Abstract
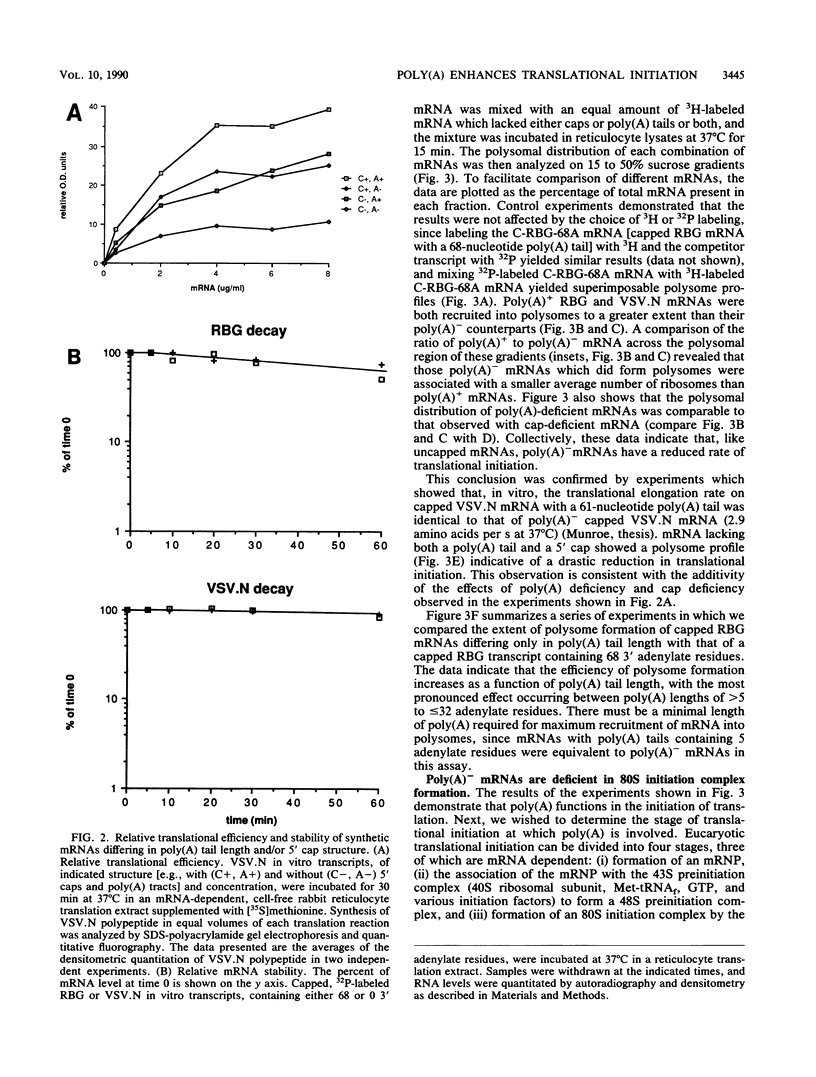
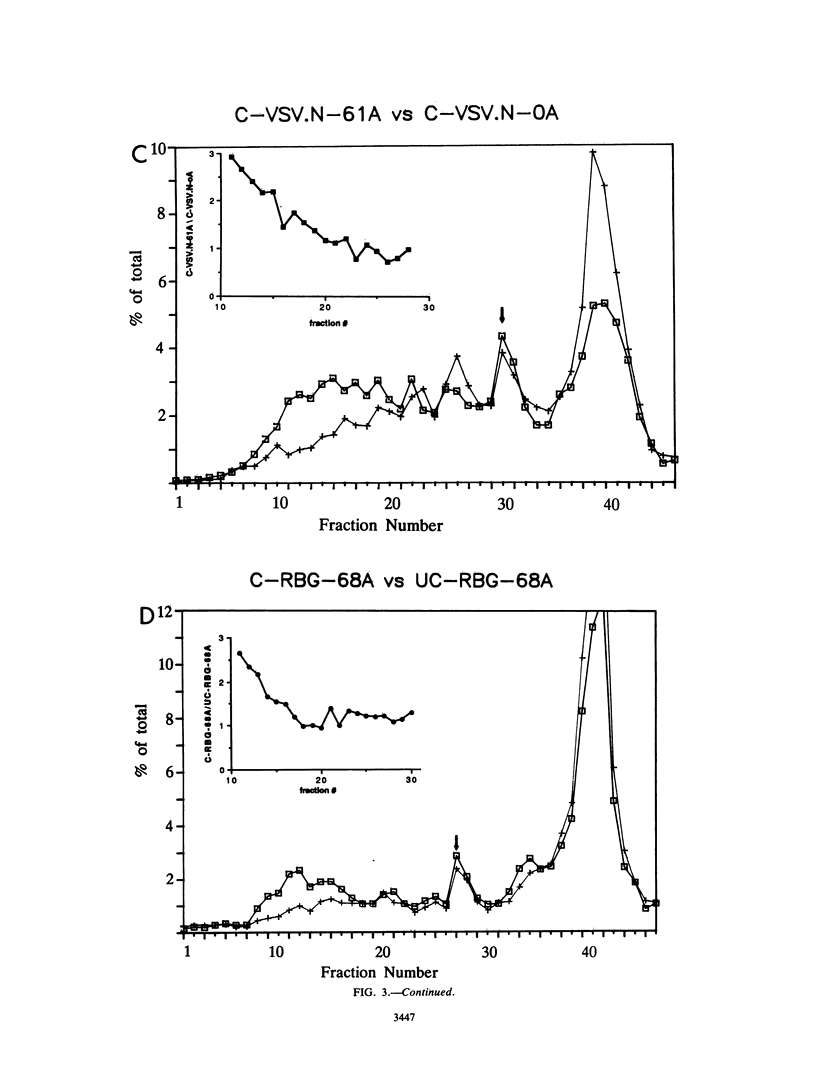
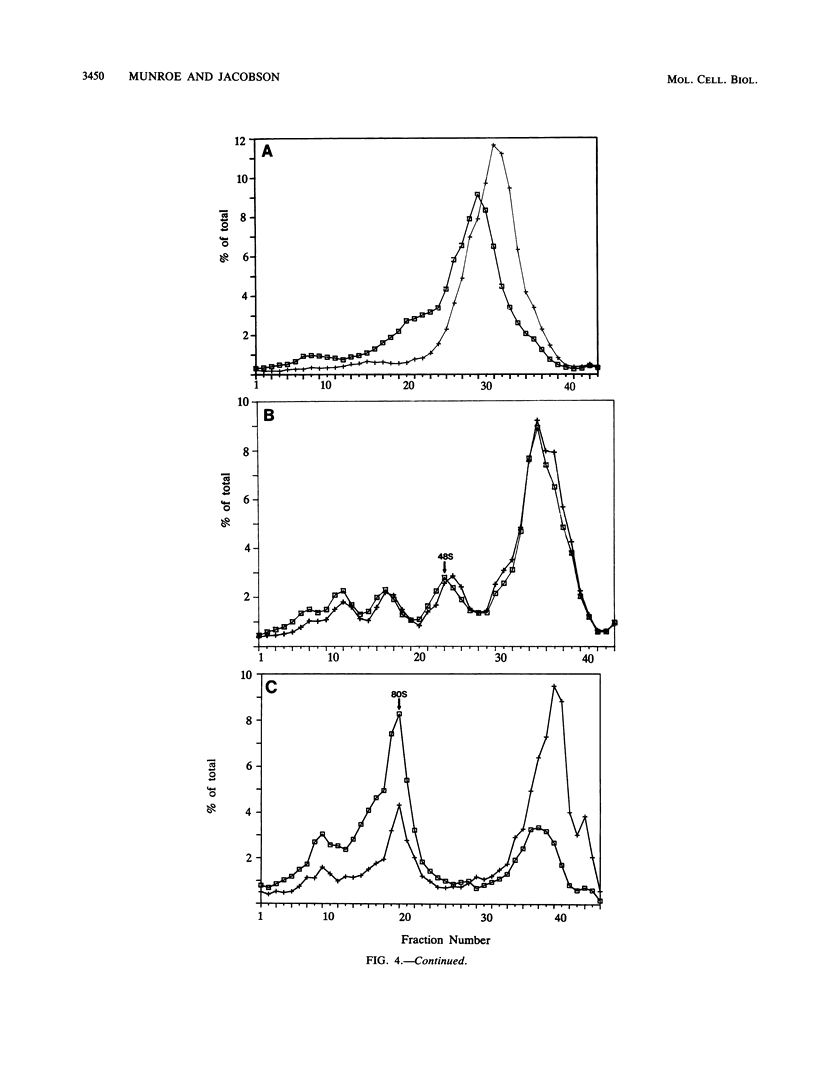
To evaluate the hypothesis that the 3' poly(A) tract of mRNA plays a role in translational initiation, we constructed derivatives of pSP65 which direct the in vitro synthesis of mRNAs with different poly(A) tail lengths and compared, in reticulocyte extracts, the relative efficiencies with which such mRNAs were translated, degraded, recruited into polysomes, and assembled into messenger ribonucleoproteins or intermediates in the translational initiation pathway. Relative to mRNAs which were polyadenylated, we found that nonpolyadenylated [poly(A)-]mRNAs had a reduced translational capacity which was not due to an increase in their decay rates, but was attributable to a reduction in their efficiency of recruitment into polysomes. The defect in poly(A)- mRNAs affected a late step in translational initiation, was distinct from the phenotype associated with cap-deficient mRNAs, and resulted in a reduced ability to form 80S initiation complexes. Moreover, poly(A) added in trans inhibited translation from capped polyadenylated mRNAs but stimulated translation from capped poly(A)- mRNAs. We suggest that the presence of a 3' poly(A) tail may facilitate the binding of an initiation factor or ribosomal subunit at the mRNA 5' end.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam S. A., Nakagawa T., Swanson M. S., Woodruff T. K., Dreyfuss G. mRNA polyadenylate-binding protein: gene isolation and sequencing and identification of a ribonucleoprotein consensus sequence. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2932–2943. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adams D. S., Jeffery W. R. Poly(adenylic acid) degradation by two distinct processes in the cytoplasmic RNA of Physarum polycephalum. Biochemistry. 1978 Oct 17;17(21):4519–4524. doi: 10.1021/bi00614a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adesnik M., Darnell J. E. Biogenesis and characterization of histone messenger RNA in HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1972 Jun 28;67(3):397–406. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90458-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bablanian R., Banerjee A. K. Poly(riboadenylic acid) preferentially inhibits in vitro translation of cellular mRNAs compared with vaccinia virus mRNAs: possible role in vaccinia virus cytopathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1290–1294. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1290. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer B. W., Kornberg R. D. Repeating structure of cytoplasmic poly(A)-ribonucleoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):1890–1892. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.1890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer B. W., Kornberg R. D. The protein responsible for the repeating structure of cytoplasmic poly(A)-ribonucleoprotein. J Cell Biol. 1983 Mar;96(3):717–721. doi: 10.1083/jcb.96.3.717. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertholet C., Van Meir E., ten Heggeler-Bordier B., Wittek R. Vaccinia virus produces late mRNAs by discontinuous synthesis. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):153–162. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90211-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. Characteristics and significance of the polyadenylate sequence in mammalian messenger RNA. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1976;17:117–148. