Abstract
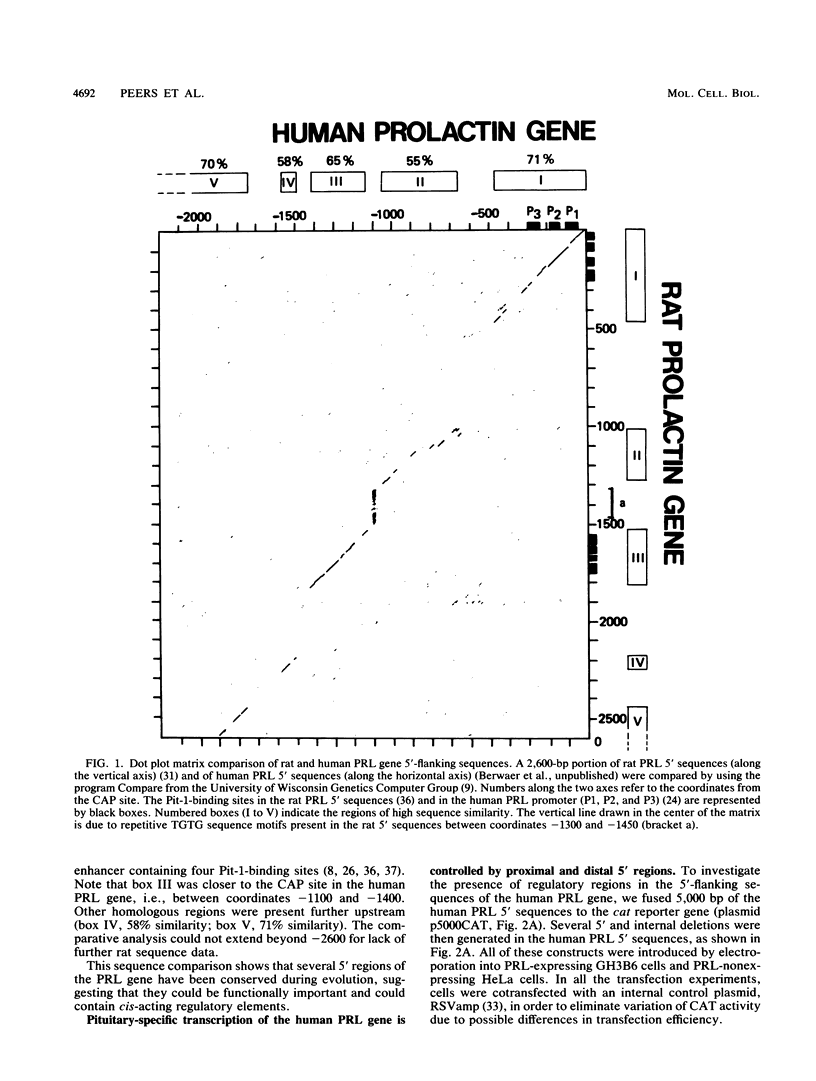
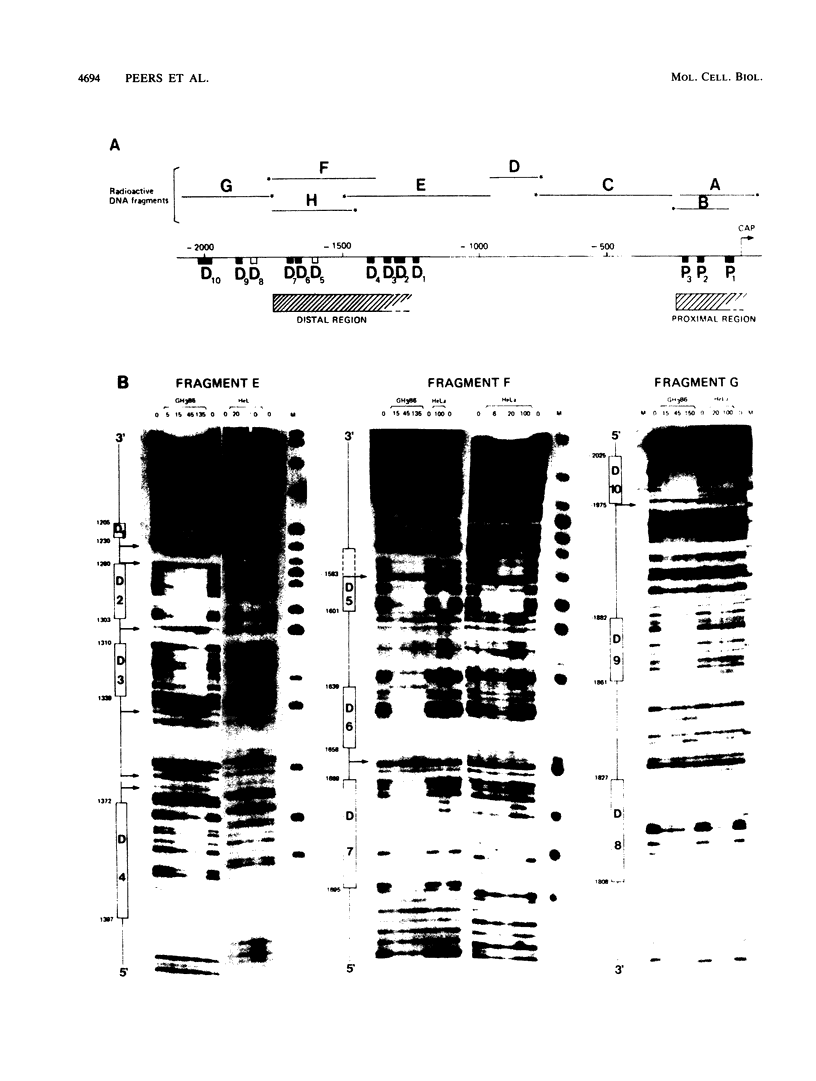
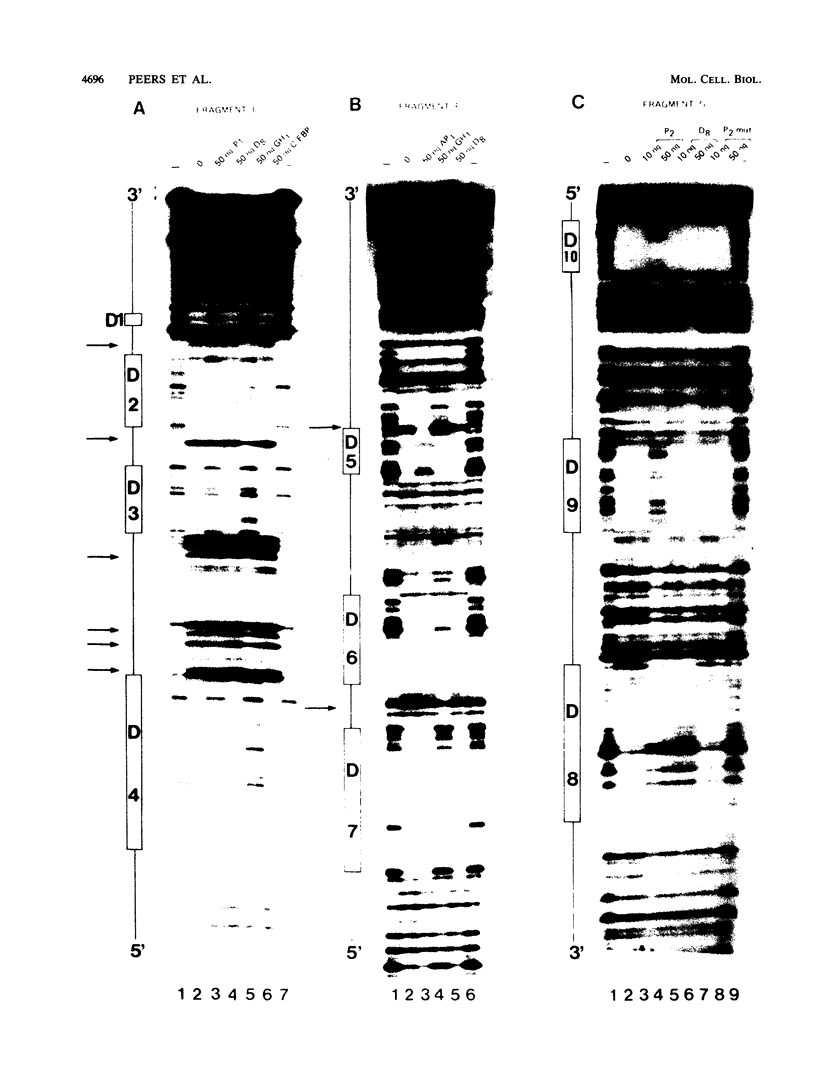
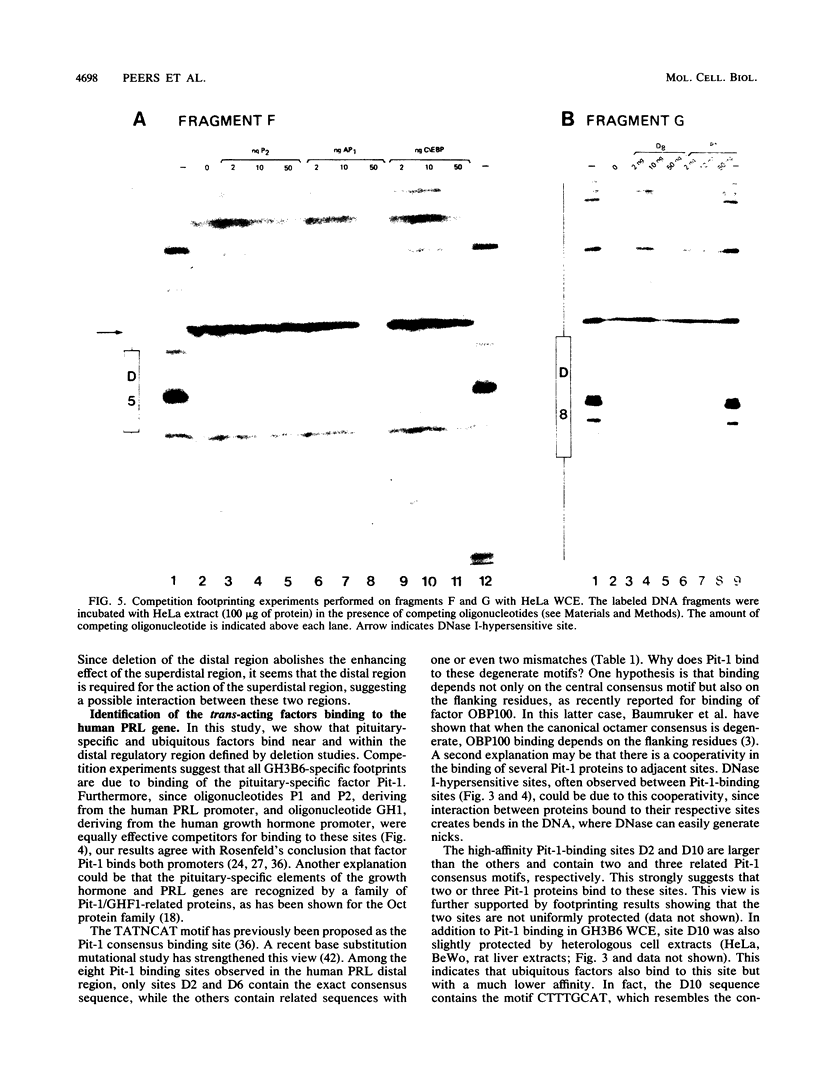
We have performed transfection and DNase I footprinting experiments to investigate pituitary-specific expression of the human prolactin (hPRL) gene. When fused to the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) reporter gene, 5,000 base pairs of the 5'-flanking sequences of the hPRL gene were able to drive high cat gene expression in prolactin-expressing GH3B6 cells specifically. Deletion analysis indicated that this pituitary-specific expression was controlled by three main positive regulatory regions. The first was located just upstream from the TATA box between coordinates -40 and -250 (proximal region). We have previously shown that three motifs of this region bind the pituitary-specific Pit-1 factor. The second positive region was located in the vicinity of coordinates -1300 to -1750 (distal region). DNase I footprinting assays revealed that eight DNA motifs of this distal region bound protein Pit-1 and that two other motifs were recognized by ubiquitous factors, one of which seems to belong to the AP-1 (jun) family. The third positive region was located further upstream, between -3500 and -5000 (superdistal region). This region appears to enhance transcription only in the presence of the distal region.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banerji J., Rusconi S., Schaffner W. Expression of a beta-globin gene is enhanced by remote SV40 DNA sequences. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):299–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90413-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumruker T., Sturm R., Herr W. OBP100 binds remarkably degenerate octamer motifs through specific interactions with flanking sequences. Genes Dev. 1988 Nov;2(11):1400–1413. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.11.1400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner M., Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E., Deerinck T., Ellisman M., Karin M. The pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1 is a homeobox-containing protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):505–518. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90037-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohmann D., Bos T. J., Admon A., Nishimura T., Vogt P. K., Tjian R. Human proto-oncogene c-jun encodes a DNA binding protein with structural and functional properties of transcription factor AP-1. Science. 1987 Dec 4;238(4832):1386–1392. doi: 10.1126/science.2825349. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Z. D., Barron E. A., Carillo A. J., Sharp Z. D. Reconstitution of cell-type-specific transcription of the rat prolactin gene in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3402–3408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Z. D., Barron E. A., Sharp Z. D. Prolactin upstream factor I mediates cell-specific transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5432–5438. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5432. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Kalla K., Simmons D. M., Swanson L. W., Rosenfeld M. G. Cell-specific expression of the prolactin gene in transgenic mice is controlled by synergistic interactions between promoter and enhancer elements. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):959–972. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.959. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollé P., Castrillo J. L., Theill L. E., Deerinck T., Ellisman M., Karin M. Expression of GHF-1 protein in mouse pituitaries correlates both temporally and spatially with the onset of growth hormone gene activity. Cell. 1990 Mar 9;60(5):809–820. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90095-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Merlino G. T., Willingham M. C., Pastan I., Howard B. H. The Rous sarcoma virus long terminal repeat is a strong promoter when introduced into a variety of eukaryotic cells by DNA-mediated transfection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(22):6777–6781. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.22.6777. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutierrez-Hartmann A., Siddiqui S., Loukin S. Selective transcription and DNase I protection of the rat prolactin gene by GH3 pituitary cell-free extracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5211–5215. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ingraham H. A., Chen R. P., Mangalam H. J., Elsholtz H. P., Flynn S. E., Lin C. R., Simmons D. M., Swanson L., Rosenfeld M. G. A tissue-specific transcription factor containing a homeodomain specifies a pituitary phenotype. Cell. 1988 Nov 4;55(3):519–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90038-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. Eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:799–839. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.004055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keech C. A., Gutierrez-Hartmann A. Analysis of rat prolactin promoter sequences that mediate pituitary-specific and 3',5'-cyclic adenosine monophosphate-regulated gene expression in vivo. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 May;3(5):832–839. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-5-832. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., Adashi E. Y., Graves B. J., McKnight S. L. Isolation of a recombinant copy of the gene encoding C/EBP. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):786–800. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laverriere J. N., Tixier-Vidal A., Buisson N., Morin A., Martial J. A., Gourdji D. Preferential role of calcium in the regulation of prolactin gene transcription by thyrotropin-releasing hormone in GH3 pituitary cells. Endocrinology. 1988 Jan;122(1):333–340. doi: 10.1210/endo-122-1-333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefevre C., Imagawa M., Dana S., Grindlay J., Bodner M., Karin M. Tissue-specific expression of the human growth hormone gene is conferred in part by the binding of a specific trans-acting factor. EMBO J. 1987 Apr;6(4):971–981. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04847.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lemaigre F. P., Peers B., Lafontaine D. A., Mathy-Hartert M., Rousseau G. G., Belayew A., Martial J. A. Pituitary-specific factor binding to the human prolactin, growth hormone, and placental lactogen genes. DNA. 1989 Apr;8(3):149–159. doi: 10.1089/dna.1.1989.8.149. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luckow B., Schütz G. CAT constructions with multiple unique restriction sites for the functional analysis of eukaryotic promoters and regulatory elements. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5490–5490. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lufkin T., Bancroft C. Identification by cell fusion of gene sequences that interact with positive trans-acting factors. Science. 1987 Jul 17;237(4812):283–286. doi: 10.1126/science.3474782. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mangalam H. J., Albert V. R., Ingraham H. A., Kapiloff M., Wilson L., Nelson C., Elsholtz H., Rosenfeld M. G. A pituitary POU domain protein, Pit-1, activates both growth hormone and prolactin promoters transcriptionally. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):946–958. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Goodbourn S., Fischer J. A. Regulation of inducible and tissue-specific gene expression. Science. 1987 Jun 5;236(4806):1237–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.3296191. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin T. F., Kowalchyk J. A. Evidence for the role of calcium and diacylglycerol as dual second messengers in thyrotropin-releasing hormone action: involvement of diacylglycerol. Endocrinology. 1984 Oct;115(4):1517–1526. doi: 10.1210/endo-115-4-1517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maurer R. A. Selective binding of the estradiol receptor to a region at least one kilobase upstream from the rat prolactin gene. DNA. 1985 Feb;4(1):1–9. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murdoch G. H., Franco R., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Polypeptide hormone regulation of gene expression. Thyrotropin-releasing hormone rapidly stimulates both transcription of the prolactin gene and the phosphorylation of a specific nuclear protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 25;258(24):15329–15335. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M. M., Ruppert S., Schaffner W., Matthias P. A cloned octamer transcription factor stimulates transcription from lymphoid-specific promoters in non-B cells. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):544–551. doi: 10.1038/336544a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C., Albert V. R., Elsholtz H. P., Lu L. I., Rosenfeld M. G. Activation of cell-specific expression of rat growth hormone and prolactin genes by a common transcription factor. Science. 