Abstract
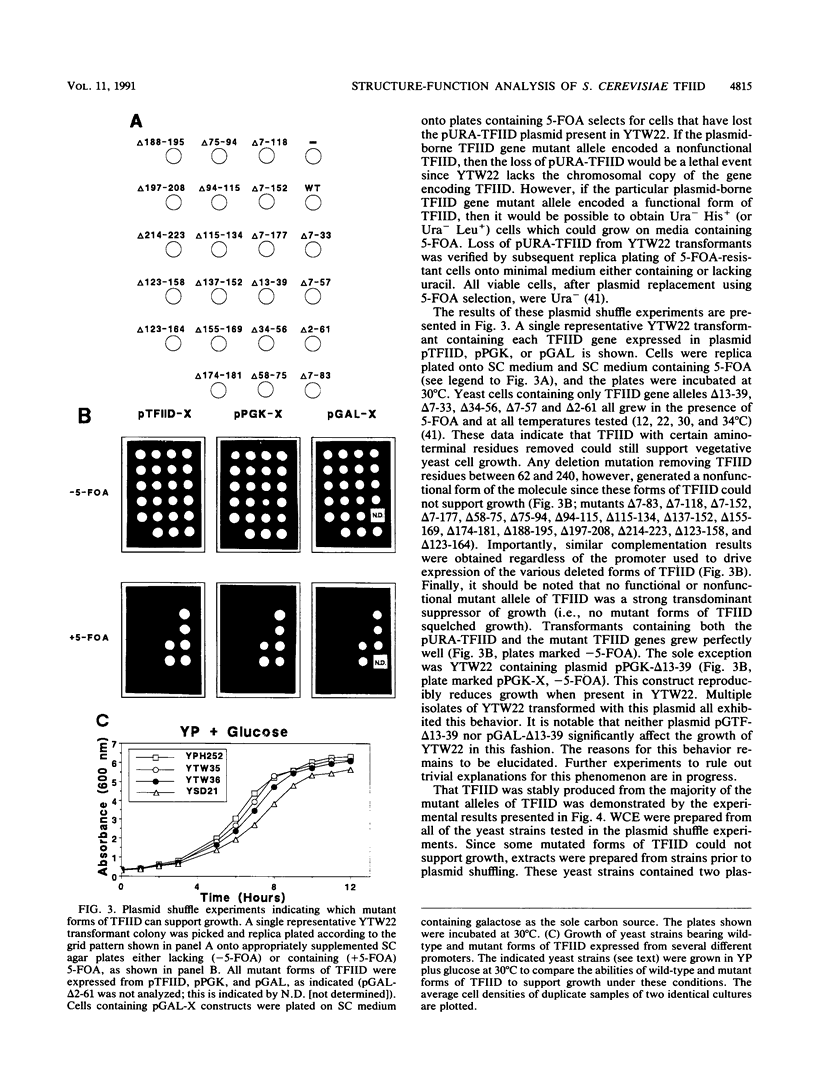
We have examined the structure-function relationships of TFIID through in vivo complementation tests. A yeast strain was constructed which lacked the chromosomal copy of SPT15, the gene encoding TFIID, and was therefore dependent on a functional plasmid-borne wild-type copy of this gene for viability. By using the plasmid shuffle technique, the plasmid-borne wild-type TFIID gene was replaced with a family of plasmids containing a series of systematically mutated TFIID genes. These various forms of TFIID were expressed from three different promoter contexts of different strengths, and the ability of each mutant form of TFIID to complement our chromosomal TFIID null allele was assessed. We found that the first 61 amino acid residues of TFIID are totally dispensable for vegetative cell growth, since yeast strains containing this deleted form of TFIID grow at wild-type rates. Amino-terminally deleted TFIID was further shown to be able to function normally in vivo by virtue of its ability both to promote accurate transcription initiation from a large number of different genes and to interact efficiently with the Gal4 protein to activate transcription of GAL1 with essentially wild-type kinetics. Any deletion removing sequences from within the conserved carboxy-terminal region of S. cerevisiae TFIID was lethal. Further, the exact sequence of the conserved carboxy-terminal portion of the molecule is critical for function, since of several heterologous TFIID homologs tested, only the highly related Schizosaccharomyces pombe gene could complement our S. cerevisiae TFIID null mutant. Taken together, these data indicate that all important functional domains of TFIID appear to lie in its carboxy-terminal 179 amino acid residues. The significance of these findings regarding TFIID function are discussed.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abmayr S. M., Workman J. L., Roeder R. G. The pseudorabies immediate early protein stimulates in vitro transcription by facilitating TFIID: promoter interactions. Genes Dev. 1988 May;2(5):542–553. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.5.542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger S. L., Cress W. D., Cress A., Triezenberg S. J., Guarente L. Selective inhibition of activated but not basal transcription by the acidic activation domain of VP16: evidence for transcriptional adaptors. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1199–1208. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90684-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bitter G. A., Egan K. M. Expression of heterologous genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae from vectors utilizing the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene promoter. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boeke J. D., Trueheart J., Natsoulis G., Fink G. R. 5-Fluoroorotic acid as a selective agent in yeast molecular genetics. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:164–175. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54076-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buratowski S., Hahn S., Guarente L., Sharp P. A. Five intermediate complexes in transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):549–561. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90578-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cavallini B., Faus I., Matthes H., Chipoulet J. M., Winsor B., Egly J. M., Chambon P. Cloning of the gene encoding the yeast protein BTF1Y, which can substitute for the human TATA box-binding factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9803–9807. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conaway R. C., Conaway J. W. Transcription initiated by RNA polymerase II and purified transcription factors from liver. Transcription factors alpha, beta gamma, and delta promote formation of intermediates in assembly of the functional preinitiation complex. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 5;265(13):7559–7563. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cormack B. P., Strubin M., Ponticelli A. S., Struhl K. Functional differences between yeast and human TFIID are localized to the highly conserved region. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90167-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison B. L., Egly J. M., Mulvihill E. R., Chambon P. Formation of stable preinitiation complexes between eukaryotic class B transcription factors and promoter sequences. Nature. 1983 Feb 24;301(5902):680–686. doi: 10.1038/301680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donahue T. F., Farabaugh P. J., Fink G. R. The nucleotide sequence of the HIS4 region of yeast. Gene. 1982 Apr;18(1):47–59. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90055-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenmann D. M., Dollard C., Winston F. SPT15, the gene encoding the yeast TATA binding factor TFIID, is required for normal transcription initiation in vivo. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1183–1191. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90516-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fikes J. D., Becker D. M., Winston F., Guarente L. Striking conservation of TFIID in Schizosaccharomyces pombe and Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature. 1990 Jul 19;346(6281):291–294. doi: 10.1038/346291a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fire A., Samuels M., Sharp P. A. Interactions between RNA polymerase II, factors, and template leading to accurate transcription. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2509–2516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gasch A., Hoffmann A., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G., Chua N. H. Arabidopsis thaliana contains two genes for TFIID. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):390–394. doi: 10.1038/346390a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Ptashne M. Negative effect of the transcriptional activator GAL4. Nature. 1988 Aug 25;334(6184):721–724. doi: 10.1038/334721a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill G., Tjian R. A highly conserved domain of TFIID displays species specificity in vivo. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):333–340. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90166-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Buratowski S., Sharp P. A., Guarente L. Isolation of the gene encoding the yeast TATA binding protein TFIID: a gene identical to the SPT15 suppressor of Ty element insertions. Cell. 1989 Sep 22;58(6):1173–1181. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90515-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley D. K., Roeder R. G. Separation and partial characterization of three functional steps in transcription initiation by human RNA polymerase II. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):8163–8172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herskowitz I. Functional inactivation of genes by dominant negative mutations. Nature. 1987 Sep 17;329(6136):219–222. doi: 10.1038/329219a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitzeman R. A., Hagie F. E., Hayflick J. S., Chen C. Y., Seeburg P. H., Derynck R. The primary structure of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae gene for 3-phosphoglycerate kinase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Dec 11;10(23):7791–7808. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.23.7791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman A., Sinn E., Yamamoto T., Wang J., Roy A., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Highly conserved core domain and unique N terminus with presumptive regulatory motifs in a human TATA factor (TFIID). Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):387–390. doi: 10.1038/346387a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman C. S., Winston F. A ten-minute DNA preparation from yeast efficiently releases autonomous plasmids for transformation of Escherichia coli. Gene. 1987;57(2-3):267–272. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90131-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoffmann A., Horikoshi M., Wang C. K., Schroeder S., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Cloning of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe TFIID gene reveals a strong conservation of functional domains present in Saccharomyces cerevisiae TFIID. Genes Dev. 1990 Jul;4(7):1141–1148. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.7.1141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Carey M. F., Kakidani H., Roeder R. G. Mechanism of action of a yeast activator: direct effect of GAL4 derivatives on mammalian TFIID-promoter interactions. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):665–669. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Hai T., Lin Y. S., Green M. R., Roeder R. G. Transcription factor ATF interacts with the TATA factor to facilitate establishment of a preinitiation complex. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1033–1042. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90118-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Wang C. K., Fujii H., Cromlish J. A., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Cloning and structure of a yeast gene encoding a general transcription initiation factor TFIID that binds to the TATA box. Nature. 1989 Sep 28;341(6240):299–303. doi: 10.1038/341299a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Yamamoto T., Ohkuma Y., Weil P. A., Roeder R. G. Analysis of structure-function relationships of yeast TATA box binding factor TFIID. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1171–1178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90681-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M., Davis R. W. Sequences that regulate the divergent GAL1-GAL10 promoter in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Aug;4(8):1440–1448. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.8.1440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kao C. C., Lieberman P. M., Schmidt M. C., Zhou Q., Pei R., Berk A. J. Cloning of a transcriptionally active human TATA binding factor. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1646–1650. doi: 10.1126/science.2194289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karnitz L., Poon D., Weil P. A., Chalkley R. Purification and properties of the Rous sarcoma virus internal enhancer binding factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 May;9(5):1929–1939. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.5.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelleher R. J., 3rd, Flanagan P. M., Kornberg R. D. A novel mediator between activator proteins and the RNA polymerase II transcription apparatus. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1209–1215. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90685-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman P. M., Schmidt M. C., Kao C. C., Berk A. J. Two distinct domains in the yeast transcription factor IID and evidence for a TATA box-induced conformational change. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jan;11(1):63–74. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.1.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell P. J., Tjian R. Transcriptional regulation in mammalian cells by sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):371–378. doi: 10.1126/science.2667136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muhich M. L., Iida C. T., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G., Parker C. S. cDNA clone encoding Drosophila transcription factor TFIID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9148–9152. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9148. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohkuma Y., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G., Desplan C. Engrailed, a homeodomain protein, can repress in vitro transcription by competition with the TATA box-binding protein transcription factor IID. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2289–2293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson M. G., Tanese N., Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Functional domains and upstream activation properties of cloned human TATA binding protein. Science. 1990 Jun 29;248(4963):1625–1630. doi: 10.1126/science.2363050. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M., Gann A. A. Activators and targets. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):329–331. doi: 10.1038/346329a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ptashne M. How eukaryotic transcriptional activators work. Nature. 1988 Oct 20;335(6192):683–689. doi: 10.1038/335683a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugh B. F., Tjian R. Mechanism of transcriptional activation by Sp1: evidence for coactivators. Cell. 1990 Jun 29;61(7):1187–1197. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90683-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy P., Hahn S. Dominant negative mutations in yeast TFIID define a bipartite DNA-binding region. Cell. 1991 Apr 19;65(2):349–357. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II. Purification and functional analysis of initiation factors IIB and IIE. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3310–3321. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg A. H., Lade B. N., Chui D. S., Lin S. W., Dunn J. J., Studier F. W. Vectors for selective expression of cloned DNAs by T7 RNA polymerase. Gene. 1987;56(1):125–135. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90165-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltzman A. G., Weinmann R. Promoter specificity and modulation of RNA polymerase II transcription. FASEB J. 1989 Apr;3(6):1723–1733. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.3.6.2649403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. C., Kao C. C., Pei R., Berk A. J. Yeast TATA-box transcription factor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(20):7785–7789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.20.7785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sikorski R. S., Hieter P. A system of shuttle vectors and yeast host strains designed for efficient manipulation of DNA in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1989 May;122(1):19–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/122.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. M., Andrésson O. S. DNA sequences of yeast H3 and H4 histone genes from two non-allelic gene sets encode identical H3 and H4 proteins. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 25;169(3):663–690. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80164-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stringer K. F., Ingles C. J., Greenblatt J. Direct and selective binding of an acidic transcriptional activation domain to the TATA-box factor TFIID. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):783–786. doi: 10.1038/345783a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sumimoto H., Ohkuma Y., Yamamoto T., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by mammalian RNA polymerase II: identification of general transcription factor TFIIG. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(23):9158–9162. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.23.9158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]