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60068-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G., Diez J. Metabolism of the polyadenylate sequence of nuclear RNA and messenger RNA in mammalian cells. Cell. 1975 Jul;5(3):271–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(75)90102-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brawerman G. The Role of the poly(A) sequence in mammalian messenger RNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1981;10(1):1–38. doi: 10.3109/10409238109114634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrazana E. J., Pasieka K. B., Majzoub J. A. The vasopressin mRNA poly(A) tract is unusually long and increases during stimulation of vasopressin gene expression in vivo. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2267–2274. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carter C., Stoltzfus C. M., Banerjee A. K., Shatkin A. J. Origin of reovirus oligo(A). J Virol. 1974 Jun;13(6):1331–1337. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.6.1331-1337.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen A. K., Kahn L. E., Bourne C. M. Circular polysomes predominate on the rough endoplasmic reticulum of somatotropes and mammotropes in the rat anterior pituitary. Am J Anat. 1987 Jan;178(1):1–10. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001780102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darnell J. E., Wall R., Tushinski R. J. An adenylic acid-rich sequence in messenger RNA of HeLa cells and its possible relationship to reiterated sites in DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1321–1325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande A. K., Chatterjee B., Roy A. K. Translation and stability of rat liver messenger RNA for alpha 2 mu-globulin in Xenopus oocyte. The role of terminal poly(A). J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 25;254(18):8937–8942. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doel M. T., Carey N. H. The translational capacity of deadenylated ovalbumin messenger RNA. Cell. 1976 May;8(1):51–58. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90184-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drummond D. R., Armstrong J., Colman A. The effect of capping and polyadenylation on the stability, movement and translation of synthetic messenger RNAs in Xenopus oocytes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7375–7394. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubochet J., Morel C., Lebleu B., Herzberg M. Structure of globin mRNA and mRNA-protein particles. Use of dark-field electron microscopy. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jul 16;36(2):465–472. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edmonds M., Vaughan M. H., Jr, Nakazato H. Polyadenylic acid sequences in the heterogeneous nuclear RNA and rapidly-labeled polyribosomal RNA of HeLa cells: possible evidence for a precursor relationship. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1336–1340. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1336. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Efstratiadis A., Kafatos F. C., Maniatis T. The primary structure of rabbit beta-globin mRNA as determined from cloned DNA. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):571–585. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90090-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galili G., Kawata E. E., Smith L. D., Larkins B. A. Role of the 3'-poly(A) sequence in translational regulation of mRNAs in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5764–5770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallie D. R., Lucas W. J., Walbot V. Visualizing mRNA expression in plant protoplasts: factors influencing efficient mRNA uptake and translation. Plant Cell. 1989 Mar;1(3):301–311. doi: 10.1105/tpc.1.3.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grange T., de Sa C. M., Oddos J., Pictet R. Human mRNA polyadenylate binding protein: evolutionary conservation of a nucleic acid binding motif. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jun 25;15(12):4771–4787. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.12.4771. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R., Carroll E., 3rd Reconstitution of functional mRNA-protein complexes in a rabbit reticulocyte cell-free translation system. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Feb;5(2):342–351. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.2.342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R., Perry R. P. Relative occurrence of polyadenylic acid sequences in messenger and heterogeneous nuclear RNA of L cells as determined by poly (U)-hydroxylapatite chromatography. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 14;72(1):91–98. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R. Proteins crosslinked to messenger RNA by irradiating polyribosomes with ultraviolet light. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5685–5701. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg J. R. Ultraviolet light-induced crosslinking of mRNA to proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Feb;6(2):715–732. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.2.715. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossi de Sa M. F., Standart N., Martins de Sa C., Akhayat O., Huesca M., Scherrer K. The poly(A)-binding protein facilitates in vitro translation of poly(A)-rich mRNA. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Oct 1;176(3):521–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14309.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey E. D., Weber L. A., Baglioni C. Inhibition of initiation of protein synthesis by 7-methylguanosine-5'-monophosphate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jan;73(1):19–23. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hruby D. E., Roberts W. K. Encephalomyocarditis virus RNA. II. Polyadenylic acid requirement for efficient translation. J Virol. 1977 Aug;23(2):338–344. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.2.338-344.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu M. T., Coca-Prados M. Electron microscopic evidence for the circular form of RNA in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):339–340. doi: 10.1038/280339a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huarte J., Belin D., Vassalli A., Strickland S., Vassalli J. D. Meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes triggers the translation and polyadenylation of dormant tissue-type plasminogen activator mRNA. Genes Dev. 1987 Dec;1(10):1201–1211. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.10.1201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman L. E., Wormington W. M. Translational inactivation of ribosomal protein mRNAs during Xenopus oocyte maturation. Genes Dev. 1988 May;2(5):598–605. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.5.598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iatrou K., Dixon G. H. The distribution of poly(A)+ and poly(A)- protamine messenger RNA sequences in the developing trout testis. Cell. 1977 Mar;10(3):433–441. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90030-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson A., Favreau M. Possible involvement of poly(A) in protein synthesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6353–6368. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6353. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson A. Purification and fractionation of poly(A)+ RNA. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:254–261. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52028-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeffery W. R., Brawerman G. Characterization of the steady-state population of messenger RNA and its poly(adenylic acid) segment in mammalian cells. Biochemistry. 1974 Oct 22;13(22):4633–4637. doi: 10.1021/bi00719a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kick D., Barrett P., Cummings A., Sommerville J. Phosphorylation of a 60 kDa polypeptide from Xenopus oocytes blocks messenger RNA translation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4099–4109. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4099. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleene K. C., Flynn J. Translation of mouse testis poly(A)+ mRNAs for testis-specific protein, protamine 1, and the precursor for protamine 2. Dev Biol. 1987 Sep;123(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90434-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleene K. C. Poly(A) shortening accompanies the activation of translation of five mRNAs during spermiogenesis in the mouse. Development. 1989 Jun;106(2):367–373. doi: 10.1242/dev.106.2.367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konarska M. M., Padgett R. A., Sharp P. A. Recognition of cap structure in splicing in vitro of mRNA precursors. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):731–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90268-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M., Shatkin A. J. Migration of 40 S ribosomal subunits on messenger RNA in the presence of edeine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6568–6577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ladhoff A. M., Uerlings I., Rosenthal S. Electron microscopic evidence of circular molecules in 9-S globin mRNA from rabbit reticulocytes. Mol Biol Rep. 1981 May 22;7(1-3):101–106. doi: 10.1007/BF00778739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee S. Y., Mendecki J., Brawerman G. A polynucleotide segment rich in adenylic acid in the rapidly-labeled polyribosomal RNA component of mouse sarcoma 180 ascites cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jun;68(6):1331–1335. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.6.1331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemay G., Millward S. Inhibition of translation in L-cell lysates by free polyadenylic acid: differences in sensitivity among different mRNAs and possible involvement of an initiation factor. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1986 Aug 15;249(1):191–198. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(86)90574-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lim L., Canellakis E. S. Adenine-rich polymer associated with rabbit reticulocyte messenger RNA. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):710–712. doi: 10.1038/227710a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lockard R. E., Currey K., Browner M., Lawrence C., Maizel J. Secondary structure model for mouse beta Maj globin mRNA derived from enzymatic digestion data, comparative sequence and computer analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5827–5841. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manrow R. E., Jacobson A. Identification and characterization of developmentally regulated mRNP proteins of Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1986 Jul;116(1):213–227. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90058-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manrow R. E., Jacobson A. Increased rates of decay and reduced levels of accumulation of the major poly(A)-associated proteins of Dictyostelium during heat shock and development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrew L. L., Dworkin-Rastl E., Dworkin M. B., Richter J. D. Poly(A) elongation during Xenopus oocyte maturation is required for translational recruitment and is mediated by a short sequence element. Genes Dev. 1989 Jun;3(6):803–815. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.6.803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson E. M., Winkler M. M. Regulation of mRNA entry into polysomes. Parameters affecting polysome size and the fraction of mRNA in polysomes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 25;262(24):11501–11506. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obrig T., Irvin J., Culp W., Hardesty B. Inhibition of peptide initiation on reticulocyte ribosomes by edeine. Eur J Biochem. 1971 Jul 15;21(1):31–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1971.tb01436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palatnik C. M., Storti R. V., Capone A. K., Jacobson A. Messenger RNA stability in Dictyostelium discoideum: does poly(A) have a regulatory role? J Mol Biol. 1980 Aug 5;141(2):99–118. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90379-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palatnik C. M., Storti R. V., Jacobson A. Fractionation and functional analysis of newly synthesized and decaying messenger RNAs from vegetative cells of Dictyostelium discoideum. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 5;128(3):371–395. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90093-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palatnik C. M., Wilkins C., Jacobson A. Translational control during early Dictyostelium development: possible involvement of poly(A) sequences. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1017–1025. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Ovalbumin messenger ribonucleic acid translation. Comparable rates of polypeptide initiation and elongation on ovalbumin and globin messenger ribonucleic acid in a rabbit reticulocyte lysate. J Biol Chem. 1973 Mar 25;248(6):2095–2106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel D. D., Pickup D. J. Messenger RNAs of a strongly-expressed late gene of cowpox virus contain 5'-terminal poly(A) sequences. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 1;6(12):3787–3794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02714.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. Gene regulation by proteins acting nearby and at a distance. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):697–701. doi: 10.1038/322697a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Restifo L. L., Guild G. M. Poly(A) shortening of coregulated transcripts in Drosophila. Dev Biol. 1986 Jun;115(2):507–510. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90271-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads R. E. Cap recognition and the entry of mRNA into the protein synthesis initiation cycle. Trends Biochem Sci. 1988 Feb;13(2):52–56. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(88)90028-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson B. G., Frim D. M., Schwartz W. J., Majzoub J. A. Vasopressin mRNA in the suprachiasmatic nuclei: daily regulation of polyadenylate tail length. Science. 1988 Jul 15;241(4863):342–344. doi: 10.1126/science.3388044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roman R., Brooker J. D., Seal S. N., Marcus A. Inhibition of the transition of a 40 S ribosome-Met-tRNA-i-Met complex to an 80 S ribosome-Met-tRNA-i-Met- complex by 7-Methylguanosine-5'-phosphate. Nature. 1976 Mar 25;260(5549):359–360. doi: 10.1038/260359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Lodish H. F. Translation in vitro of vesicular stomatitis virus mRNA lacking 5'-terminal 7-methylguanosine. Nature. 1976 Jul 1;262(5563):32–37. doi: 10.1038/262032a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal E. T., Tansey T. R., Ruderman J. V. Sequence-specific adenylations and deadenylations accompany changes in the translation of maternal messenger RNA after fertilization of Spisula oocytes. J Mol Biol. 1983 May 25;166(3):309–327. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80087-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin H. N., Halim M. N. A direct evidence for the involvement of poly(A) in protein synthesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Apr 29;144(2):649–656. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(87)80015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Bond M. W., Kornberg R. D. A single gene from yeast for both nuclear and cytoplasmic polyadenylate-binding proteins: domain structure and expression. Cell. 1986 Jun 20;45(6):827–835. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90557-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Davis R. W., Kornberg R. D. A single domain of yeast poly(A)-binding protein is necessary and sufficient for RNA binding and cell viability. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3268–3276. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sachs A. B., Davis R. W. The poly(A) binding protein is required for poly(A) shortening and 60S ribosomal subunit-dependent translation initiation. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):857–867. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90938-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider R. J., Weinberger C., Shenk T. Adenovirus VAI RNA facilitates the initiation of translation in virus-infected cells. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):291–298. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90325-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwer B., Visca P., Vos J. C., Stunnenberg H. G. Discontinuous transcription or RNA processing of vaccinia virus late messengers results in a 5' poly(A) leader. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):163–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90212-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro R. A., Herrick D., Manrow R. E., Blinder D., Jacobson A. Determinants of mRNA stability in Dictyostelium discoideum amoebae: differences in poly(A) tail length, ribosome loading, and mRNA size cannot account for the heterogeneity of mRNA decay rates. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):1957–1969. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiness D., Darnell J. E. Polyadenylic acid segment in mRNA becomes shorter with age. Nat New Biol. 1973 Feb 28;241(113):265–268. doi: 10.1038/newbio241265a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague J., Condra J. H., Arnheiter H., Lazzarini R. A. Expression of a recombinant DNA gene coding for the vesicular stomatitis virus nucleocapsid protein. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):773–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.773-781.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltzfus C. M., Morgan M., Banerjee A. K., Shatkin A. J. Poly(A) polymerase activity in reovirus. J Virol. 1974 Jun;13(6):1338–1345. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.6.1338-1345.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swiderski R. E., Richter J. D. Photocrosslinking of proteins to maternal mRNA in Xenopus oocytes. Dev Biol. 1988 Aug;128(2):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Huarte J., Belin D., Gubler P., Vassalli A., O'Connell M. L., Parton L. A., Rickles R. J., Strickland S. Regulated polyadenylation controls mRNA translation during meiotic maturation of mouse oocytes. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2163–2171. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2163. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. R., Rich A., Hall C. E. Electron Microscope Studies of Ribosomal Clusters Synthesizing Hemoglobin. Science. 1962 Dec 28;138(3548):1399–1403. doi: 10.1126/science.138.3548.1399. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells D., Kedes L. Structure of a human histone cDNA: evidence that basally expressed histone genes have intervening sequences and encode polyadenylylated mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2834–2838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zingg H. H., Lefebvre D. L., Almazan G. Regulation of poly(A) tail size of vasopressin mRNA. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11041–11043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




