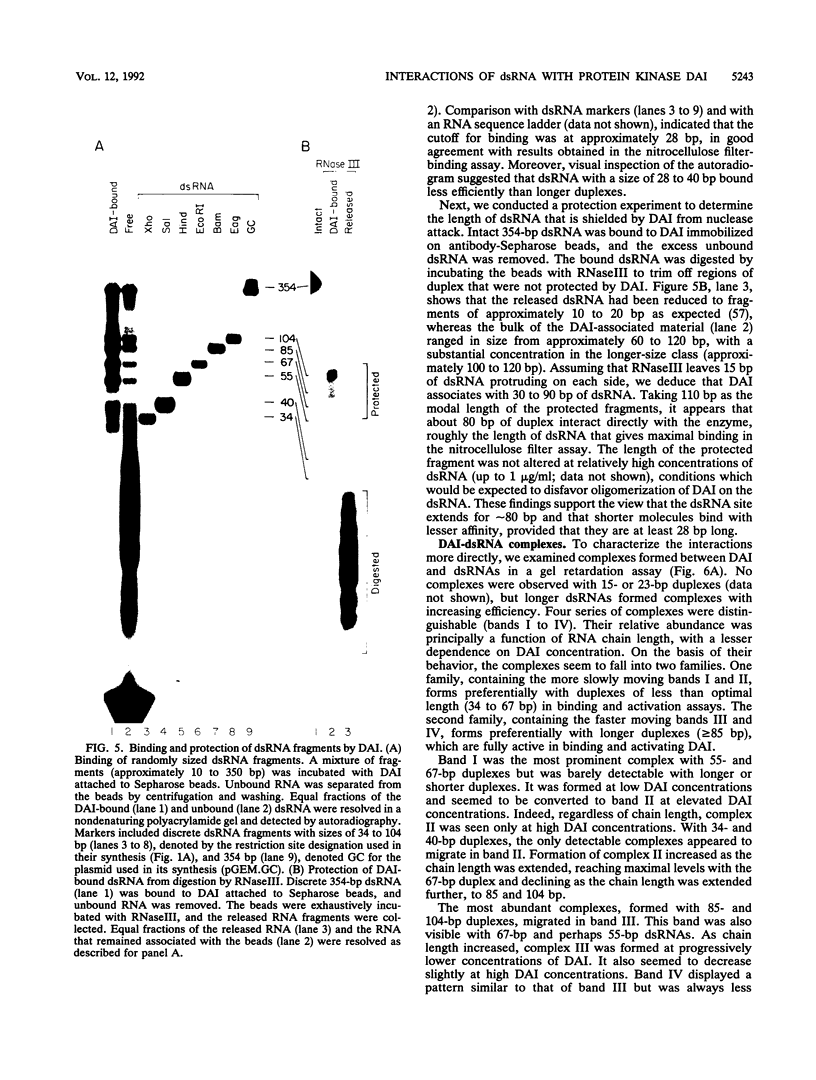
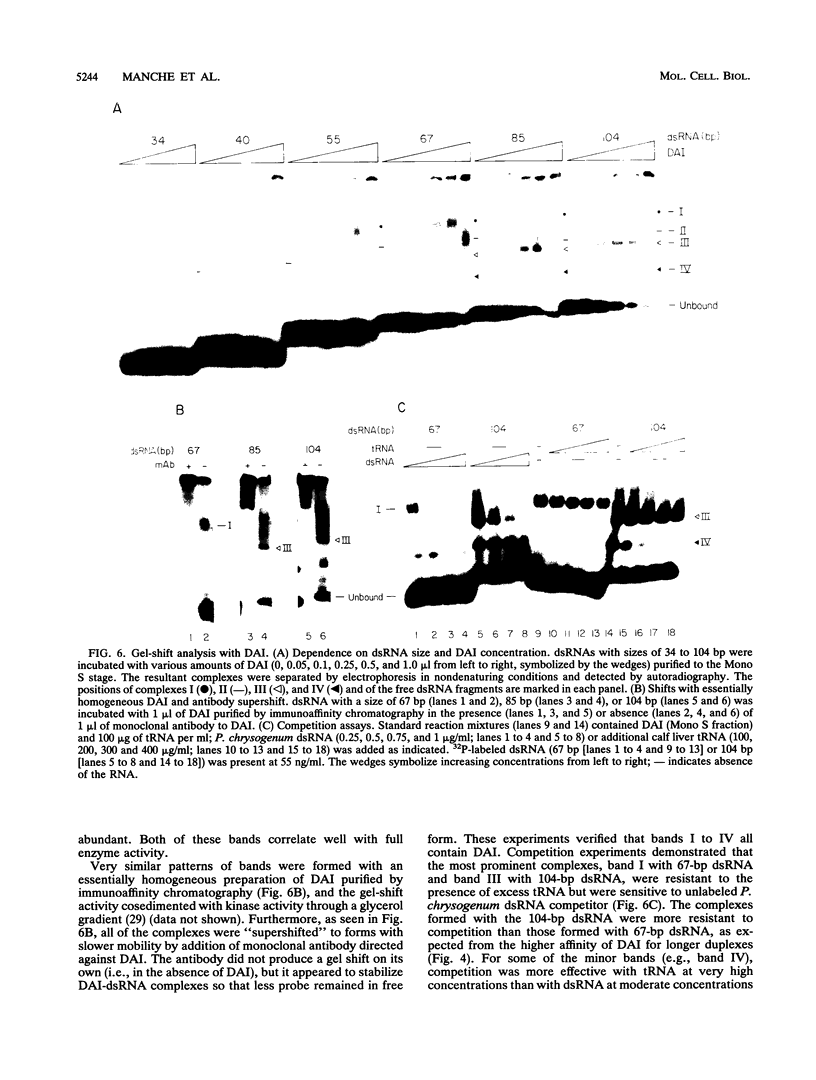
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baglioni C., Maroney P. A. Inhibition of double-stranded ribonucleic acid activated protein kinase and 2',5'-oligo(adenylic acid) polymerase by ethidium bromide. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 17;20(4):758–762. doi: 10.1021/bi00507a016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baglioni C., Minks M. A., De Clercq E. Structural requirements of polynucleotides for the activation of (2' - 5')An polymerase and protein kinase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Oct 10;9(19):4939–4950. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.19.4939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry M. J., Knutson G. S., Lasky S. R., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Purification and substrate specificities of the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase from untreated and interferon-treated mouse fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 15;260(20):11240–11247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bhat R. A., Thimmappaya B. Construction and analysis of additional adenovirus substitution mutants confirm the complementation of VAI RNA function by two small RNAs encoded by Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1985 Dec;56(3):750–756. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.3.750-756.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bischoff J. R., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Activation of the human P1/eIF-2 alpha protein kinase by individual reovirus s-class mRNAs: s1 mRNA is a potent activator relative to s4 mRNA. Virology. 1989 Sep;172(1):106–115. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90112-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chong K. L., Feng L., Schappert K., Meurs E., Donahue T. F., Friesen J. D., Hovanessian A. G., Williams B. R. Human p68 kinase exhibits growth suppression in yeast and homology to the translational regulator GCN2. EMBO J. 1992 Apr;11(4):1553–1562. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05200.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke P. A., Sharp N. A., Clemens M. J. Translational control by the Epstein-Barr virus small RNA EBER-1. Reversal of the double-stranded RNA-induced inhibition of protein synthesis in reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Nov 13;193(3):635–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Benedetti A., Baglioni C. Inhibition of mRNA binding to ribosomes by localized activation of dsRNA-dependent protein kinase. Nature. 1984 Sep 6;311(5981):79–81. doi: 10.1038/311079a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dever T. E., Feng L., Wek R. C., Cigan A. M., Donahue T. F., Hinnebusch A. G. Phosphorylation of initiation factor 2 alpha by protein kinase GCN2 mediates gene-specific translational control of GCN4 in yeast. Cell. 1992 Feb 7;68(3):585–596. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90193-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois M. F., Galabru J., Lebon P., Safer B., Hovanessian A. G. Reduced activity of the interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase during a heat shock stress. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 25;264(21):12165–12171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farrell P. J., Balkow K., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Trachsel H. Phosphorylation of initiation factor elF-2 and the control of reticulocyte protein synthesis. Cell. 1977 May;11(1):187–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90330-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feng G. S., Chong K., Kumar A., Williams B. R. Identification of double-stranded RNA-binding domains in the interferon-induced double-stranded RNA-activated p68 kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5447–5451. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Hovanessian A. G. Two interferon-induced proteins are involved in the protein kinase complex dependent on double-stranded RNA. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):685–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90241-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Hovanessian A. Autophosphorylation of the protein kinase dependent on double-stranded RNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15538–15544. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galabru J., Katze M. G., Robert N., Hovanessian A. G. The binding of double-stranded RNA and adenovirus VAI RNA to the interferon-induced protein kinase. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Jan 2;178(3):581–589. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb14485.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grodberg J., Dunn J. J. ompT encodes the Escherichia coli outer membrane protease that cleaves T7 RNA polymerase during purification. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1245–1253. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1245-1253.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gunnery S., Rice A. P., Robertson H. D., Mathews M. B. Tat-responsive region RNA of human immunodeficiency virus 1 can prevent activation of the double-stranded-RNA-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Nov;87(22):8687–8691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.22.8687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Protein phosphorylation controls translation rates. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 15;264(35):20823–20826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hershey J. W. Translational control in mammalian cells. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:717–755. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.003441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hovanessian A. G. The double stranded RNA-activated protein kinase induced by interferon: dsRNA-PK. J Interferon Res. 1989 Dec;9(6):641–647. doi: 10.1089/jir.1989.9.641. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Hunt T., Jackson R. J., Robertson H. D. The characteristics of inhibition of protein synthesis by double-stranded ribonucleic acid in reticulocyte lysates. J Biol Chem. 1975 Jan 25;250(2):409–417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Judware R., Petryshyn R. Partial characterization of a cellular factor that regulates the double-stranded RNA-dependent eIF-2 alpha kinase in 3T3-F442A fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jun;11(6):3259–3267. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.6.3259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Detjen B. M., Safer B., Krug R. M. Translational control by influenza virus: suppression of the kinase that phosphorylates the alpha subunit of initiation factor eIF-2 and selective translation of influenza viral mRNAs. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1741–1750. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katze M. G., Wambach M., Wong M. L., Garfinkel M., Meurs E., Chong K., Williams B. R., Hovanessian A. G., Barber G. N. Functional expression and RNA binding analysis of the interferon-induced, double-stranded RNA-activated, 68,000-Mr protein kinase in a cell-free system. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Nov;11(11):5497–5505. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.11.5497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaufman R. J., Murtha P. Translational control mediated by eucaryotic initiation factor-2 is restricted to specific mRNAs in transfected cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1568–1571. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimchi A., Zilberstein A., Schmidt A., Shulman L., Revel M. The interferon-induced protein kinase PK-i from mouse L cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 10;254(19):9846–9853. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitajewski J., Schneider R. J., Safer B., Munemitsu S. M., Samuel C. E., Thimmappaya B., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA antagonizes the antiviral action of interferon by preventing activation of the interferon-induced eIF-2 alpha kinase. Cell. 1986 Apr 25;45(2):195–200. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90383-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kostura M., Mathews M. B. Purification and activation of the double-stranded RNA-dependent eIF-2 kinase DAI. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1576–1586. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lasky S. R., Jacobs B. L., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action. Characterization of sites of phosphorylation in the interferon-induced phosphoprotein P1 from mouse fibroblasts: evidence for two forms of P1. