Abstract
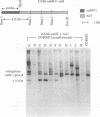
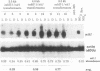
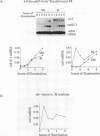
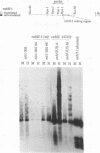
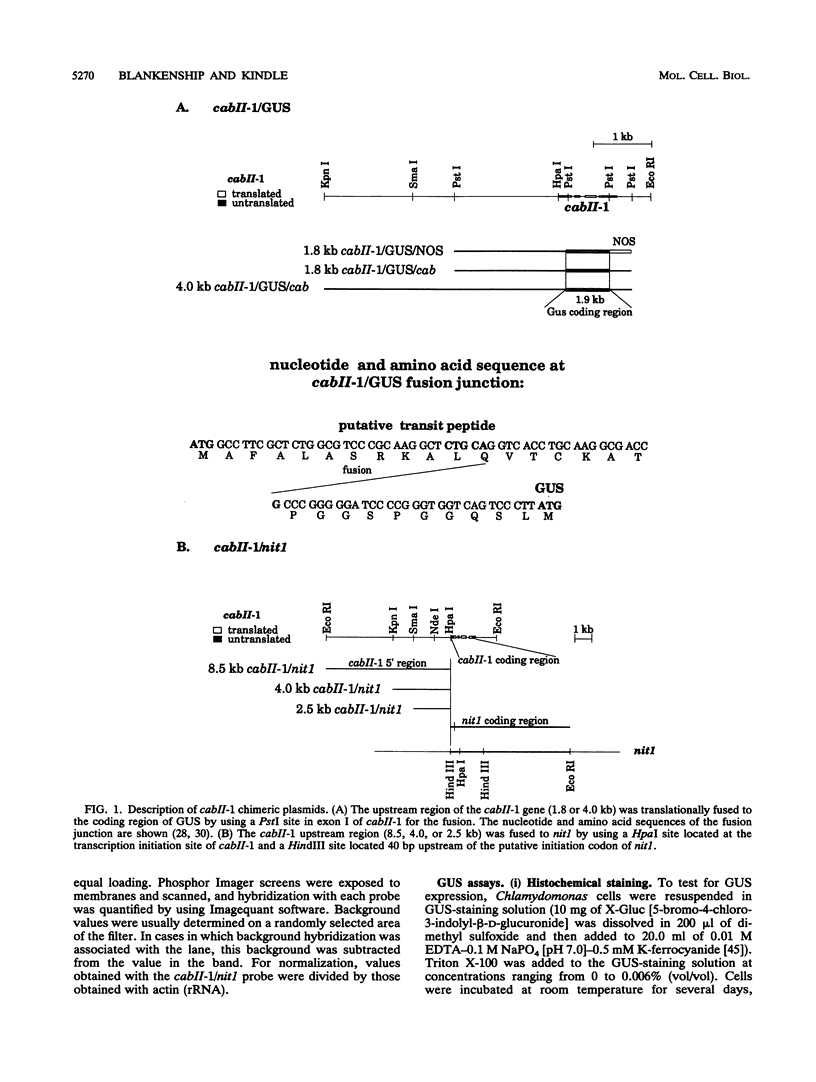
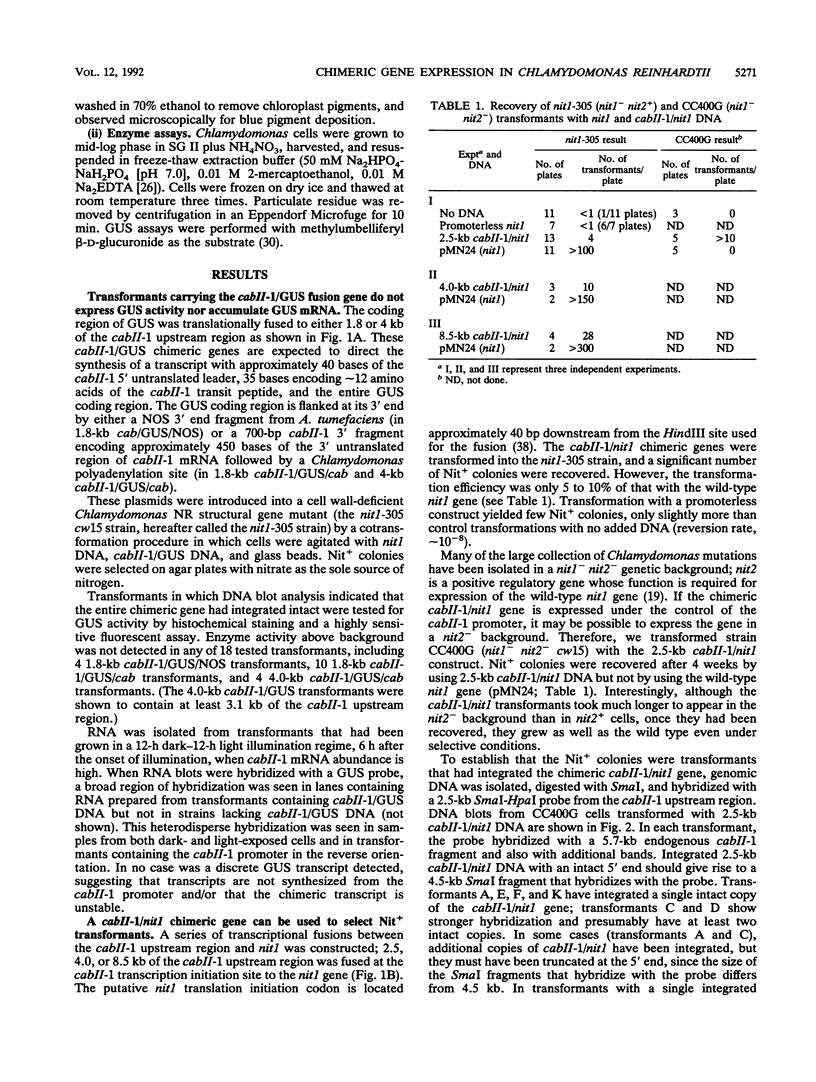
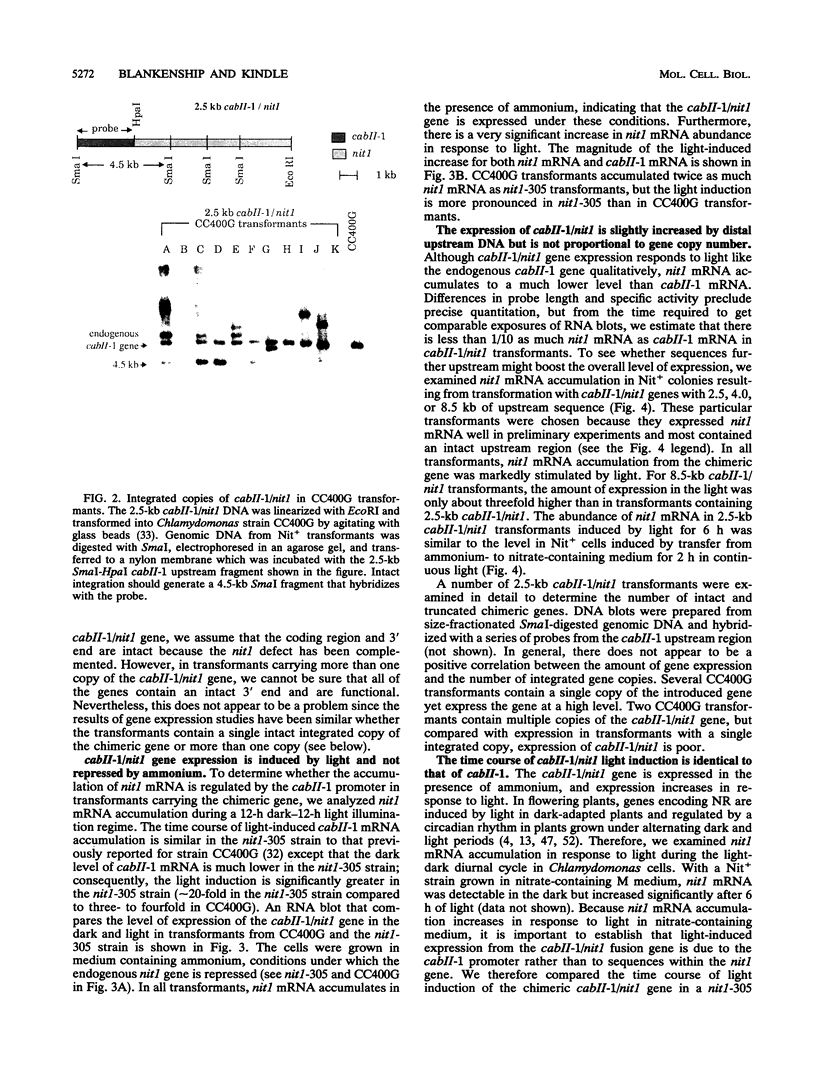
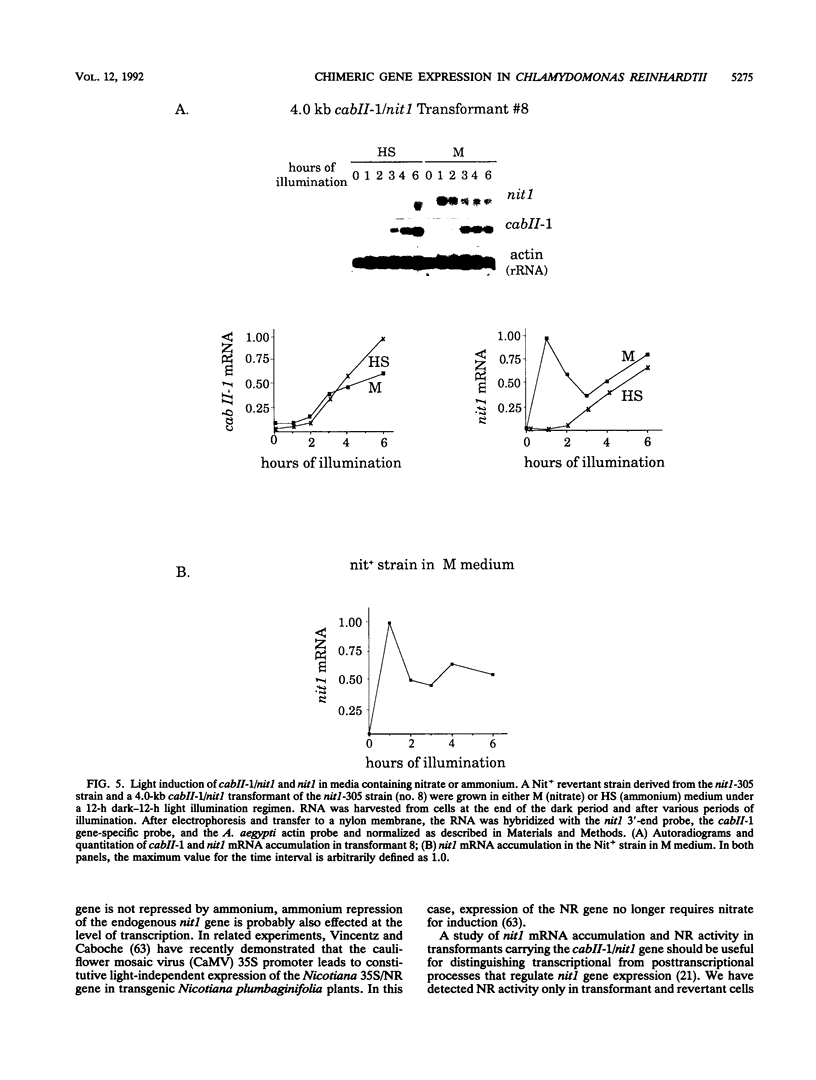
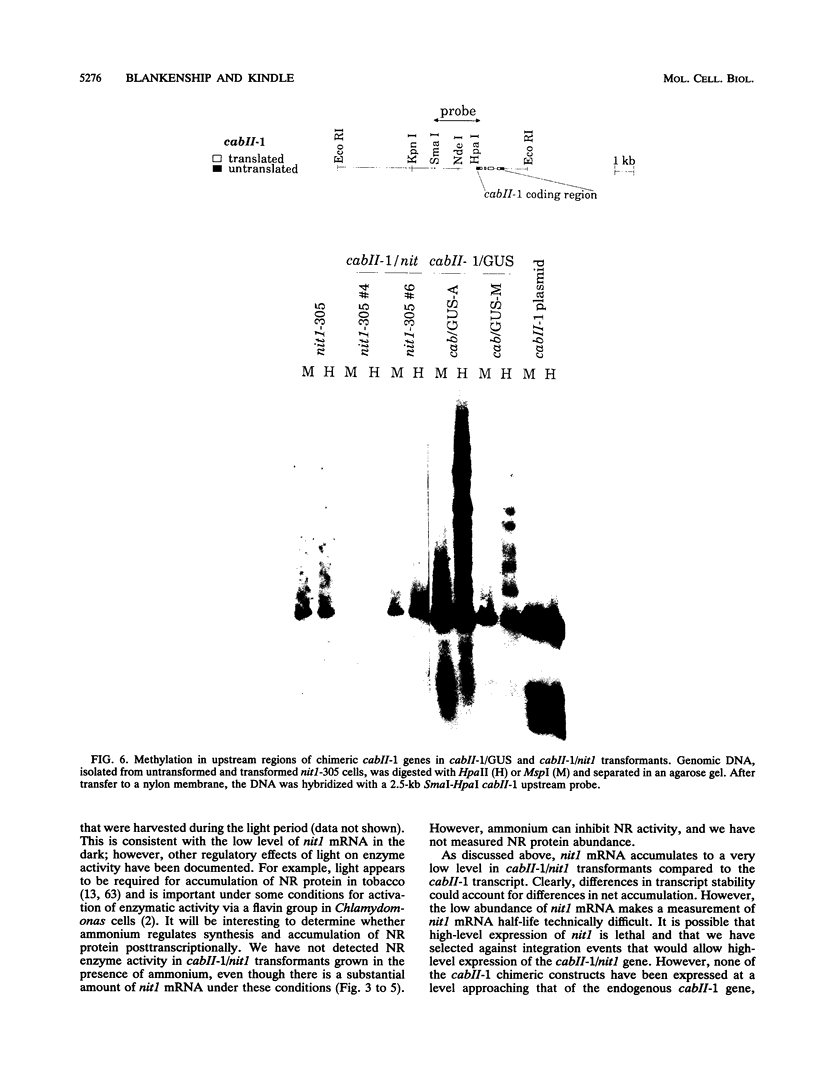
In Chlamydomonas reinhardtii, expression of the cabII-1 gene increases dramatically in response to light (cabII-1 encodes one of the light-harvesting chlorophyll a/b-binding proteins of photosystem II). We have used a region upstream of the cabII-1 gene in translational fusions to the bacterial uidA gene (encodes beta-glucuronidase) and transcriptional fusions to the Chlamydomonas nitrate reductase gene (nit1). Chlamydomonas transformants carrying intact copies of the chimeric uidA gene do not express beta-glucuronidase at the level of enzyme activity or mRNA accumulation. Methylation in the cabII-1 promoter region of the introduced gene is extensive in these strains, suggesting that newly introduced foreign genes may be recognized and silenced by a cellular mechanism that is correlated with increased methylation. Transformants that express the chimeric cabII-1/nit1 gene have been recovered. In contrast to the endogenous nit1 gene, the chimeric cabII-1/nit1 gene is expressed in ammonium-containing medium. Moreover, nit1 mRNA accumulation is dramatically stimulated by light, with a time course that is indistinguishable from that of the endogenous cabII-1 gene. The cabII-1/nit1 gene has been used to select transformants in a nit1- nit2- Chlamydomonas strain (CC400G) and should be useful for transformation of the large number of mutants in the Ebersold-Levine lineage, which carry the same mutations.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adamse P., Jaspers P. A., Bakker J. A., Kendrick R. E., Koornneef M. Photophysiology and phytochrome content of long-hypocotyl mutant and wild-type cucumber seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1988 May;87(1):264–268. doi: 10.1104/pp.87.1.264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng C. L., Acedo G. N., Dewdney J., Goodman H. M., Conkling M. A. Differential expression of the two Arabidopsis nitrate reductase genes. Plant Physiol. 