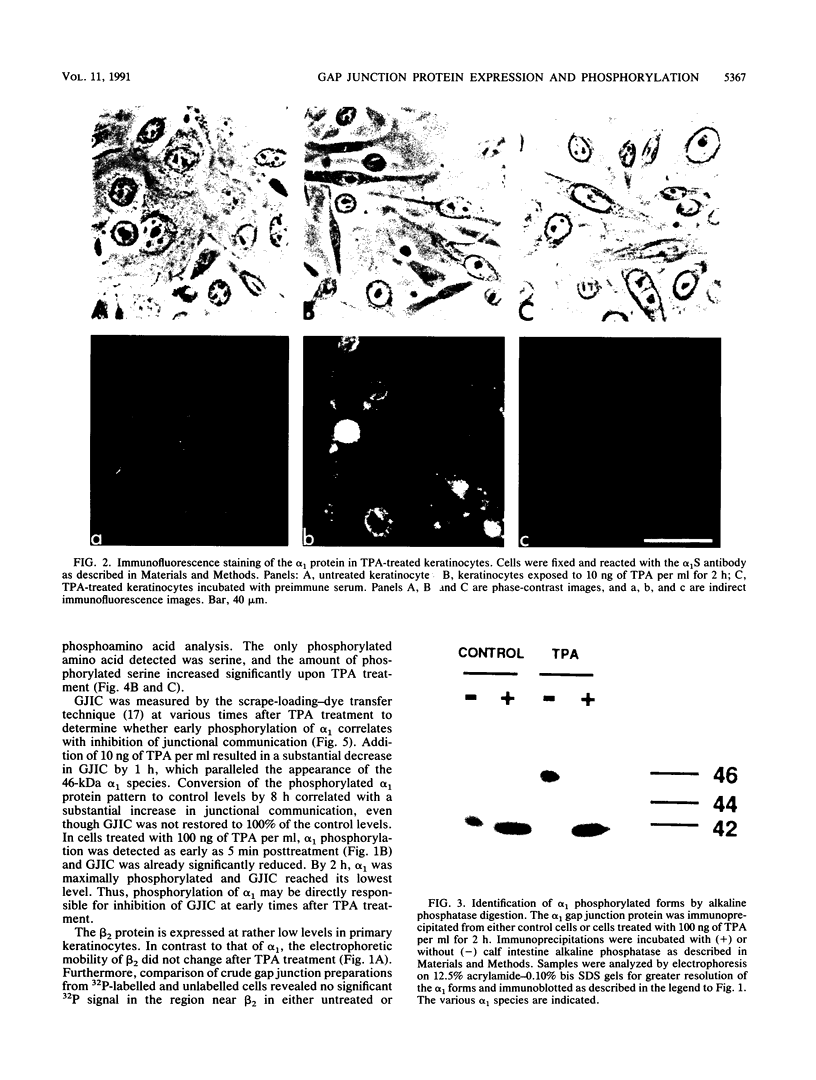
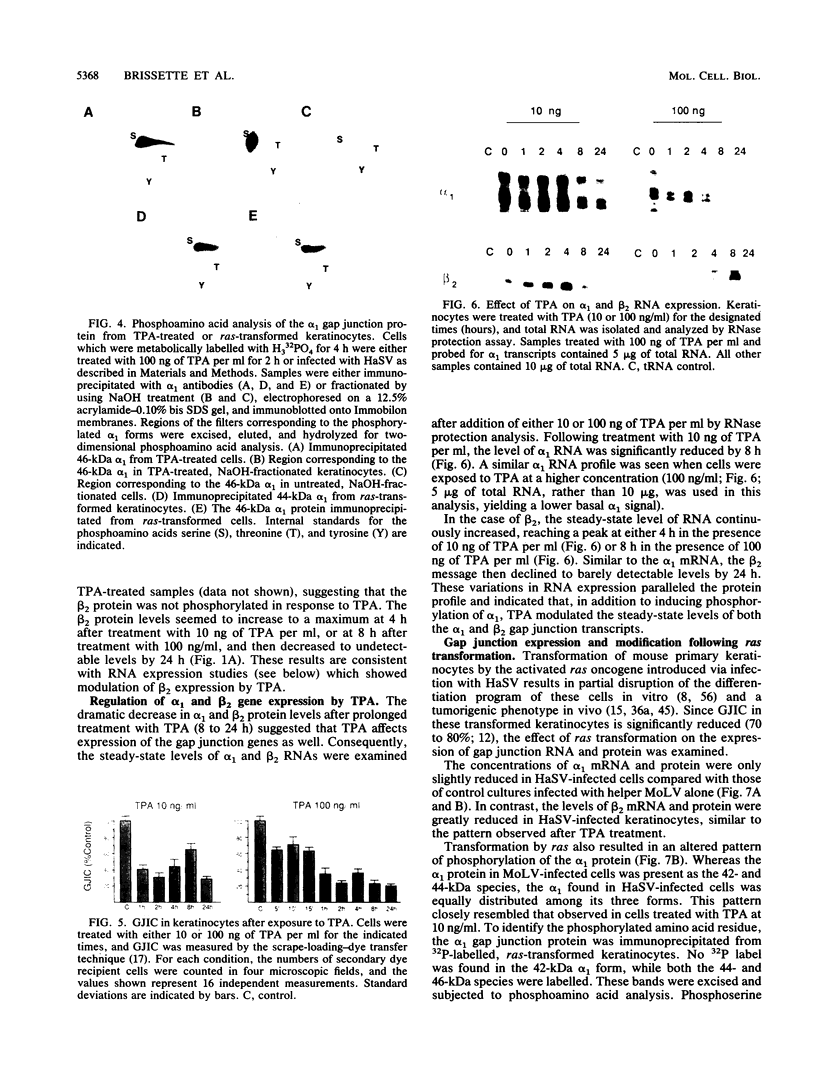
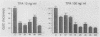Abstract
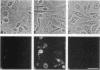
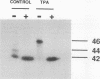
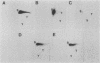
Gap junctional intercellular communication is inhibited in response to tumor promoters and oncogene transformation, suggesting that loss of this function is an important step in tumor formation. To elucidate the molecular mechanisms responsible for this inhibition, we examined the expression of gap junction proteins and mRNA in mouse primary keratinocytes after treatment with the tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) and/or ras transformation. During normal cell growth, keratinocytes expression the alpha 1 (connexin 43) and beta 2 (connexin 26) proteins. Within 5 min of TPA treatment, the alpha 1 protein became rapidly phosphorylated on serine residues and its expression was dramatically reduced by 24 h. The beta 2 protein, after an initial increase in expression, was also significantly reduced 24 h after treatment with TPA. ras transformation caused changes similar to those induced by TPA. The alpha 1 protein underwent an increase in serine phosphorylation, although its expression declined only slightly, while beta 2 expression was greatly reduced. The effects of TPA and ras on alpha 1 expression were additive; treatment of ras-transformed cells with TPA resulted in increased alpha 1 phosphorylation, with greatly decreased protein levels, much lower than those generated by either agent alone. These data provide a likely explanation for the similar and synergistic inhibition of gap junctional intercellular communication by phorbol esters and ras.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azarnia R., Reddy S., Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D., Loewenstein W. R. The cellular src gene product regulates junctional cell-to-cell communication. Science. 1988 Jan 22;239(4838):398–401. doi: 10.1126/science.2447651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett M. V., Goodenough D. A. Gap junctions, electrotonic coupling, and intercellular communication. Neurosci Res Program Bull. 1978 Sep;16(3):1–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beyer E. C., Paul D. L., Goodenough D. A. Connexin43: a protein from rat heart homologous to a gap junction protein from liver. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2621–2629. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignami M., Rosa S., Falcone G., Tató F., Katoh F., Yamasaki H. Specific viral oncogenes cause differential effects on cell-to-cell communication, relevant to the suppression of the transformed phenotype by normal cells. Mol Carcinog. 1988;1(1):67–75. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940010113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K., Quintanilla M., Ramsden M., Kerr I. B., Young S., Balmain A. v-ras genes from Harvey and BALB murine sarcoma viruses can act as initiators of two-stage mouse skin carcinogenesis. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):447–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90665-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. C., Trosko J. E., Kung H. J., Bombick D., Matsumura F. Potential role of the src gene product in inhibition of gap-junctional communication in NIH/3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5360–5364. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5360. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng C., Kilkenny A. E., Roop D., Yuspa S. H. The v-ras oncogene inhibits the expression of differentiation markers and facilitates expression of cytokeratins 8 and 18 in mouse keratinocytes. Mol Carcinog. 1990;3(6):363–373. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940030608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Sacchi N. Single-step method of RNA isolation by acid guanidinium thiocyanate-phenol-chloroform extraction. Anal Biochem. 1987 Apr;162(1):156–159. doi: 10.1006/abio.1987.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Diverse mitogenic agents induce the phosphorylation of two related 42,000-dalton proteins on tyrosine in quiescent chick cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):30–37. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crow D. S., Beyer E. C., Paul D. L., Kobe S. S., Lau A. F. Phosphorylation of connexin43 gap junction protein in uninfected and Rous sarcoma virus-transformed mammalian fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1754–1763. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1754. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotto G. P., Gilman M. Z., Maruyama M., Weinberg R. A. c-myc and c-fos expression in differentiating mouse primary keratinocytes. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2853–2857. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04579.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotto G. P., Parada L. F., Weinberg R. A. Specific growth response of ras-transformed embryo fibroblasts to tumour promoters. Nature. 1985 Dec 5;318(6045):472–475. doi: 10.1038/318472a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotto G. P., Weinberg R. A., Ariza A. Malignant transformation of mouse primary keratinocytes by Harvey sarcoma virus and its modulation by surrounding normal cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6389–6393. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotto G. P., el-Fouly M. H., Nelson C., Trosko J. E. Similar and synergistic inhibition of gap-junctional communication by ras transformation and tumor promoter treatment of mouse primary keratinocytes. Oncogene. 1989 May;4(5):637–641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filson A. J., Azarnia R., Beyer E. C., Loewenstein W. R., Brugge J. S. Tyrosine phosphorylation of a gap junction protein correlates with inhibition of cell-to-cell communication. Cell Growth Differ. 1990 Dec;1(12):661–668. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Filvaroff E., Stern D. F., Dotto G. P. Tyrosine phosphorylation is an early and specific event involved in primary keratinocyte differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1164–1173. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fishman G. I., Spray D. C., Leinwand L. A. Molecular characterization and functional expression of the human cardiac gap junction channel. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):589–598. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.589. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilula N. B., Reeves O. R., Steinbach A. Metabolic coupling, ionic coupling and cell contacts. Nature. 1972 Feb 4;235(5336):262–265. doi: 10.1038/235262a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennings H., Michael D., Cheng C., Steinert P., Holbrook K., Yuspa S. H. Calcium regulation of growth and differentiation of mouse epidermal cells in culture. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90406-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoh J. H., John S. A., Revel J. P. Molecular cloning and characterization of a new member of the gap junction gene family, connexin-31. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 5;266(10):6524–6531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsiao W. L., Gattoni-Celli S., Weinstein I. B. Oncogene-induced transformation of C3H 10T1/2 cells is enhanced by tumor promoters. Science. 1984 Nov 2;226(4674):552–555. doi: 10.1126/science.6436974. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen-Timmen U., Traub O., Dermietzel R., Rabes H. M., Willecke K. Reduced number of gap junctions in rat hepatocarcinomas detected by monoclonal antibody. Carcinogenesis. 1986 Sep;7(9):1475–1482. doi: 10.1093/carcin/7.9.1475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalimi G. H., Sirsat S. M. The relevance of gap junctions to stage I tumor promotion in mouse epidermis. Carcinogenesis. 1984 Dec;5(12):1671–1677. doi: 10.1093/carcin/5.12.1671. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Acid and base hydrolysis of phosphoproteins bound to immobilon facilitates analysis of phosphoamino acids in gel-fractionated proteins. Anal Biochem. 1989 Jan;176(1):22–27. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90266-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamps M. P., Sefton B. M. Identification of multiple novel polypeptide substrates of the v-src, v-yes, v-fps, v-ros, and v-erb-B oncogenic tyrosine protein kinases utilizing antisera against phosphotyrosine. Oncogene. 