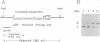Abstract
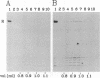
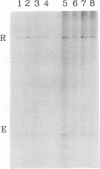
A synthetic analog of an abasic site in DNA is efficiently repaired by a short-patch repair mechanism in soluble extracts of Xenopus laevis oocytes (Y. Matsumoto and D. F. Bogenhagen, Mol. Cell. Biol. 9:3750-3757, 1989). We present a detailed analysis of the repair mechanism, using extracts depleted of endogenous nucleotide pools. ATP was required for repair with a sharp optimal concentration of 5 mM. The initial rate of repair was increased by preincubation of the DNA in the extract in the presence of ATP. During this preincubation, the DNA was cleaved on the 5' side of the lesion by a class II apurinic-apyrimidinic endonuclease, but removal of the abasic sugar residue was not observed prior to addition of deoxynucleotides to the reaction. Immediately following DNA synthesis, excision and ligation proceeded in a coordinated manner to complete repair. DNA preincubated in the extract in the absence of deoxynucleotides remained associated with repair enzymes during gel filtration. These observations suggest that the enzymes involved in concerted repair of the abasic site form a complex on DNA.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Glikin G. C., Ruberti I., Worcel A. Chromatin assembly in Xenopus oocytes: in vitro studies. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):33–41. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90298-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson J., Grossman L., Lindahl T., Wood R. D. Complementation of the xeroderma pigmentosum DNA repair synthesis defect with Escherichia coli UvrABC proteins in a cell-free system. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Jan 11;18(1):35–40. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.1.35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson J., Munn M., Rupp W. D., Kahn R., Wood R. D. Localization of DNA repair synthesis by human cell extracts to a short region at the site of a lesion. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21788–21792. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labarca C., Paigen K. A simple, rapid, and sensitive DNA assay procedure. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):344–352. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90165-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl T., Nyberg B. Rate of depurination of native deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1972 Sep 12;11(19):3610–3618. doi: 10.1021/bi00769a018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loeb L. A. Apurinic sites as mutagenic intermediates. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):483–484. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90191-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto Y., Bogenhagen D. F. Repair of a synthetic abasic site in DNA in a Xenopus laevis oocyte extract. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;9(9):3750–3757. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.9.3750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randahl H., Elliott G. C., Linn S. DNA-repair reactions by purified HeLa DNA polymerases and exonucleases. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12228–12234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanssens P., Opsomer C., McKeown Y. M., Kramer W., Zabeau M., Fritz H. J. Efficient oligonucleotide-directed construction of mutations in expression vectors by the gapped duplex DNA method using alternating selectable markers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4441–4454. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeshita M., Chang C. N., Johnson F., Will S., Grollman A. P. Oligodeoxynucleotides containing synthetic abasic sites. Model substrates for DNA polymerases and apurinic/apyrimidinic endonucleases. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10171–10179. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. C., Roberts J. D., Kunkel T. A. Heteroduplex repair in extracts of human HeLa cells. J Biol Chem. 1991 Feb 25;266(6):3744–3751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varlet I., Radman M., Brooks P. DNA mismatch repair in Xenopus egg extracts: repair efficiency and DNA repair synthesis for all single base-pair mismatches. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(20):7883–7887. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.20.7883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiebauer K., Jiricny J. Mismatch-specific thymine DNA glycosylase and DNA polymerase beta mediate the correction of G.T mispairs in nuclear extracts from human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Aug;87(15):5842–5845. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.15.5842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R. D., Robins P., Lindahl T. Complementation of the xeroderma pigmentosum DNA repair defect in cell-free extracts. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):97–106. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90491-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]