Abstract
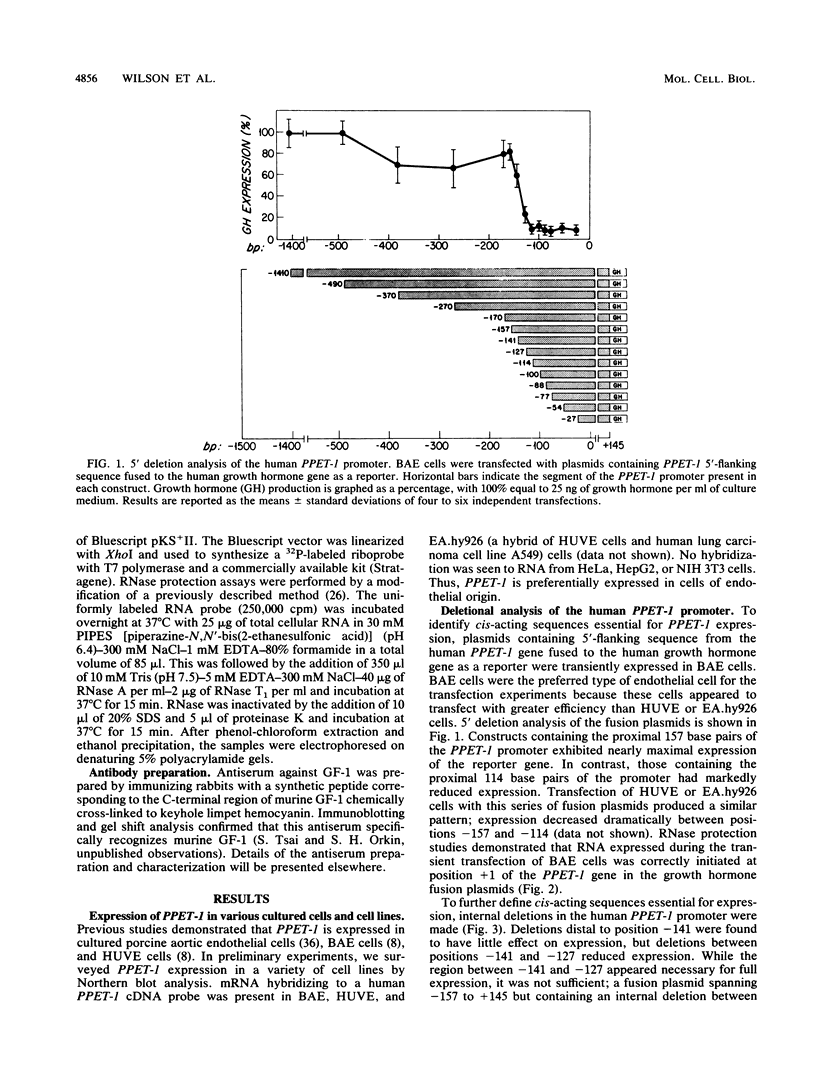
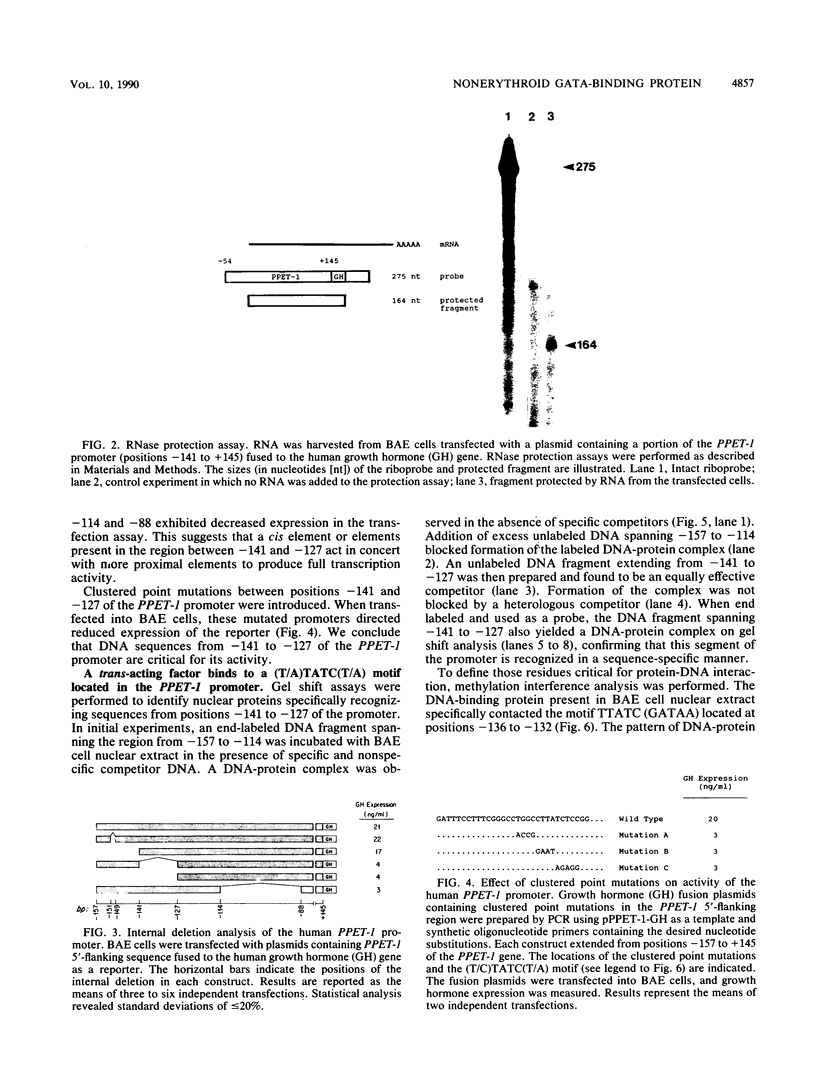
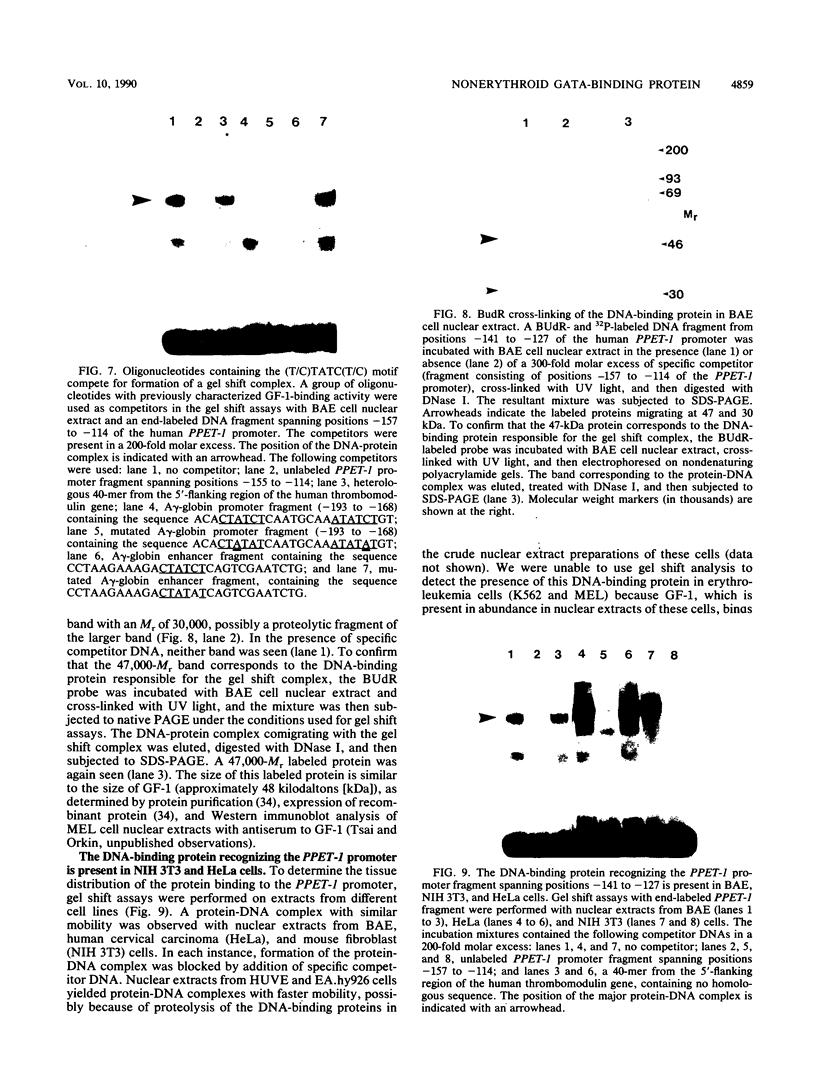
Endothelin-1 (ET-1) is a 21-amino-acid peptide synthesized by endothelial cells that has potent vasoconstrictor activity. Human ET-1 is derived from a 212-amino-acid prepropeptide, termed preproendothelin-1 (PPET-1). To identify cis-acting sequences essential for PPET-1 gene transcription, bovine aortic endothelial (BAE) cells were transfected with plasmids containing 5'-flanking sequences of the human PPET-1 gene fused to the human growth hormone gene as a reporter. Deletional analysis of these fusion plasmids showed that the sequence spanning positions -141 to -127 of the human PPET-1 promoter is required for full transcription activity. Introduction of clustered point mutations into this region of the promoter reduced transcription activity. Gel shift analysis, methylation interference, protein-DNA cross-linking, and oligonucleotide competition studies revealed that BAE cell nuclear extract contains a 47-kilodalton DNA-binding protein recognizing the core motif TATC (GATA) located at positions -135 to -132 of the PPET-1 promoter. The size and specificity of this DNA-binding protein resemble GF-1, a previously described transcription factor of erythroid cells that binds to the same core motif. Gel shift analysis indicated that GF-1 and the DNA-binding protein interacting with the PPET-1 promoter have different tissue distributions; the former is restricted to a subset of hematopoietic cells, and the latter is found in various cell types, including BAE, NIH 3T3, and HeLa cells. By using an antiserum to the C-terminal region of GF-1, the two proteins were also found to be antigenically distinct. When a growth hormone fusion plasmid containing the proximal 141 nucleotides of the PPET-1 promoter was transfected into a variety of cell types, these was preferential expression in cells of endothelial origin. We conclude that a nuclear factor with binding specificity for a GATA motif similar to that of the transcriptional activator GF-1 is necessary for the efficient and cell-specific expression of the human PPET-1 gene.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brenner B. M., Troy J. L., Ballermann B. J. Endothelium-dependent vascular responses. Mediators and mechanisms. J Clin Invest. 1989 Nov;84(5):1373–1378. doi: 10.1172/JCI114309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C., Okayama H. High-efficiency transformation of mammalian cells by plasmid DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2745–2752. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis M. A., Hynes M. J. Complementation of areA- regulatory gene mutations of Aspergillus nidulans by the heterologous regulatory gene nit-2 of Neurospora crassa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3753–3757. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edgell C. J., McDonald C. C., Graham J. B. Permanent cell line expressing human factor VIII-related antigen established by hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3734–3737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emori T., Hirata Y., Ohta K., Shichiri M., Shimokado K., Marumo F. Concomitant secretion of big endothelin and its C-terminal fragment from human and bovine endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jul 14;162(1):217–223. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91984-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Felsenfeld G. The erythroid-specific transcription factor Eryf1: a new finger protein. Cell. 1989 Sep 8;58(5):877–885. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90940-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Reitman M., Felsenfeld G. An erythrocyte-specific DNA-binding factor recognizes a regulatory sequence common to all chicken globin genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5976–5980. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu Y. H., Marzluf G. A. nit-2, the major nitrogen regulatory gene of Neurospora crassa, encodes a protein with a putative zinc finger DNA-binding domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1056–1065. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ginsburg D., Handin R. I., Bonthron D. T., Donlon T. A., Bruns G. A., Latt S. A., Orkin S. H. Human von Willebrand factor (vWF): isolation of complementary DNA (cDNA) clones and chromosomal localization. Science. 1985 Jun 21;228(4706):1401–1406. doi: 10.1126/science.3874428. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gumucio D. L., Rood K. L., Gray T. A., Riordan M. F., Sartor C. I., Collins F. S. Nuclear proteins that bind the human gamma-globin gene promoter: alterations in binding produced by point mutations associated with hereditary persistence of fetal hemoglobin. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;8(12):5310–5322. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.12.5310. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hai T. W., Liu F., Coukos W. J., Green M. R. Transcription factor ATF cDNA clones: an extensive family of leucine zipper proteins able to selectively form DNA-binding heterodimers. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2083–2090. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue A., Yanagisawa M., Kimura S., Kasuya Y., Miyauchi T., Goto K., Masaki T. The human endothelin family: three structurally and pharmacologically distinct isopeptides predicted by three separate genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2863–2867. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2863. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue A., Yanagisawa M., Takuwa Y., Mitsui Y., Kobayashi M., Masaki T. The human preproendothelin-1 gene. Complete nucleotide sequence and regulation of expression. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14954–14959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue A., Yanagisawa M., Takuwa Y., Mitsui Y., Kobayashi M., Masaki T. The human preproendothelin-1 gene. Complete nucleotide sequence and regulation of expression. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14954–14959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh Y., Yanagisawa M., Ohkubo S., Kimura C., Kosaka T., Inoue A., Ishida N., Mitsui Y., Onda H., Fujino M. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA encoding the precursor of a human endothelium-derived vasoconstrictor peptide, endothelin: identity of human and porcine endothelin. FEBS Lett. 1988 Apr 25;231(2):440–444. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80867-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacCumber M. W., Ross C. A., Glaser B. M., Snyder S. H. Endothelin: visualization of mRNAs by in situ hybridization provides evidence for local action. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(18):7285–7289. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.18.7285. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. I., Tsai S. F., Orkin S. H. Increased gamma-globin expression in a nondeletion HPFH mediated by an erythroid-specific DNA-binding factor. Nature. 1989 Mar 30;338(6214):435–438. doi: 10.1038/338435a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin D. I., Zon L. I., Mutter G., Orkin S. H. Expression of an erythroid transcription factor in megakaryocytic and mast cell lineages. Nature. 1990 Mar 29;344(6265):444–447. doi: 10.1038/344444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melton D. A., Krieg P. A., Rebagliati M. R., Maniatis T., Zinn K., Green M. R. Efficient in vitro synthesis of biologically active RNA and RNA hybridization probes from plasmids containing a bacteriophage SP6 promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Sep 25;12(18):7035–7056. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.18.7035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Frampton J., Wainwright H., Walker M., Macleod K., Goodwin G., Harrison P. GATAAG; a cis-control region binding an erythroid-specific nuclear factor with a role in globin and non-globin gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 11;17(1):73–92. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.1.73. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawamura T., Kimura S., Shinmi O., Sugita Y., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T. Analysis of endothelin related peptides in culture supernatant of porcine aortic endothelial cells: evidence for biosynthetic pathway of endothelin-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 15;162(3):1287–1294. