Abstract
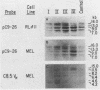
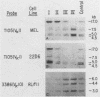
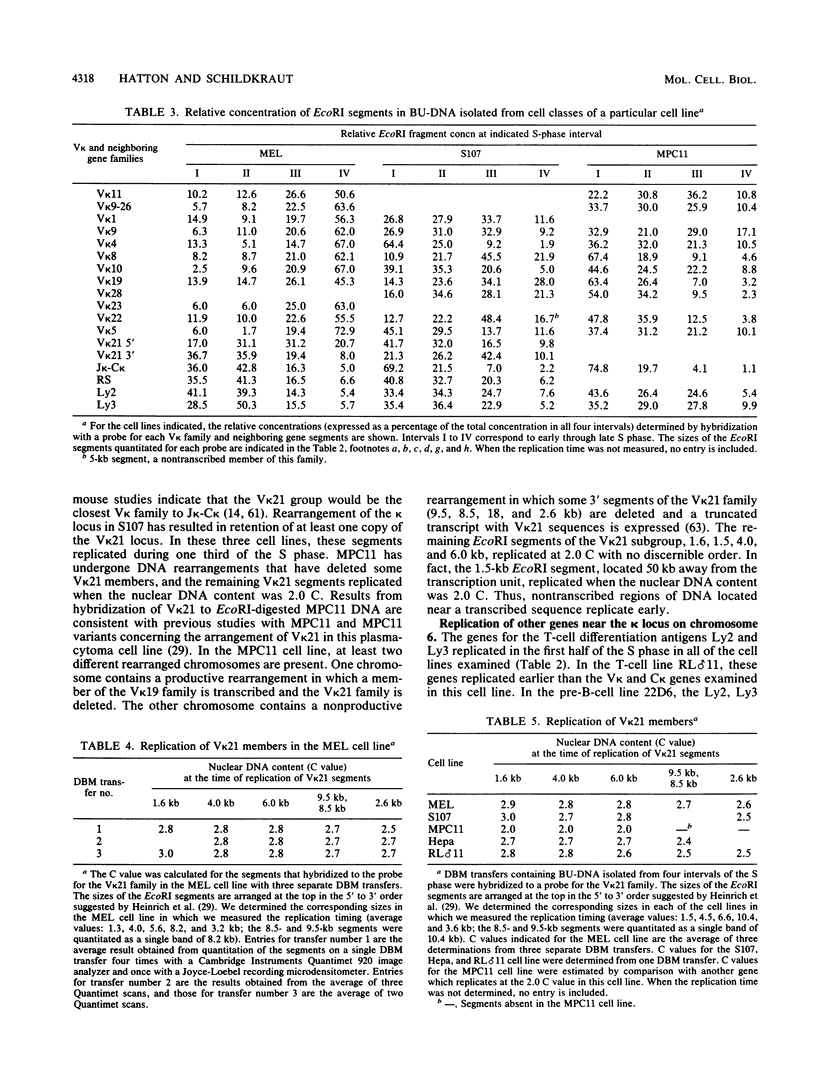
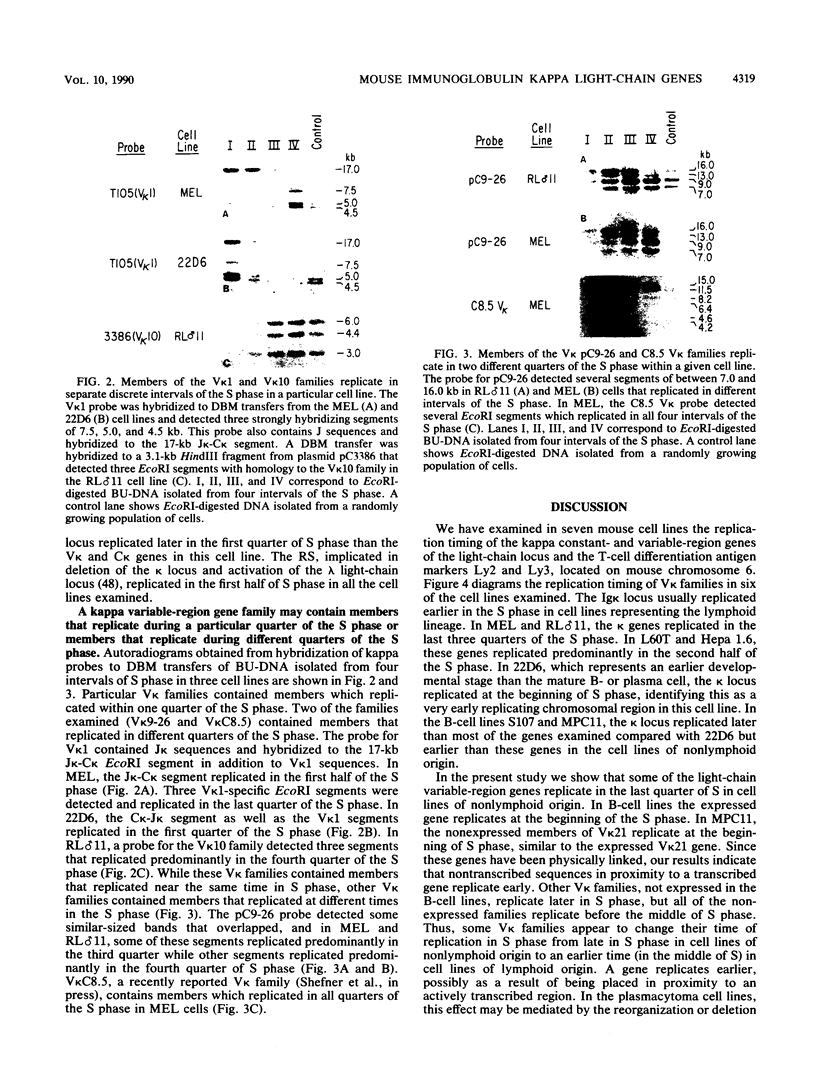
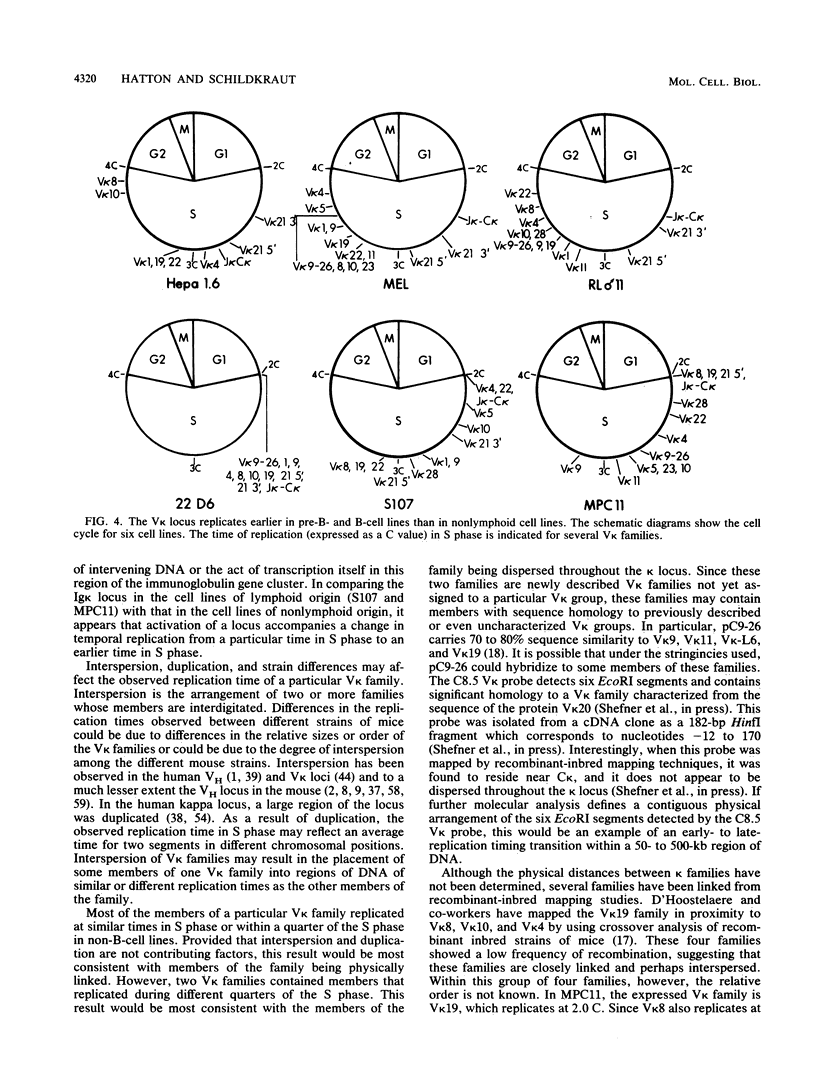
The murine immunoglobulin kappa (kappa) light-chain multigene family includes the constant region (C kappa), joining-region genes, and approximately 30 kappa-variable (V kappa) region families. The entire region occupies an estimated 1,000 to 3,000 kilobases, and some V kappa families have been linked by recombinant inbred mapping. The C kappa gene and 14 V kappa families replicated differently among cell lines of lymphoid and nonlymphoid origin. In nonlymphoid cells, the C kappa gene replicated earlier than the V kappa families. A transition from replication during the second third of S phase for the C kappa gene to later replication during S for V kappa families was observed. The V kappa family (V kappa 21) that maps closest to the C kappa gene, replicated during the first half of the S phase; most of the other V kappa families replicated during the second half of S, and some replicated during the last quarter of the S phase. In lymphoid cells, the kappa locus replicated earlier in the pre-B than in the B-cell lines. In one pre-B-cell line, 22D6, the kappa genes examined replicated at the beginning of the S phase. In the B-cell lines, the EcoRI segment containing the transcribed gene replicated near the beginning of the S phase. Other V kappa families replicated within the first two-thirds of S phase. Some linked V kappa families replicated at similar times. In the B-cell lines, a transition from replication at the beginning of S for the transcribed C kappa and V kappa genes and surrounding DNA sequences to later replication for the other V kappa families was observed. However, in contrast to the non-lymphoid cell lines, the replication of this locus occurred predominantly during the first half of S. The kappa locus contains both early- and late-replicating genes, and early replication is usually associated with transcriptional activity. The results are discussed with respect to the organization of transcriptionally active chromatin domains.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berman J. E., Mellis S. J., Pollock R., Smith C. L., Suh H., Heinke B., Kowal C., Surti U., Chess L., Cantor C. R. Content and organization of the human Ig VH locus: definition of three new VH families and linkage to the Ig CH locus. EMBO J. 1988 Mar;7(3):727–738. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02869.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blankenstein T., Krawinkel U. Immunoglobulin VH region genes of the mouse are organized in overlapping clusters. Eur J Immunol. 1987 Sep;17(9):1351–1357. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830170920. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. Gene gating: a hypothesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8527–8529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8527. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd R. T., Goldrick M. M., Gottlieb P. D. Genetic polymorphism at the mouse immunoglobulin J kappa locus (Igk-J) as demonstrated by Southern hybridization and nucleotide sequence analysis. Immunogenetics. 1986;24(3):150–157. doi: 10.1007/BF00364742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd R. T., Goldrick M. M., Gottlieb P. D. Structural differences in a single gene encoding the V kappa Ser group of light chains explain the existence of two mouse light-chain genetic markers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9134–9138. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braunstein J. D., Schulze D., DelGiudice T., Furst A., Schildkraut C. L. The temporal order of replication of murine immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region sequences corresponds to their linear order in the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6887–6902. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briles D. E., Carroll R. J. A simple method for estimating the probable numbers of different antibodies by examining the repeat frequencies of sequences or isoelectric focusing patterns. Mol Immunol. 1981 Jan;18(1):29–38. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(81)90045-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur P. H., Osman G. E., Mackle J. J., Lalor T. M. The organization of the mouse Igh-V locus. Dispersion, interspersion, and the evolution of VH gene family clusters. J Exp Med. 1988 Dec 1;168(6):2261–2278. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.6.2261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodeur P. H., Riblet R. The immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (Igh-V) locus in the mouse. I. One hundred Igh-V genes comprise seven families of homologous genes. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):922–930. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E. H., Iqbal M. A., Stuart S., Hatton K. S., Valinsky J., Schildkraut C. L. Rate of replication of the murine immunoglobulin heavy-chain locus: evidence that the region is part of a single replicon. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):450–457. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calza R. E., Eckhardt L. A., DelGiudice T., Schildkraut C. L. Changes in gene position are accompanied by a change in time of replication. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):689–696. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90349-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cory S., Tyler B. M., Adams J. M. Sets of immunoglobulin V kappa genes homologous to ten cloned V kappa sequences: implications for the number of germline V kappa genes. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(2):103–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Hoostelaere L. A., Gibson D. M. The organization of immunoglobulin variable kappa chain genes on mouse chromosome 6. Immunogenetics. 1986;23(4):260–265. doi: 10.1007/BF00373021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Hoostelaere L. A., Huppi K., Mock B., Mallett C., Potter M. The Ig kappa L chain allelic groups among the Ig kappa haplotypes and Ig kappa crossover populations suggest a gene order. J Immunol. 1988 Jul 15;141(2):652–661. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar V., Mager D., Iqbal A., Schildkraut C. L. The coordinate replication of the human beta-globin gene domain reflects its transcriptional activity and nuclease hypersensitivity. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Nov;8(11):4958–4965. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.11.4958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dhar V., Skoultchi A. I., Schildkraut C. L. Activation and repression of a beta-globin gene in cell hybrids is accompanied by a shift in its temporal replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3524–3532. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eissenberg J. C., Cartwright I. L., Thomas G. H., Elgin S. C. Selected topics in chromatin structure. Annu Rev Genet. 