Abstract
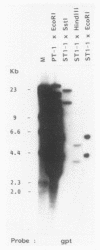
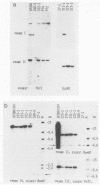
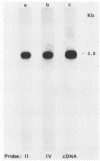
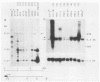
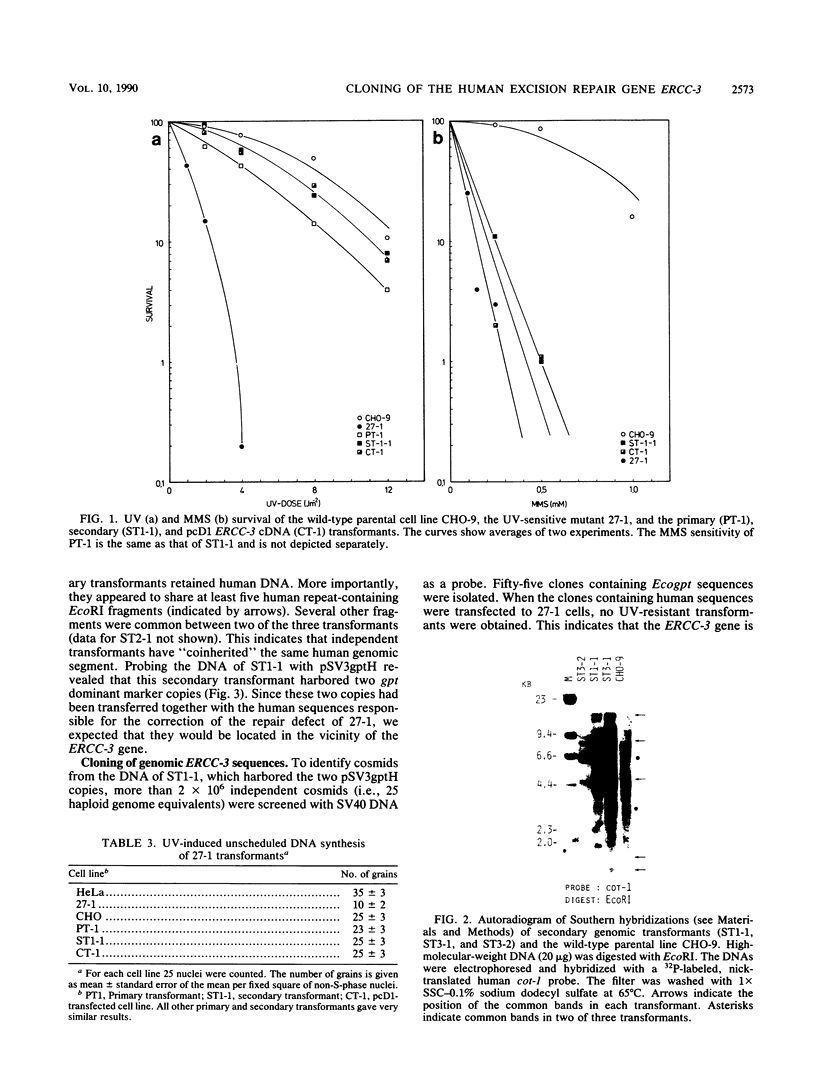
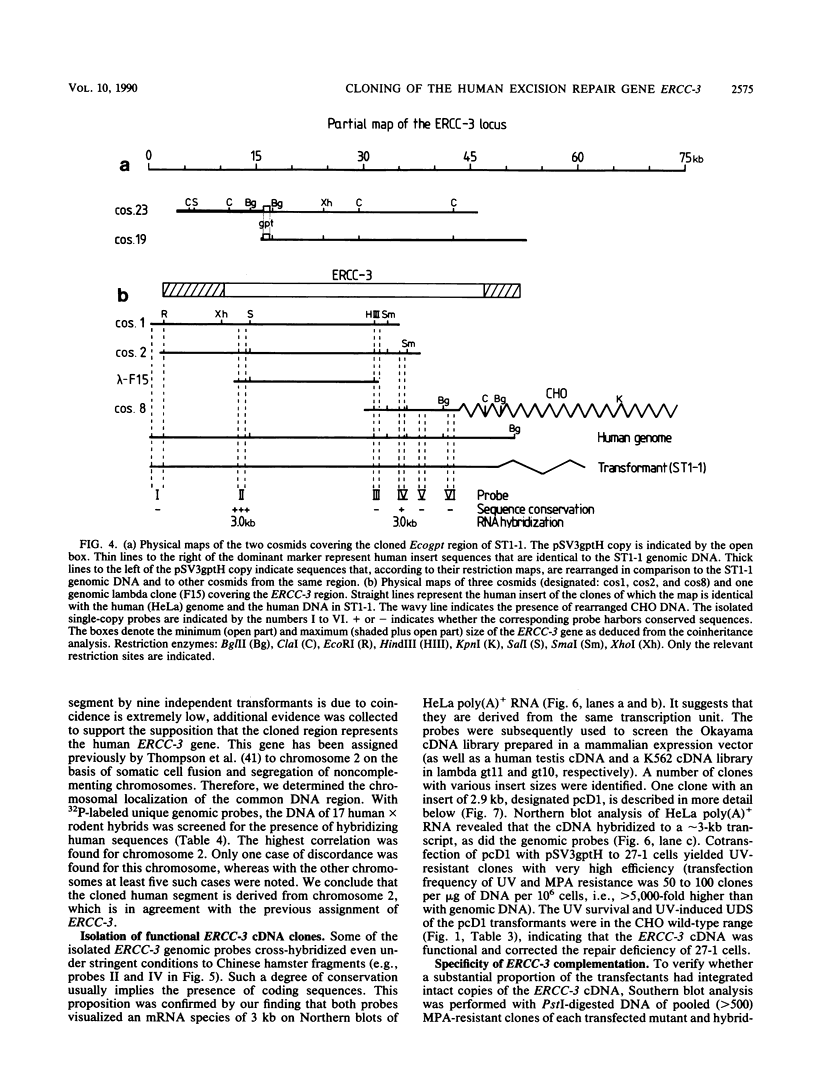
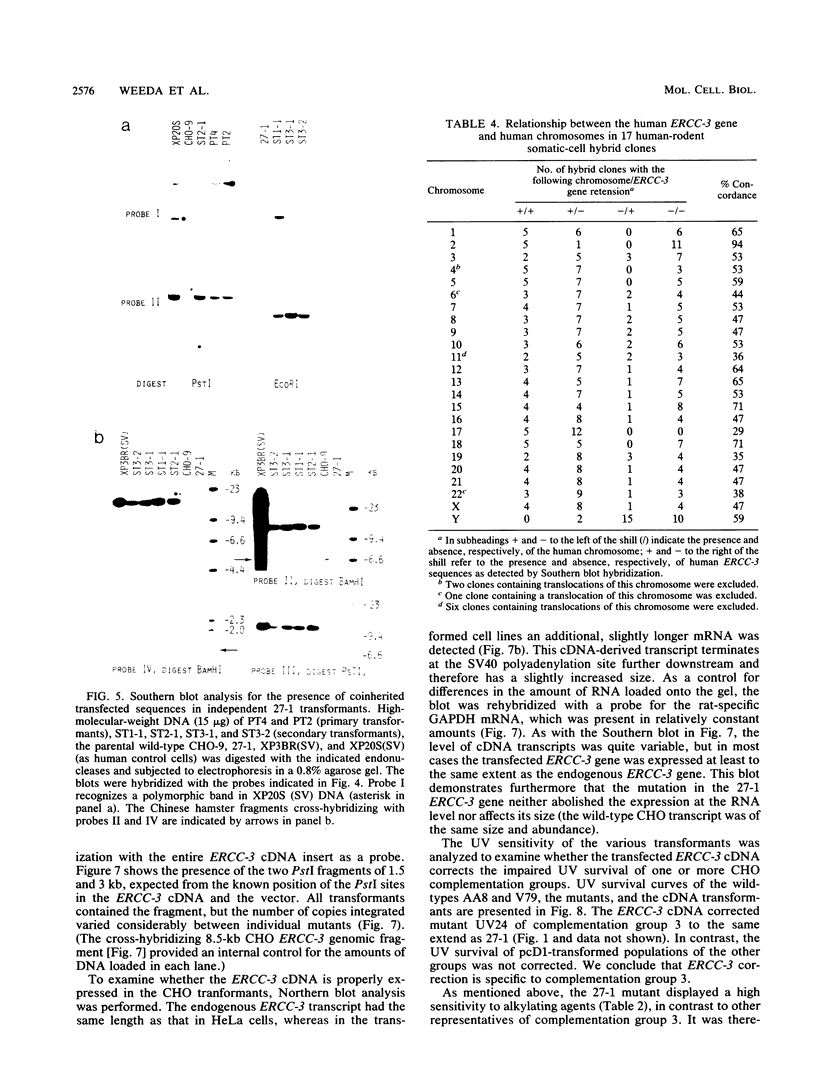
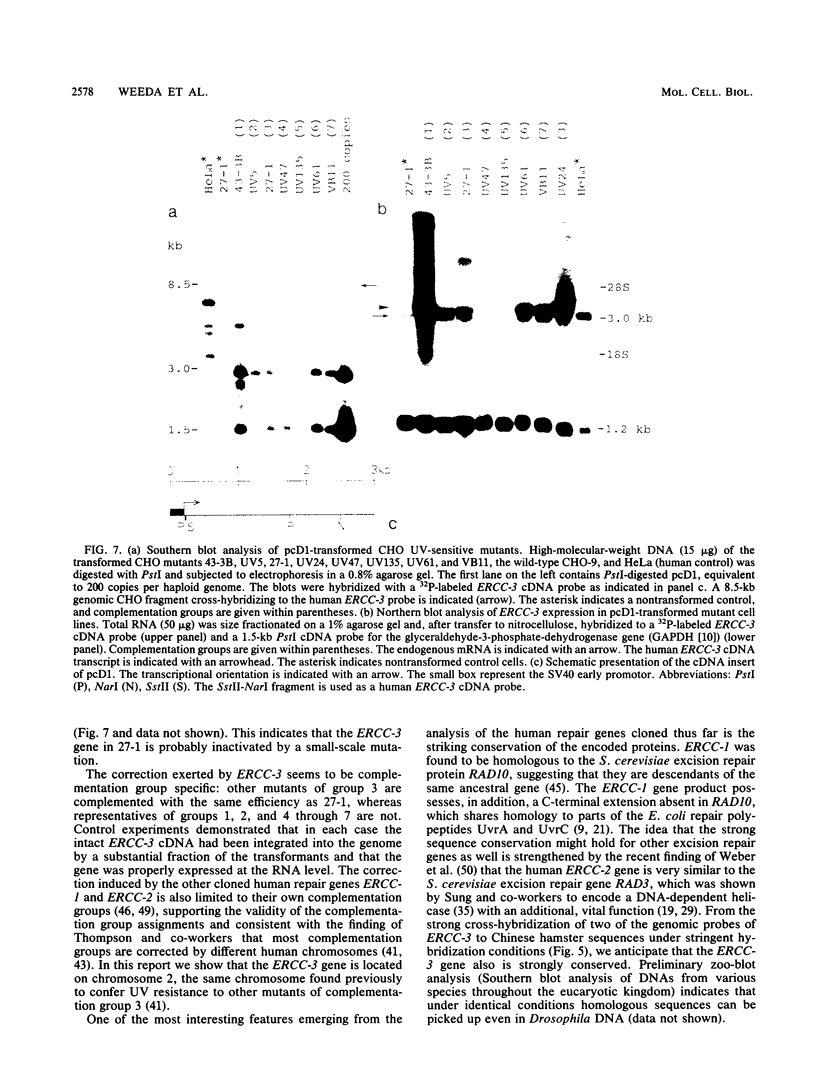
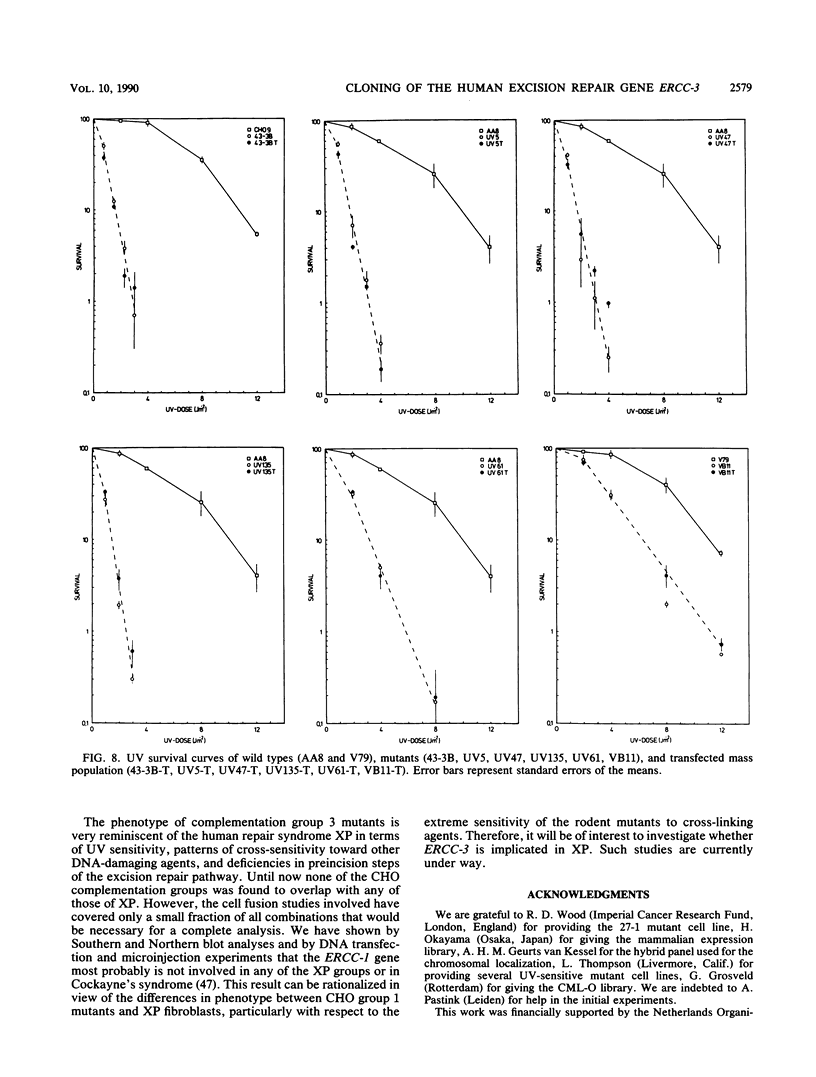
In this report we present the cloning, partial characterization, and preliminary studies of the biological activity of a human gene, designated ERCC-3, involved in early steps of the nucleotide excision repair pathway. The