Abstract
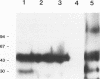
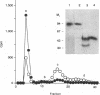
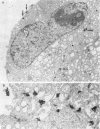
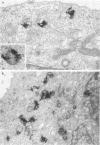
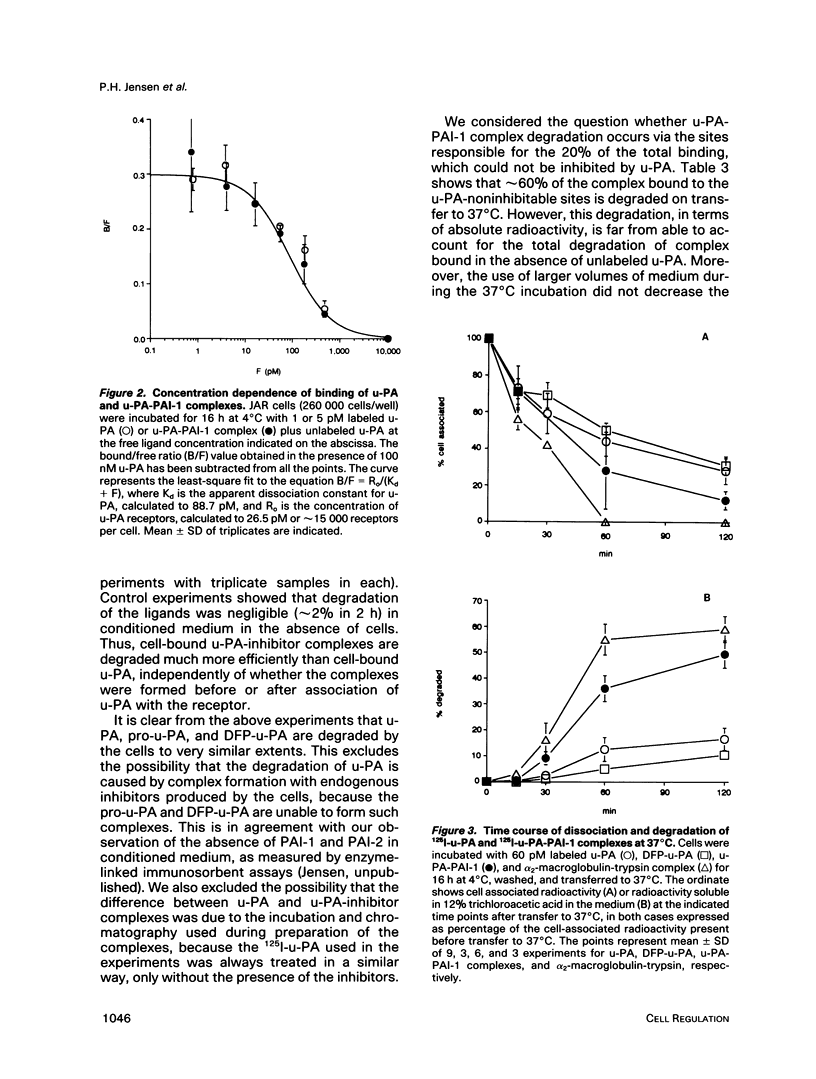
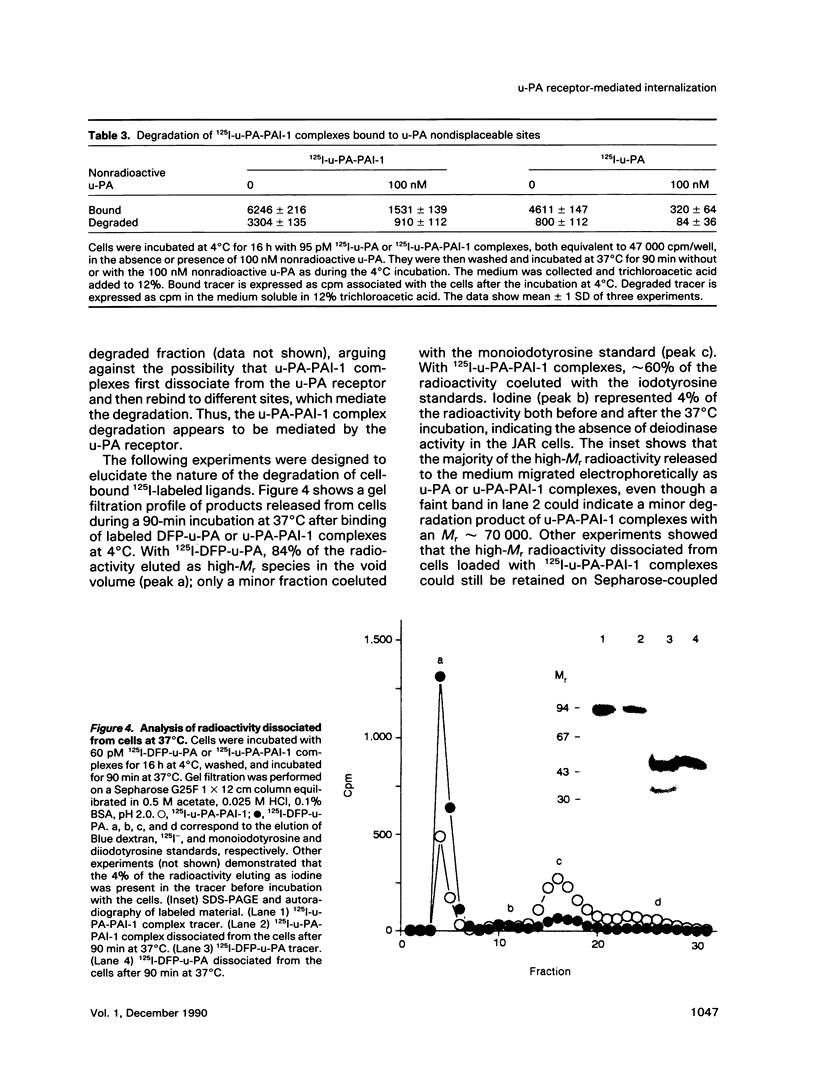
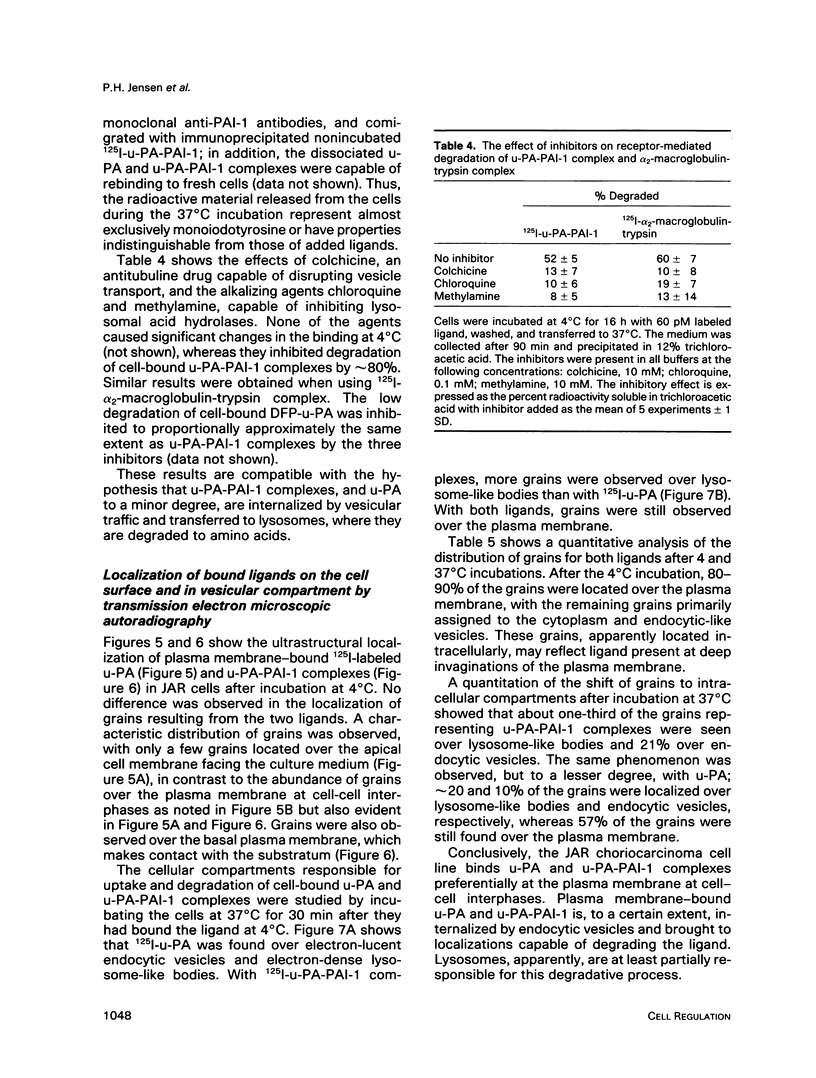
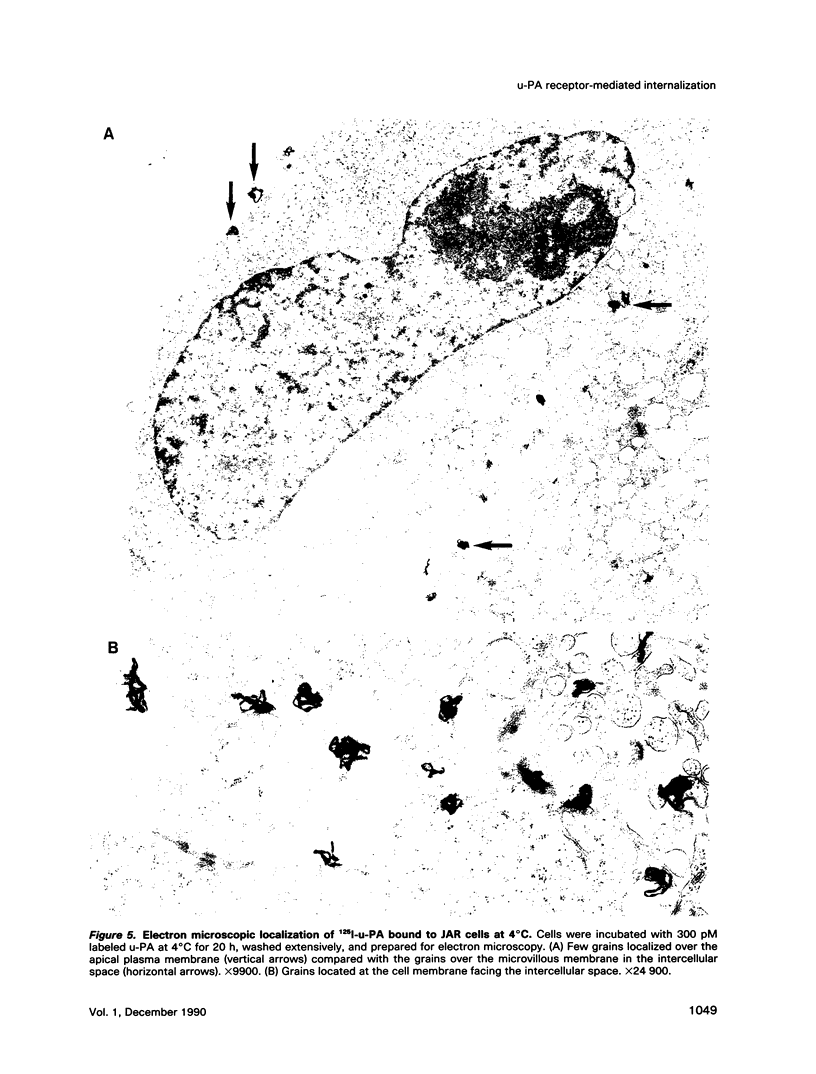
We have studied the effect of plasminogen activator inhibitors PAI-1 and PAI-2 on the binding of urokinase-type plasminogen activator (u-PA) to its receptor in the human choriocarcinoma cell line JAR. With 125I-labeled ligands in whole-cell binding assays, both uncomplexed u-PA and u-PA-inhibitor complexes bound to the receptor with a Kd of approximately 100 pM at 4 degrees C. Transferring the cells to 37 degrees C led to degradation to amino acids of up to 50% of the cell-bound u-PA-inhibitor complexes, whereas the degradation of uncomplexed u-PA was 15%; the remaining ligand was recovered in an apparently intact form in the medium or was still cell associated. The degradation could be inhibited by inhibitors of vesicle transport and lysosomal hydrolases. By electron microscopic autoradiography, both 125I-u-PA and 125I-u-PA-inhibitor complexes were located over the cell membrane at 4 degrees C, with the highest density of grains over the membrane at cell-cell interphases, but, after incubation at 37 degrees C, 17 and 27% of the grains for u-PA and u-PA-PAI-1 complexes, respectively, appeared over lysosomal-like bodies. These findings suggest that the u-PA receptor possesses a clearance function for the removal of u-PA after its complex formation with a specific inhibitor. The data suggest a novel mechanism by which receptor-mediated endocytosis is initiated by the binding of a secondary ligand.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andreasen P. A., Georg B., Lund L. R., Riccio A., Stacey S. N. Plasminogen activator inhibitors: hormonally regulated serpins. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1990 Jan 2;68(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(90)90164-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen P. A., Nielsen L. S., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Skriver L., Zeuthen J., Stephens R. W., Danø K. Inactive proenzyme to tissue-type plasminogen activator from human melanoma cells, identified after affinity purification with a monoclonal antibody. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):51–56. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01760.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andreasen P. A., Nielsen L. S., Kristensen P., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Skriver L., Danø K. Plasminogen activator inhibitor from human fibrosarcoma cells binds urokinase-type plasminogen activator, but not its proenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7644–7651. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astedt B., Hägerstrand I., Lecander I. Cellular localisation in placenta of placental type plasminogen activator inhibitor. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Aug 20;56(1):63–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Astedt B., Lecander I., Brodin T., Lundblad A., Löw K. Purification of a specific placental plasminogen activator inhibitor by monoclonal antibody and its complex formation with plasminogen activator. Thromb Haemost. 1985 Feb 18;53(1):122–125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubellis M. V., Andreasen P., Ragno P., Mayer M., Danø K., Blasi F. Accessibility of receptor-bound urokinase to type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jul;86(13):4828–4832. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.13.4828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cubellis M. V., Wun T. C., Blasi F. Receptor-mediated internalization and degradation of urokinase is caused by its specific inhibitor PAI-1. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1079–1085. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidsen O., Christensen E. I., Gliemann J. The plasma clearance of human alpha 2-macroglobulin-trypsin complex in the rat is mainly accounted for by uptake into hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jul 30;846(1):85–92. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(85)90113-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis V., Scully M. F., Kakkar V. V. Plasminogen activation initiated by single-chain urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Potentiation by U937 monocytes. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 5;264(4):2185–2188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis V., Wun T. C., Behrendt N., Rønne E., Danø K. Inhibition of receptor-bound urokinase by plasminogen-activator inhibitors. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9904–9908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estreicher A., Mühlhauser J., Carpentier J. L., Orci L., Vassalli J. D. The receptor for urokinase type plasminogen activator polarizes expression of the protease to the leading edge of migrating monocytes and promotes degradation of enzyme inhibitor complexes. J Cell Biol. 1990 Aug;111(2):783–792. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.2.783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Estreicher A., Wohlwend A., Belin D., Schleuning W. D., Vassalli J. D. Characterization of the cellular binding site for the urokinase-type plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 15;264(2):1180–1189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg R. F., Kao L. C., Haimowitz J. E., Queenan J. T., Jr, Wun T. C., Strauss J. F., 3rd, Kliman H. J. Plasminogen activator inhibitor types 1 and 2 in human trophoblasts. PAI-1 is an immunocytochemical marker of invading trophoblasts. Lab Invest. 