1991 May;96(1):275–279. doi: 10.1104/pp.96.1.275. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chory J., Nagpal P., Peto C. A. Phenotypic and Genetic Analysis of det2, a New Mutant That Affects Light-Regulated Seedling Development in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell. 1991 May;3(5):445–459. doi: 10.1105/tpc.3.5.445. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chory J., Peto C. A., Ashbaugh M., Saganich R., Pratt L., Ausubel F. Different Roles for Phytochrome in Etiolated and Green Plants Deduced from Characterization of Arabidopsis thaliana Mutants. Plant Cell. 1989 Sep;1(9):867–880. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.9.867. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chory J., Peto C., Feinbaum R., Pratt L., Ausubel F. Arabidopsis thaliana mutant that develops as a light-grown plant in the absence of light. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):991–999. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90950-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collis P., Antoniou M., Grosveld F. Definition of the minimal requirements within the human beta-globin gene and the dominant control region for high level expression. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):233–240. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08100.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debuchy R., Purton S., Rochaix J. D. The argininosuccinate lyase gene of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: an important tool for nuclear transformation and for correlating the genetic and molecular maps of the ARG7 locus. EMBO J. 1989 Oct;8(10):2803–2809. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08426.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng X. W., Caspar T., Quail P. H. cop1: a regulatory locus involved in light-controlled development and gene expression in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev. 1991 Jul;5(7):1172–1182. doi: 10.1101/gad.5.7.1172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diener D. R., Curry A. M., Johnson K. A., Williams B. D., Lefebvre P. A., Kindle K. L., Rosenbaum J. L. Rescue of a paralyzed-flagella mutant of Chlamydomonas by transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5739–5743. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dionisio-Sese M. L., Fukuzawa H., Miyachi S. Light-Induced Carbonic Anhydrase Expression in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1990 Nov;94(3):1103–1110. doi: 10.1104/pp.94.3.1103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández E., Matagne R. F. In vivo complementation analysis of nitrate reductase-deficient mutants in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Curr Genet. 1986;10(5):397–403. doi: 10.1007/BF00418413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernández E., Schnell R., Ranum L. P., Hussey S. C., Silflow C. D., Lefebvre P. A. Isolation and characterization of the nitrate reductase structural gene of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6449–6453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galván A., Cárdenas J., Fernández E. Nitrate Reductase Regulates Expression of Nitrite Uptake and Nitrite Reductase Activities in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol. 1992 Feb;98(2):422–426. doi: 10.1104/pp.98.2.422. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldschmidt-Clermont M., Rahire M. Sequence, evolution and differential expression of the two genes encoding variant small subunits of ribulose bisphosphate carboxylase/oxygenase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Mol Biol. 1986 Oct 5;191(3):421–432. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90137-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goring D. R., Thomson L., Rothstein S. J. Transformation of a partial nopaline synthase gene into tobacco suppresses the expression of a resident wild-type gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1770–1774. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1770. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hobbs S. L., Kpodar P., DeLong C. M. The effect of T-DNA copy number, position and methylation on reporter gene expression in tobacco transformants. Plant Mol Biol. 1990 Dec;15(6):851–864. doi: 10.1007/BF00039425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imbault P., Wittemer C., Johanningmeier U., Jacobs J. D., Howell S. H. Structure of the Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cabII-1 gene encoding a chlorophyll-a/b-binding protein. Gene. 1988 Dec 20;73(2):397–407. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90504-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Shalom D., Kloppstech K., Ohad I. Light regulation of the 22 kd heat shock gene transcription and its translation product accumulation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. EMBO J. 1990 Sep;9(9):2657–2661. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07450.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johanningmeier U., Howell S. H. Regulation of light-harvesting chlorophyll-binding protein mRNA accumulation in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Possible involvement of chlorophyll synthesis precursors. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13541–13549. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindle K. L. High-frequency nuclear transformation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(3):1228–1232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.3.1228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindle K. L., Schnell R. A., Fernández E., Lefebvre P. A. Stable nuclear transformation of Chlamydomonas using the Chlamydomonas gene for nitrate reductase. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2589–2601. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makoff A. J., Oxer M. D., Romanos M. A., Fairweather N. F., Ballantine S. Expression of tetanus toxin fragment C in E. coli: high level expression by removing rare codons. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 25;17(24):10191–10202. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.24.10191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzke M. A., Primig M., Trnovsky J., Matzke A. J. Reversible methylation and inactivation of marker genes in sequentially transformed tobacco plants. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):643–649. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03421.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mayfield S. P., Kindle K. L. Stable nuclear transformation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii by using a C. reinhardtii gene as the selectable marker. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2087–2091. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McElroy D., Zhang W., Cao J., Wu R. Isolation of an efficient actin promoter for use in rice transformation. Plant Cell. 1990 Feb;2(2):163–171. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.2.163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell D. R., Kang Y. Identification of oda6 as a Chlamydomonas dynein mutant by rescue with the wild-type gene. J Cell Biol. 1991 May;113(4):835–842. doi: 10.1083/jcb.113.4.835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mittelsten Scheid O., Paszkowski J., Potrykus I. Reversible inactivation of a transgene in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Aug;228(1-2):104–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00282454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooibroek H., Kuipers A. G., Sietsma J. H., Punt P. J., Wessels J. G. Introduction of hygromycin B resistance into Schizophyllum commune: preferential methylation of donor DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jun;222(1):41–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00283021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Napoli C., Lemieux C., Jorgensen R. Introduction of a Chimeric Chalcone Synthase Gene into Petunia Results in Reversible Co-Suppression of Homologous Genes in trans. Plant Cell. 1990 Apr;2(4):279–289. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.4.279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajasekhar V. K., Gowri G., Campbell W. H. Phytochrome-mediated light regulation of nitrate reductase expression in squash cotyledons. Plant Physiol. 