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 25;257(18):11087–11093. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurent A. G., Krust B., Galabru J., Svab J., Hovanessian A. G. Monoclonal antibodies to an interferon-induced Mr 68,000 protein and their use for the detection of double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase in human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4341–4345. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4341. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lebleu B., Sen G. C., Shaila S., Cabrer B., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3107–3111. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenz J. R., Baglioni C. Inhibition of protein synthesis by double-stranded RNA and phosphorylation of initiation factor, eIF-2. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 25;253(12):4219–4223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D. H., Petryshyn R., London I. M. Characterization of double-stranded-RNA-activated kinase that phosphorylates alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 (eIF-2 alpha) in reticulocyte lysates. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):832–836. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levin D., London I. M. Regulation of protein synthesis: activation by double-stranded RNA of a protein kinase that phosphorylates eukaryotic initiation factor 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Mar;75(3):1121–1125. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.3.1121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B. Control of translation in adenovirus-infected cells. Enzyme. 1990;44(1-4):250–264. doi: 10.1159/000468763. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Shenk T. Adenovirus virus-associated RNA and translation control. J Virol. 1991 Nov;65(11):5657–5662. doi: 10.1128/jvi.65.11.5657-5662.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormack S. J., Thomis D. C., Samuel C. E. Mechanism of interferon action: identification of a RNA binding domain within the N-terminal region of the human RNA-dependent P1/eIF-2 alpha protein kinase. Virology. 1992 May;188(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(92)90733-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellits K. H., Kostura M., Mathews M. B. Interaction of adenovirus VA RNAl with the protein kinase DAI: nonequivalence of binding and function. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):843–852. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90194-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellits K. H., Mathews M. B. Effects of mutations in stem and loop regions on the structure and function of adenovirus VA RNAI. EMBO J. 1988 Sep;7(9):2849–2859. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03141.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mellits K. H., Pe'ery T., Manche L., Robertson H. D., Mathews M. B. Removal of double-stranded contaminants from RNA transcripts: synthesis of adenovirus VA RNAI from a T7 vector. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5401–5406. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meurs E., Chong K., Galabru J., Thomas N. S., Kerr I. M., Williams B. R., Hovanessian A. G. Molecular cloning and characterization of the human double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase induced by interferon. Cell. 1990 Jul 27;62(2):379–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90374-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minks M. A., West D. K., Benvin S., Baglioni C. Structural requirements of double-stranded RNA for the activation of 2',5'-oligo(A) polymerase and protein kinase of interferon-treated HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1979 Oct 25;254(20):10180–10183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minks M. A., West D. K., Benvin S., Greene J. J., Ts'o P. O., Baglioni C. Activation of 2',5'-oligo(A) polymerase and protein kinase of interferon-treated HeLa cells by 2'-O-methylated poly (inosinic acid) . poly(cytidylic acid), Correlations with interferon-inducing activity. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6403–6407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley R. P., Duncan R. F., Hershey J. W., Mathews M. B. Modification of protein synthesis initiation factors and the shut-off of host protein synthesis in adenovirus-infected cells. Virology. 