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)90813-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber E., Matthias P., Müller M. M., Schaffner W. Rapid detection of octamer binding proteins with 'mini-extracts', prepared from a small number of cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6419–6419. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schöler H. R., Hatzopoulos A. K., Balling R., Suzuki N., Gruss P. A family of octamer-specific proteins present during mouse embryogenesis: evidence for germline-specific expression of an Oct factor. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2543–2550. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08392.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trainor C. D., Evans T., Felsenfeld G., Boguski M. S. Structure and evolution of a human erythroid transcription factor. Nature. 1990 Jan 4;343(6253):92–96. doi: 10.1038/343092a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai S. F., Martin D. I., Zon L. I., D'Andrea A. D., Wong G. G., Orkin S. H. Cloning of cDNA for the major DNA-binding protein of the erythroid lineage through expression in mammalian cells. Nature. 1989 Jun 8;339(6224):446–451. doi: 10.1038/339446a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wall L., deBoer E., Grosveld F. The human beta-globin gene 3' enhancer contains multiple binding sites for an erythroid-specific protein. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1089–1100. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1089. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagisawa M., Kurihara H., Kimura S., Tomobe Y., Kobayashi M., Mitsui Y., Yazaki Y., Goto K., Masaki T. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988 Mar 31;332(6163):411–415. doi: 10.1038/332411a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizumi M., Kurihara H., Morita T., Yamashita T., Oh-hashi Y., Sugiyama T., Takaku F., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T., Yazaki Y. Interleukin 1 increases the production of endothelin-1 by cultured endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Jan 15;166(1):324–329. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91948-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshizumi M., Kurihara H., Sugiyama T., Takaku F., Yanagisawa M., Masaki T., Yazaki Y. Hemodynamic shear stress stimulates endothelin production by cultured endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 15;161(2):859–864. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92679-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zon L. I., Tsai S. F., Burgess S., Matsudaira P., Bruns G. A., Orkin S. H. The major human erythroid DNA-binding protein (GF-1): primary sequence and localization of the gene to the X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):668–672. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.668. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]