Abstract
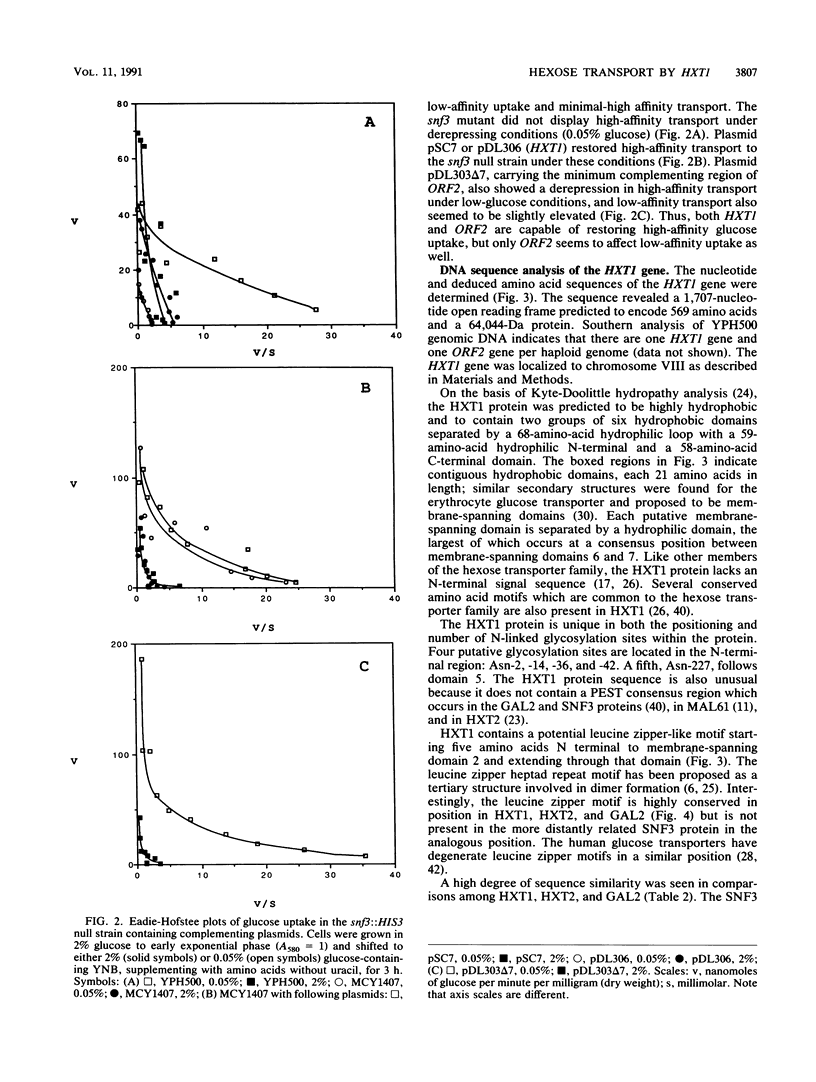
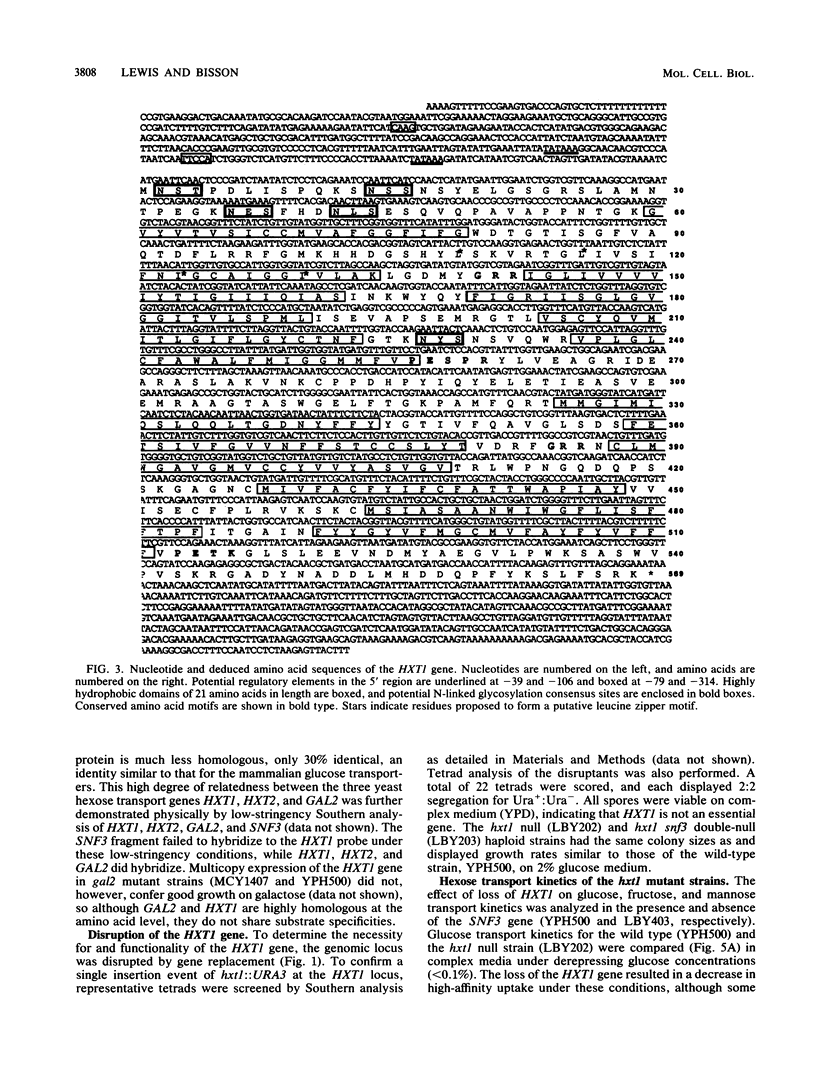
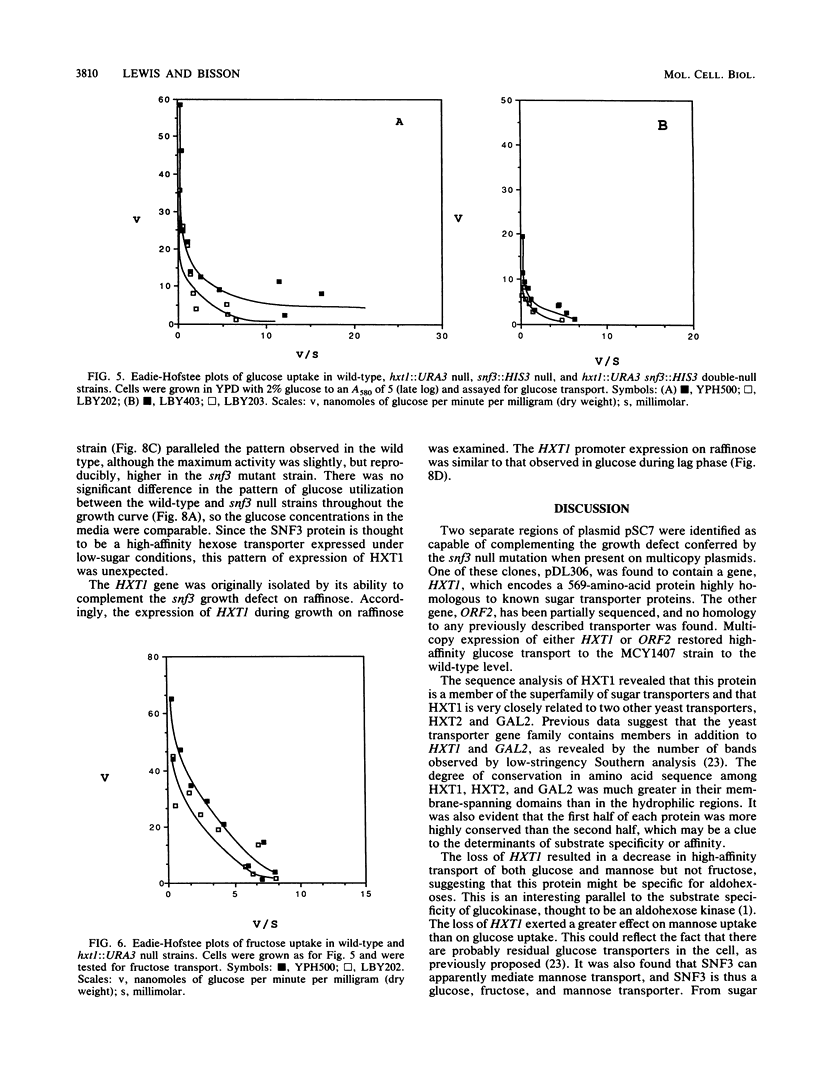
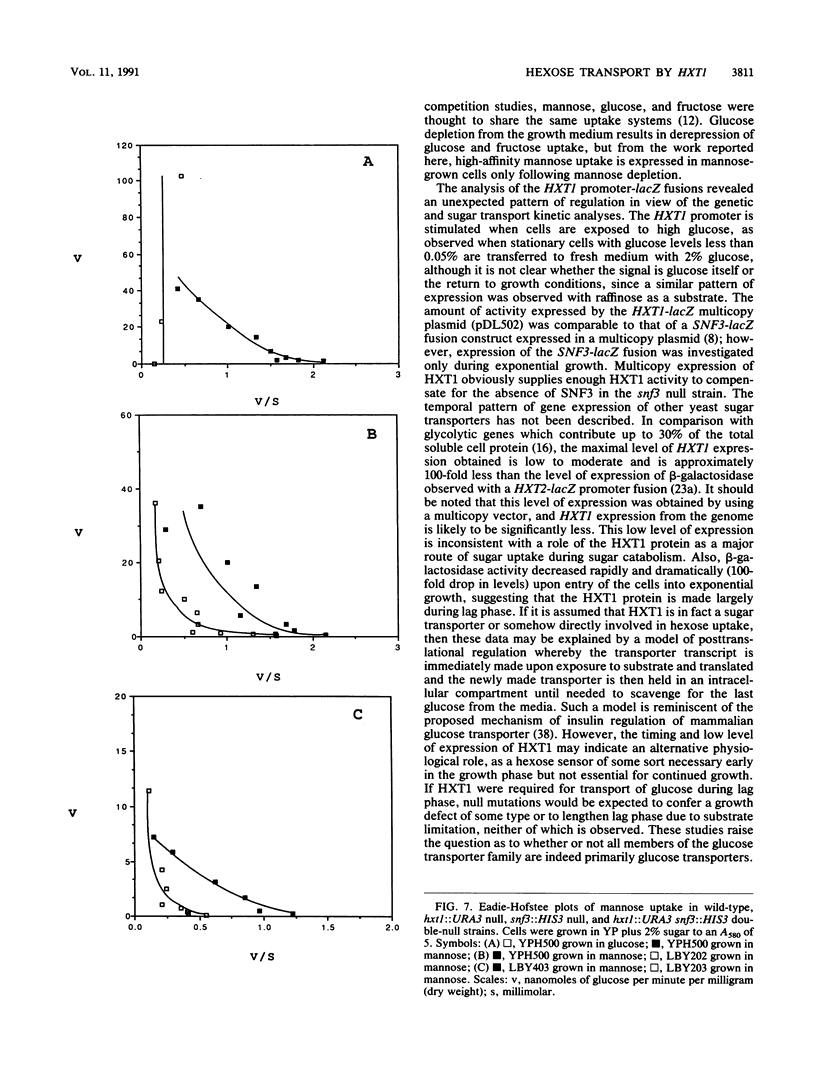
Two novel genes affecting hexose transport in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae have been identified. The gene HXT1 (hexose transport), isolated from plasmid pSC7, was sequenced and found to encode a hydrophobic protein which is highly homologous to the large family of sugar transporter proteins from eucaryotes and procaryotes. Multicopy expression of the HXT1 gene restored high-affinity glucose transport to the snf3 mutant, which is deficient in a significant proportion of high-affinity glucose transport. HXT1 was unable to complement the snf3 growth defect in low copy number. The HXT1 protein was found to contain 12 putative membrane-spanning domains with a central hydrophilic domain and hydrophilic N- and C-terminal domains. The HXT1 protein is 69% identical to GAL2 and 66% identical to HXT2, and all three proteins were found to have a putative leucine zipper motif at a consensus location in membrane-spanning domain 2. Disruption of the HXT1 gene resulted in loss of a portion of high-affinity glucose and mannose transport, and wild-type levels of transport required both the HXT1 and SNF3 genes. Unexpectedly, expression of beta-galactosidase activity by using a fusion of the lacZ gene to the HXT1 promoter in a multicopy plasmid was maximal during lag and early exponential phases of growth, decreasing approximately 100-fold upon further entry into exponential growth. Deletion analysis of pSC7 revealed the presence of another gene (called ORF2) capable of suppressing the snf3 null mutant phenotype by restoring high-affinity glucose transport and increased low-affinity transport.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albig W., Entian K. D. Structure of yeast glucokinase, a strongly diverged specific aldo-hexose-phosphorylating isoenzyme. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):141–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90320-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaum M. J., Haspel H. C., Rosen O. M. Cloning and characterization of a cDNA encoding the rat brain glucose-transporter protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5784–5788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisson L. F., Fraenkel D. G. Involvement of kinases in glucose and fructose uptake by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1730–1734. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisson L. F., Fraenkel D. G. Transport of 6-deoxyglucose in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):995–1000. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.995-1000.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisson L. F., Neigeborn L., Carlson M., Fraenkel D. G. The SNF3 gene is required for high-affinity glucose transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1987 Apr;169(4):1656–1662. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.4.1656-1662.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boscoboinik D., Debanne M. T., Stafford A. R., Jung C. Y., Gupta R. S., Epand R. M. Dimerization of the P-glycoprotein in membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Sep 7;1027(3):225–228. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90311-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M., Osmond B. C., Botstein D. Mutants of yeast defective in sucrose utilization. Genetics. 1981 May;98(1):25–40. doi: 10.1093/genetics/98.1.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celenza J. L., Marshall-Carlson L., Carlson M. The yeast SNF3 gene encodes a glucose transporter homologous to the mammalian protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(7):2130–2134. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.7.2130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y. D., Dickson R. C. Primary structure of the lactose permease gene from the yeast Kluyveromyces lactis. Presence of an unusual transcript structure. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16696–16703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng Q., Michels C. A. The maltose permease encoded by the MAL61 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae exhibits both sequence and structural homology to other sugar transporters. Genetics. 