1989 Jan;168(1):112–118. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(89)90409-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Malley R. P., Mariano T. M., Siekierka J., Mathews M. B. A mechanism for the control of protein synthesis by adenovirus VA RNAI. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):391–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ochoa S. Regulation of protein synthesis initiation in eucaryotes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1983 Jun;223(2):325–349. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90598-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel R. C., Sen G. C. Identification of the double-stranded RNA-binding domain of the human interferon-inducible protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1992 Apr 15;267(11):7671–7676. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S., Langer J. A., Zoon K. C., Samuel C. E. Interferons and their actions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:727–777. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petryshyn R., Chen J. J., London I. M. Growth-related expression of a double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase in 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 10;259(23):14736–14742. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice A. P., Kostura M., Mathews M. B. Identification of a 90-kDa polypeptide which associates with adenovirus VA RNAI and is phosphorylated by the double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 5;264(34):20632–20637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samuel C. E. Antiviral actions of interferon. Interferon-regulated cellular proteins and their surprisingly selective antiviral activities. Virology. 1991 Jul;183(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(91)90112-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Shenk T. Impact of virus infection on host cell protein synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:317–332. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweitz H., Ebel J. P. A study of the mechanism of action of E. coli ribonuclease 3. Biochimie. 1971;53(5):585–593. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(71)80014-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sen G. C., Taira H., Lengyel P. Interferon, double-stranded RNA, and protein phosphorylation. Characteristics of a double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase system partially purified from interferon treated Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 10;253(17):5915–5921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sonenberg N. Measures and countermeasures in the modulation of initiation factor activities by viruses. New Biol. 1990 May;2(5):402–409. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svensson C., Akusjärvi G. Adenovirus VA RNAI mediates a translational stimulation which is not restricted to the viral mRNAs. EMBO J. 1985 Apr;4(4):957–964. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03724.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiwari R. K., Kusari J., Kumar R., Sen G. C. Gene induction by interferons and double-stranded RNA: selective inhibition by 2-aminopurine. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4289–4294. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torrence P. F., Johnston M. I., Epstein D. A., Jacobsen H., Friedman R. M. Activation of human and mouse 2-5A synthetases and mouse protein P1 kinase by nucleic acids. Structure-activity relationships and correlations with inhibition of protein synthesis and interferon induction. FEBS Lett. 1981 Aug 3;130(2):291–296. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)81142-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Kimchi A., Schmidt A., Revel M. Isolation of two interferon-induced translational inhibitors: a protein kinase and an oligo-isoadenylate synthetase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4734–4738. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinn K., Keller A., Whittemore L. A., Maniatis T. 2-Aminopurine selectively inhibits the induction of beta-interferon, c-fos, and c-myc gene expression. Science. 1988 Apr 8;240(4849):210–213. doi: 10.1126/science.3281258. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]