1988 Oct;88(2):242–244. doi: 10.1104/pp.88.2.242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SAGER R., GRANICK S. Nutritional studies with Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1953 Oct 14;56(5):831–838. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1953.tb30261.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepherd H. S., Ledoigt G., Howell S. H. Regulation of light-harvesting chlorophyll-binding protein (LHCP) mRNA accumulation during the cell cycle in Chlamydomonas reinhardi. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):99–107. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90500-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suárez T., Eslava A. P. Transformation of Phycomyces with a bacterial gene for kanamycin resistance. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Apr;212(1):120–123. doi: 10.1007/BF00322453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vincentz M., Caboche M. Constitutive expression of nitrate reductase allows normal growth and development of Nicotiana plumbaginifolia plants. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1027–1035. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08041.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Hostos E. L., Schilling J., Grossman A. R. Structure and expression of the gene encoding the periplasmic arylsulfatase of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Aug;218(2):229–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00331273. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Krol A. R., Mur L. A., Beld M., Mol J. N., Stuitje A. R. Flavonoid genes in petunia: addition of a limited number of gene copies may lead to a suppression of gene expression. Plant Cell. 1990 Apr;2(4):291–299. doi: 10.1105/tpc.2.4.291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Gromoff E. D., Treier U., Beck C. F. Three light-inducible heat shock genes of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3911–3918. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3911. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]