Abstract
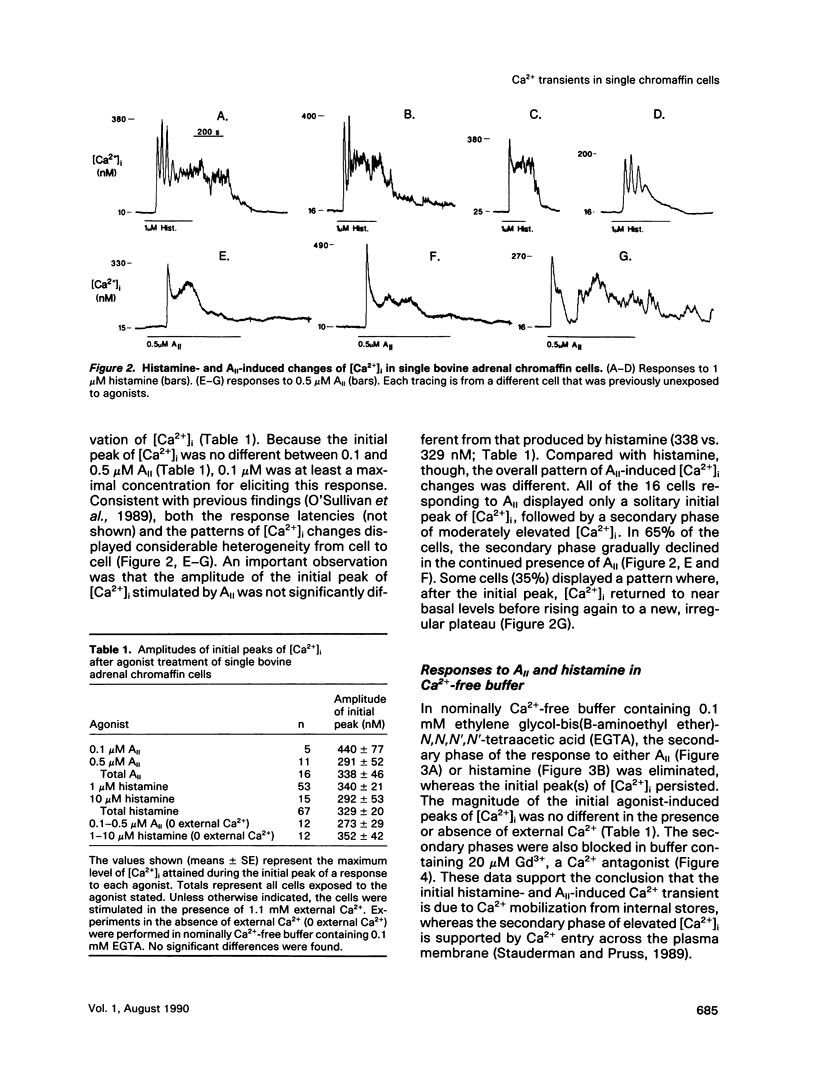
The patterns of agonist-induced elevations of cytosolic free Ca2+ ([Ca2+]i) were characterized and compared by the use of single adrenal chromaffin cells. Initial histamine- or angiotensin II (AII)-induced elevations of [Ca2+]i were equal in magnitude (peaks 329 +/- 20 [SE] and 338 +/- 46 nM, respectively). These initial increases of [Ca2+]i were transient, insensitive to either Gd3+ or removing external Ca2+, and were primarily the result of Ca2+ release from intracellular stores. After the initial peak(s) of [Ca2+]i, a second phase of moderately elevated [Ca2+]i was observed, and this response was sensitive to either Gd3+ or removing external Ca2+, supporting a role for Ca2+ entry. In most cases, the second phase of elevated [Ca2+]i was sustained during histamine stimulation but transient during AII stimulation. Maintenance of the second phase was a property of the agonist rather than of the particular cell being stimulated. Thus, individual cells exposed sequentially to histamine and AII displayed distinct patterns of [Ca2+]i changes to each agonist, regardless of the order of addition. Histamine also stimulated twice as much [3H]catecholamine release as AII, and release was completely dependent on external Ca2+. Therefore, the ability of histamine and AII to sustain (or promote) Ca2+ entry appears to underlie their efficacy as secretagogues. These data provide evidence linking agonist-dependent patterns of [Ca2+]i changes in single cells with agonist-dependent functional responses.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bader M. F., Sontag J. M., Thiersé D., Aunis D. A reassessment of guanine nucleotide effects on catecholamine secretion from permeabilized adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 5;264(28):16426–16434. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Cobbold P. H., Cuthbertson K. S. Spatial and temporal aspects of cell signalling. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1988 Jul 26;320(1199):325–343. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1988.0080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boksa P., Livett B. G. Desensitization to nicotinic cholinergic agonists and K+, agents that stimulate catecholamine secretion, in isolated adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1984 Mar;42(3):607–617. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb02726.