gene was cloned after genomic DNA transfection of human (HeLa) chromosomal DNA together with dominant marker pSV3gptH to the UV-sensitive, incision-defective Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) mutant 27-1. This mutant belongs to complementation group 3 of repair-deficient rodent mutants. After selection of UV-resistant primary and secondary 27-1 transformants, human sequences associated with the induced UV resistance were rescued in cosmids from the DNA of a secondary transformant by using a linked dominant marker copy and human repetitive DNA as probes. From coinheritance analysis of the ERCC-3 region in independent transformants, we deduce that the gene has a size of 35 to 45 kilobases, of which one essential segment has so far been refractory to cloning. Conserved unique human sequences hybridizing to a 3.0-kilobase mRNA were used to isolate apparently full-length cDNA clones. Upon transfection to 27-1 cells, the ERCC-3 cDNA, inserted in a mammalian expression vector, induced specific and (virtually) complete correction of the UV sensitivity and unscheduled DNA synthesis of mutants of complementation group 3 with very high efficiency. Mutant 27-1 is, unlike other mutants of complementation group 3, also very sensitive toward small alkylating agents. This unique property of the mutant is not corrected by introduction of the ERCC-3 cDNA, indicating that it may be caused by an independent second mutation in another repair function. By hybridization to DNA of a human x rodent hybrid cell panel, the ERCC-3 gene was assigned to chromosome 2, in agreement with data based on cell fusion (L. H. Thompson, A. V. Carrano, K. Sato, E. P. Salazar, B. F. White, S. A. Stewart, J. L. Minkler, and M. J. Siciliano, Somat. Cell. Mol. Genet. 13:539-551, 1987).
