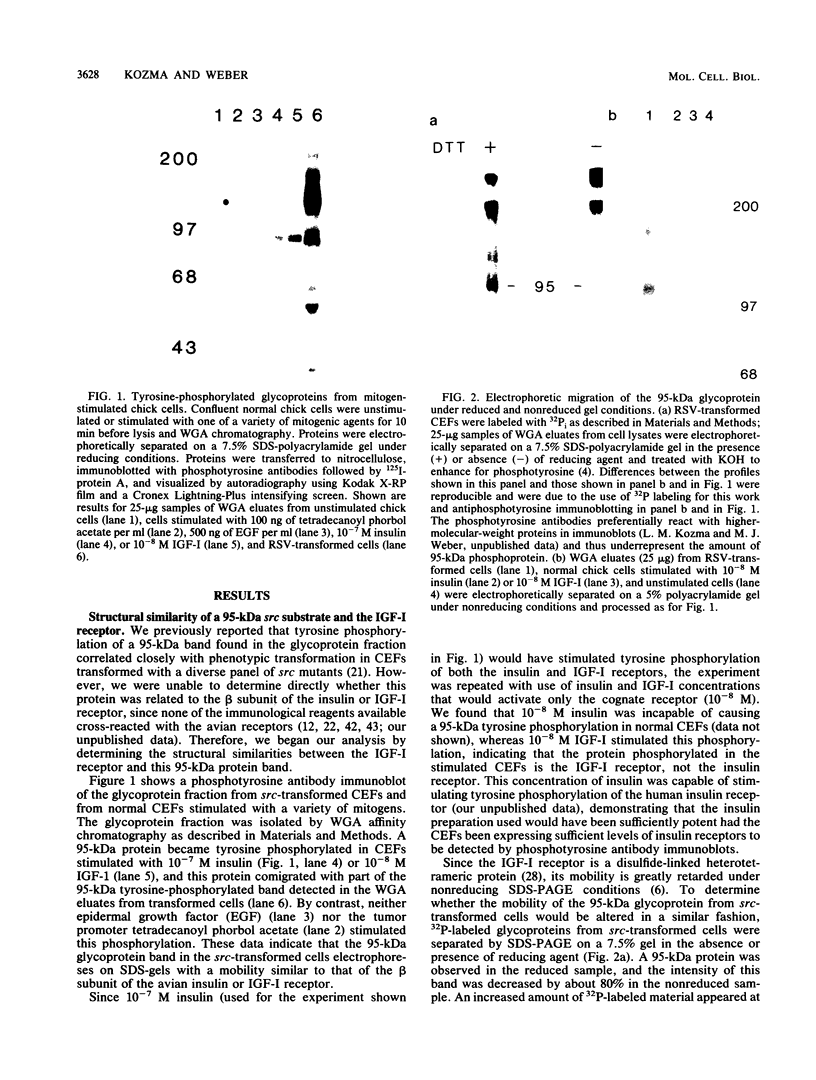
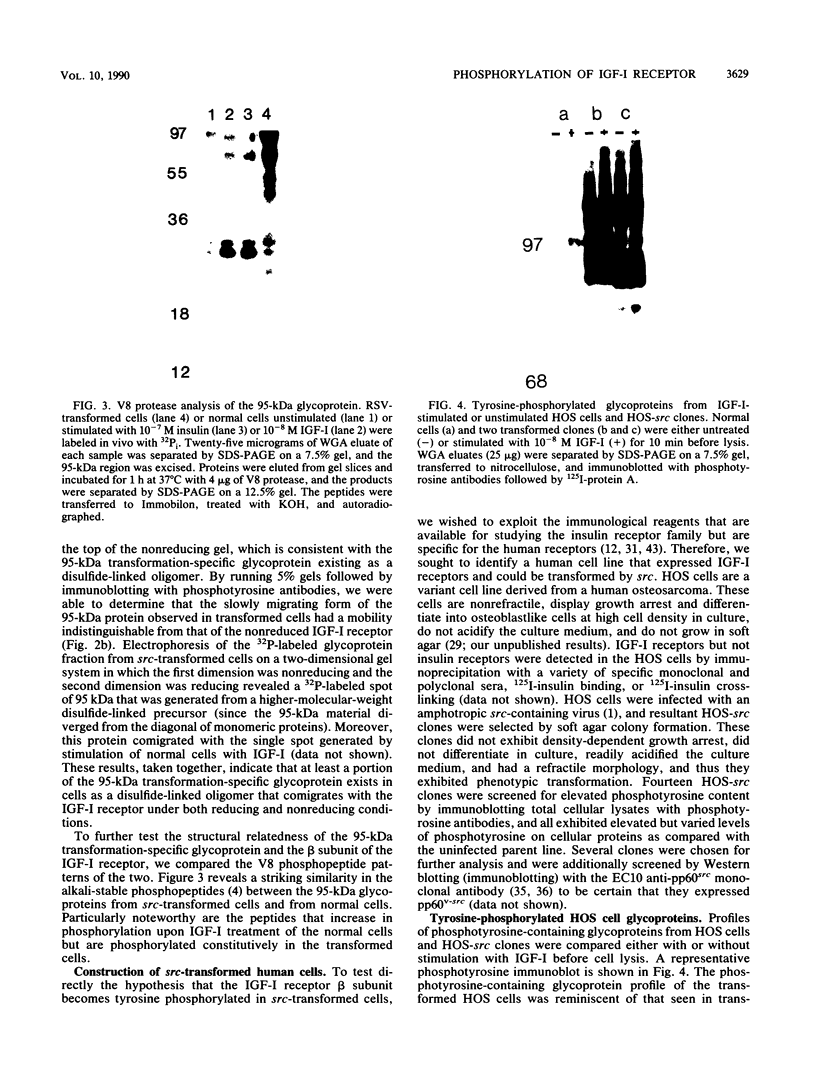
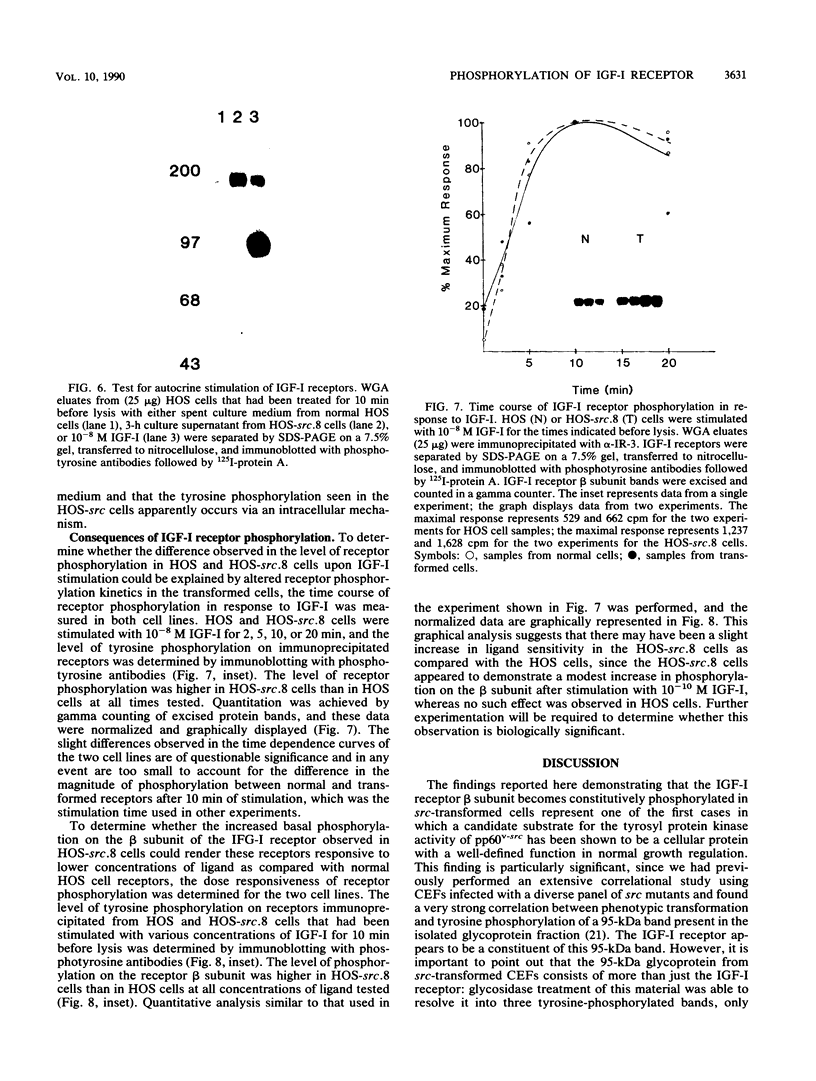
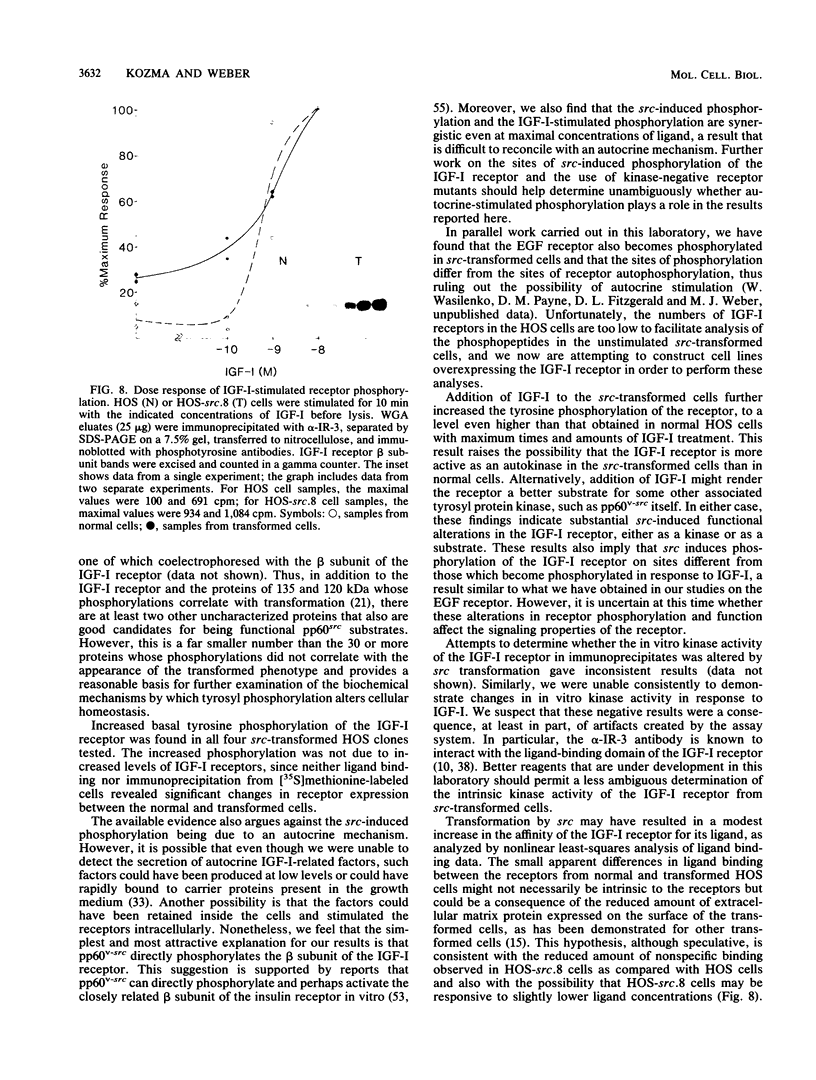
Abstract
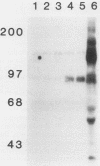
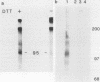
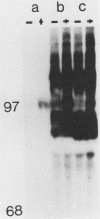
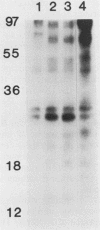
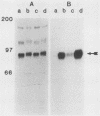
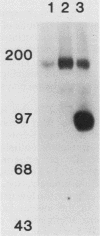
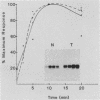
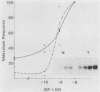
Many oncogene products have been shown to bear strong homology to or to interact with components of normal cellular signal transduction. We have previously shown that a glycoprotein band of 95 kilodaltons (kDa) becomes tyrosine phosphorylated in chick cells transformed by Rous sarcoma virus and that tyrosine phosphorylation of this protein band correlates tightly with phenotypic transformation in cells infected with a large and diverse panel of src mutants (L. M. Kozma, A. B. Reynolds, and M. J. Weber, Mol. Cell. Biol. 10:837-841, 1990). In this communication, we report that a component of the 95-kDa glycoprotein band is related or identical to the 95-kDa beta subunit of the receptor for insulinlike growth factor I (IGF-I). We found that the beta subunit of the IGF-I receptor comigrated on polyacrylamide gels with a component of the 95-kDa glycoprotein region from src-transformed cells under both reducing and nonreducing gel conditions and had a very similar partial phosphopeptide map. To further test the hypothesis that the beta subunit of the IGF-I receptor becomes tyrosine phosphorylated in cells transformed by pp60src, a human cell line that expressed the IGF-I receptor was transformed by src. Comparison of IGF-I receptors immunoprecipitated from normal and transformed cells revealed that the beta subunit of the IGF-I receptor became constitutively tyrosine phosphorylated in src-transformed cells. Moreover, IGF-I receptor phosphorylation induced by src was synergistic with that induced by the hormone: IGF-I-stimulated autophosphorylation of the receptor was much greater in src-transformed cells than in untransformed HOS cells even at maximal concentrations of IGF-I. This increased responsiveness to IGF-I was not due to increases in receptor number, time course of phosphorylation, or affinity for hormone. Finally, no IGF-I-like activity could be detected in culture supernatants collected from the src-transformed cells, suggesting that the increased receptor phosphorylation observed in the src-transformed cells may be mediated by an intracellular mechanism rather than an external autocrine stimulation. Our data demonstrate that the IGF-I receptor becomes constitutively tyrosine phosphorylated in src-transformed cells. This finding raises the possibility that pp60v-src alters growth regulation at least in part by phosphorylating and activating this growth factor receptor.