1989 Jul;61(1):20–26. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. J., Cui T. Y., Zhang L., Hartman L., Grahl K., Zhang G. Y., Tarpey J., Damsky C. H. Adhesive and degradative properties of human placental cytotrophoblast cells in vitro. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):891–902. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S. J., Leitch M. S., Kantor M. S., Basbaum C. B., Kramer R. H. Degradation of extracellular matrix by the trophoblastic cells of first-trimester human placentas. J Cell Biochem. 1985;27(1):31–41. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240270105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gliemann J., Davidsen O. Characterization of receptors for alpha 2-macroglobulin-trypsin complex in rat hepatocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986 Jan 23;885(1):49–57. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(86)90037-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grøndahl-Hansen J., Ralfkiaer E., Nielsen L. S., Kristensen P., Frentz G., Danø K. Immunohistochemical localization of urokinase- and tissue-type plasminogen activators in psoriatic skin. J Invest Dermatol. 1987 Jan;88(1):28–32. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12464827. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HE C. S., Wilhelm S. M., Pentland A. P., Marmer B. L., Grant G. A., Eisen A. Z., Goldberg G. I. Tissue cooperation in a proteolytic cascade activating human interstitial collagenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Apr;86(8):2632–2636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.8.2632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen S. H., Behrendt N., Danø K., Kristensen P. Localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor on U937 cells: phorbol ester PMA induces heterogeneity. Exp Cell Res. 1990 Apr;187(2):255–262. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(90)90089-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hébert C. A., Baker J. B. Linkage of extracellular plasminogen activator to the fibroblast cytoskeleton: colocalization of cell surface urokinase with vinculin. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1241–1247. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1241. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. H., Ebbesen P., Gliemann J. Low alpha 2-macroglobulin-proteinase complex binding: a common but not exclusive characteristic of malignant cells. In Vivo. 1989 Jan-Feb;3(1):7–9. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jensen P. H., Nykjaer A., Andreasen P. A., Lund L. R., Astedt B., Lecander I., Gliemann J. Urokinase binds to a plasminogen activator inhibitor type-2-like molecule in placental microvillous membranes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Nov 17;986(1):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(89)90282-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchheimer J. C., Remold H. G. Functional characteristics of receptor-bound urokinase on human monocytes: catalytic efficiency and susceptibility to inactivation by plasminogen activator inhibitors. Blood. 