1988 Mar 18;239(4846):1400–1405. doi: 10.1126/science.2831625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C., Crenshaw E. B., 3rd, Franco R., Lira S. A., Albert V. R., Evans R. M., Rosenfeld M. G. Discrete cis-active genomic sequences dictate the pituitary cell type-specific expression of rat prolactin and growth hormone genes. Nature. 1986 Aug 7;322(6079):557–562. doi: 10.1038/322557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Callaghan C. H., Morris A., Kirby S. M., Shingler A. H. Novel method for detection of beta-lactamases by using a chromogenic cephalosporin substrate. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1972 Apr;1(4):283–288. doi: 10.1128/aac.1.4.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheidereit C., Cromlish J. A., Gerster T., Kawakami K., Balmaceda C. G., Currie R. A., Roeder R. G. A human lymphoid-specific transcription factor that activates immunoglobulin genes is a homoeobox protein. Nature. 1988 Dec 8;336(6199):551–557. doi: 10.1038/336551a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuster W. A., Treacy M. N., Martin F. Tissue specific trans-acting factor interaction with proximal rat prolactin gene promoter sequences. EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1721–1733. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03001.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp Z. D., Helsel S., Cao Z. D., Barron E. A., Sanchez Y. DNA recognition element required for PUF-I mediated cell-type-specific transcription of the rat prolactin gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2705–2722. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theill L. E., Castrillo J. L., Wu D., Karin M. Dissection of functional domains of the pituitary-specific transcription factor GHF-1. Nature. 1989 Dec 21;342(6252):945–948. doi: 10.1038/342945a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Truong A. T., Duez C., Belayew A., Renard A., Pictet R., Bell G. I., Martial J. A. Isolation and characterization of the human prolactin gene. EMBO J. 1984 Feb;3(2):429–437. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01824.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Preston G. M., Lufkin T. C., Bancroft C. Detection of two chromatin proteins which bind specifically to the 5'-flanking region of the rat prolactin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2967–2974. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]