Abstract
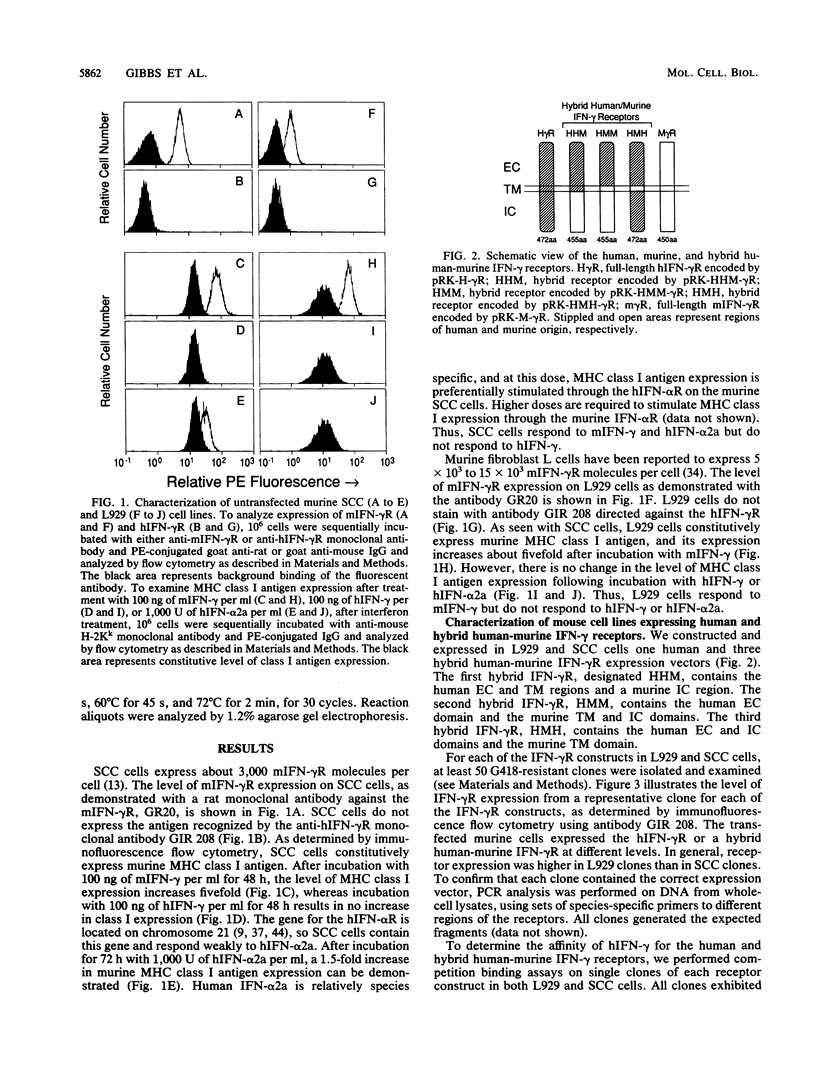
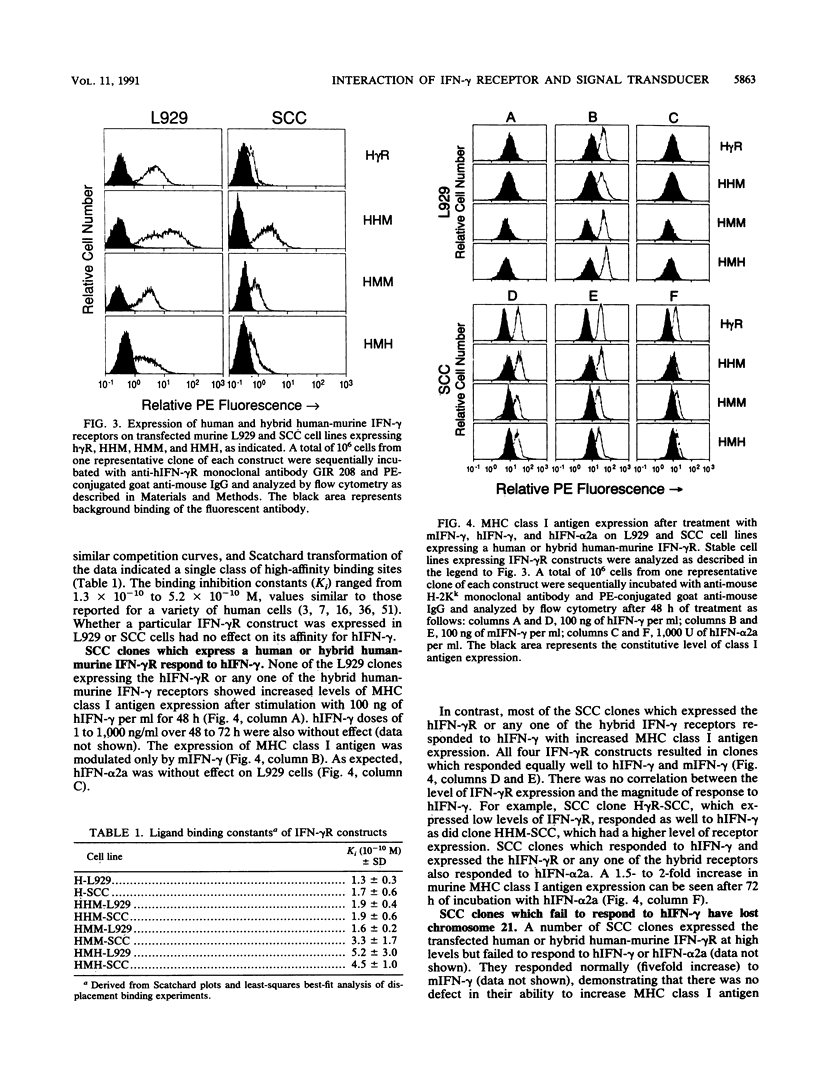
At least two species-specific gene products are required for signal transduction by interferon gamma (IFN-gamma). The first is the IFN-gamma receptor, which binds ligand with high affinity in a species-specific manner. The second is an undetermined species-specific signal transducer(s). To determine whether the human IFN-gamma receptor (hIFN-gamma R) interacts directly with this signal transducer(s) and, if so, with what functional domain(s), we constructed expression vectors for the hIFN-gamma R and three hybrid human-murine IFN-gamma receptors. The hybrid receptors contained the extracellular, human IFN-gamma (hIFN-gamma) binding domain of the hIFN-gamma R, either the human or murine transmembrane domain, and either the human or murine intracellular domain. The vectors encoding these receptors were stably transfected into two mouse cell lines, one of which (SCC-16-5) contains a single copy of human chromosome 21. The resulting cell lines were treated with hIFN-gamma, and murine major histocompatibility complex class I antigen expression was analyzed by immunofluorescence flow cytometry. All transfected cell lines lacking human chromosome 21 remained insensitive to hIFN-gamma. However, all four of the IFN-gamma receptors were able to signal when expressed in the cell line containing human chromosome 21. We conclude that the extracellular domain of the IFN-gamma receptor is involved not only in the species specificity of IFN-gamma binding but also in signalling through interaction with an as yet unidentified species-specific factor(s) encoded by a gene(s) on human chromosome 21.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aguet M., Dembić Z., Merlin G. Molecular cloning and expression of the human interferon-gamma receptor. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):273–280. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90050-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguet M., Merlin G. Purification of human gamma interferon receptors by sequential affinity chromatography on immobilized monoclonal antireceptor antibodies and human gamma interferon. J Exp Med. 1987 Apr 1;165(4):988–999. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.4.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguet M. The interferon-gamma receptor: a comparison with other cytokine receptors. J Interferon Res. 1990 Dec;10(6):551–558. doi: 10.1089/jir.1990.10.551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Basu M., Pace J. L., Pinson D. M., Hayes M. P., Trotta P. P., Russell S. W. Purification and partial characterization of a receptor protein for mouse interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(17):6282–6286. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.17.6282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderon J., Sheehan K. C., Chance C., Thomas M. L., Schreiber R. D. Purification and characterization of the human interferon-gamma receptor from placenta. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(13):4837–4841. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.13.4837. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celada A., Allen R., Esparza I., Gray P. W., Schreiber R. D. Demonstration and partial characterization of the interferon-gamma receptor on human mononuclear phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1985 Dec;76(6):2196–2205. doi: 10.1172/JCI112228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Celada A., Gray P. W., Rinderknecht E., Schreiber R. D. Evidence for a gamma-interferon receptor that regulates macrophage tumoricidal activity. J Exp Med. 1984 Jul 1;160(1):55–74. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.1.55. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chany C., Vignal M., Couillin P., Van Cong N., Boué J., Boué A. Chromosomal localization of human genes governing the interferon-induced antiviral state. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Aug;72(8):3129–3133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.8.3129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. A., Okayama H. Calcium phosphate-mediated gene transfer: a highly efficient transfection system for stably transforming cells with plasmid DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Jul-Aug;6(7):632–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cofano F., Moore S. K., Tanaka S., Yuhki N., Landolfo S., Appella E. Affinity purification, peptide analysis, and cDNA sequence of the mouse interferon gamma receptor. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):4064–4071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J., Fogler W. E., Kleinerman E. S., Saiki I. Abrogation of species specificity for activation of tumoricidal properties in macrophages by recombinant mouse or human interferon-gamma encapsulated in liposomes. J Immunol. 1985 Dec;135(6):4289–4296. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finbloom D. S., Hoover D. L., Wahl L. M. The characteristics of binding of human recombinant interferon-gamma to its receptor on human monocytes and human monocyte-like cell lines. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):300–305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer D. G., Novick D., Orchansky P., Rubinstein M. Two molecular forms of the human interferon-gamma receptor. Ligand binding, internalization, and down-regulation. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2632–2637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischer T., Rehm A., Aguet M., Pfizenmaier K. Human chromosome 21 is necessary and sufficient to confer human IFN gamma responsiveness to somatic cell hybrids expressing the cloned human IFN gamma receptor gene. Cytokine. 1990 May;2(3):157–161. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(90)90010-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fountoulakis M., Juranville J. F., Stüber D., Weibel E. K., Garotta G. Purification and biochemical characterization of a soluble human interferon gamma receptor expressed in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13268–13275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fountoulakis M., Kania M., Ozmen L., Loetscher H. R., Garotta G., van Loon A. P. Structure and membrane topology of the high-affinity receptor for human IFN-gamma: requirements for binding IFN-gamma. One single 90-kilodalton IFN-gamma receptor can lead to multiple cross-linked products and isolated proteins. J Immunol. 1989 Nov 15;143(10):3266–3276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garotta G., Ozmen L., Fountoulakis M., Dembic Z., van Loon A. P., Stüber D. Human interferon-gamma receptor. Mapping of epitopes recognized by neutralizing antibodies using native and recombinant receptor proteins. J Biol Chem. 1990 Apr 25;265(12):6908–6915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gearing D. P., King J. A., Gough N. M., Nicola N. A. Expression cloning of a receptor for human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor. EMBO J. 1989 Dec 1;8(12):3667–3676. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Goeddel D. V. Cloning and expression of murine immune interferon cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(19):5842–5846. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.19.5842. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray P. W., Leong S., Fennie E. H., Farrar M. A., Pingel J. T., Fernandez-Luna J., Schreiber R. D. Cloning and expression of the cDNA for the murine interferon gamma receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8497–8501. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashida K., Kitamura T., Gorman D. M., Arai K., Yokota T., Miyajima A. Molecular cloning of a second subunit of the receptor for human granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF): reconstitution of a high-affinity GM-CSF receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Dec;87(24):9655–9659. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.24.9655. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemmi S., Peghini P., Metzler M., Merlin G., Dembic Z., Aguet M. Cloning of murine interferon gamma receptor cDNA: expression in human cells mediates high-affinity binding but is not sufficient to confer sensitivity to murine interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):9901–9905. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.9901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibi M., Murakami M., Saito M., Hirano T., Taga T., Kishimoto T. Molecular cloning and expression of an IL-6 signal transducer, gp130. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1149–1157. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90411-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janssen J. W., Collard J. G., Tulp A., Cox D., Millington-Ward A., Pearson P. Construction and analysis of an EMBL-3 phage library containing partially digested human chromosome 21-specific DNA inserts (15-20 kb). Cytometry. 1986 Sep;7(5):411–417. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990070504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung V., Jones C., Kumar C. S., Stefanos S., O'Connell S., Pestka S. Expression and reconstitution of a biologically active human interferon-gamma receptor in hamster cells. J Biol Chem. 1990 Feb 5;265(4):1827–1830. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung V., Rashidbaigi A., Jones C., Tischfield J. A., Shows T. B., Pestka S. Human chromosomes 6 and 21 are required for sensitivity to human interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(12):4151–4155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.12.4151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King D. P., Jones P. P. Induction of Ia and H-2 antigens on a macrophage cell line by immune interferon. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):315–318. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar C. S., Muthukumaran G., Frost L. J., Noe M., Ahn Y. H., Mariano T. M., Pestka S. Molecular characterization of the murine interferon gamma receptor cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 25;264(30):17939–17946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer J. A., Pestka S. Interferon receptors. Immunol Today. 1988 Dec;9(12):393–400. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(88)91241-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer J. A., Rashidbaigi A., Pestka S. Preparation of 32P-labeled murine immune interferon and its binding to the mouse immune interferon receptor. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 25;261(21):9801–9804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibson H. J., Gefter M., Zlotnik A., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. Role of gamma-interferon in antibody-producing responses. 1984 Jun 28-Jul 4Nature. 