Abstract
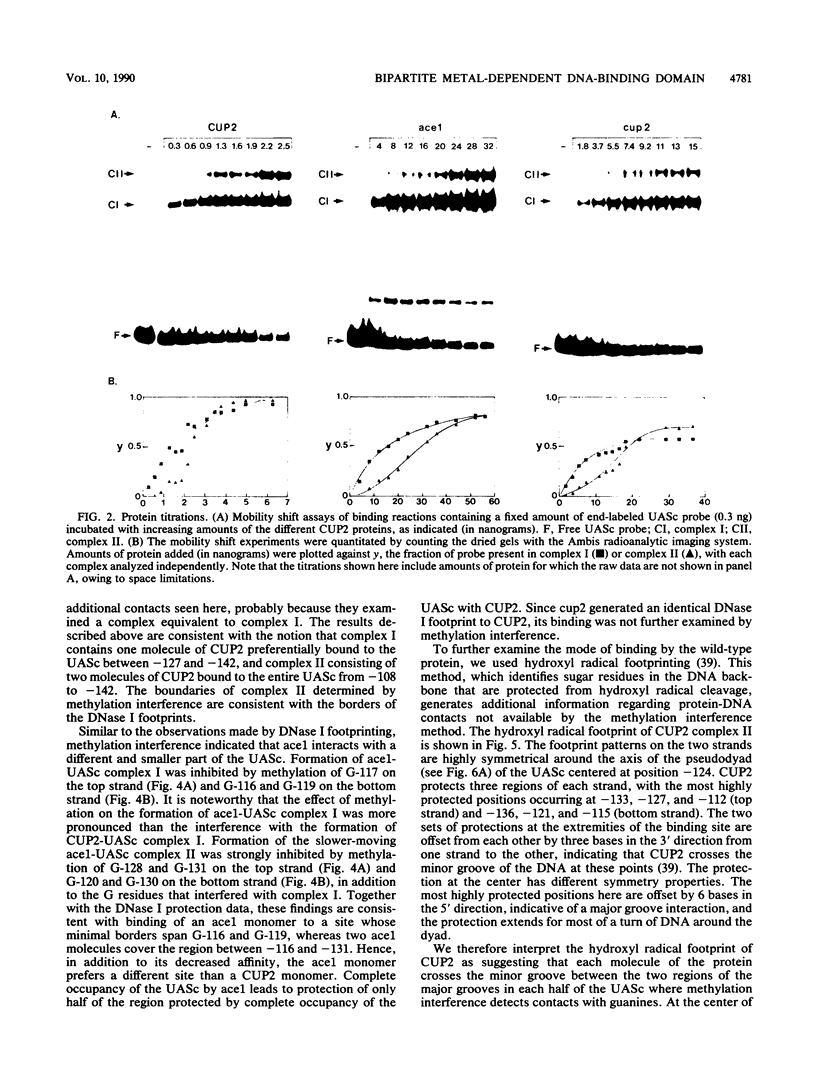
CUP2 is a copper-dependent transcriptional activator of the yeast CUP1 metallothionein gene. In the presence of Cu+ and Ag+) ions its DNA-binding domain is thought to fold as a cysteine-coordinated Cu cluster which recognizes the palindromic CUP1 upstream activation sequence (UASc). Using mobility shift, methylation interference, and DNase I and hydroxyl radical footprinting assays, we examined the interaction of wild-type and variant CUP2 proteins produced in Escherichia coli with the UASc. Our results suggest that CUP2 has a complex Cu-coordinated DNA-binding domain containing different parts that function as DNA-binding elements recognizing distinct sequence motifs embedded within the UASc. A single-amino-acid substitution of cysteine 11 with a tyrosine results in decreased Cu binding, apparent inactivation of one of the DNA-binding elements and a dramatic change in the recognition properties of CUP2. This variant protein interacts with only one part of the wild-type site and prefers to bind to a different half-site from the wild-type protein. Although the variant has about 10% of wild-type DNA-binding activity, it appears to be completely incapable of activating transcription.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Imagawa M., Chiu R., Stein B., Imbra R. J., Rahmsdorf H. J., Jonat C., Herrlich P., Karin M. Phorbol ester-inducible genes contain a common cis element recognized by a TPA-modulated trans-acting factor. Cell. 1987 Jun 19;49(6):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90611-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beato M. Gene regulation by steroid hormones. Cell. 1989 Feb 10;56(3):335–344. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90237-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. DNA binding specificity of steroid receptors. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1065–1068. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90042-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman C., Skroch P., Welch J., Fogel S., Karin M. The CUP2 gene product, regulator of yeast metallothionein expression, is a copper-activated DNA-binding protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):4091–4095. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.4091. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culotta V. C., Hsu T., Hu S., Fürst P., Hamer D. Copper and the ACE1 regulatory protein reversibly induce yeast metallothionein gene transcription in a mouse extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8377–8381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Danielsen M., Hinck L., Ringold G. M. Two amino acids within the knuckle of the first zinc finger specify DNA response element activation by the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1131–1138. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90050-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinter H., Chiu R., Imagawa M., Karin M., Jones K. A. In vitro activation of the HIV-1 enhancer in extracts from cells treated with a phorbol ester tumor promoter. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4067–4071. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02752.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst P., Hamer D. Cooperative activation of a eukaryotic transcription factor: interaction between Cu(I) and yeast ACE1 protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(14):5267–5271. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.14.5267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst P., Hu S., Hackett R., Hamer D. Copper activates metallothionein gene transcription by altering the conformation of a specific DNA binding protein. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):705–717. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90229-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. M., Revzin A. A gel electrophoresis method for quantifying the binding of proteins to specific DNA regions: application to components of the Escherichia coli lactose operon regulatory system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3047–3060. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson T. J., Postma J. P., Brown R. S., Argos P. A model for the tertiary structure of the 28 residue DNA-binding motif ('zinc finger') common to many eukaryotic transcriptional regulatory proteins. Protein Eng. 1988 Sep;2(3):209–218. doi: 10.1093/protein/2.3.209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Ptashne M. Negative effect of the transcriptional activator GAL4. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):721–724. doi: 10.1038/334721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Evans R. M. Multiple and cooperative trans-activation domains of the human glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):899–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90145-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hope I. A., Struhl K. Functional dissection of a eukaryotic transcriptional activator protein, GCN4 of yeast. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):885–894. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90070-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huibregtse J. M., Engelke D. R., Thiele D. J. Copper-induced binding of cellular factors to yeast metallothionein upstream activation sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jan;86(1):65–69. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.1.65. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Najarian R., Haslinger A., Valenzuela P., Welch J., Fogel S. Primary structure and transcription of an amplified genetic locus: the CUP1 locus of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):337–341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. S., Guarente L. Mutations that alter transcriptional activation but not DNA binding in the zinc finger of yeast activator HAPI. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):200–203. doi: 10.1038/342200a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. S., Gippert G. P., Soman K. V., Case D. A., Wright P. E. Three-dimensional solution structure of a single zinc finger DNA-binding domain. Science. 1989 Aug 11;245(4918):635–637. doi: 10.1126/science.2503871. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mader S., Kumar V., de Verneuil H., Chambon P. Three amino acids of the oestrogen receptor are essential to its ability to distinguish an oestrogen from a glucocorticoid-responsive element. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):271–274. doi: 10.1038/338271a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick A., Wu D., Castrillo J. L., Dana S., Strobl J., Thompson E. B., Karin M. Extinction of growth hormone expression in somatic cell hybrids involves repression of the specific trans-activator GHF-1. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):379–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90061-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., McLachlan A. D., Klug A. Repetitive zinc-binding domains in the protein transcription factor IIIA from Xenopus oocytes. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1609–1614. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03825.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhodes D., Klug A. An underlying repeat in some transcriptional control sequences corresponding to half a double helical turn of DNA. Cell. 1986 Jul 4;46(1):123–132. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90866-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakonju S., Bogenhagen D. F., Brown D. D. A control region in the center of the 5S RNA gene directs specific initiation of transcription: I. The 5' border of the region. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):13–25. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90384-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Severne Y., Wieland S., Schaffner W., Rusconi S. Metal binding 'finger' structures in the glucocorticoid receptor defined by site-directed mutagenesis. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2503–2508. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03097.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siebenlist U., Gilbert W. Contacts between Escherichia coli RNA polymerase and an early promoter of phage T7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):122–126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slater E. P., Rabenau O., Karin M., Baxter J. D., Beato M. Glucocorticoid receptor binding and activation of a heterologous promoter by dexamethasone by the first intron of the human growth hormone gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2984–2992. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sorger P. K., Pelham H. R. Yeast heat shock factor is an essential DNA-binding protein that exhibits temperature-dependent phosphorylation. Cell. 1988 Sep 9;54(6):855–864. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szczypka M. S., Thiele D. J. A cysteine-rich nuclear protein activates yeast metallothionein gene transcription. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):421–429. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiele D. J. ACE1 regulates expression of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae metallothionein gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. Y., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Cooperative binding of steroid hormone receptors contributes to transcriptional synergism at target enhancer elements. Cell. 1989 May 5;57(3):443–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90919-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullius T. D., Dombroski B. A. Hydroxyl radical "footprinting": high-resolution information about DNA-protein contacts and application to lambda repressor and Cro protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5469–5473. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5469. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tullius T. D., Dombroski B. A. Iron(II) EDTA used to measure the helical twist along any DNA molecule. Science. 1985 Nov 8;230(4726):679–681. doi: 10.1126/science.2996145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umesono K., Evans R. M. Determinants of target gene specificity for steroid/thyroid hormone receptors. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1139–1146. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90051-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrana K. E., Churchill M. E., Tullius T. D., Brown D. D. Mapping functional regions of transcription factor TFIIIA. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1684–1696. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1684. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch J., Fogel S., Buchman C., Karin M. The CUP2 gene product regulates the expression of the CUP1 gene, coding for yeast metallothionein. EMBO J. 1989 Jan;8(1):255–260. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03371.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolffe A. P., Jordan E., Brown D. D. A bacteriophage RNA polymerase transcribes through a Xenopus 5S RNA gene transcription complex without disrupting it. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90459-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]