1989 Nov;123(3):477–484. doi: 10.1093/genetics/123.3.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cirillo V. P. Galactose transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. I. Nonmetabolized sugars as substrates and inducers of the galactose transport system. J Bacteriol. 1968 May;95(5):1727–1731. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.5.1727-1731.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elledge S. J., Davis R. W. A family of versatile centromeric vectors designed for use in the sectoring-shuffle mutagenesis assay in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Gene. 1988 Oct 30;70(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90202-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gierasch L. M. Signal sequences. Biochemistry. 1989 Feb 7;28(3):923–930. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters and lacZ fusions designed to study expression of cloned genes in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:181–191. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill J. E., Myers A. M., Koerner T. J., Tzagoloff A. Yeast/E. coli shuttle vectors with multiple unique restriction sites. Yeast. 1986 Sep;2(3):163–167. doi: 10.1002/yea.320020304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruckeberg A. L., Bisson L. F. The HXT2 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae is required for high-affinity glucose transport. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;10(11):5903–5913. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.11.5903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landschulz W. H., Johnson P. F., McKnight S. L. The leucine zipper: a hypothetical structure common to a new class of DNA binding proteins. Science. 1988 Jun 24;240(4860):1759–1764. doi: 10.1126/science.3289117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leucine-zipper motif update. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):103–104. doi: 10.1038/340103a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leucine-zipper motif update. Nature. 