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgoyne R. D., Cheek T. R., Morgan A., O'Sullivan A. J., Moreton R. B., Berridge M. J., Mata A. M., Colyer J., Lee A. G., East J. M. Distribution of two distinct Ca2+-ATPase-like proteins and their relationships to the agonist-sensitive calcium store in adrenal chromaffin cells. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):72–74. doi: 10.1038/342072a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek T. R., Jackson T. R., O'Sullivan A. J., Moreton R. B., Berridge M. J., Burgoyne R. D. Simultaneous measurements of cytosolic calcium and secretion in single bovine adrenal chromaffin cells by fluorescent imaging of fura-2 in cocultured cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Sep;109(3):1219–1227. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.3.1219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheek T. R., Thastrup O. Internal Ca2+ mobilization and secretion in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Cell Calcium. 1989 May-Jun;10(4):213–221. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(89)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldbeter A., Dupont G., Berridge M. J. Minimal model for signal-induced Ca2+ oscillations and for their frequency encoding through protein phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Feb;87(4):1461–1465. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.4.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grynkiewicz G., Poenie M., Tsien R. Y. A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3440–3450. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. T., Westhead E. W. Cellular responses to Ca2+ from extracellular and intracellular sources are different as shown by simultaneous measurements of cytosolic Ca2+ and secretion from bovine chromaffin cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9881–9885. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble E. P., Bommer M., Liebisch D., Herz A. H1-histaminergic activation of catecholamine release by chromaffin cells. Biochem Pharmacol. 1988 Jan 15;37(2):221–228. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(88)90721-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble E. P., Bommer M., Sincini E., Costa T., Herz A. H1-histaminergic activation stimulates inositol-1-phosphate accumulation in chromaffin cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Mar 13;135(2):566–573. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90031-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan A. J., Burgoyne R. D. A comparison of bradykinin, angiotensin II and muscarinic stimulation of cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Biosci Rep. 1989 Apr;9(2):243–252. doi: 10.1007/BF01116001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan A. J., Burgoyne R. D. The role of cytoplasmic pH in the inhibitory action of high osmolarity on secretion from bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 May 13;969(3):211–216. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(88)90054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Sullivan A. J., Cheek T. R., Moreton R. B., Berridge M. J., Burgoyne R. D. Localization and heterogeneity of agonist-induced changes in cytosolic calcium concentration in single bovine adrenal chromaffin cells from video imaging of fura-2. EMBO J. 1989 Feb;8(2):401–411. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03391.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oakes S. G., Martin W. J., 2nd, Lisek C. A., Powis G. Incomplete hydrolysis of the calcium indicator precursor fura-2 pentaacetoxymethyl ester (fura-2 AM) by cells. Anal Biochem. 1988 Feb 15;169(1):159–166. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(88)90267-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plevin R., Boarder M. R. Stimulation of formation of inositol phosphates in primary cultures of bovine adrenal chromaffin cells by angiotensin II, histamine, bradykinin, and carbachol. J Neurochem. 1988 Aug;51(2):634–641. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1988.tb01085.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocotte S. L., Frye R. A., Senter R. A., TerBush D. R., Lee S. A., Holz R. W. Effects of phorbol ester on catecholamine secretion and protein phosphorylation in adrenal medullary cell cultures. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):930–934. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.930. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poenie M. Alteration of intracellular Fura-2 fluorescence by viscosity: a simple correction. Cell Calcium. 1990 Feb-Mar;11(2-3):85–91. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(90)90062-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
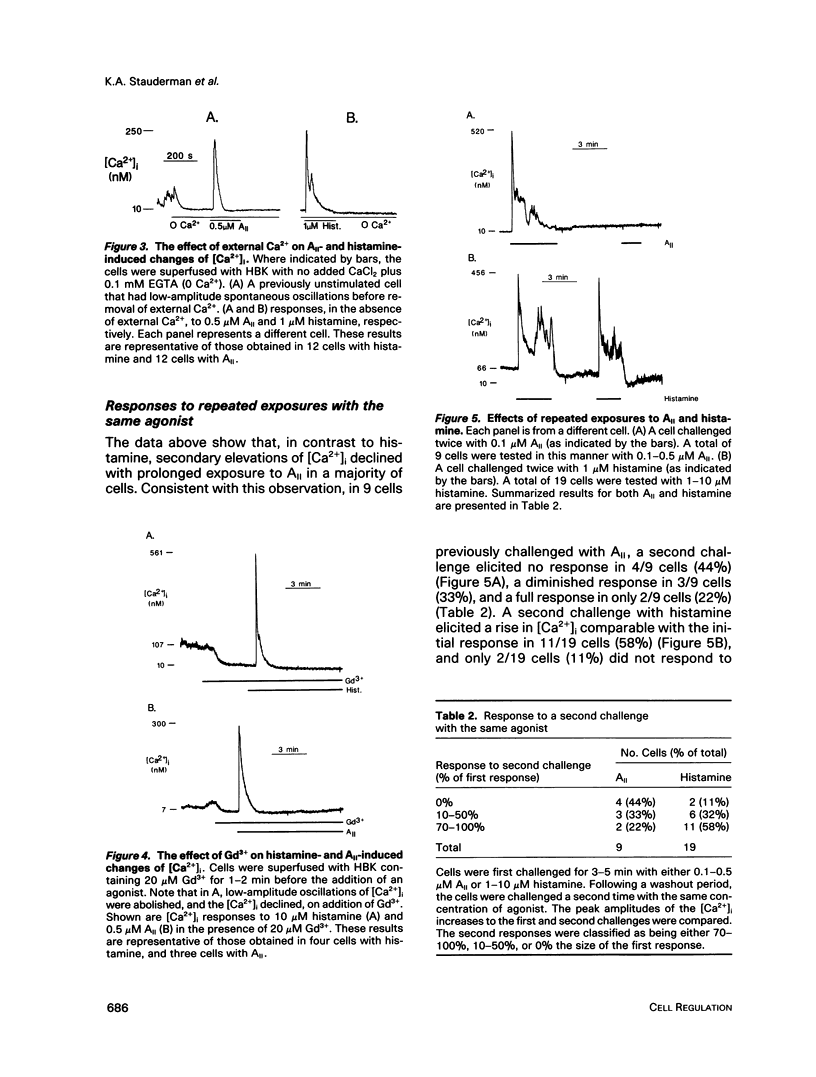
- Prentki M., Glennon M. C., Thomas A. P., Morris R. L., Matschinsky F. M., Corkey B. E. Cell-specific patterns of oscillating free Ca2+ in carbamylcholine-stimulated insulinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 15;263(23):11044–11047. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M., Moskal J. R., Eiden L. E., Beinfeld M. C. Specific regulation of vasoactive intestinal polypeptide biosynthesis by phorbol ester in bovine chromaffin cells. Endocrinology. 