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auffray C., Rougeon F. Purification of mouse immunoglobulin heavy-chain messenger RNAs from total myeloma tumor RNA. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jun;107(2):303–314. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb06030.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates P. F., Swift R. A. Double cos site vectors: simplified cosmid cloning. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):137–146. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90183-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bootsma D., Keijzer W., Jung E. G., Bohnert E. Xeroderma pigmentosum complementation group XP-I withdrawn. Mutat Res. 1989 Sep;218(2):149–151. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(89)90021-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busch D., Greiner C., Lewis K., Ford R., Adair G., Thompson L. Summary of complementation groups of UV-sensitive CHO cell mutants isolated by large-scale screening. Mutagenesis. 1989 Sep;4(5):349–354. doi: 10.1093/mutage/4.5.349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins A., Johnson R. T. DNA repair mutants in higher eukaryotes. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;6:61–82. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1984.supplement_6.4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Weerd-Kastelein E. A., Keijzer W., Bootsma D. Genetic heterogeneity of xeroderma pigmentosum demonstrated by somatic cell hybridization. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jul 19;238(81):80–83. doi: 10.1038/newbio238080a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F., Johnson M. S., Husain I., Van Houten B., Thomas D. C., Sancar A. Domainal evolution of a prokaryotic DNA repair protein and its relationship to active-transport proteins. Nature. 1986 Oct 2;323(6087):451–453. doi: 10.1038/323451a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Marty L., Piechaczyk M., el Sabrouty S., Dani C., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Various rat adult tissues express only one major mRNA species from the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate-dehydrogenase multigenic family. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 11;13(5):1431–1442. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.5.1431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg E. C. Deoxyribonucleic acid repair in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Mar;52(1):70–102. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.1.70-102.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Poustka A., Murray N. Lambda replacement vectors carrying polylinker sequences. J Mol Biol. 1983 Nov 15;170(4):827–842. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80190-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geurts van Kessel A. H., ten Brinke H., Boere W. A., den Boer W. C., de Groot P. G., Hagemeijer A., Meera Khan P., Pearson P. L. Characterization of the Philadelphia chromosome by gene mapping. Cytogenet Cell Genet. 1981;30(2):83–91. doi: 10.1159/000131595. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman L., Caron P. R., Mazur S. J., Oh E. Y. Repair of DNA-containing pyrimidine dimers. FASEB J. 1988 Aug;2(11):2696–2701. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.2.11.3294078. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickson I. D., Harris A. L. Mammalian DNA repair--use of mutants hypersensitive to cytotoxic agents. Trends Genet. 1988 Apr;4(4):101–106. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90097-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. R., Prakash S., Reynolds P., Polakowska R., Weber S., Prakash L. Isolation and characterization of the RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae and inviability of rad3 deletion mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Sep;80(18):5680–5684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.18.5680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeijmakers J. H., Odijk H., Westerveld A. Differences between rodent and human cell lines in the amount of integrated DNA after transfection. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Mar;169(1):111–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90230-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoeijmakers J. H., van Duin M., Westerveld A., Yasui A., Bootsma D. Identification of DNA repair genes in the human genome. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1986;51(Pt 1):91–101. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1986.051.01.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoy C. A., Thompson L. H., Salazar E. P., Stewart S. A. Different genetic alterations underlie dual hypersensitivity of CHO mutant UV-1 to DNA methylating and cross-linking agents. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Nov;11(6):523–532. doi: 10.1007/BF01534718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffreys A. J., Flavell R. A. A physical map of the DNA regions flanking the rabbit beta-globin gene. Cell. 1977 Oct;12(2):429–439. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90119-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer K. H., Lee M. M., Scotto J. DNA repair protects against cutaneous and internal neoplasia: evidence from xeroderma pigmentosum. Carcinogenesis. 1984 Apr;5(4):511–514. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.4.511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulligan R. C., Berg P. Selection for animal cells that express the Escherichia coli gene coding for xanthine-guanine phosphoribosyltransferase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2072–2076. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naumovski L., Friedberg E. C. A DNA repair gene required for the incision of damaged DNA is essential for viability in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4818–4821. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4818. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okayama H., Berg P. A cDNA cloning vector that permits expression of cDNA inserts in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Feb;3(2):280–289. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.2.280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Sancar G. B. DNA repair enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:29–67. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.000333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier P. I., Bernards R., Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Expression of class I major histocompatibility antigens switched off by highly oncogenic adenovirus 12 in transformed rat cells. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):771–775. doi: 10.1038/305771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sealey P. G., Whittaker P. A., Southern E. M. Removal of repeated sequences from hybridisation probes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):1905–1922. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.1905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stefanini M., Keijzer W., Westerveld A., Bootsma D. Interspecies complementation analysis of xeroderma pigmentosum and UV-sensitive Chinese hamster cells. Exp Cell Res. 1985 Dec;161(2):373–380. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(85)90094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Prakash L., Matson S. W., Prakash S. RAD3 protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is a DNA helicase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8951–8955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sung P., Prakash L., Weber S., Prakash S. The RAD3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae encodes a DNA-dependent ATPase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Sep;84(17):6045–6049. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.17.6045. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanaka K., Satokata I., Ogita Z., Uchida T., Okada Y. Molecular cloning of a mouse DNA repair gene that complements the defect of group-A xeroderma pigmentosum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5512–5516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Brookman K. W., Dillehay L. E., Mooney C. L., Carrano A. V. Hypersensitivity to mutation and sister-chromatid-exchange induction in CHO cell mutants defective in incising DNA containing UV lesions. Somatic Cell Genet. 1982 Nov;8(6):759–773. doi: 10.1007/BF01543017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Busch D. B., Brookman K., Mooney C. L., Glaser D. A. Genetic diversity of UV-sensitive DNA repair mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3734–3737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Carrano A. V., Sato K., Salazar E. P., White B. F., Stewart S. A., Minkler J. L., Siciliano M. J. Identification of nucleotide-excision-repair genes on human chromosomes 2 and 13 by functional complementation in hamster-human hybrids. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1987 Sep;13(5):539–551. doi: 10.1007/BF01534495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Mooney C. L., Brookman K. W. Genetic complementation between UV-sensitive CHO mutants and xeroderma pigmentosum fibroblasts. Mutat Res. 1985 Jun-Jul;150(1-2):423–429. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(85)90139-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Mooney C. L., Burkhart-Schultz K., Carrano A. V., Siciliano M. J. Correction of a nucleotide-excision-repair mutation by human chromosome 19 in hamster-human hybrid cells. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Jan;11(1):87–92. doi: 10.1007/BF01534738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Salazar E. P., Brookman K. W., Collins C. C., Stewart S. A., Busch D. B., Weber C. A. Recent progress with the DNA repair mutants of Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1987;6:97–110. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1984.supplement_6.6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Shiomi T., Salazar E. P., Stewart S. A. An eighth complementation group of rodent cells hypersensitive to ultraviolet radiation. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1988 Nov;14(6):605–612. doi: 10.1007/BF01535314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vermeulen W., Osseweijer P., de Jonge A. J., Hoeijmakers J. H. Transient correction of excision repair defects in fibroblasts of 9 xeroderma pigmentosum complementation groups by microinjection of crude human cell extracts. Mutat Res. 1986 May;165(3):199–206. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(86)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber C. A., Salazar E. P., Stewart S. A., Thompson L. H. Molecular cloning and biological characterization of a human gene, ERCC2, that corrects the nucleotide excision repair defect in CHO UV5 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1137–1146. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerveld A., Hoeijmakers J. H., van Duin M., de Wit J., Odijk H., Pastink A., Wood R. D., Bootsma D. Molecular cloning of a human DNA repair gene. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):425–429. doi: 10.1038/310425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. D., Burki H. J. Repair capability and the cellular age response for killing and mutation induction after UV. Mutat Res. 1982 Aug;95(2-3):505–514. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(82)90281-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zdzienicka M. Z., Roza L., Westerveld A., Bootsma D., Simons J. W. Biological and biochemical consequences of the human ERCC-1 repair gene after transfection into a repair-deficient CHO cell line. Mutat Res. 1987 Jan;183(1):69–74. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(87)90047-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zdzienicka M. Z., Simons J. W. Analysis of repair processes by the determination of the induction of cell killing and mutations in two repair-deficient Chinese hamster ovary cell lines. Mutat Res. 1986 Jul;166(1):59–69. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(86)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zdzienicka M. Z., van der Schans G. P., Simons J. W. Identification of a new seventh complementation group of UV-sensitive mutants in Chinese hamster cells. Mutat Res. 1988 Sep;194(2):165–170. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(88)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wit J., Hoeksema H. L., Bootsma D., Westerveld A. Assignment of structural beta-galactosidase loci to human chromosomes 3 and 22. Hum Genet. 1979 Oct 2;51(3):259–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00283392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin M., Janssen J. H., de Wit J., Hoeijmakers J. H., Thompson L. H., Bootsma D., Westerveld A. Transfection of the cloned human excision repair gene ERCC-1 to UV-sensitive CHO mutants only corrects the repair defect in complementation group-2 mutants. Mutat Res. 1988 Mar;193(2):123–130. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(88)90042-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin M., Vredeveldt G., Mayne L. V., Odijk H., Vermeulen W., Klein B., Weeda G., Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D., Westerveld A. The cloned human DNA excision repair gene ERCC-1 fails to correct xeroderma pigmentosum complementation groups A through I. Mutat Res. 1989 Mar;217(2):83–92. doi: 10.1016/0921-8777(89)90059-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Duin M., de Wit J., Odijk H., Westerveld A., Yasui A., Koken M. H., Hoeijmakers J. H., Bootsma D. Molecular characterization of the human excision repair gene ERCC-1: cDNA cloning and amino acid homology with the yeast DNA repair gene RAD10. Cell. 1986 Mar 28;44(6):913–923. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]