Abstract
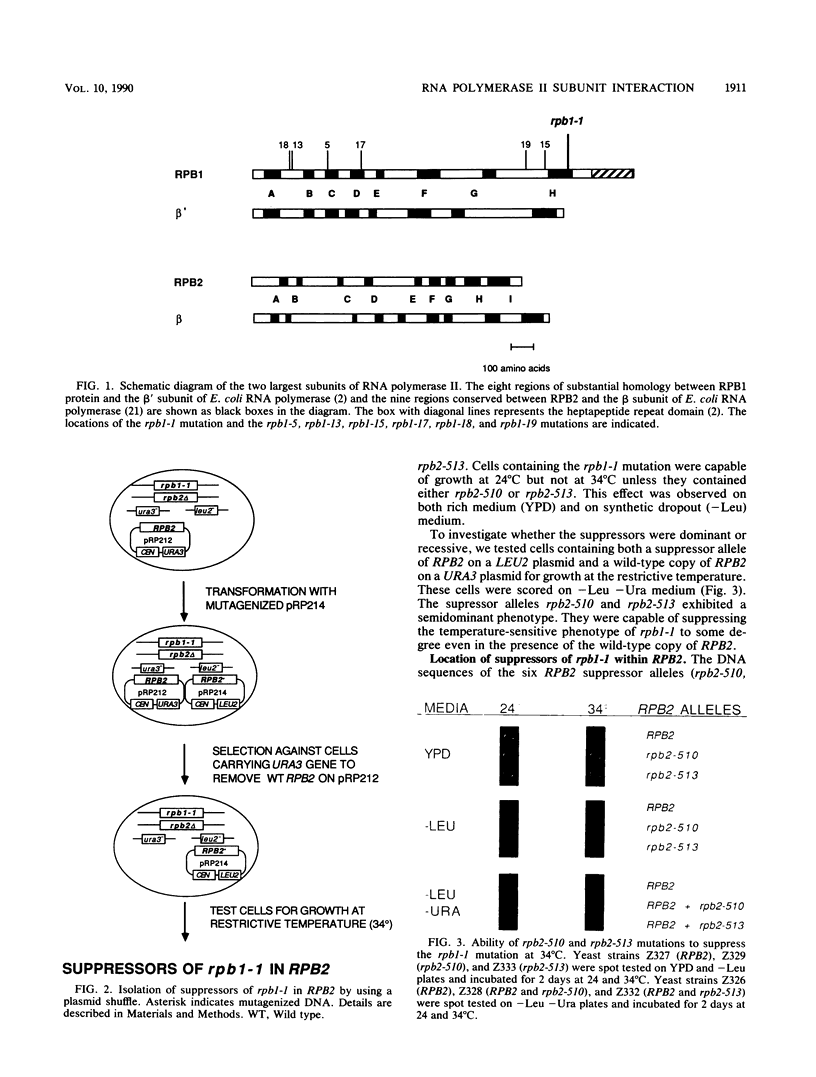
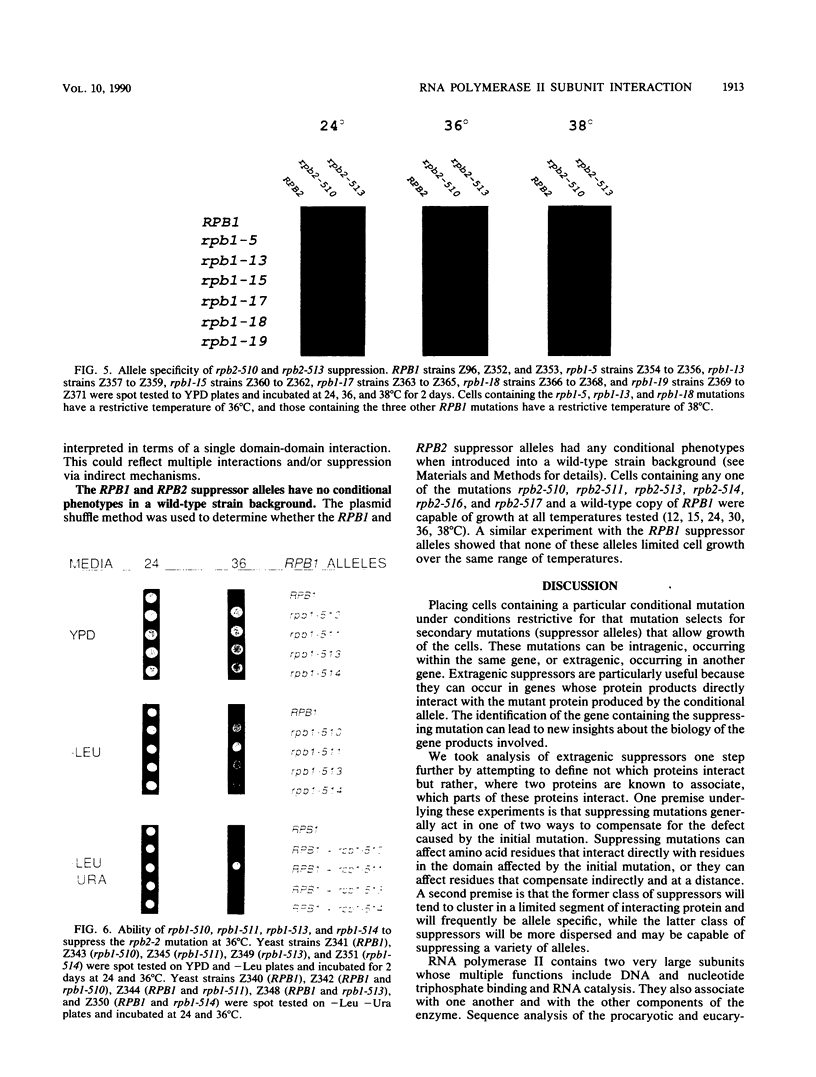
The two large subunits of RNA polymerase II, RPB1 and RPB2, contain regions of extensive homology to the two large subunits of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. These homologous regions may represent separate protein domains with unique functions. We investigated whether suppressor genetics could provide evidence for interactions between specific segments of RPB1 and RPB2 in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. A plasmid shuffle method was used to screen thoroughly for mutations in RPB2 that suppress a temperature-sensitive mutation, rpb1-1, which is located in region H of RPB1. All six RPB2 mutations that suppress rpb1-1 were clustered in region I of RPB2. The location of these mutations and the observation that they were allele specific for suppression of rpb1-1 suggests an interaction between region H of RPB1 and region I of RPB2. A similar experiment was done to isolate and map mutations in RPB1 that suppress a temperature-sensitive mutation, rpb2-2, which occurs in region I of RPB2. These suppressor mutations were not clustered in a particular region. Thus, fine structure suppressor genetics can provide evidence for interactions between specific segments of two proteins, but the results of this type of analysis can depend on the conditional mutation to be suppressed.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adams A. E., Botstein D., Drubin D. G. A yeast actin-binding protein is encoded by SAC6, a gene found by suppression of an actin mutation. Science. 1989 Jan 13;243(4888):231–233. doi: 10.1126/science.2643162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison L. A., Moyle M., Shales M., Ingles C. J. Extensive homology among the largest subunits of eukaryotic and prokaryotic RNA polymerases. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90117-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Trueheart J., Natsoulis G., Fink G. R. 5-Fluoroorotic acid as a selective agent in yeast molecular genetics. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:164–175. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartman P. E., Roth J. R. Mechanisms of suppression. Adv Genet. 1973;17:1–105. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2660(08)60170-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarvik J., Botstein D. Conditional-lethal mutations that suppress genetic defects in morphogenesis by altering structural proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2738–2742. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jokerst R. S., Weeks J. R., Zehring W. A., Greenleaf A. L. Analysis of the gene encoding the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II in Drosophila. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Jan;215(2):266–275. doi: 10.1007/BF00339727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luck D. J. Genetic and biochemical dissection of the eucaryotic flagellum. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):789–794. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R., Osmond B. C., Botstein D. Genetic analysis of DNA replication in bacteria: dnaB mutations that suppress dnaC mutations and dnaQ mutations that suppress dnaE mutations in Salmonella typhimurium. Genetics. 