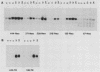
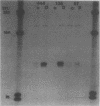
Abstract
We have identified a regulatory region in the human thymidine kinase gene promoter. A set of promoter deletion mutants was constructed, linked to the bacterial neomycin resistance gene, and stably transfected into Rat3 cells. It was shown that the region between 135 and 67 base pairs upstream of the cap site is required for conveying G1-S-phase regulation to the linked neo gene. In addition, primer extension assays demonstrated that the same transcriptional start sites were used in G1- and S-phase cells and in the various deletion mutants tested.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arcot S. S., Flemington E. K., Deininger P. L. The human thymidine kinase gene promoter. Deletion analysis and specific protein binding. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2343–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coppock D. L., Pardee A. B. Control of thymidine kinase mRNA during the cell cycle. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2925–2932. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2925. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg S. P., Coen D. M., McKnight S. L. Promoter domains required for expression of plasmid-borne copies of the herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase gene in virus-infected mouse fibroblasts and microinjected frog oocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):1940–1947. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.1940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Favaloro J., Treisman R., Kamen R. Transcription maps of polyoma virus-specific RNA: analysis by two-dimensional nuclease S1 gel mapping. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):718–749. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65070-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito M., Conrad S. E. Independent regulation of thymidine kinase mRNA and enzyme levels in serum-stimulated cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6954–6960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson L. F., Rao L. G., Muench A. J. Regulation of thymidine kinase enzyme level in serum-stimulated mouse 3T6 fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Mar;138(1):79–85. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90093-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. K., Wells S., Lau Y. F., Lee A. S. Sequences contained within the promoter of the human thymidine kinase gene can direct cell-cycle regulation of heterologous fusion genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5894–5898. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5894. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knight G. B., Gudas J. M., Pardee A. B. Cell-cycle-specific interaction of nuclear DNA-binding proteins with a CCAAT sequence from the human thymidine kinase gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8350–8354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreidberg J. A., Kelly T. J. Genetic analysis of the human thymidine kinase gene promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2903–2909. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman H. B., Lin P. F., Yeh D. B., Ruddle F. H. Transcriptional and posttranscriptional mechanisms regulate murine thymidine kinase gene expression in serum-stimulated cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5280–5291. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipson K. E., Chen S. T., Koniecki J., Ku D. H., Baserga R. S-phase-specific regulation by deletion mutants of the human thymidine kinase promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):6848–6852. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.6848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrill G. F., Hauschka S. D., McKnight S. L. tk Enzyme expression in differentiating muscle cells is regulated through an internal segment of the cellular tk gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1777–1784. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherley J. L., Kelly T. J. Regulation of human thymidine kinase during the cell cycle. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jun 15;263(17):8350–8358. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart C. J., Ito M., Conrad S. E. Evidence for transcriptional and post-transcriptional control of the cellular thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):1156–1163. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.1156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart P., Ito M., Stewart C., Conrad S. E. Induction of cellular thymidine kinase occurs at the mRNA level. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1490–1497. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topp W. C. Normal rat cell lines deficient in nuclear thymidine kinase. Virology. 1981 Aug;113(1):408–411. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90168-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Travali S., Lipson K. E., Jaskulski D., Lauret E., Baserga R. Role of the promoter in the regulation of the thymidine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1551–1557. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1551. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R. Biochemical transfer of single-copy eucaryotic genes using total cellular DNA as donor. Cell. 1978 Jul;14(3):725–731. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90254-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]