1989 Sep;74(4):1396–1402. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliman H. J., Feinberg R. F. Human trophoblast-extracellular matrix (ECM) interactions in vitro: ECM thickness modulates morphology and proteolytic activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3057–3061. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund L. R., Georg B., Nielsen L. S., Mayer M., Danø K., Andreasen P. A. Plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1: cell-specific and differentiation-induced expression and regulation in human cell lines, as determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1988 Nov;60(1):43–53. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(88)90118-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maunsbach A. B. Absorption of I-125-labeled homologous albumin by rat kidney proximal tubule cells. A study of microperfused single proximal tubules by electron microscopic autoradiography and histochemistry. J Ultrastruct Res. 1966 Jun;15(3):197–241. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(66)80108-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miles L. A., Dahlberg C. M., Levin E. G., Plow E. F. Gangliosides interact directly with plasminogen and urokinase and may mediate binding of these fibrinolytic components to cells. Biochemistry. 1989 Nov 28;28(24):9337–9343. doi: 10.1021/bi00450a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen L. S., Andreasen P. A., Grøndahl-Hansen J., Huang J. Y., Kristensen P., Danø K. Monoclonal antibodies to human 54,000 molecular weight plasminogen activator inhibitor from fibrosarcoma cells--inhibitor neutralization and one-step affinity purification. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Apr 30;55(2):206–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen L. S., Kellerman G. M., Behrendt N., Picone R., Danø K., Blasi F. A 55,000-60,000 Mr receptor protein for urokinase-type plasminogen activator. Identification in human tumor cell lines and partial purification. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2358–2363. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nykjaer A., Petersen C. M., Christensen E. I., Davidsen O., Gliemann J. Urokinase receptors in human monocytes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 22;1052(3):399–407. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(90)90149-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ossowski L., Reich E. Antibodies to plasminogen activator inhibit human tumor metastasis. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):611–619. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oswald R. E., Bogusky M. J., Bamberger M., Smith R. A., Dobson C. M. Dynamics of the multidomain fibrinolytic protein urokinase from two-dimensional NMR. Nature. 1989 Feb 9;337(6207):579–582. doi: 10.1038/337579a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottosen P. D. Reversible peritubular binding of a cationic protein (lysozyme) to flounder kidney tubules. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Nov 20;194(2):207–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00220389. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Philips M., Juul A. G., Thorsen S., Selmer J., Zeuthen J. Immunological relationship between the fast-acting plasminogen activator inhibitors from plasma, blood platelets and endothelial cells demonstrated with a monoclonal antibody against an inhibitor from placenta. Thromb Haemost. 1986 Apr 30;55(2):213–217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pérez Maceda B., Linde S., Sonne O., Gliemann J. [125I]diiodoinsulins. Binding affinities, biologic potencies, and properties of their decay products. Diabetes. 1982 Jul;31(7):634–640. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöllänen J., Hedman K., Nielsen L. S., Danø K., Vaheri A. Ultrastructural localization of plasma membrane-associated urokinase-type plasminogen activator at focal contacts. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;106(1):87–95. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.1.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pöllänen J., Saksela O., Salonen E. M., Andreasen P., Nielsen L., Danø K., Vaheri A. Distinct localizations of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its type 1 inhibitor under cultured human fibroblasts and sarcoma cells. J Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;104(4):1085–1096. doi: 10.1083/jcb.104.4.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queenan J. T., Jr, Kao L. C., Arboleda C. E., Ulloa-Aguirre A., Golos T. G., Cines D. B., Strauss J. F., 3rd Regulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator production by cultured human cytotrophoblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 15;262(23):10903–10906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roldan A. L., Cubellis M. V., Masucci M. T., Behrendt N., Lund L. R., Danø K., Appella E., Blasi F. Cloning and expression of the receptor for human urokinase plasminogen activator, a central molecule in cell surface, plasmin dependent proteolysis. EMBO J. 1990 Feb;9(2):467–474. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08132.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saksela O., Rifkin D. B. Cell-associated plasminogen activation: regulation and physiological functions. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1988;4:93–126. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.04.110188.000521. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salpeter M. M., Fertuck H. C., Salpeter E. E. Resolution in electron microscope autoradiography. III. Iodine-125, the effect of heavy metal staining, and a reassessment of critical parameters. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jan;72(1):161–173. doi: 10.1083/jcb.72.1.161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sappino A. P., Huarte J., Belin D., Vassalli J. D. Plasminogen activators in tissue remodeling and invasion: mRNA localization in mouse ovaries and implanting embryos. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2471–2479. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2471. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sottrup-Jensen L., Petersen T. E., Magnusson S. A thiol-ester in alpha 2-macroglobulin cleaved during proteinase complex formation. FEBS Lett. 1980 Dec 1;121(2):275–279. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(80)80361-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoppelli M. P., Corti A., Soffientini A., Cassani G., Blasi F., Assoian R. K. Differentiation-enhanced binding of the amino-terminal fragment of human urokinase plasminogen activator to a specific receptor on U937 monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):4939–4943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.4939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strickland S., Reich E., Sherman M. I. Plasminogen activator in early embryogenesis: enzyme production by trophoblast and parietal endoderm. Cell. 1976 Oct;9(2):231–240. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokumitsu Y., Michio U. I. Separation and determination of 14C-labelled intermediates of the citric acid cycle and related compounds. Anal Biochem. 1974 May;59(1):110–121. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(74)90015-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vassalli J. D., Baccino D., Belin D. A cellular binding site for the Mr 55,000 form of the human plasminogen activator, urokinase. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;100(1):86–92. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.1.86. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Werb Z., Mainardi C. L., Vater C. A., Harris E. D., Jr Endogenous activiation of latent collagenase by rheumatoid synovial cells. Evidence for a role of plasminogen activator. N Engl J Med. 1977 May 5;296(18):1017–1023. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197705052961801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagel S., Parhar R. S., Jeffrey J. J., Lala P. K. Normal nonmetastatic human trophoblast cells share in vitro invasive properties of malignant cells. J Cell Physiol. 1988 Sep;136(3):455–462. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041360309. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]