Abstract
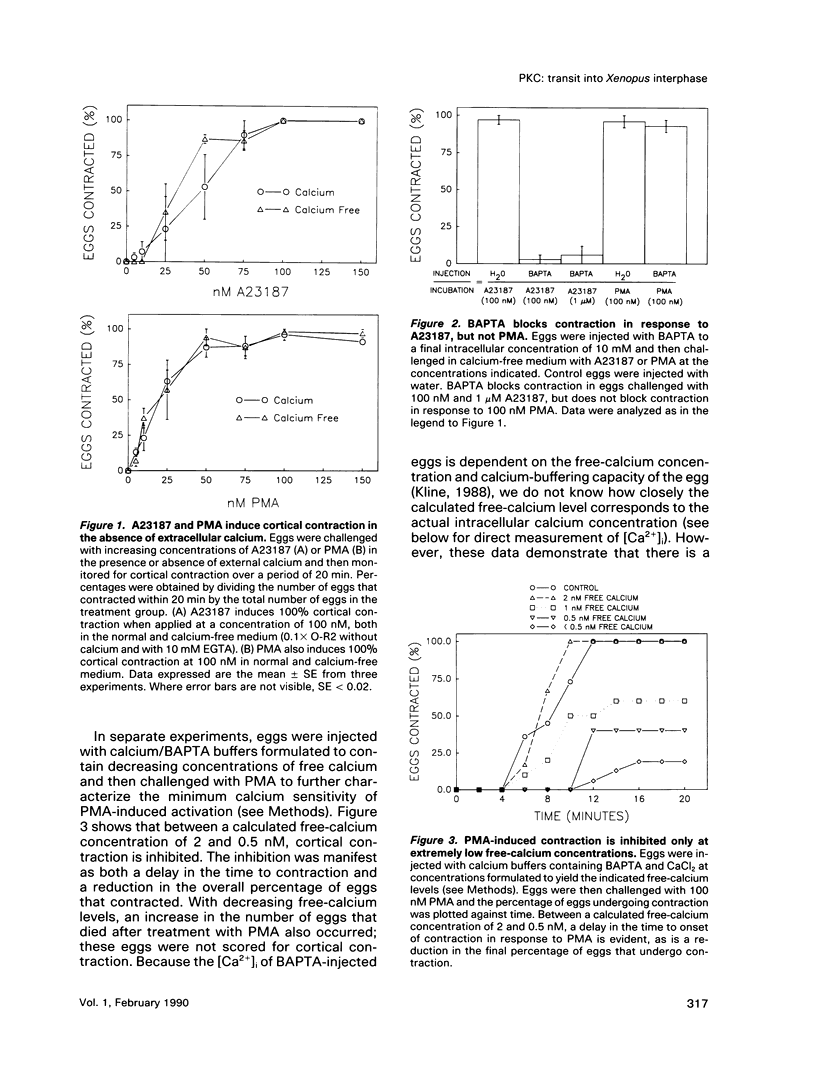
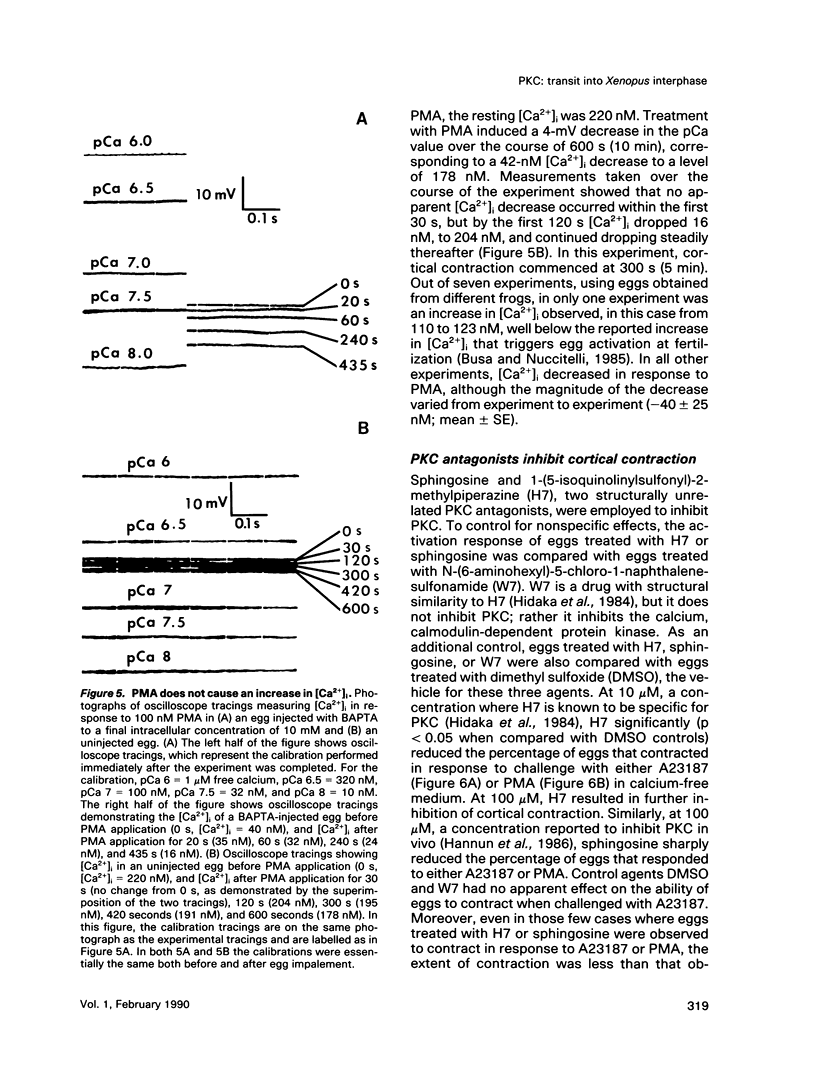
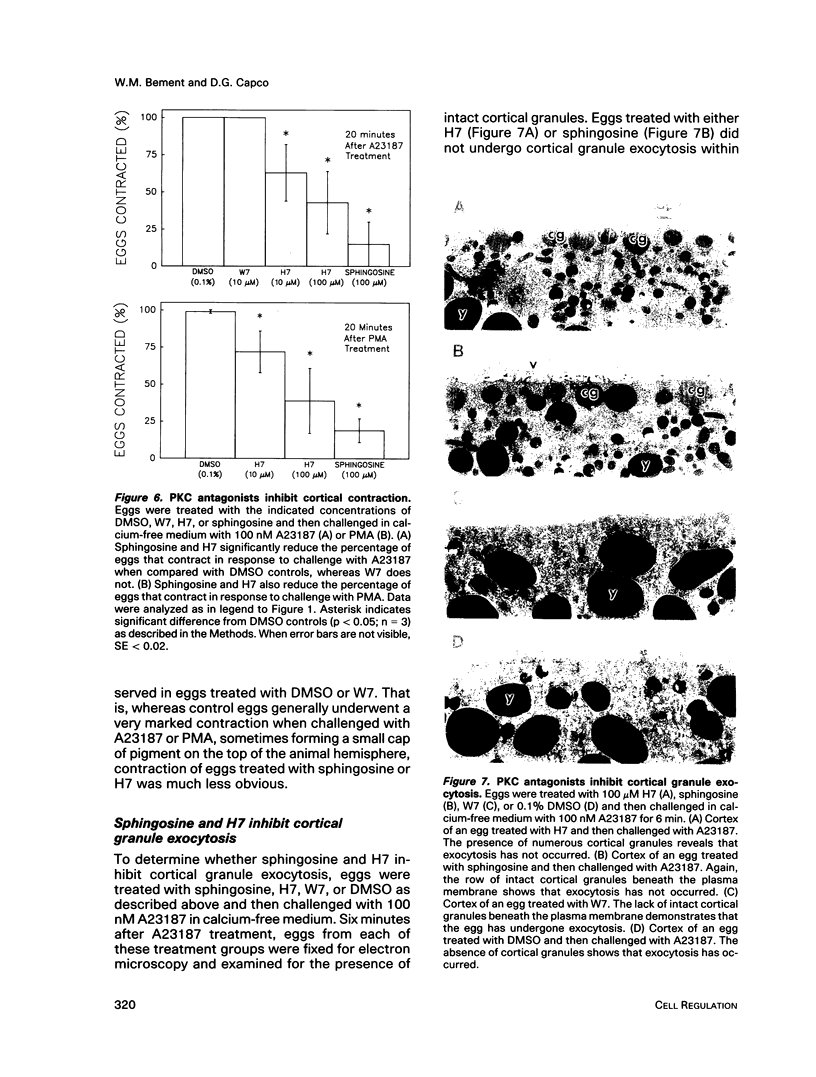
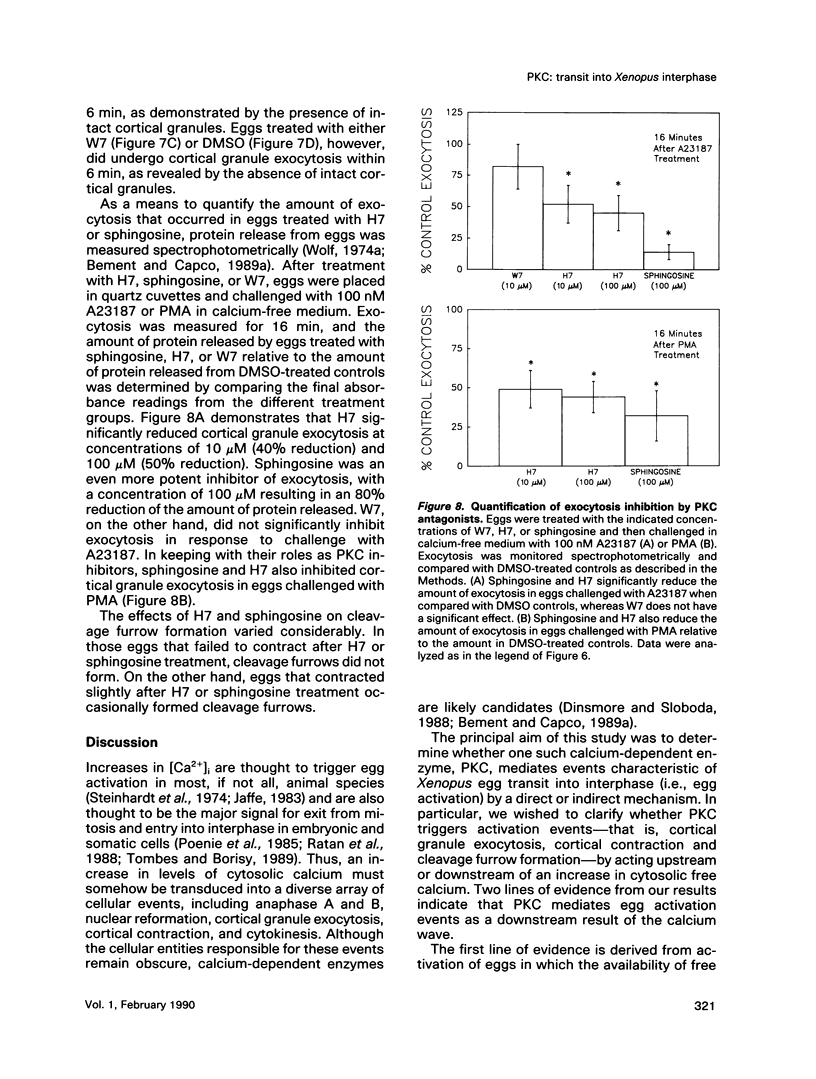
Transit into interphase of the first mitotic cell cycle in amphibian eggs is a process referred to as activation and is accompanied by an increase in intracellular free calcium [( Ca2+]i), which may be transduced into cytoplasmic events characteristic of interphase by protein kinase C (PKC). To investigate the respective roles of [Ca2+]i and PKC in Xenopus laevis egg activation, the calcium signal was blocked by microinjection of the calcium chelator BAPTA, or the activity of PKC was blocked by PKC inhibitors sphingosine or H7. Eggs were then challenged for activation by treatment with either calcium ionophore A23187 or the PKC activator PMA. BAPTA prevented cortical contraction, cortical granule exocytosis, and cleavage furrow formation in eggs challenged with A23187 but not with PMA. In contrast, sphingosine and H7 inhibited cortical granule exocytosis, cortical contraction, and cleavage furrow formation in eggs challenged with either A23187 or PMA. Measurement of egg [Ca2+]i with calcium-sensitive electrodes demonstrated that PMA treatment does not increase egg [Ca2+]i in BAPTA-injected eggs. Further, PMA does not increase [Ca2+]i in eggs that have not been injected with BAPTA. These results show that PKC acts downstream of the [Ca2+]i increase to induce cytoplasmic events of the first Xenopus mitotic cell cycle.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albert P. R., Wolfson G., Tashjian A. H., Jr Diacylglycerol increases cytosolic free Ca2+ concentration in rat pituitary cells. Relationship to thyrotropin-releasing hormone action. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6577–6581. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol: two interacting second messengers. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:159–193. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.001111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busa W. B., Ferguson J. E., Joseph S. K., Williamson J. R., Nuccitelli R. Activation of frog (Xenopus laevis) eggs by inositol trisphosphate. I. Characterization of Ca2+ release from intracellular stores. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):677–682. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busa W. B. Measuring intracellular free Ca2+ with single- and double- barreled ion-specific microelectrodes. Prog Clin Biol Res. 1986;210:57–69. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Busa W. B., Nuccitelli R. An elevated free cytosolic Ca2+ wave follows fertilization in eggs of the frog, Xenopus laevis. J Cell Biol. 1985 Apr;100(4):1325–1329. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.4.1325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charbonneau M., Grey R. D. The onset of activation responsiveness during maturation coincides with the formation of the cortical endoplasmic reticulum in oocytes of Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1984 Mar;102(1):90–97. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90177-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheung W. Y. Calmodulin plays a pivotal role in cellular regulation. Science. 1980 Jan 4;207(4426):19–27. doi: 10.1126/science.6243188. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christensen K., Sauterer R., Merriam R. W. Role of soluble myosin in cortical contractions of Xenopus eggs. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):150–151. doi: 10.1038/310150a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciapa B., Crossley I., De Renzis G. Structural modifications induced by TPA (12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate) in sea urchin eggs. Dev Biol. 1988 Jul;128(1):142–149. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90276-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciapa B., Whitaker M. Two phases of inositol polyphosphate and diacylglycerol production at fertilisation. FEBS Lett. 1986 Jan 20;195(1-2):347–351. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)80191-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colonna R., Tatone C., Malgaroli A., Eusebi F., Mangia F. Effects of protein kinase C stimulation and free Ca2+ rise in mammalian egg activation. Gamete Res. 1989 Oct;24(2):171–183. doi: 10.1002/mrd.1120240205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coussens L., Parker P. J., Rhee L., Yang-Feng T. L., Chen E., Waterfield M. D., Francke U., Ullrich A. Multiple, distinct forms of bovine and human protein kinase C suggest diversity in cellular signaling pathways. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):859–866. doi: 10.1126/science.3755548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Phorbol ester and sperm activate mouse oocytes by inducing sustained oscillations in cell Ca2+. Nature. 1985 Aug 8;316(6028):541–542. doi: 10.1038/316541a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuthbertson K. S., Whittingham D. G., Cobbold P. H. Free Ca2+ increases in exponential phases during mouse oocyte activation. Nature. 1981 Dec 24;294(5843):754–757. doi: 10.1038/294754a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeRiemer S. A., Strong J. A., Albert K. A., Greengard P., Kaczmarek L. K. Enhancement of calcium current in Aplysia neurones by phorbol ester and protein kinase C. Nature. 1985 Jan 24;313(6000):313–316. doi: 10.1038/313313a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Virgilio F., Lew D. P., Pozzan T. Protein kinase C activation of physiological processes in human neutrophils at vanishingly small cytosolic Ca2+ levels. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):691–693. doi: 10.1038/310691a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinsmore J. H., Sloboda R. D. Calcium and calmodulin-dependent phosphorylation of a 62 kd protein induces microtubule depolymerization in sea urchin mitotic apparatuses. Cell. 1988 Jun 3;53(5):769–780. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90094-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo Y., Schultz R. M., Kopf G. S. Effects of phorbol esters and a diacylglycerol on mouse eggs: inhibition of fertilization and modification of the zona pellucida. Dev Biol. 1987 Jan;119(1):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90221-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilkey J. C., Jaffe L. F., Ridgway E. B., Reynolds G. T. A free calcium wave traverses the activating egg of the medaka, Oryzias latipes. J Cell Biol. 1978 Feb;76(2):448–466. doi: 10.1083/jcb.76.2.448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gingell D. Contractile responses at the surface of an amphibian egg. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1970 Jun;23(3):583–609. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grey R. D., Wolf D. P., Hedrick J. L. Formation and structure of the fertilization envelope in Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1974 Jan;36(1):44–61. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90189-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler P. K. Calcium restriction prolongs metaphase in dividing Tradescantia stamen hair cells. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1363–1368. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepler P. K., Callaham D. A. Free calcium increases during anaphase in stamen hair cells of Tradescantia. J Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;105(5):2137–2143. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.5.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirota K., Hirota T., Aguilera G., Catt K. J. Hormone-induced redistribution of calcium-activated phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in pituitary gonadotrophs. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3243–3246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollinger T. G., Schuetz A. W. "Cleavage" and cortical granule breakdown in Rana pipiens oocytes induced by direct microinjection of calcium. J Cell Biol. 1976 Nov;71(2):395–401. doi: 10.1083/jcb.71.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Housey G. M., O'Brian C. A., Johnson M. D., Kirschmeier P., Weinstein I. B. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding protein kinase C: evidence for a protein kinase C-related gene family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(4):1065–1069. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.4.1065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito T., Tanaka T., Yoshida T., Onoda K., Ohta H., Hagiwara M., Itoh Y., Ogura M., Saito H., Hidaka H. Immunocytochemical evidence for translocation of protein kinase C in human megakaryoblastic leukemic cells: synergistic effects of Ca2+ and activators of protein kinase C on the plasma membrane association. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):929–937. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izant J. G. The role of calcium ions during mitosis. Calcium participates in the anaphase trigger. Chromosoma. 1983;88(1):1–10. doi: 10.1007/BF00329497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe L. F. Sources of calcium in egg activation: a review and hypothesis. Dev Biol. 1983 Oct;99(2):265–276. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(83)90276-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karsenti E., Newport J., Hubble R., Kirschner M. Interconversion of metaphase and interphase microtubule arrays, as studied by the injection of centrosomes and nuclei into Xenopus eggs. J Cell Biol. 1984 May;98(5):1730–1745. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.5.1730. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Kishimoto A., Nishizuka Y. The protein kinase C family: heterogeneity and its implications. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:31–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kline D. Calcium-dependent events at fertilization of the frog egg: injection of a calcium buffer blocks ion channel opening, exocytosis, and formation of pronuclei. Dev Biol. 1988 Apr;126(2):346–361. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90145-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kubota H. Y., Yoshimoto Y., Yoneda M., Hiramoto Y. Free calcium wave upon activation in Xenopus eggs. Dev Biol. 1987 Jan;119(1):129–136. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90214-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larsen P. M., Chen T. L., Wolniak S. M. Quin2-induced metaphase arrest in stamen hair cells can be reversed by 1,2-dioctanoylglycerol but not by 1,3-dioctanoylglycerol. Eur J Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;48(2):212–219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach K. L., Powers E. A., Ruff V. A., Jaken S., Kaufmann S. Type 3 protein kinase C localization to the nuclear envelope of phorbol ester-treated NIH 3T3 cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):685–695. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.685. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lohka M. J., Masui Y. Effects of Ca2+ ions on the formation of metaphase chromosomes and sperm pronuclei in cell-free preparations from unactivated Rana pipiens eggs. Dev Biol. 1984 Jun;103(2):434–442. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90331-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Löffelholz K. Receptor regulation of choline phospholipid hydrolysis. A novel source of diacylglycerol and phosphatidic acid. Biochem Pharmacol. 1989 May 15;38(10):1543–1549. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(89)90299-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki S., Hashimoto N., Yoshimoto Y., Kishimoto T., Igusa Y., Hiramoto Y. Temporal and spatial dynamics of the periodic increase in intracellular free calcium at fertilization of golden hamster eggs. Dev Biol. 1986 Nov;118(1):259–267. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(86)90093-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuccitelli R., Kline D., Busa W. B., Talevi R., Campanella C. A highly localized activation current yet widespread intracellular calcium increase in the egg of the frog, Discoglossus pictus. Dev Biol. 1988 Nov;130(1):120–132. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(88)90419-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuccitelli R. The wave of activation current in the egg of the medaka fish. Dev Biol. 1987 Aug;122(2):522–534. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90316-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pace C. S. Influence of a tumor-promoting phorbol ester on the electrical response of B-cells to glucose and glyburide. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Sep;26(2):267–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Picard A., Giraud F., Le Bouffant F., Sladeczek F., Le Peuch C., Dorée M. Inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate microinjection triggers activation, but not meiotic maturation in amphibian and starfish oocytes. FEBS Lett. 1985 Mar 25;182(2):446–450. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80351-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenie M., Alderton J., Steinhardt R., Tsien R. Calcium rises abruptly and briefly throughout the cell at the onset of anaphase. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):886–889. doi: 10.1126/science.3755550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenie M., Alderton J., Tsien R. Y., Steinhardt R. A. Changes of free calcium levels with stages of the cell division cycle. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):147–149. doi: 10.1038/315147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratan R. R., Maxfield F. R., Shelanski M. L. Long-lasting and rapid calcium changes during mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1988 Sep;107(3):993–999. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.3.993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratan R. R., Shelanski M. L., Maxfield F. R. Transition from metaphase to anaphase is accompanied by local changes in cytoplasmic free calcium in Pt K2 kidney epithelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5136–5140. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5136. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroeder T. E., Strickland D. L. Ionophore A23187, calcium and contractility in frog eggs. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Jan;83(1):139–142. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90696-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. S., Burgart L. J. 1,2-Diacylglycerols mimic phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate activation of the sea urchin egg. J Cell Physiol. 1986 May;127(2):330–340. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041270222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen S. S. Na+-H+ antiport during fertilization of the sea urchin egg is blocked by W-7 but is insensitive to K252a and H-7. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Jun 30;161(3):1100–1108. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)91356-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. B. Nuclear envelope breakdown and mitosis in sand dollar embryos is inhibited by microinjection of calcium buffers in a calcium-reversible fashion, and by antagonists of intracellular Ca2+ channels. Dev Biol. 1989 Jan;131(1):11–26. doi: 10.1016/s0012-1606(89)80034-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhardt R. A., Epel D., Carroll E. J., Jr, Yanagimachi R. Is calcium ionophore a universal activator for unfertilised eggs? Nature. 1974 Nov 1;252(5478):41–43. doi: 10.1038/252041a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinhardt R., Zucker R., Schatten G. Intracellular calcium release at fertilization in the sea urchin egg. Dev Biol. 1977 Jul 1;58(1):185–196. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90084-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swann K., Whitaker M. The part played by inositol trisphosphate and calcium in the propagation of the fertilization wave in sea urchin eggs. J Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;103(6 Pt 1):2333–2342. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.6.2333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tombes R. M., Borisy G. G. Intracellular free calcium and mitosis in mammalian cells: anaphase onset is calcium modulated, but is not triggered by a brief transient. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):627–636. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.627. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. A., Jared D. W., Dumont J. N., Sega M. W. Protein incorporation by isolated amphibian oocytes. 3. Optimum incubation conditions. J Exp Zool. 1973 Jun;184(3):321–333. doi: 10.1002/jez.1401840305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf D. P. The cortical granule reaction in living eggs of the toad, Xenopus laevis. Dev Biol. 1974 Jan;36(1):62–71. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(74)90190-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolniak S. M., Bart K. M. The buffering of calcium with quin2 reversibly forestalls anaphase onset in stamen hair cells of Tradescantia. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;39(1):33–40. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]