Abstract
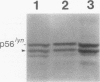
We previously cloned a lyn cDNA-encoding 56-kd Src-like protein-tyrosine kinase, p56lyn. Anti-Lyn antibodies raised against a sequence of 95 amino acids (Arg-25 to Ala-119 of p56lyn) recognized two species of the protein, p56lyn and p53lyn. V8 proteinase analysis showed that p53lyn differs only slightly from p56lyn. Analysis of mRNA from B lymphocytes by the polymerase chain reaction indicated the presence of two forms of alternatively spliced lyn mRNA. Nucleotide sequencing of the corresponding cDNAs revealed that these two forms of lyn mRNA differ in the presence and absence of a 63 nucleotides sequence near the 5'-terminus of the coding region; 21 amino acid residues (Pro-23 to Arg-43 or Val-24 to Pro-44) of p56lyn were tentatively concluded to be missing in p53lyn. On cross-linking of the membrane-bound IgM (mIgM) on the surface of B lymphocytes, the kinetics of down-regulations of the two Lyn proteins demonstrated to be associated with the mIgM antigen receptor were found to be different. This observation suggests that the amino terminal proximal sequence of the Lyn protein is important for determining its mode of interaction with mIgM.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barber E. K., Dasgupta J. D., Schlossman S. F., Trevillyan J. M., Rudd C. E. The CD4 and CD8 antigens are coupled to a protein-tyrosine kinase (p56lck) that phosphorylates the CD3 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 May;86(9):3277–3281. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.9.3277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bijsterbosch M. K., Meade C. J., Turner G. A., Klaus G. G. B lymphocyte receptors and polyphosphoinositide degradation. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80080-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A. W., Schrader J. W. The regulation of growth and differentiation of a murine B cell lymphoma. II. The inhibition of WEHI 231 by anti-immunoglobulin antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Jun;126(6):2466–2469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. A., Sefton B. M. Protein tyrosine phosphorylation is induced in murine B lymphocytes in response to stimulation with anti-immunoglobulin. EMBO J. 1990 Jul;9(7):2125–2131. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07381.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantley L. C., Auger K. R., Carpenter C., Duckworth B., Graziani A., Kapeller R., Soltoff S. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell. 1991 Jan 25;64(2):281–302. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90639-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H. L., Blattner F. R., Fitzmaurice L., Mushinski J. F., Tucker P. W. Structure of genes for membrane and secreted murine IgD heavy chains. Nature. 1982 Apr 1;296(5856):410–415. doi: 10.1038/296410a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke M. P., Perlmutter R. M. Expression of a novel form of the fyn proto-oncogene in hematopoietic cells. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):66–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFranco A. L. Immunology. Tolerance: a second mechanism. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):340–341. doi: 10.1038/342340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. R., Law D. A., DeFranco A. L. Stimulation of protein tyrosine phosphorylation by the B-lymphocyte antigen receptor. Nature. 1990 Jun 28;345(6278):810–813. doi: 10.1038/345810a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodnow C. C., Crosbie J., Jorgensen H., Brink R. A., Basten A. Induction of self-tolerance in mature peripheral B lymphocytes. Nature. 1989 Nov 23;342(6248):385–391. doi: 10.1038/342385a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grupp S. A., Harmony J. A. Increased phosphatidylinositol metabolism is an important but not an obligatory early event in B lymphocyte activation. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4087–4094. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanks S. K., Quinn A. M., Hunter T. The protein kinase family: conserved features and deduced phylogeny of the catalytic domains. Science. 1988 Jul 1;241(4861):42–52. doi: 10.1126/science.3291115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayashi S., Kunisada T., Ogawa M., Sudo T., Kodama H., Suda T., Nishikawa S., Nishikawa S. Stepwise progression of B lineage differentiation supported by interleukin 7 and other stromal cell molecules. J Exp Med. 1990 May 1;171(5):1683–1695. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.5.1683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim K. J., Kanellopoulos-Langevin C., Merwin R. M., Sachs D. H., Asofsky R. Establishment and characterization of BALB/c lymphoma lines with B cell properties. J Immunol. 1979 Feb;122(2):549–554. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaus G. G., Bijsterbosch M. K., O'Garra A., Harnett M. M., Rigley K. P. Receptor signalling and crosstalk in B lymphocytes. Immunol Rev. 1987 Oct;99:19–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb01170.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. B., Brugge J. S. Biological and biochemical properties of the c-src+ gene product overexpressed in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;9(8):3332–3341. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.8.3332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. B., Dorai T., Wang L. H., Brugge J. S. The structurally distinct form of pp60c-src detected in neuronal cells is encoded by a unique c-src mRNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4142–4145. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinez R., Mathey-Prevot B., Bernards A., Baltimore D. Neuronal pp60c-src contains a six-amino acid insertion relative to its non-neuronal counterpart. Science. 