Abstract
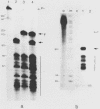
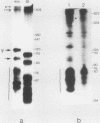
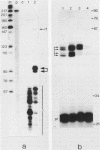
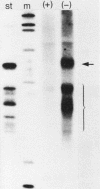
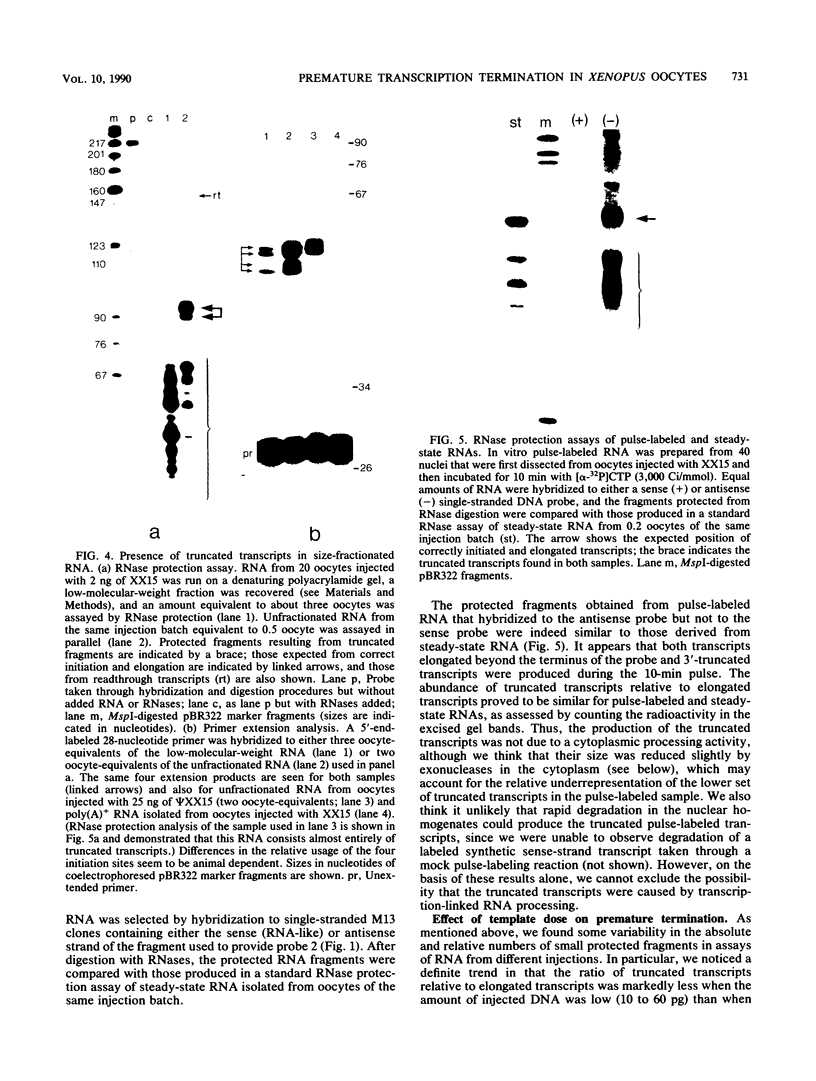
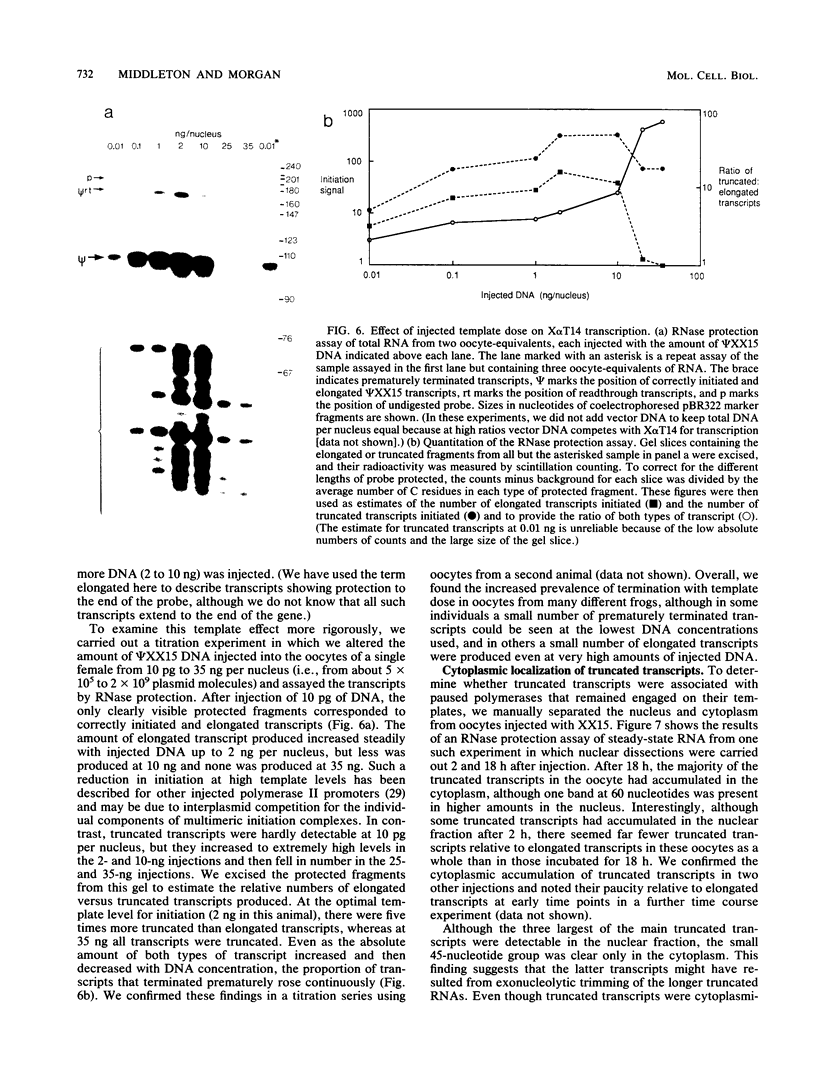
The Xenopus laevis alpha-tubulin gene X alpha T14, which is highly expressed during oogenesis, exhibits accurate and efficient transcription initiation when microinjected into X. laevis oocytes. However, we found previously in nuclease protection assays of transcripts from injected X alpha T14 that many protected fragments that were shorter than expected could be produced. We show here by exonuclease VII mapping, Northern (RNA) blotting, and gel fractionation of RNA that these fragments were caused by truncated transcripts that share the same initiation sites as mature transcripts but whose 3' ends are located in the 5' leader just 45 to 72 nucleotides downstream. We present evidence from the analysis of in vitro pulse-labeled RNA that these truncated transcripts are formed by premature transcription termination rather than by RNA processing. At low template levels, very little premature termination occurred, but as more DNA was injected, the proportion of transcripts that were prematurely terminated increased steadily, even at template levels at which the initiation machinery was unsaturated. At high template levels, most transcripts were prematurely terminated. These results suggest that some sort of saturable antitermination function operates in oocytes in a manner that is dependent on the number of appropriate templates available rather than on the number of polymerases that initiate transcription. They also suggest that measures of initiation frequency may not always be a reliable means of assessing the amount of transcription of injected genes in oocytes.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bender T. P., Thompson C. B., Kuehl W. M. Differential expression of c-myb mRNA in murine B lymphomas by a block to transcription elongation. Science. 1987 Sep 18;237(4821):1473–1476. doi: 10.1126/science.3498214. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. A block to elongation is largely responsible for decreased transcription of c-myc in differentiated HL60 cells. Nature. 1986 Jun 12;321(6071):702–706. doi: 10.1038/321702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L., Groudine M. Sequence requirements for premature termination of transcription in the human c-myc gene. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):245–256. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90386-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bentley D. L. Most kappa immunoglobulin mRNA in human lymphocytes is homologous to a small family of germ-line V genes. Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):77–80. doi: 10.1038/307077a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chase J. W., Vales L. D. Exonuclease VII of E. coli. Gene Amplif Anal. 1981;2:147–168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eick D., Bornkamm G. W. Transcriptional arrest within the first exon is a fast control mechanism in c-myc gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Nov 11;14(21):8331–8346. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.21.8331. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fort P., Rech J., Vie A., Piechaczyk M., Bonnieu A., Jeanteur P., Blanchard J. M. Regulation of c-fos gene expression in hamster fibroblasts: initiation and elongation of transcription and mRNA degradation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 24;15(14):5657–5667. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.14.5657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harland R., Weintraub H. Translation of mRNA injected into Xenopus oocytes is specifically inhibited by antisense RNA. J Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;101(3):1094–1099. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.3.1094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay N., Skolnik-David H., Aloni Y. Attenuation in the control of SV40 gene expression. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):183–193. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90102-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hernandez N., Weiner A. M. Formation of the 3' end of U1 snRNA requires compatible snRNA promoter elements. Cell. 1986 Oct 24;47(2):249–258. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90447-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hipskind R. A., Reeder R. H. Initiation of ribosomal RNA chains in homogenates of oocyte nuclei. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 25;255(16):7896–7906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao S. Y., Calman A. F., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Anti-termination of transcription within the long terminal repeat of HIV-1 by tat gene product. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):489–493. doi: 10.1038/330489a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerppola T. K., Kane C. M. Intrinsic sites of transcription termination and pausing in the c-myc gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4389–4394. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krieg P. A., Melton D. A. In vitro RNA synthesis with SP6 RNA polymerase. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:397–415. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55027-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Characterization of three sites of RNA 3' end formation in the Xenopus ribosomal gene spacer. Cell. 1986 May 9;45(3):431–443. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90329-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labhart P., Reeder R. H. Ribosomal precursor 3' end formation requires a conserved element upstream of the promoter. Cell. 1987 Jul 3;50(1):51–57. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90661-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Middleton K. M., Morgan G. T. An oocyte-expressed alpha-tubulin gene in Xenopus laevis; sequences required for the initiation of transcription. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jul 11;17(13):5041–5055. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.13.5041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mok M., Maderious A., Chen-Kiang S. Premature termination by human RNA polymerase II occurs temporally in the adenovirus major late transcriptional unit. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;4(10):2031–2040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.10.2031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan G. T., Roan J. G., Bakken A. H., Reeder R. H. Variations in transcriptional activity of rDNA spacer promoters. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Aug 10;12(15):6043–6052. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.15.6043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepveu A., Marcu K. B. Intragenic pausing and anti-sense transcription within the murine c-myc locus. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2859–2865. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proudfoot N. J. How RNA polymerase II terminates transcription in higher eukaryotes. Trends Biochem Sci. 1989 Mar;14(3):105–110. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(89)90132-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Resnekov O., Ben-Asher E., Bengal E., Choder M., Hay N., Kessler M., Ragimov N., Seiberg M., Skolnik-David H., Aloni Y. Transcription termination in animal viruses and cells. Gene. 1988 Dec 10;72(1-2):91–104. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90130-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rougvie A. E., Lis J. T. The RNA polymerase II molecule at the 5' end of the uninduced hsp70 gene of D. melanogaster is transcriptionally engaged. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):795–804. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91087-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salditt-Georgieff M., Harpold M., Chen-Kiang S., Darnell J. E., Jr The addition of 5' cap structures occurs early in hnRNA synthesis and prematurely terminated molecules are capped. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):69–78. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90389-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selby M. J., Bain E. S., Luciw P. A., Peterlin B. M. Structure, sequence, and position of the stem-loop in tar determine transcriptional elongation by tat through the HIV-1 long terminal repeat. Genes Dev. 1989 Apr;3(4):547–558. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.4.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. J. The complete sequence of a frog alpha-tubulin gene and its regulated expression in mouse L-cells. Biochem J. 1988 Jan 15;249(2):465–472. doi: 10.1042/bj2490465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toohey M. G., Jones K. A. In vitro formation of short RNA polymerase II transcripts that terminate within the HIV-1 and HIV-2 promoter-proximal downstream regions. Genes Dev. 1989 Mar;3(3):265–282. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.3.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley M. E., Patient R. K. Highly efficient beta globin transcription in the absence of both a viral enhancer and erythroid factors. Development. 1987 Dec;101(4):815–827. doi: 10.1242/dev.101.4.815. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen T. J., Machlin P. S., Cleveland D. W. Autoregulated instability of beta-tubulin mRNAs by recognition of the nascent amino terminus of beta-tubulin. Nature. 1988 Aug 18;334(6183):580–585. doi: 10.1038/334580a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]