1985;19:485–536. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.19.120185.002413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaudette M. F., Benbow R. M. Replication forks are underrepresented in chromosomal DNA of Xenopus laevis embryos. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5953–5957. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. M., MacLean S. J., Anctil D., Mathieson B. J. Recombination between kappa chain genetic markers in the mouse. Immunogenetics. 1984;20(5):493–501. doi: 10.1007/BF00364352. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson D. M., Maclean S. J., Cherry M. Recombination between kappa chain genetic markers and the Lyt-3 locus. Immunogenetics. 1983;18(2):111–116. doi: 10.1007/BF00368538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. A. The chromatin domain as a unit of gene regulation. Bioessays. 1988 Aug-Sep;9(2-3):50–55. doi: 10.1002/bies.950090204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldrick M. M., Boyd R. T., Ponath P. D., Lou S. Y., Gottlieb P. D. Molecular genetic analysis of the V kappa Ser group associated with two mouse light chain genetic markers. Complementary DNA cloning and southern hybridization analysis. J Exp Med. 1985 Aug 1;162(2):713–728. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.2.713. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M., Webb E. A., Cory S., Adams J. M. Molecular cloning of seven mouse immunoglobulin kappa chain messenger ribonucleic acids. Biochemistry. 1980 Jun 10;19(12):2702–2710. doi: 10.1021/bi00553a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gross D. S., Garrard W. T. Nuclease hypersensitive sites in chromatin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1988;57:159–197. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.57.070188.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatton K. S., Dhar V., Brown E. H., Iqbal M. A., Stuart S., Didamo V. T., Schildkraut C. L. Replication program of active and inactive multigene families in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 May;8(5):2149–2158. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.5.2149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrich G., Traunecker A., Tonegawa S. Somatic mutation creates diversity in the major group of mouse immunoglobulin kappa light chains. J Exp Med. 1984 Feb 1;159(2):417–435. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.2.417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengartner H., Meo T., Müller E. Assignment of genes for immunoglobulin kappa and heavy chains to chromosomes 6 and 12 in mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4494–4498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henson P. The presence of single-stranded regions in mammalian DNA. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 15;119(4):487–506. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90198-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hutchison N., Weintraub H. Localization of DNAase I-sensitive sequences to specific regions of interphase nuclei. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):471–482. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90177-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal M. A., Chinsky J., Didamo V., Schildkraut C. L. Replication of proto-oncogenes early during the S phase in mammalian cell lines. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jan 12;15(1):87–103. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joho R., Weissman I. L., Early P., Cole J., Hood L. Organization of kappa light chain genes in germ-line and somatic tissue. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):1106–1110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.1106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley D. E., Coleclough C., Perry R. P. Functional significance and evolutionary development of the 5'-terminal regions of immunoglobulin variable-region genes. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):681–689. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90184-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley D. E., Wiedemann L. M., Pittet A. C., Strauss S., Nelson K. J., Davis J., Van Ness B., Perry R. P. Nonproductive kappa immunoglobulin genes: recombinational abnormalities and other lesions affecting transcription, RNA processing, turnover, and translation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;5(7):1660–1675. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.7.1660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kemp D. J., Tyler B., Bernard O., Gough N., Gerondakis S., Adams J. M., Cory S. Organization of genes and spacers within the mouse immunoglobulin VH locus. J Mol Appl Genet. 1981;1(3):245–261. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klobeck H. G., Zimmer F. J., Combriato G., Zachau H. G. Linking of the human immunoglobulin VK and JKCK regions by chromosomal walking. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9655–9665. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kodaira M., Kinashi T., Umemura I., Matsuda F., Noma T., Ono Y., Honjo T. Organization and evolution of variable region genes of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 20;190(4):529–541. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90239-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kofler R., Duchosal M. A., Dixon F. J. Complexity, polymorphism, and connectivity of mouse Vk gene families. Immunogenetics. 1989;29(2):65–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00395853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan S. P., Max E. E., Seidman J. G., Leder P., Scharff M. D. Two kappa immunoglobulin genes are expressed in the myeloma S107. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):57–66. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90033-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kwan S. P., Rudikoff S., Seidman J. G., Leder P., Scharff M. D. Nucleic acid and protein sequences of phosphocholine-binding light chains. J Exp Med. 1981 May 1;153(5):1366–1370. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.5.1366. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lenhard-Schuller R., Hohn B., Brack C., Hirama M., Tonegawa S. DNA clones containing mouse immunoglobulin kappa chain genes isolated by in vitro packaging into phage lambda coats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Oct;75(10):4709–4713. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.10.4709. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lorenz W., Straubinger B., Zachau H. G. Physical map of the human immunoglobulin K locus and its implications for the mechanisms of VK-JK rearrangement. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Dec 10;15(23):9667–9676. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.23.9667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather E. L., Perry R. P. Methylation status and DNase I sensitivity of immunoglobulin genes: changes associated with rearrangement. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4689–4693. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4689. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Maizel J. V., Jr, Leder P. The nucleotide sequence of a 5.5-kilobase DNA segment containing the mouse kappa immunoglobulin J and C region genes. J Biol Chem. 1981 May 25;256(10):5116–5120. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Max E. E., Seidman J. G., Leder P. Sequences of five potential recombination sites encoded close to an immunoglobulin kappa constant region gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3450–3454. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. W., Durdik J., Persiani D. M., Selsing E. Deletions of kappa chain constant region genes in mouse lambda chain-producing B cells involve intrachromosomal DNA recombinations similar to V-J joining. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Sep;82(18):6211–6215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.18.6211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakauchi H., Shinkai Y., Okumura K. Molecular cloning of Lyt-3, a membrane glycoprotein marking a subset of mouse T lymphocytes: molecular homology to immunoglobulin and T-cell receptor variable and joining regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4210–4214. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4210. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakauchi H., Tagawa M., Nolan G. P., Herzenberg L. A. Isolation and characterization of the gene for the murine T cell differentiation antigen and immunoglobulin-related molecule, Lyt-2. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):4337–4347. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.4337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishi M., Kataoka T., Honjo T. Preferential rearrangement of the immunoglobulin kappa chain joining region J kappa 1 and J kappa 2 segments in mouse spleen DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6399–6403. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parslow T. G., Blair D. L., Murphy W. J., Granner D. K. Structure of the 5' ends of immunoglobulin genes: a novel conserved sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2650–2654. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2650. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pech M., Smola H., Pohlenz H. D., Straubinger B., Gerl R., Zachau H. G. A large section of the gene locus encoding human immunoglobulin variable regions of the kappa type is duplicated. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 5;183(3):291–299. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90001-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter M., Newell J. B., Rudikoff S., Haber E. Classification of mouse VK groups based on the partial amino acid sequence to the first invariant tryptophan: impact of 14 new sequences from IgG myeloma proteins. Mol Immunol. 1982 Dec;19(12):1619–1630. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90273-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RICHARDSON C. C., INMAN R. B., KORNBERG A. ENZYMIC SYNTHESIS OF DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID. 18. THE REPAIR OF PARTIALLY SINGLE-STRANDED DNA TEMPLATES BY DNA POLYMERASE. J Mol Biol. 1964 Jul;9:46–69. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(64)80090-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbitts T. H. A molecular hybridization approach for the determination of the immunoglobulin V-gene pool size. Immunol Rev. 1977;36:29–50. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1977.tb00381.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rathbun G. A., Capra J. D., Tucker P. W. Organization of the murine immunoglobulin VH complex in the inbred strains. EMBO J. 1987 Oct;6(10):2931–2937. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02597.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reth M. G., Jackson S., Alt F. W. VHDJH formation and DJH replacement during pre-B differentiation: non-random usage of gene segments. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2131–2138. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04476.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rueff-Juy D., Drapier A. M., Cazenave P. A. Mapping of Igk-V genes using backcrossed laboratory and wild mice. Immunogenetics. 1988;28(4):233–239. doi: 10.1007/BF00345499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakano H., Hüppi K., Heinrich G., Tonegawa S. Sequences at the somatic recombination sites of immunoglobulin light-chain genes. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):288–294. doi: 10.1038/280288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidman J. G., Leder P. A mutant immunoglobulin light chain is formed by aberrant DNA- and RNA-splicing events. Nature. 1980 Aug 21;286(5775):779–783. doi: 10.1038/286779a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. A., Weigert M. How immunoglobulin V kappa genes rearrange. J Immunol. 1987 Dec 1;139(11):3834–3839. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith-Gill S. J., Mainhart C., Lavoie T. B., Feldmann R. J., Drohan W., Brooks B. R. A three-dimensional model of an anti-lysozyme antibody. J Mol Biol. 1987 Apr 20;194(4):713–724. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90249-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swan D., D'Eustachio P., Leinwand L., Seidman J., Keithley D., Ruddle F. H. Chromosomal assignment of the mouse kappa light chain genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2735–2739. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapiero H., Caneva R., Schildkraut C. L. Fractions of Chinese hamster DNA differing in their content of guanine+cytosine and evidence for the presence of single-stranded DNA. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Jul 20;272(3):350–360. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90388-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor B. A., Rowe L., Gibson D. M., Riblet R., Yetter R., Gottlieb P. D. Linkage of a 7S RNA sequence and kappa light chain genes in the mouse. Immunogenetics. 1985;22(5):471–481. doi: 10.1007/BF00418092. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valbuena O., Marcu K. B., Croce C. M., Huebner K., Weigert M., Perry R. P. Chromosomal locations of mouse immunoglobulin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2883–2887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zamoyska R., Vollmer A. C., Sizer K. C., Liaw C. W., Parnes J. R. Two Lyt-2 polypeptides arise from a single gene by alternative splicing patterns of mRNA. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):153–163. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90020-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeelon E. P., Bothwell A. L., Kantor F., Schechter I. An experimental approach to enumerate the genes coding for immunoglobulin variable-regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3809–3820. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3809. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]