1987 Jul 24;237(4813):411–415. doi: 10.1126/science.2440106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuguchi J., Tsang W., Morrison S. L., Beaven M. A., Paul W. E. Membrane IgM, IgD, and IgG act as signal transmission molecules in a series of B lymphomas. J Immunol. 1986 Oct 1;137(7):2162–2167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullis K. B., Faloona F. A. Specific synthesis of DNA in vitro via a polymerase-catalyzed chain reaction. Methods Enzymol. 1987;155:335–350. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)55023-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Métézeau P., Elguindi I., Goldberg M. E. Endocytosis of the membrane immunoglobulins of mouse spleen B-cells: a quantitative study of its rate, amount and sensitivity to physiological, physical and cross-linking agents. EMBO J. 1984 Oct;3(10):2235–2242. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02121.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nossal G. J. Cellular mechanisms of immunologic tolerance. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:33–62. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.000341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa M., Ikuta K., Katsura Y., Nishikawa S. Stepwise progression of B cell malignancy occurred in a bone marrow stromal cell-dependent pre-B cell clone. Leukemia. 1989 Apr;3(4):282–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki K., Nishikawa S., Sakano H. Aberrant immunoglobulin gene rearrangement in scid mouse bone marrow cells. J Immunol. 1988 Aug 15;141(4):1348–1352. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT J. V. CYTOLOGY OF BURKITT'S TUMOUR (AFRICAN LYMPHOMA). Lancet. 1964 Feb 1;1(7327):238–240. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(64)92345-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pyper J. M., Bolen J. B. Identification of a novel neuronal C-SRC exon expressed in human brain. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 May;10(5):2035–2040. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.5.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J., Early P., Carter C., Calame K., Bond M., Hood L., Wall R. Two mRNAs with different 3' ends encode membrane-bound and secreted forms of immunoglobulin mu chain. Cell. 1980 Jun;20(2):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90616-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E., Trevillyan J. M., Dasgupta J. D., Wong L. L., Schlossman S. F. The CD4 receptor is complexed in detergent lysates to a protein-tyrosine kinase (pp58) from human T lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5190–5194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw A. S., Amrein K. E., Hammond C., Stern D. F., Sefton B. M., Rose J. K. The lck tyrosine protein kinase interacts with the cytoplasmic tail of the CD4 glycoprotein through its unique amino-terminal domain. Cell. 1989 Nov 17;59(4):627–636. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90008-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley E., Ralph S., McEwen S., Boulet I., Holtzman D. A., Lock P., Dunn A. R. Alternatively spliced murine lyn mRNAs encode distinct proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 Jul;11(7):3399–3406. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.7.3399. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyler B. M., Cowman A. F., Gerondakis S. D., Adams J. M., Bernard O. mRNA for surface immunoglobulin gamma chains encodes a highly conserved transmembrane sequence and a 28-residue intracellular domain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2008–2012. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Bolen J. B. The CD4 and CD8 T cell surface antigens are associated with the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Cell. 1988 Oct 21;55(2):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90053-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veillette A., Bookman M. A., Horak E. M., Samelson L. E., Bolen J. B. Signal transduction through the CD4 receptor involves the activation of the internal membrane tyrosine-protein kinase p56lck. Nature. 1989 Mar 16;338(6212):257–259. doi: 10.1038/338257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Fukushige S., Semba K., Sukegawa J., Miyajima N., Matsubara K., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. The yes-related cellular gene lyn encodes a possible tyrosine kinase similar to p56lck. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):237–243. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Kakiuchi T., Mizuguchi J., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Association of B cell antigen receptor with protein tyrosine kinase Lyn. Science. 1991 Jan 11;251(4990):192–194. doi: 10.1126/science.1702903. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanashi Y., Mori S., Yoshida M., Kishimoto T., Inoue K., Yamamoto T., Toyoshima K. Selective expression of a protein-tyrosine kinase, p56lyn, in hematopoietic cells and association with production of human T-cell lymphotropic virus type I. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Sep;86(17):6538–6542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.17.6538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamawaki-Kataoka Y., Nakai S., Miyata T., Honjo T. Nucleotide sequences of gene segments encoding membrane domains of immunoglobulin gamma chains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2623–2627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2623. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yi T. L., Bolen J. B., Ihle J. N. Hematopoietic cells express two forms of lyn kinase differing by 21 amino acids in the amino terminus. Mol Cell Biol. 1991 May;11(5):2391–2398. doi: 10.1128/mcb.11.5.2391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]