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson S. M., Scolnick E. M. Construction and isolation of a transforming murine retrovirus containing the src gene of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):594–605. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.594-605.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Changes in protein phosphorylation in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):165–178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Detection and quantification of phosphotyrosine in proteins. Methods Enzymol. 1983;99:387–402. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)99075-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J., Nakamura K. D., Hunter T., Weber M. J. Phosphotyrosine-containing proteins and expression of transformation parameters in cells infected with partial transformation mutants of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):15–28. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.15-28.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvera S., Whitehead R. E., Mottola C., Czech M. P. The insulin-like growth factor II receptor is phosphorylated by a tyrosine kinase in adipocyte plasma membranes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7675–7679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P., Lewis R. E., Corvera S. Multifunctional glycoprotein receptors for insulin and the insulin-like growth factors. Ciba Found Symp. 1989;145:27–44. doi: 10.1002/9780470513828.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czech M. P. Structural and functional homologies in the receptors for insulin and the insulin-like growth factors. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):8–10. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90399-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebina Y., Ellis L., Jarnagin K., Edery M., Graf L., Clauser E., Ou J. H., Masiarz F., Kan Y. W., Goldfine I. D. The human insulin receptor cDNA: the structural basis for hormone-activated transmembrane signalling. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):747–758. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90334-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falco J. P., Taylor W. G., Di Fiore P. P., Weissman B. E., Aaronson S. A. Interactions of growth factors and retroviral oncogenes with mitogenic signal transduction pathways of Balb/MK keratinocytes. Oncogene. 1988 Jun;2(6):573–578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Usher P., Moses A. C. Monoclonal antibody to the type I insulin-like growth factor (IGF-I) receptor blocks IGF-I receptor-mediated DNA synthesis: clarification of the mitogenic mechanisms of IGF-I and insulin in human skin fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(3):664–668. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.3.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froesch E. R., Schmid C., Schwander J., Zapf J. Actions of insulin-like growth factors. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:443–467. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldfine I. D., Roth R. A. Monoclonal antibodies to the insulin receptor as probes of insulin receptor structure and function. Horiz Biochem Biophys. 1986;8:471–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst R., Horwitz A., Buck C., Rohrschneider L. Phosphorylation of the fibronectin receptor complex in cells transformed by oncogenes that encode tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(17):6470–6474. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.17.6470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Transforming gene product of Rous sarcoma virus phosphorylates tyrosine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Mar;77(3):1311–1315. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.3.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ignotz R. A., Massagué J. Cell adhesion protein receptors as targets for transforming growth factor-beta action. Cell. 1987 Oct 23;51(2):189–197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90146-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Buss J. E., Sefton B. M. Mutation of NH2-terminal glycine of p60src prevents both myristoylation and morphological transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4625–4628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Acid and base hydrolysis of phosphoproteins bound to immobilon facilitates analysis of phosphoamino acids in gel-fractionated proteins. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jan;176(1):22–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Identification of multiple novel polypeptide substrates of the v-src, v-yes, v-fps, v-ros, and v-erb-B oncogenic tyrosine protein kinases utilizing antisera against phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kojima I., Matsunaga H., Kurokawa K., Ogata E., Nishimoto I. Calcium influx: an intracellular message of the mitogenic action of insulin-like growth factor-I. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16561–16567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozma L. M., Reynolds A. B., Weber M. J. Glycoprotein tyrosine phosphorylation in Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):837–841. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S., Su Y. F., Svoboda M. E., Van Wyk J. J., Cuatrecasas P. Monoclonal antibodies to receptors for insulin and somatomedin-C. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 25;258(10):6561–6566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lammers R., Gray A., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. Differential signalling potential of insulin- and IGF-1-receptor cytoplasmic domains. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1369–1375. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder M. E., Burr J. G. Nonmyristoylated p60v-src fails to phosphorylate proteins of 115-120 kDa in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2608–2612. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2608. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luttrell D. K., Luttrell L. M., Parsons S. J. Augmented mitogenic responsiveness to epidermal growth factor in murine fibroblasts that overexpress pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):497–501. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Markwell M. A., Haas S. M., Bieber L. L., Tolbert N. E. A modification of the Lowry procedure to simplify protein determination in membrane and lipoprotein samples. Anal Biochem. 1978 Jun 15;87(1):206–210. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90586-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R., Nakamura K. D., Weber M. J. Identification of phosphotyrosine-containing proteins in untransformed and Rous sarcoma virus-transformed chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;2(6):653–665. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.6.653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Czech M. P. The subunit structures of two distinct receptors for insulin-like growth factors I and II and their relationship to the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1982 May 10;257(9):5038–5045. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister R. M., Gardner M. B., Greene A. E., Bradt C., Nichols W. W., Landing B. H. Cultivation in vitro of cells derived from a human osteosarcoma. Cancer. 1971 Feb;27(2):397–402. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197102)27:2<397::aid-cncr2820270224>3.0.co;2-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan D. O., Roth R. A. Identification of a monoclonal antibody which can distinguish between two distinct species of the type I receptor for insulin-like growth factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Aug 14;138(3):1341–1347. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(86)80430-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moxham C. P., Duronio V., Jacobs S. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor beta-subunit heterogeneity. Evidence for hybrid tetramers composed of insulin-like growth factor I and insulin receptor heterodimers. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13238–13244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi G. T., Herington A. C. The biological and structural characterization of specific serum binding proteins for the insulin-like growth factors. J Endocrinol. 1988 Jul;118(1):7–18. doi: 10.1677/joe.0.1180007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons J. T., Weber M. J. Genetics of src: structure and functional organization of a protein tyrosine kinase. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1989;147:79–127. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-74697-0_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons S. J., McCarley D. J., Ely C. M., Benjamin D. C., Parsons J. T. Monoclonal antibodies to Rous sarcoma virus pp60src react with enzymatically active cellular pp60src of avian and mammalian origin. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):272–282. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.272-282.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons S. J., McCarley D. J., Raymond V. W., Parsons J. T. Localization of conserved and nonconserved epitopes within the Rous sarcoma virus-encoded src protein. J Virol. 1986 Sep;59(3):755–758. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.3.755-758.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Roesel D. J., Kanner S. B., Parsons J. T. Transformation-specific tyrosine phosphorylation of a novel cellular protein in chicken cells expressing oncogenic variants of the avian cellular src gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):629–638. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.629. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohlik Q. T., Adams D., Kull F. C., Jr, Jacobs S. An antibody to the receptor for insulin-like growth factor I inhibits the growth of MCF-7 cells in tissue culture. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Nov 30;149(1):276–281. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91635-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Herrera R., Olowe Y., Petruzzelli L. M., Cobb M. H. Phosphorylation activates the insulin receptor tyrosine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3237–3240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Hunter T., Ball E. H., Singer S. J. Vinculin: a cytoskeletal target of the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1981 Apr;24(1):165–174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90512-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddle K., Soos M. A., O'Brien R. M., Ganderton R. H., Taylor R. Monoclonal antibodies as probes of the structure and function of insulin receptors. Biochem Soc Trans. 1987 Feb;15(1):47–51. doi: 10.1042/bst0150047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soos M. A., O'Brien R. M., Brindle N. P., Stigter J. M., Okamoto A. K., Whittaker J., Siddle K. Monoclonal antibodies to the insulin receptor mimic metabolic effects of insulin but do not stimulate receptor autophosphorylation in transfected NIH 3T3 fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5217–5221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Gray A., Tam A. W., Yang-Feng T., Tsubokawa M., Collins C., Henzel W., Le Bon T., Kathuria S., Chen E. Insulin-like growth factor I receptor primary structure: comparison with insulin receptor suggests structural determinants that define functional specificity. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2503–2512. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04528.