1988 Apr;2(4):305–315. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Kishimoto A., Nishizuka Y. The protein kinase C family: heterogeneity and its implications. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:31–44. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.000335. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar N. M., Gilula N. B. Cloning and characterization of human and rat liver cDNAs coding for a gap junction protein. J Cell Biol. 1986 Sep;103(3):767–776. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.3.767. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd A. C., Paterson H. F., Morris J. D., Hall A., Marshall C. J. p21H-ras-induced morphological transformation and increases in c-myc expression are independent of functional protein kinase C. EMBO J. 1989 Apr;8(4):1099–1104. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03479.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Junctional intercellular communication and the control of growth. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Feb 4;560(1):1–65. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(79)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewenstein W. R. Junctional intercellular communication: the cell-to-cell membrane channel. Physiol Rev. 1981 Oct;61(4):829–913. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1981.61.4.829. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milks L. C., Kumar N. M., Houghten R., Unwin N., Gilula N. B. Topology of the 32-kd liver gap junction protein determined by site-directed antibody localizations. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):2967–2975. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03159.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray A. W., Fitzgerald D. J. Tumor promoters inhibit metabolic cooperation in cocultures of epidermal and 3T3 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Nov 28;91(2):395–401. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91535-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musil L. S., Beyer E. C., Goodenough D. A. Expression of the gap junction protein connexin43 in embryonic chick lens: molecular cloning, ultrastructural localization, and post-translational phosphorylation. J Membr Biol. 1990 Jun;116(2):163–175. doi: 10.1007/BF01868674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Musil L. S., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M., Goodenough D. A. Differential phosphorylation of the gap junction protein connexin43 in junctional communication-competent and -deficient cell lines. J Cell Biol. 1990 Nov;111(5 Pt 1):2077–2088. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.5.2077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul D. L. Molecular cloning of cDNA for rat liver gap junction protein. J Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;103(1):123–134. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.1.123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pitts J. D., Finbow M. E. The gap junction. J Cell Sci Suppl. 1986;4:239–266. doi: 10.1242/jcs.1986.supplement_4.15. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Risek B., Guthrie S., Kumar N., Gilula N. B. Modulation of gap junction transcript and protein expression during pregnancy in the rat. J Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;110(2):269–282. doi: 10.1083/jcb.110.2.269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers M., Berestecky J. M., Hossain M. Z., Guo H. M., Kadle R., Nicholson B. J., Bertram J. S. Retinoid-enhanced gap junctional communication is achieved by increased levels of connexin 43 mRNA and protein. Mol Carcinog. 1990;3(6):335–343. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940030605. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roop D. R., Lowy D. R., Tambourin P. E., Strickland J., Harper J. R., Balaschak M., Spangler E. F., Yuspa S. H. An activated Harvey ras oncogene produces benign tumours on mouse epidermal tissue. 1986 Oct 30-Nov 5Nature. 323(6091):822–824. doi: 10.1038/323822a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simmons D. L., Levy D. B., Yannoni Y., Erikson R. L. Identification of a phorbol ester-repressible v-src-inducible gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1178–1182. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi R., Batzer A., Kolb H. A. Inhibition of electrical coupling in pairs of murine pancreatic acinar cells by OAG and isolated protein kinase C. J Membr Biol. 1989 Jun;108(3):273–282. doi: 10.1007/BF01871742. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swenson K. I., Piwnica-Worms H., McNamee H., Paul D. L. Tyrosine phosphorylation of the gap junction protein connexin43 is required for the pp60v-src-induced inhibition of communication. Cell Regul. 1990 Dec;1(13):989–1002. doi: 10.1091/mbc.1.13.989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sáez J. C., Nairn A. C., Czernik A. J., Spray D. C., Hertzberg E. L., Greengard P., Bennett M. V. Phosphorylation of connexin 32, a hepatocyte gap-junction protein, by cAMP-dependent protein kinase, protein kinase C and Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Sep 11;192(2):263–273. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb19223.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub O., Look J., Dermietzel R., Brümmer F., Hülser D., Willecke K. Comparative characterization of the 21-kD and 26-kD gap junction proteins in murine liver and cultured hepatocytes. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):1039–1051. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.1039. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner A. E., Guthrie S. C., Gilula N. B. Antibodies to gap-junctional protein selectively disrupt junctional communication in the early amphibian embryo. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):127–131. doi: 10.1038/311127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfman A., Macara I. G. Elevated levels of diacylglycerol and decreased phorbol ester sensitivity in ras-transformed fibroblasts. Nature. 1987 Jan 22;325(6102):359–361. doi: 10.1038/325359a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki H., Hollstein M., Mesnil M., Martel N., Aguelon A. M. Selective lack of intercellular communication between transformed and nontransformed cells as a common property of chemical and oncogene transformation of BALB/c 3T3 cells. Cancer Res. 1987 Nov 1;47(21):5658–5664. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yotti L. P., Chang C. C., Trosko J. E. Elimination of metabolic cooperation in Chinese hamster cells by a tumor promoter. Science. 1979 Nov 30;206(4422):1089–1091. doi: 10.1126/science.493994. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuspa S. H., Ben T., Hennings H., Lichti U. Divergent responses in epidermal basal cells exposed to the tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Cancer Res. 1982 Jun;42(6):2344–2349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuspa S. H., Kilkenny A. E., Stanley J., Lichti U. Keratinocytes blocked in phorbol ester-responsive early stage of terminal differentiation by sarcoma viruses. Nature. 1985 Apr 4;314(6010):459–462. doi: 10.1038/314459a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuspa S. H., Kulesz-Martin M., Ben T., Hennings H. Transformation of epidermal cells in culture. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jul;81(1 Suppl):162s–168s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12540999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang J. T., Nicholson B. J. Sequence and tissue distribution of a second protein of hepatic gap junctions, Cx26, as deduced from its cDNA. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 2):3391–3401. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Fouly M. H., Trosko J. E., Chang C. C. Scrape-loading and dye transfer. A rapid and simple technique to study gap junctional intercellular communication. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Feb;168(2):422–430. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90014-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Fouly M. H., Trosko J. E., Chang C. C., Warren S. T. Potential role of the human Ha-ras oncogene in the inhibition of gap junctional intercellular communication. Mol Carcinog. 1989;2(3):131–135. doi: 10.1002/mc.2940020305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]