Abstract
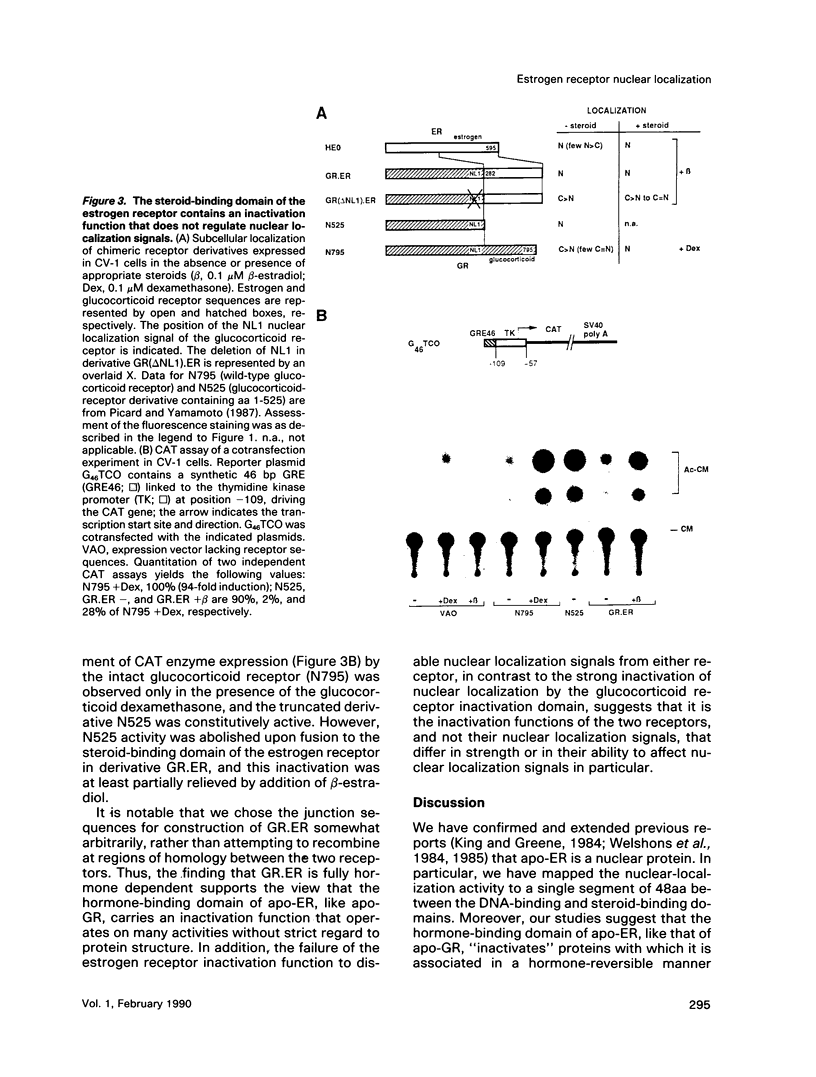
The glucocorticoid receptor accumulates in nuclei only in the presence of bound hormone, whereas the estrogen receptor has been reported to be constitutively nuclear. To investigate this distinction, we compared the nuclear localization domains of the two receptors and the capacity of their respective hormone-binding regions to regulate nuclear localization activity. As with the glucocorticoid receptor, we showed that the human estrogen receptor contained a nuclear localization signal between the DNA-binding and hormone-binding regions (amino acids 256-303); however, in contrast to the glucocorticoid receptor, the estrogen receptor lacked a second nuclear localization domain within the hormone-binding region. Moreover, the hormone-binding domain of the unliganded estrogen receptor failed to regulate nuclear localization signals, although it efficiently regulated other receptor functions. We conclude that the two receptors employ a common mechanism for signal transduction involving a novel "inactivation" function, but that they differ in their control of nuclear localization. Thus, despite the strong relatedness of the estrogen and glucocorticoid receptors in structure and activity, certain differences in their properties could have important functional implications.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagchi M. K., Elliston J. F., Tsai S. Y., Edwards D. P., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Steroid hormone-dependent interaction of human progesterone receptor with its target enhancer element. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Dec;2(12):1221–1229. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-12-1221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berthois Y., Katzenellenbogen J. A., Katzenellenbogen B. S. Phenol red in tissue culture media is a weak estrogen: implications concerning the study of estrogen-responsive cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2496–2500. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M. Protein migration into nuclei. I. Frog oocyte nuclei in vivo accumulate microinjected histones, allow entry to small proteins, and exclude large proteins. J Cell Biol. 1975 Feb;64(2):421–430. doi: 10.1083/jcb.64.2.421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bresnick E. H., Dalman F. C., Sanchez E. R., Pratt W. B. Evidence that the 90-kDa heat shock protein is necessary for the steroid binding conformation of the L cell glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 25;264(9):4992–4997. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Catelli M. G., Binart N., Jung-Testas I., Renoir J. M., Baulieu E. E., Feramisco J. R., Welch W. J. The common 90-kd protein component of non-transformed '8S' steroid receptors is a heat-shock protein. EMBO J. 1985 Dec 1;4(12):3131–3135. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb04055.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damm K., Thompson C. C., Evans R. M. Protein encoded by v-erbA functions as a thyroid-hormone receptor antagonist. Nature. 1989 Jun 22;339(6226):593–597. doi: 10.1038/339593a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denis M., Gustafsson J. A., Wikström A. C. Interaction of the Mr = 90,000 heat shock protein with the steroid-binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1988 Dec 5;263(34):18520–18523. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilers M., Picard D., Yamamoto K. R., Bishop J. M. Chimaeras of myc oncoprotein and steroid receptors cause hormone-dependent transformation of cells. Nature. 1989 Jul 6;340(6228):66–68. doi: 10.1038/340066a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehring U., Arndt H. Heteromeric nature of glucocorticoid receptors. FEBS Lett. 1985 Jan 1;179(1):138–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Picard D. Steroid receptors. How to be both a receptor and a transcription factor. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 Oct 1;38(19):3135–3143. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90605-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godowski P. J., Rusconi S., Miesfeld R., Yamamoto K. R. Glucocorticoid receptor mutants that are constitutive activators of transcriptional enhancement. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):365–368. doi: 10.1038/325365a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. Nuclear receptors enhance our understanding of transcription regulation. Trends Genet. 1988 Nov;4(11):309–314. doi: 10.1016/0168-9525(88)90108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Walter P., Kumar V., Krust A., Bornert J. M., Argos P., Chambon P. Human oestrogen receptor cDNA: sequence, expression and homology to v-erb-A. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):134–139. doi: 10.1038/320134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene G. L., Gilna P., Waterfield M., Baker A., Hort Y., Shine J. Sequence and expression of human estrogen receptor complementary DNA. Science. 1986 Mar 7;231(4742):1150–1154. doi: 10.1126/science.3753802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guiochon-Mantel A., Loosfelt H., Lescop P., Sar S., Atger M., Perrot-Applanat M., Milgrom E. Mechanisms of nuclear localization of the progesterone receptor: evidence for interaction between monomers. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1147–1154. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90052-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howard K. J., Distelhorst C. W. Evidence for intracellular association of the glucocorticoid receptor with the 90-kDa heat shock protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 5;263(7):3474–3481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King W. J., Greene G. L. Monoclonal antibodies localize oestrogen receptor in the nuclei of target cells. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):745–747. doi: 10.1038/307745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koike S., Sakai M., Muramatsu M. Molecular cloning and characterization of rat estrogen receptor cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Mar 25;15(6):2499–2513. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.6.2499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krust A., Green S., Argos P., Kumar V., Walter P., Bornert J. M., Chambon P. The chicken oestrogen receptor sequence: homology with v-erbA and the human oestrogen and glucocorticoid receptors. EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):891–897. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04300.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Chambon P. The estrogen receptor binds tightly to its responsive element as a ligand-induced homodimer. Cell. 1988 Oct 7;55(1):145–156. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Green S., Stack G., Berry M., Jin J. R., Chambon P. Functional domains of the human estrogen receptor. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):941–951. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90581-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar V., Green S., Staub A., Chambon P. Localisation of the oestradiol-binding and putative DNA-binding domains of the human oestrogen receptor. EMBO J. 1986 Sep;5(9):2231–2236. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04489.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lang I., Scholz M., Peters R. Molecular mobility and nucleocytoplasmic flux in hepatoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1183–1190. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Craig E. A. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631–677. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson M., Silver P. Context affects nuclear protein localization in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Feb;9(2):384–389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.2.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okret S., Wikström A. C., Wrange O., Andersson B., Gustafsson J. A. Monoclonal antibodies against the rat liver glucocorticoid receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1609–1613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paine P. L., Moore L. C., Horowitz S. B. Nuclear envelope permeability. Nature. 1975 Mar 13;254(5496):109–114. doi: 10.1038/254109a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdew G. H. Association of the Ah receptor with the 90-kDa heat shock protein. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 25;263(27):13802–13805. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrot-Applanat M., Groyer-Picard M. T., Logeat F., Milgrom E. Ultrastructural localization of the progesterone receptor by an immunogold method: effect of hormone administration. J Cell Biol. 1986 Apr;102(4):1191–1199. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.4.1191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perrot-Applanat M., Logeat F., Groyer-Picard M. T., Milgrom E. Immunocytochemical study of mammalian progesterone receptor using monoclonal antibodies. Endocrinology. 1985 Apr;116(4):1473–1484. doi: 10.1210/endo-116-4-1473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Salser S. J., Yamamoto K. R. A movable and regulable inactivation function within the steroid binding domain of the glucocorticoid receptor. Cell. 1988 Sep 23;54(7):1073–1080. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90122-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard D., Yamamoto K. R. Two signals mediate hormone-dependent nuclear localization of the glucocorticoid receptor. EMBO J. 1987 Nov;6(11):3333–3340. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02654.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pratt W. B., Jolly D. J., Pratt D. V., Hollenberg S. M., Giguere V., Cadepond F. M., Schweizer-Groyer G., Catelli M. G., Evans R. M., Baulieu E. E. A region in the steroid binding domain determines formation of the non-DNA-binding, 9 S glucocorticoid receptor complex. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jan 5;263(1):267–273. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rafestin-Oblin M. E., Couette B., Radanyi C., Lombes M., Baulieu E. E. Mineralocorticosteroid receptor of the chick intestine. Oligomeric structure and transformation. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 5;264(16):9304–9309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts B. L., Richardson W. D., Smith A. E. The effect of protein context on nuclear location signal function. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):465–475. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90500-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothman J. E. Polypeptide chain binding proteins: catalysts of protein folding and related processes in cells. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):591–601. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90005-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rüther U., Müller-Hill B. Easy identification of cDNA clones. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1791–1794. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01659.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai D. D., Helms S., Carlstedt-Duke J., Gustafsson J. A., Rottman F. M., Yamamoto K. R. Hormone-mediated repression: a negative glucocorticoid response element from the bovine prolactin gene. Genes Dev. 1988 Sep;2(9):1144–1154. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.9.1144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez E. R., Meshinchi S., Tienrungroj W., Schlesinger M. J., Toft D. O., Pratt W. B. Relationship of the 90-kDa murine heat shock protein to the untransformed and transformed states of the L cell glucocorticoid receptor. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):6986–6991. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez E. R., Toft D. O., Schlesinger M. J., Pratt W. B. Evidence that the 90-kDa phosphoprotein associated with the untransformed L-cell glucocorticoid receptor is a murine heat shock protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 15;260(23):12398–12401. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh S., Yonemoto W., Brugge J., Bauer V. J., Riehl R. M., Sullivan W. P., Toft D. O. A 90,000-dalton binding protein common to both steroid receptors and the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein, pp60v-src. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 15;260(26):14292–14296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver P., Goodson H. Nuclear protein transport. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. 1989;24(4):419–435. doi: 10.3109/10409238909082557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szego C. M. The lysosome as a mediator of hormone action. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1974;30(0):171–233. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-571130-2.50009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tora L., Mullick A., Metzger D., Ponglikitmongkol M., Park I., Chambon P. The cloned human oestrogen receptor contains a mutation which alters its hormone binding properties. EMBO J. 1989 Jul;8(7):1981–1986. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03604.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welshons W. V., Krummel B. M., Gorski J. Nuclear localization of unoccupied receptors for glucocorticoids, estrogens, and progesterone in GH3 cells. Endocrinology. 1985 Nov;117(5):2140–2147. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-5-2140. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welshons W. V., Lieberman M. E., Gorski J. Nuclear localization of unoccupied oestrogen receptors. Nature. 1984 Feb 23;307(5953):747–749. doi: 10.1038/307747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White R., Lees J. A., Needham M., Ham J., Parker M. Structural organization and expression of the mouse estrogen receptor. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Oct;1(10):735–744. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-10-735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. R., Godowski P. J., Picard D. Ligand-regulated nonspecific inactivation of receptor function: a versatile mechanism for signal transduction. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):803–811. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]