1985 Sep;117(3):1020–1026. doi: 10.1210/endo-117-3-1020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pruss R. M., Stauderman K. A. Voltage-regulated calcium channels involved in the regulation of enkephalin synthesis are blocked by phorbol ester treatment. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 15;263(26):13173–13178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney T. A., Sass E. J., Thomas A. P. Characterization of cytosolic calcium oscillations induced by phenylephrine and vasopressin in single fura-2-loaded hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17131–17141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
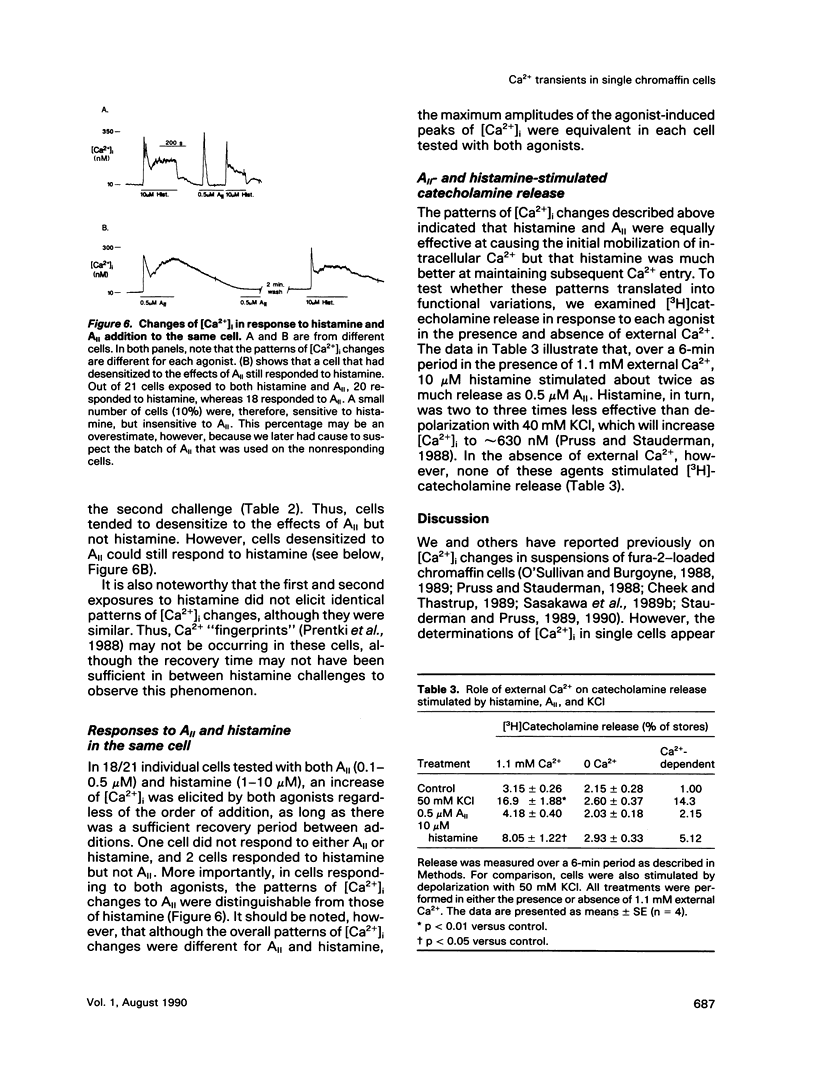
- Sasakawa N., Nakaki T., Yamamoto S., Kato R. Stimulation by ATP of inositol trisphosphate accumulation and calcium mobilization in cultured adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1989 Feb;52(2):441–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb09140.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scanlon M., Williams D. A., Fay F. S. A Ca2+-insensitive form of fura-2 associated with polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Assessment and accurate Ca2+ measurement. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 5;262(13):6308–6312. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauderman K. A., Pruss R. M. Different patterns of agonist-stimulated increases of 3H-inositol phosphate isomers and cytosolic Ca2+ in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells: comparison of the effects of histamine and angiotensin II. J Neurochem. 1990 Mar;54(3):946–953. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1990.tb02342.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stauderman K. A., Pruss R. M. Dissociation of Ca2+ entry and Ca2+ mobilization responses to angiotensin II in bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 Nov 5;264(31):18349–18355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan D. C., Bunn S. J., Livett B. G. Effects of phorbol esters and forskolin on basal and histamine-induced accumulation of inositol phosphates in cultured bovine adrenal chromaffin cells. J Neurochem. 1989 Oct;53(4):1219–1227. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1989.tb07418.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods N. M., Cuthbertson K. S., Cobbold P. H. Agonist-induced oscillations in cytoplasmic free calcium concentration in single rat hepatocytes. Cell Calcium. 1987 Feb;8(1):79–100. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(87)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]