1984 Sep;108(1):25–38. doi: 10.1093/genetics/108.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. A., Serio G. F., Howard R. A., Bear J. L., Evans J. E., Kimball A. P. Subunit localizations of zinc(II) in DNA-dependent RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli B. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Aug 28;579(2):291–297. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(79)90056-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris N. R., Lai M. H., Oakley C. E. Identification of a gene for alpha-tubulin in Aspergillus nidulans. Cell. 1979 Feb;16(2):437–442. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90019-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Morgan E. A. Genetics of bacterial ribosomes. Annu Rev Genet. 1977;11:297–347. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.11.120177.001501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonet M. L., Young R. A. Intragenic and extragenic suppressors of mutations in the heptapeptide repeat domain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae RNA polymerase II. Genetics. 1989 Dec;123(4):715–724. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.4.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonet M., Scafe C., Sexton J., Young R. Eucaryotic RNA polymerase conditional mutant that rapidly ceases mRNA synthesis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1602–1611. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1602. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonet M., Sweetser D., Young R. A. Functional redundancy and structural polymorphism in the large subunit of RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):909–915. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90517-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scafe C., Martin C., Nonet M., Podos S., Okamura S., Young R. A. Conditional mutations occur predominantly in highly conserved residues of RNA polymerase II subunits. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1270–1275. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scafe C., Nonet M., Young R. A. RNA polymerase II mutants defective in transcription of a subset of genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1010–1016. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sentenac A. Eukaryotic RNA polymerases. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(1):31–90. doi: 10.3109/10409238509082539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweetser D., Nonet M., Young R. A. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic RNA polymerases have homologous core subunits. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1192–1196. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. W., Wu F. Y., Speckhard D. C. Subunit location of the intrinsic divalent metal ions in RNA polymerase from Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1977 Dec 13;16(25):5449–5454. doi: 10.1021/bi00644a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yura T., Ishihama A. Genetics of bacterial RNA polymerases. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:59–97. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.000423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]