309(5971):799–801. doi: 10.1038/309799a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littman S. J., Faltynek C. R., Baglioni C. Binding of human recombinant 125I-interferon gamma to receptors on human cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1191–1195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lutfalla G., Roeckel N., Mogensen K. E., Mattei M. G., Uzé G. Assignment of the human interferon-alpha receptor gene to chromosome 21q22.1 by in situ hybridization. J Interferon Res. 1990 Oct;10(5):515–517. doi: 10.1089/jir.1990.10.515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munro S., Maniatis T. Expression cloning of the murine interferon gamma receptor cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9248–9252. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9248. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick D., Orchansky P., Revel M., Rubinstein M. The human interferon-gamma receptor. Purification, characterization, and preparation of antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8483–8487. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfizenmaier K., Wiegmann K., Scheurich P., Krönke M., Merlin G., Aguet M., Knowles B. B., Ucer U. High affinity human IFN-gamma-binding capacity is encoded by a single receptor gene located in proximity to c-ros on human chromosome region 6q16 to 6q22. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 1;141(3):856–860. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raziuddin A., Sarkar F. H., Dutkowski R., Shulman L., Ruddle F. H., Gupta S. L. Receptors for human alpha and beta interferon but not for gamma interferon are specified by human chromosome 21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(17):5504–5508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.17.5504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheehan K. C., Calderon J., Schreiber R. D. Generation and characterization of monoclonal antibodies specific for the human IFN-gamma receptor. J Immunol. 1988 Jun 15;140(12):4231–4237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snapper C. M., Paul W. E. Interferon-gamma and B cell stimulatory factor-1 reciprocally regulate Ig isotype production. Science. 1987 May 22;236(4804):944–947. doi: 10.1126/science.3107127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steeg P. S., Moore R. N., Oppenheim J. J. Regulation of murine macrophage Ia-antigen expression by products of activated spleen cells. J Exp Med. 1980 Dec 1;152(6):1734–1744. doi: 10.1084/jem.152.6.1734. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucer U., Bartsch H., Scheurich P., Berkovic D., Ertel C., Pfizenmaier K. Quantitation and characterization of gamma-interferon receptors on human tumor cells. Cancer Res. 1986 Oct;46(10):5339–5343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ucer U., Bartsch H., Scheurich P., Pfizenmaier K. Biological effects of gamma-interferon on human tumor cells: quantity and affinity of cell membrane receptors for gamma-IFN in relation to growth inhibition and induction of HLA-DR expression. Int J Cancer. 1985 Jul 15;36(1):103–108. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910360116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamasaki K., Taga T., Hirata Y., Yawata H., Kawanishi Y., Seed B., Taniguchi T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Cloning and expression of the human interleukin-6 (BSF-2/IFN beta 2) receptor. Science. 1988 Aug 12;241(4867):825–828. doi: 10.1126/science.3136546. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yon J., Fried M. Precise gene fusion by PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4895–4895. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


