Abstract
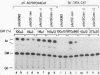
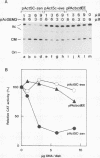
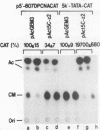
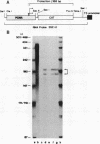
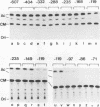
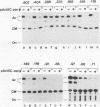
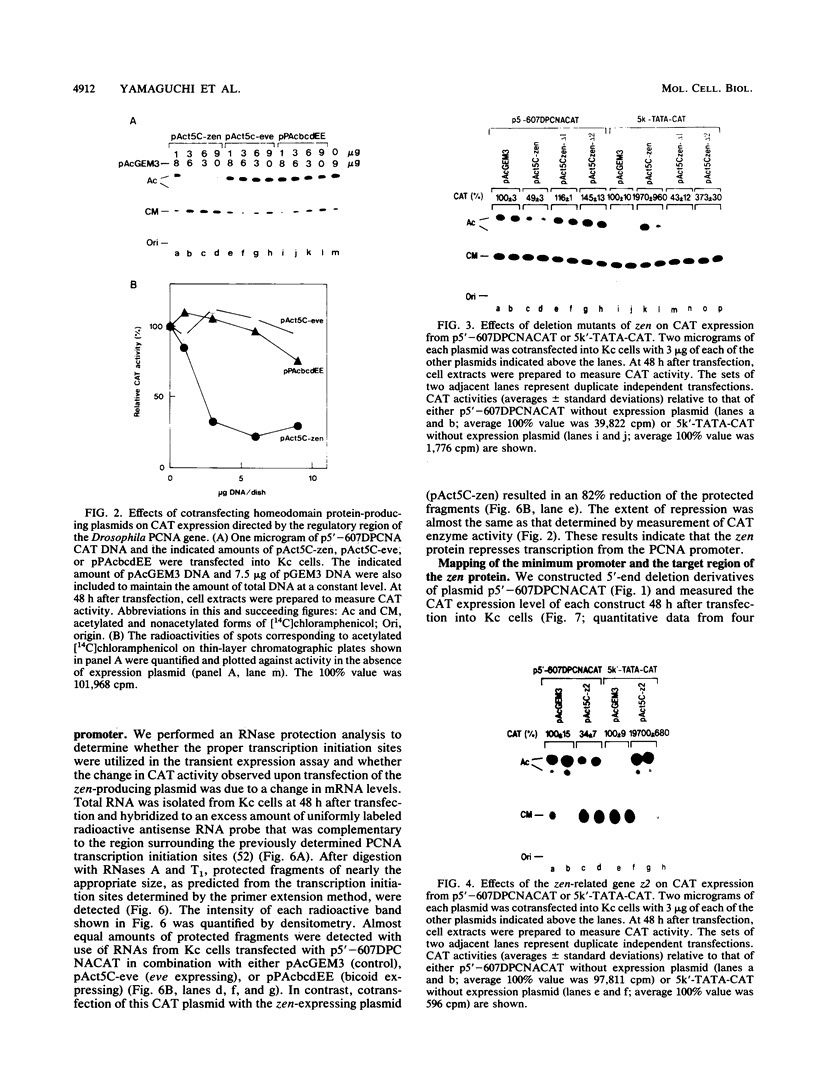
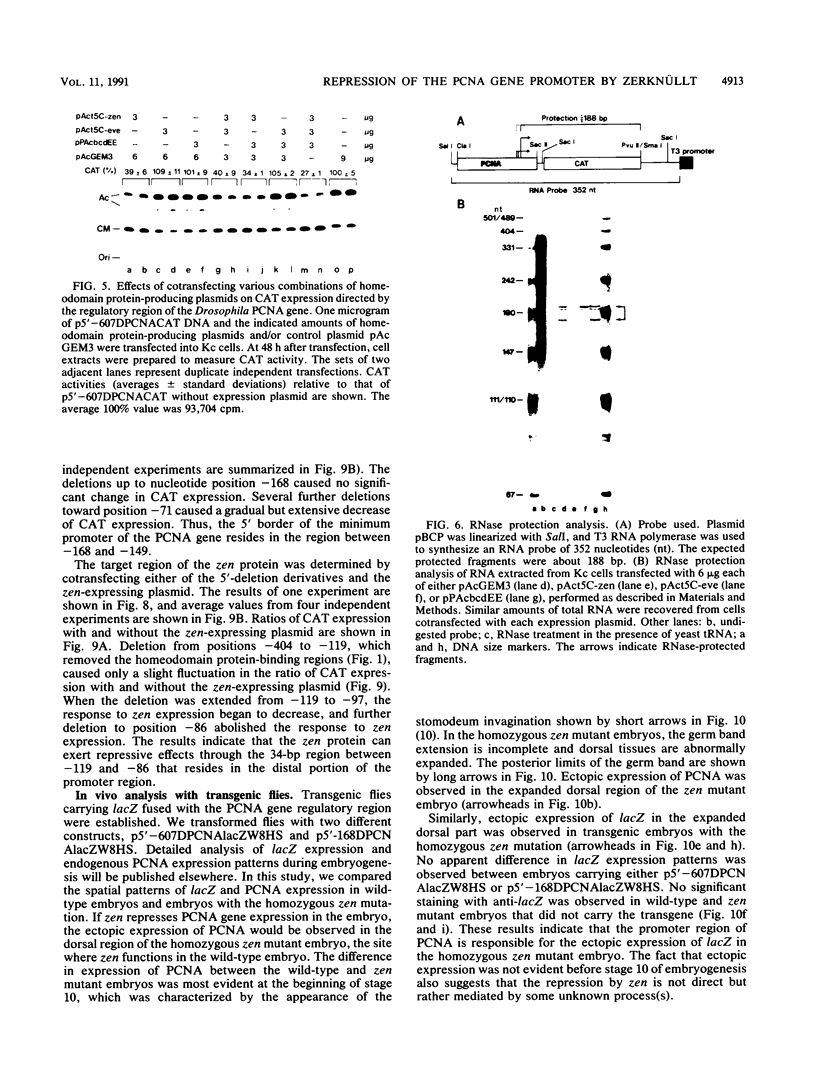
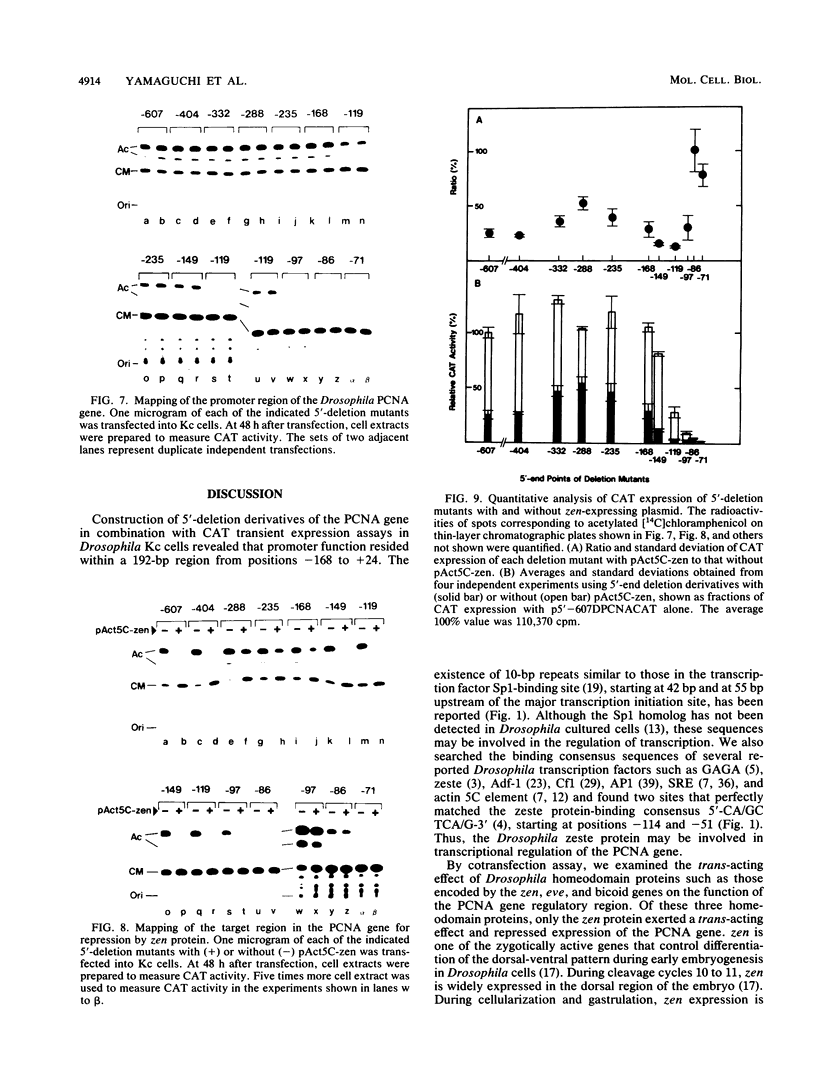
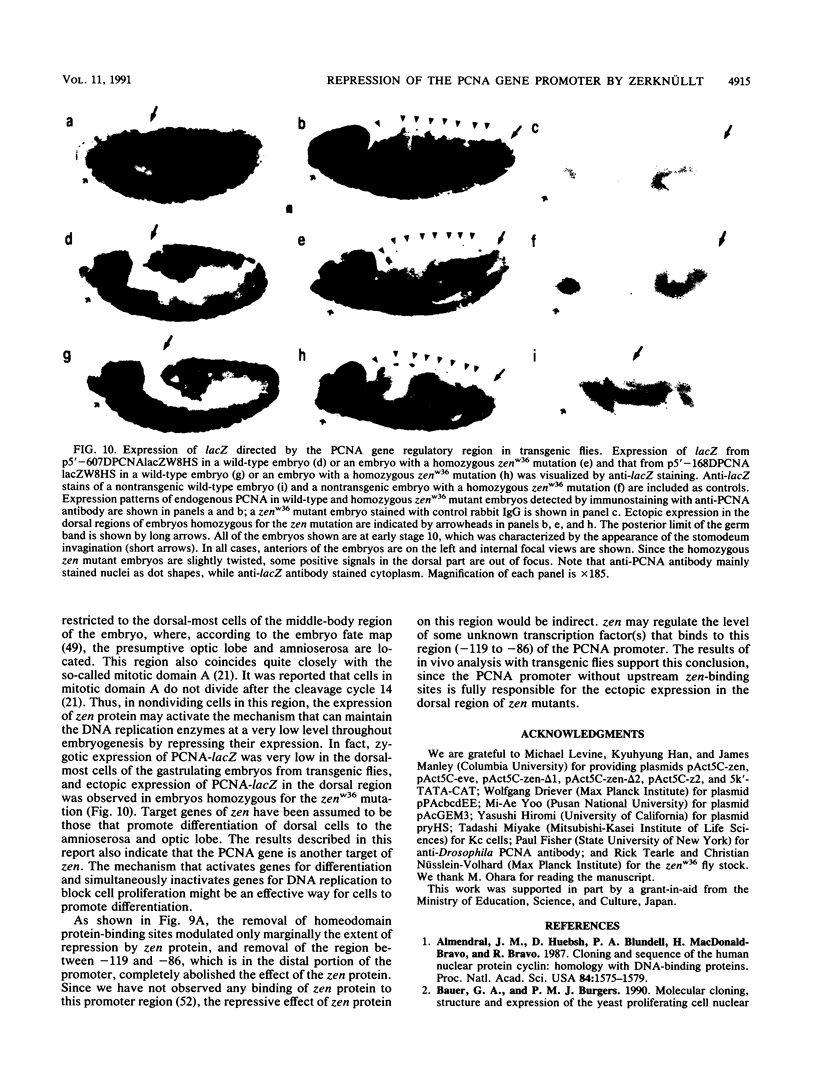
A 631-bp fragment containing the 5'-flanking region of the Drosophila melanogaster proliferating-cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) gene was placed upstream of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene of a CAT vector. A transient expression assay of CAT activity in Drosophila Kc cells transfected with this plasmid and a set of 5'-deletion derivatives revealed that the promoter function resided within a 192-bp region (-168 to +24 with respect to the transcription initiation site). Cotransfection with a zerknüllt (zen)-expressing plasmid specifically repressed CAT expression. However, cotransfection with expression plasmids for a nonfunctional zen mutation, even-skipped, or bicoid showed no significant effect on CAT expression. RNase protection analysis revealed that the repression by zen was at the transcription step. The target sequence of zen was mapped within the 34-bp region (-119 to -86) of the PCNA gene promoter, even though it lacked zen protein-binding sites. Transgenic flies carrying the PCNA gene regulatory region (-607 to +137 or -168 to +137) fused with lacZ were established. When these flies were crossed with the zen mutant, ectopic expression of lacZ was observed in the dorsal region of gastrulating embryos carrying the transgene with either construct. These results indicate that zen indirectly represses PCNA gene expression, probably by regulating the expression of some transcription factor(s) that binds to the PCNA gene promoter.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Almendral J. M., Huebsch D., Blundell P. A., Macdonald-Bravo H., Bravo R. Cloning and sequence of the human nuclear protein cyclin: homology with DNA-binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(6):1575–1579. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.6.1575. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson M., Pirrotta V. The Drosophila zeste protein binds cooperatively to sites in many gene regulatory regions: implications for transvection and gene regulation. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 1;7(12):3907–3915. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03277.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Bickel S., Benson M., Pirrotta V., Tjian R. Zeste encodes a sequence-specific transcription factor that activates the Ultrabithorax promoter in vitro. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):713–722. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90089-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Tjian R. Transcription factors that activate the Ultrabithorax promoter in developmentally staged extracts. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):699–711. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90088-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond-Matthews B., Davidson N. Transcription from each of the Drosophila act5C leader exons is driven by a separate functional promoter. Gene. 1988;62(2):289–300. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90566-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bond B. J., Davidson N. The Drosophila melanogaster actin 5C gene uses two transcription initiation sites and three polyadenylation sites to express multiple mRNA species. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2080–2088. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Fey S. J., Bellatin J., Larsen P. M., Arevalo J., Celis J. E. Identification of a nuclear and of a cytoplasmic polypeptide whose relative proportions are sensitive to changes in the rate of cell proliferation. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Dec;136(2):311–319. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90009-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bravo R., Frank R., Blundell P. A., Macdonald-Bravo H. Cyclin/PCNA is the auxiliary protein of DNA polymerase-delta. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):515–517. doi: 10.1038/326515a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung Y. T., Keller E. B. Regulatory elements mediating transcription from the Drosophila melanogaster actin 5C proximal promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Jan;10(1):206–216. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.1.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courey A. J., Tjian R. Analysis of Sp1 in vivo reveals multiple transcriptional domains, including a novel glutamine-rich activation motif. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):887–898. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90144-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross D. P., Sang J. H. Cell culture of individual Drosophila embryos. I. Development of wild-type cultures. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1978 Jun;45:161–172. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desplan C., Theis J., O'Farrell P. H. The sequence specificity of homeodomain-DNA interaction. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1081–1090. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90123-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Nocera P. P., Dawid I. B. Transient expression of genes introduced into cultured cells of Drosophila. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7095–7098. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle H. J., Kraut R., Levine M. Spatial regulation of zerknüllt: a dorsal-ventral patterning gene in Drosophila. Genes Dev. 1989 Oct;3(10):1518–1533. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.10.1518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driever W., Nüsslein-Volhard C. The bicoid protein is a positive regulator of hunchback transcription in the early Drosophila embryo. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):138–143. doi: 10.1038/337138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Sazer S., Tjian R., Schimke R. T. Transcription factor Sp1 recognizes a DNA sequence in the mouse dihydrofolate reductase promoter. Nature. 1986 Jan 16;319(6050):246–248. doi: 10.1038/319246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echalier G., Ohanessian A. In vitro culture of Drosophila melanogaster embryonic cells. In Vitro. 1970 Nov-Dec;6(3):162–172. doi: 10.1007/BF02617759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foe V. E. Mitotic domains reveal early commitment of cells in Drosophila embryos. Development. 1989 Sep;107(1):1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han K., Levine M. S., Manley J. L. Synergistic activation and repression of transcription by Drosophila homeobox proteins. Cell. 1989 Feb 24;56(4):573–583. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90580-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein U., England B., Tjian R. Characterization of Drosophila transcription factors that activate the tandem promoters of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):965–977. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hiromi Y., Kuroiwa A., Gehring W. J. Control elements of the Drosophila segmentation gene fushi tarazu. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):603–613. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90232-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoey T., Levine M. Divergent homeo box proteins recognize similar DNA sequences in Drosophila. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):858–861. doi: 10.1038/332858a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hultmark D., Klemenz R., Gehring W. J. Translational and transcriptional control elements in the untranslated leader of the heat-shock gene hsp22. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):429–438. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90464-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaskulski D., deRiel J. K., Mercer W. E., Calabretta B., Baserga R. Inhibition of cellular proliferation by antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to PCNA cyclin. Science. 1988 Jun 10;240(4858):1544–1546. doi: 10.1126/science.2897717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes J. B., O'Farrell P. H. Activation and repression of transcription by homoeodomain-containing proteins that bind a common site. Nature. 1988 Dec 22;336(6201):744–749. doi: 10.1038/336744a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson W. A., Hirsh J. Binding of a Drosophila POU-domain protein to a sequence element regulating gene expression in specific dopaminergic neurons. Nature. 1990 Feb 1;343(6257):467–470. doi: 10.1038/343467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klemenz R., Weber U., Gehring W. J. The white gene as a marker in a new P-element vector for gene transfer in Drosophila. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 May 26;15(10):3947–3959. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.10.3947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klingensmith J., Noll E., Perrimon N. The segment polarity phenotype of Drosophila involves differential tendencies toward transformation and cell death. Dev Biol. 1989 Jul;134(1):130–145. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(89)90084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis R. A., Wakimoto B. T., Denell R. E., Kaufman T. C. Genetic Analysis of the Antennapedia Gene Complex (Ant-C) and Adjacent Chromosomal Regions of DROSOPHILA MELANOGASTER. II. Polytene Chromosome Segments 84A-84B1,2. Genetics. 1980 Jun;95(2):383–397. doi: 10.1093/genetics/95.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews M. B., Bernstein R. M., Franza B. R., Jr, Garrels J. I. Identity of the proliferating cell nuclear antigen and cyclin. Nature. 1984 May 24;309(5966):374–376. doi: 10.1038/309374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Moriuchi T., Koji T., Nakane P. K. Molecular cloning of cDNA coding for rat proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)/cyclin. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):637–642. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04802.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyachi K., Fritzler M. J., Tan E. M. Autoantibody to a nuclear antigen in proliferating cells. J Immunol. 1978 Dec;121(6):2228–2234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohun T., Garrett N., Treisman R. Xenopus cytoskeletal actin and human c-fos gene promoters share a conserved protein-binding site. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):667–673. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04806.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller M., Affolter M., Leupin W., Otting G., Wüthrich K., Gehring W. J. Isolation and sequence-specific DNA binding of the Antennapedia homeodomain. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4299–4304. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03328.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng L., Prelich G., Anderson C. W., Stillman B., Fisher P. A. Drosophila proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Structural and functional homology with its mammalian counterpart. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jul 15;265(20):11948–11954. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perkins K. K., Dailey G. M., Tjian R. Novel Jun- and Fos-related proteins in Drosophila are functionally homologous to enhancer factor AP-1. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4265–4273. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03324.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Kostura M., Marshak D. R., Mathews M. B., Stillman B. The cell-cycle regulated proliferating cell nuclear antigen is required for SV40 DNA replication in vitro. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):471–475. doi: 10.1038/326471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Stillman B. Coordinated leading and lagging strand synthesis during SV40 DNA replication in vitro requires PCNA. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):117–126. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90493-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prelich G., Tan C. K., Kostura M., Mathews M. B., So A. G., Downey K. M., Stillman B. Functional identity of proliferating cell nuclear antigen and a DNA polymerase-delta auxiliary protein. Nature. 1987 Apr 2;326(6112):517–520. doi: 10.1038/326517a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson H. M., Preston C. R., Phillis R. W., Johnson-Schlitz D. M., Benz W. K., Engels W. R. A stable genomic source of P element transposase in Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics. 1988 Mar;118(3):461–470. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.3.461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuka I., Daidoji H., Matsuoka M., Kadowaki K., Takasaki Y., Nakane P. K., Moriuchi T. Gene for proliferating-cell nuclear antigen (DNA polymerase delta auxiliary protein) is present in both mammalian and higher plant genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3189–3193. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takasaki Y., Fishwild D., Tan E. M. Characterization of proliferating cell nuclear antigen recognized by autoantibodies in lupus sera. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):981–992. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakimoto B. T., Turner F. R., Kaufman T. C. Defects in embryogenesis in mutants associated with the antennapedia gene complex of Drosophila melanogaster. Dev Biol. 1984 Mar;102(1):147–172. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Hayashi Y., Hirose F., Matsuoka S., Moriuchi T., Shiroishi T., Moriwaki K., Matsukage A. Molecular cloning and structural analysis of mouse gene and pseudogenes for proliferating cell nuclear antigen. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 May 11;19(9):2403–2410. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.9.2403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Hayashi Y., Matsukage A. Mouse DNA polymerase beta gene promoter: fine mapping and involvement of Sp1-like mouse transcription factor in its function. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):8773–8787. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.8773. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Nishida Y., Moriuchi T., Hirose F., Hui C. C., Suzuki Y., Matsukage A. Drosophila proliferating cell nuclear antigen (cyclin) gene: structure, expression during development, and specific binding of homeodomain proteins to its 5'-flanking region. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):872–879. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]