Abstract
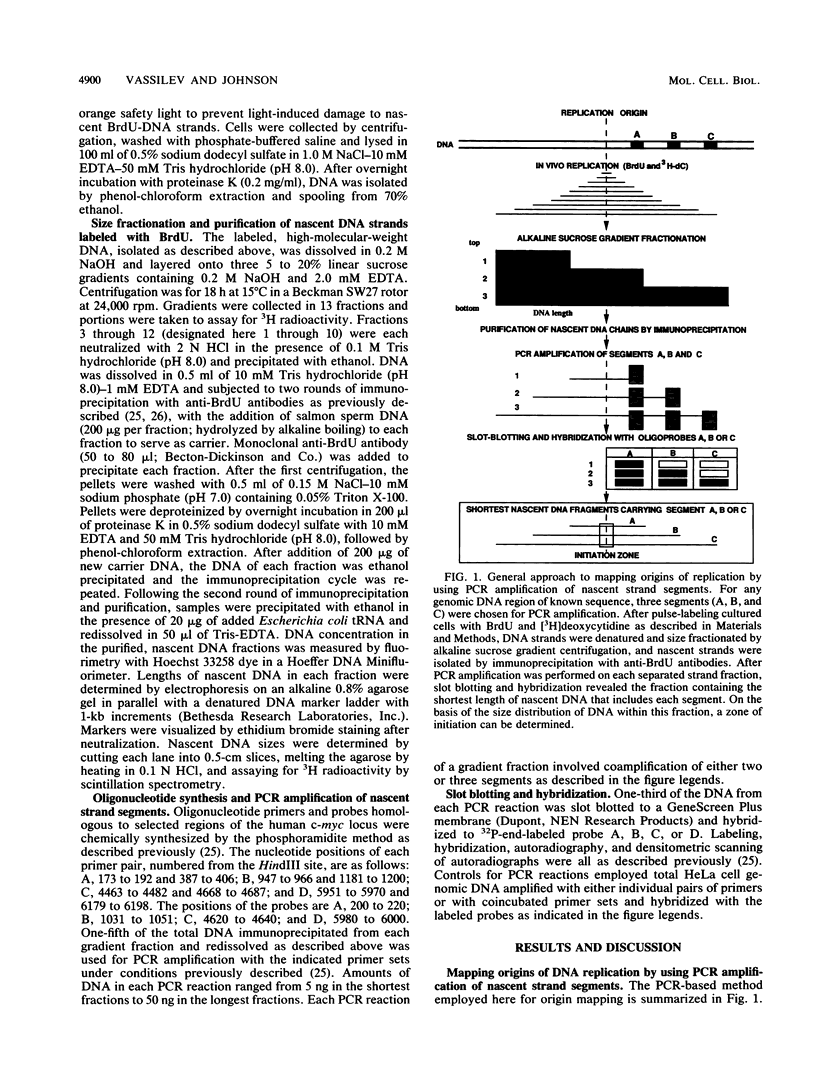
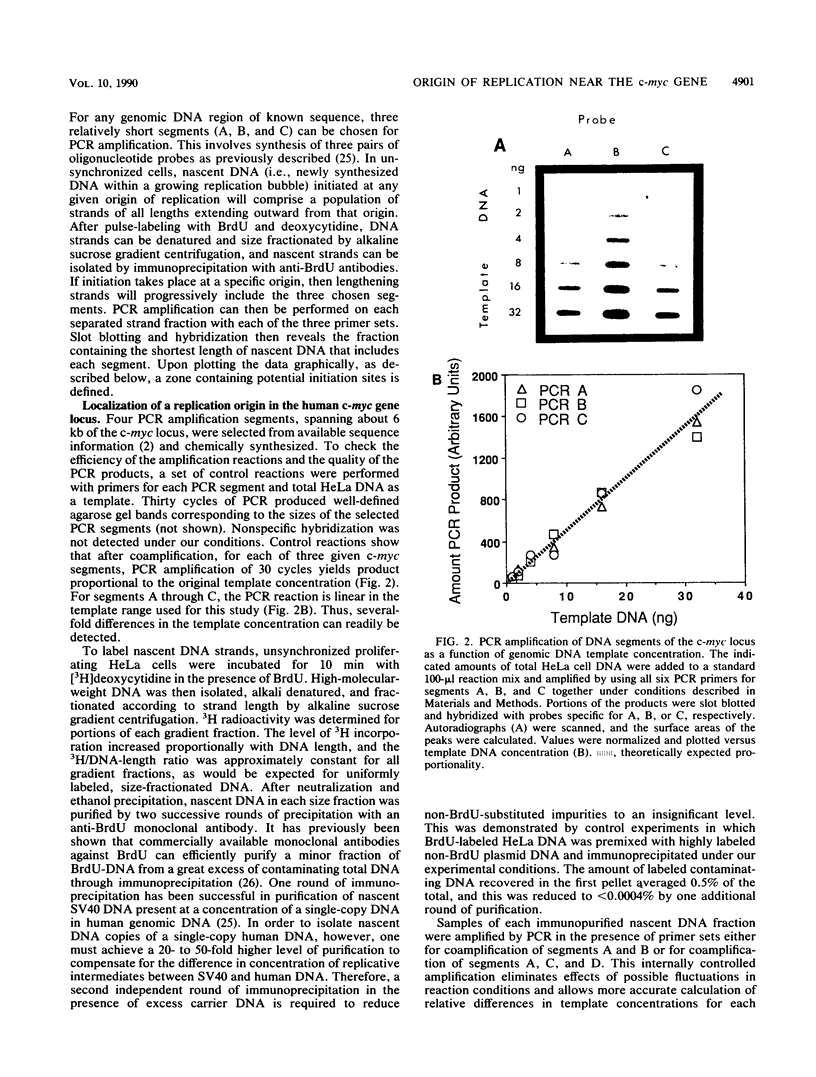
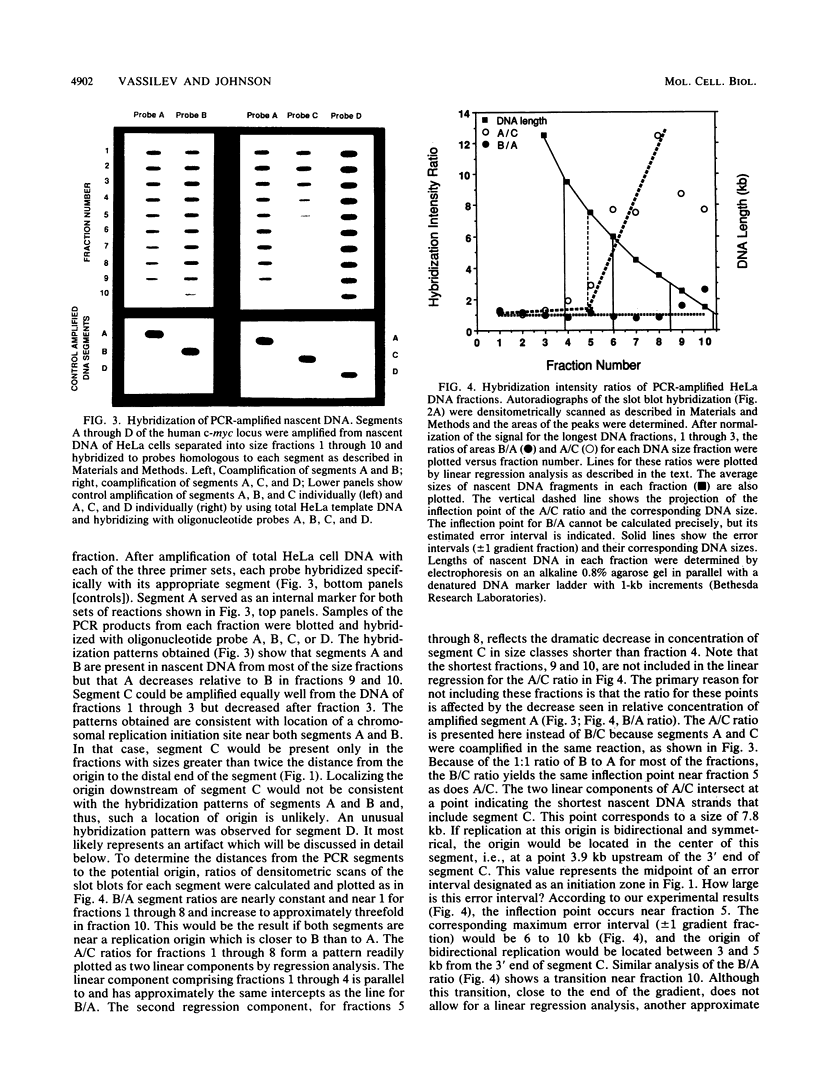
Studies on origins of DNA replication in mammalian cells have long been hampered by a lack of methods sensitive enough for the localization of such origins in chromosomal DNA. We have employed a new method for mapping origins, based on polymerase chain reaction amplification of nascent strand segments, to examine replication initiated in vivo near the c-myc gene in human cells. Nascent DNA, pulse-labeled in unsynchronized HeLa cells, was size fractionated and purified by immunoprecipitation with anti-bromodeoxyuridine antibodies. Lengths of the nascent strands that allow polymerase chain reaction amplification were determined by hybridization to probes homologous to amplified segments and used to calculate the position of the origin. We found that DNA replication through the c-myc gene initiates in a zone centered approximately 1.5 kilobases upstream of exon I. Replication proceeds bidirectionally from the origin, as indicated by comparison of hybridization patterns for three amplified segments. The initiation zone includes segments of the c-myc locus previously reported to drive autonomous replication of plasmids in human cells.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alitalo K., Schwab M., Lin C. C., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Homogeneously staining chromosomal regions contain amplified copies of an abundantly expressed cellular oncogene (c-myc) in malignant neuroendocrine cells from a human colon carcinoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1707–1711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battey J., Moulding C., Taub R., Murphy W., Stewart T., Potter H., Lenoir G., Leder P. The human c-myc oncogene: structural consequences of translocation into the IgH locus in Burkitt lymphoma. Cell. 1983 Oct;34(3):779–787. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90534-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brewer B. J., Fangman W. L. A replication fork barrier at the 3' end of yeast ribosomal RNA genes. Cell. 1988 Nov 18;55(4):637–643. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90222-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burhans W. C., Selegue J. E., Heintz N. H. Isolation of the origin of replication associated with the amplified Chinese hamster dihydrofolate reductase domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(20):7790–7794. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.20.7790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell J. L. Eukaryotic DNA replication. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:733–771. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.003505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng L., Kelly T. J. Transcriptional activator nuclear factor I stimulates the replication of SV40 minichromosomes in vivo and in vitro. Cell. 1989 Nov 3;59(3):541–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90037-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalla-Favera R., Wong-Staal F., Gallo R. C. Onc gene amplification in promyelocytic leukaemia cell line HL-60 and primary leukaemic cells of the same patient. Nature. 1982 Sep 2;299(5878):61–63. doi: 10.1038/299061a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniel D. C., Johnson E. M. Selective initiation of replication at origin sequences of the rDNA molecule of Physarum polycephalum using synchronous plasmodial extracts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 25;17(20):8343–8362. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.20.8343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dyson P. J., Rabbitts T. H. Chromatin structure around the c-myc gene in Burkitt lymphomas with upstream and downstream translocation points. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1984–1988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gahn T. A., Schildkraut C. L. The Epstein-Barr virus origin of plasmid replication, oriP, contains both the initiation and termination sites of DNA replication. Cell. 1989 Aug 11;58(3):527–535. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90433-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand R. Eucaryotic DNA: organization of the genome for replication. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):317–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90001-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Handeli S., Klar A., Meuth M., Cedar H. Mapping replication units in animal cells. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):909–920. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90329-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Riggs A. D. On the mechanism of DNA replication in mammalian chromosomes. J Mol Biol. 1968 Mar 14;32(2):327–341. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Spotila L. D., Nawotka K. A., el-Assouli S. M., Davis L. R. The in vivo replication origin of the yeast 2 microns plasmid. Cell. 1987 Nov 6;51(3):473–481. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90643-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman J. A., Zhu J. G., Davis L. R., Newlon C. S. Close association of a DNA replication origin and an ARS element on chromosome III of the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jul 25;16(14A):6373–6384. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.14.6373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iguchi-Ariga S. M., Okazaki T., Itani T., Ogata M., Sato Y., Ariga H. An initiation site of DNA replication with transcriptional enhancer activity present upstream of the c-myc gene. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3135–3142. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03180.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson E. M., Jelinek W. R. Replication of a plasmid bearing a human Alu-family repeat in monkey COS-7 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4660–4664. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4660. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leffak M., James C. D. Opposite replication polarity of the germ line c-myc gene in HeLa cells compared with that of two Burkitt lymphoma cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):586–593. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.586. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leu T. H., Hamlin J. L. High-resolution mapping of replication fork movement through the amplified dihydrofolate reductase domain in CHO cells by in-gel renaturation analysis. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):523–531. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McWhinney C., Leffak M. Autonomous replication of a DNA fragment containing the chromosomal replication origin of the human c-myc gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Mar 11;18(5):1233–1242. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.5.1233. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nawotka K. A., Huberman J. A. Two-dimensional gel electrophoretic method for mapping DNA replicons. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1408–1413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenfeld P. J., O'Neill E. A., Wides R. J., Kelly T. J. Sequence-specific interactions between cellular DNA-binding proteins and the adenovirus origin of DNA replication. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):875–886. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev L., Johnson E. M. Mapping initiation sites of DNA replication in vivo using polymerase chain reaction amplification of nascent strand segments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 11;17(19):7693–7705. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.19.7693. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassilev L., Russev G. Purification of nascent DNA chains by immunoprecipitation with anti-BrdU antibodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Nov 11;16(21):10397–10397. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.21.10397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Von Hoff D. D., Needham-VanDevanter D. R., Yucel J., Windle B. E., Wahl G. M. Amplified human MYC oncogenes localized to replicating submicroscopic circular DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4804–4808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]