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Obberghen E., Rossi B., Kowalski A., Gazzano H., Ponzio G. Receptor-mediated phosphorylation of the hepatic insulin receptor: evidence that the Mr 95,000 receptor subunit is its own kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(4):945–949. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.4.945. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldhuis J. D., Rodgers R. J., Furlanetto R. W. Synergistic actions of estradiol and the insulin-like growth factor somatomedin-C on swine ovarian (granulosa) cells. Endocrinology. 1986 Aug;119(2):530–538. doi: 10.1210/endo-119-2-530. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veldhuis J. D., Rodgers R. J. Mechanisms subserving the steroidogenic synergism between follicle-stimulating hormone and insulin-like growth factor I (somatomedin C). Alterations in cellular sterol metabolism in swine granulosa cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 5;262(16):7658–7664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velicelebi G., Aiyer R. A. Identification of the alpha beta monomer of the adipocyte insulin receptor by insulin binding and autophosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7693–7697. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber M. J., Friis R. R. Dissociation of transformation parameters using temperature-conditional mutants of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1979 Jan;16(1):25–32. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90184-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Shoelson S. E., Keutmann H., Kahn C. R. A cascade of tyrosine autophosphorylation in the beta-subunit activates the phosphotransferase of the insulin receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2969–2980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White M. F., Werth D. K., Pastan I., Kahn C. R. Phosphorylation of the solubilized insulin receptor by the gene product of the Rous sarcoma virus, pp60src. J Cell Biochem. 1984;26(3):169–179. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240260305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson L. K., Luttrell D. K., Parsons J. T., Parsons S. J. pp60c-src tyrosine kinase, myristylation, and modulatory domains are required for enhanced mitogenic responsiveness to epidermal growth factor seen in cells overexpressing c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1536–1544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1536. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu K. T., Werth D. K., Pastan I. H., Czech M. P. src kinase catalyzes the phosphorylation and activation of the insulin receptor kinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5838–5846. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhan X., Goldfarb M. Growth factor requirements of oncogene-transformed NIH 3T3 and BALB/c 3T3 cells cultured in defined media. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3541–3544. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]