1989 Jul 13;340(6229):103–104. doi: 10.1038/340103a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maiden M. C., Davis E. O., Baldwin S. A., Moore D. C., Henderson P. J. Mammalian and bacterial sugar transport proteins are homologous. Nature. 1987 Feb 12;325(6105):641–643. doi: 10.1038/325641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mueckler M., Caruso C., Baldwin S. A., Panico M., Blench I., Morris H. R., Allard W. J., Lienhard G. E., Lodish H. F. Sequence and structure of a human glucose transporter. Science. 1985 Sep 6;229(4717):941–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3839598. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. M., Tzagoloff A., Kinney D. M., Lusty C. J. Yeast shuttle and integrative vectors with multiple cloning sites suitable for construction of lacZ fusions. Gene. 1986;45(3):299–310. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90028-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neigeborn L., Schwartzberg P., Reid R., Carlson M. Null mutations in the SNF3 gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae cause a different phenotype than do previously isolated missense mutations. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3569–3574. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3569. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simpson I. A., Cushman S. W. Hormonal regulation of mammalian glucose transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:1059–1089. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.005211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szkutnicka K., Tschopp J. F., Andrews L., Cirillo V. P. Sequence and structure of the yeast galactose transporter. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4486–4493. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4486-4493.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. M., Weber D. K., Johnson T., Sakaguchi A. Y. Supercoil sequencing using unpurified templates produced by rapid boiling. Biotechniques. 1988 Oct;6(9):839, 841-3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


