Abstract
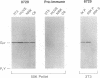
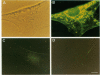
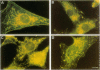
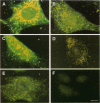
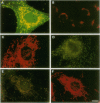
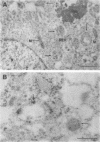
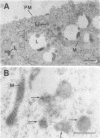
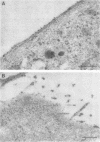
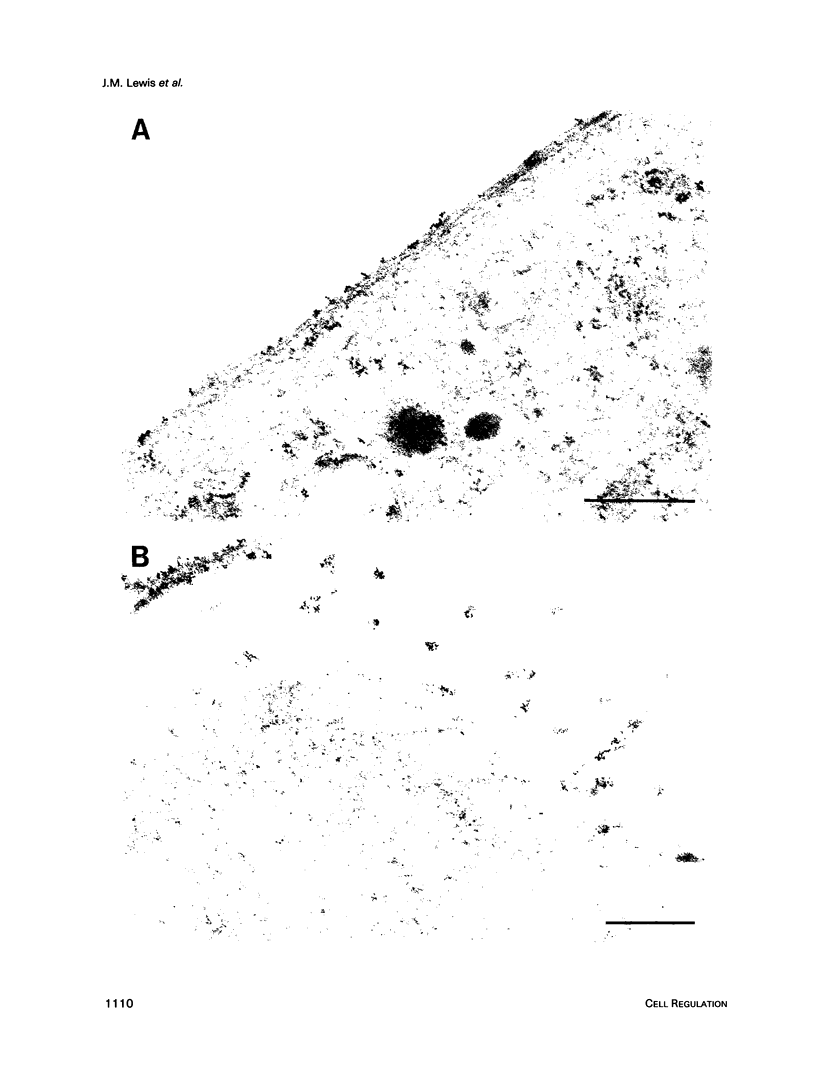
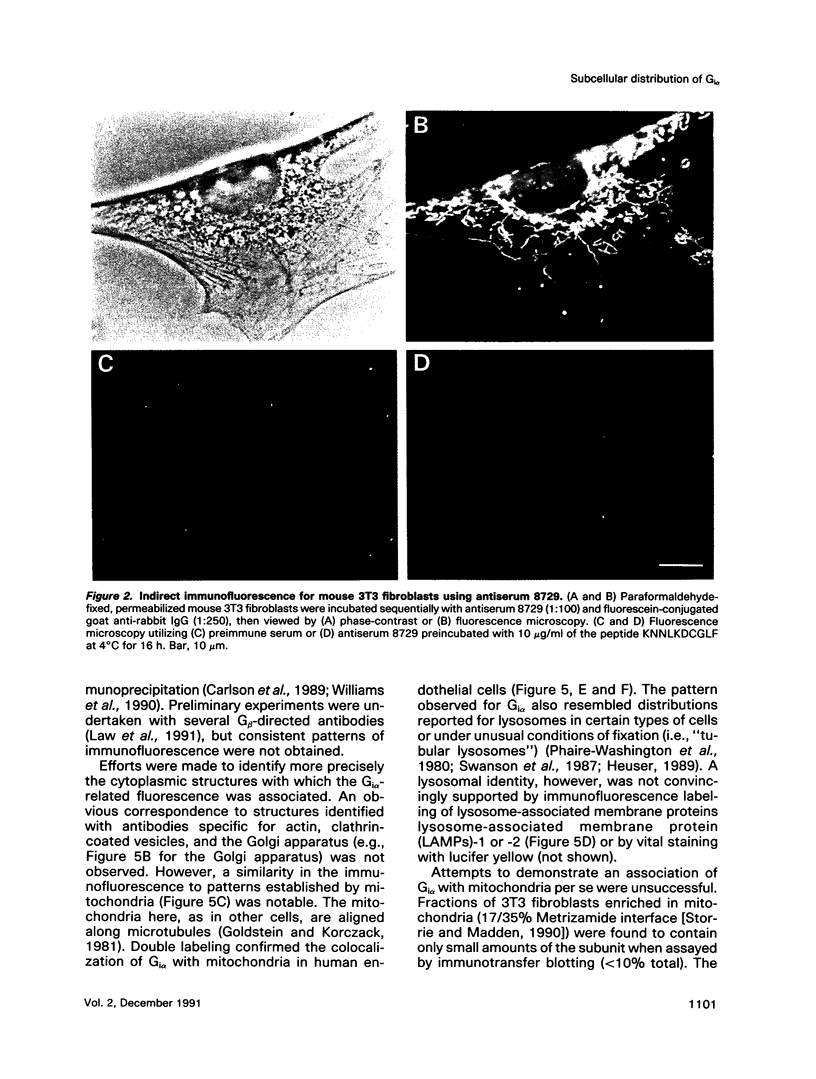
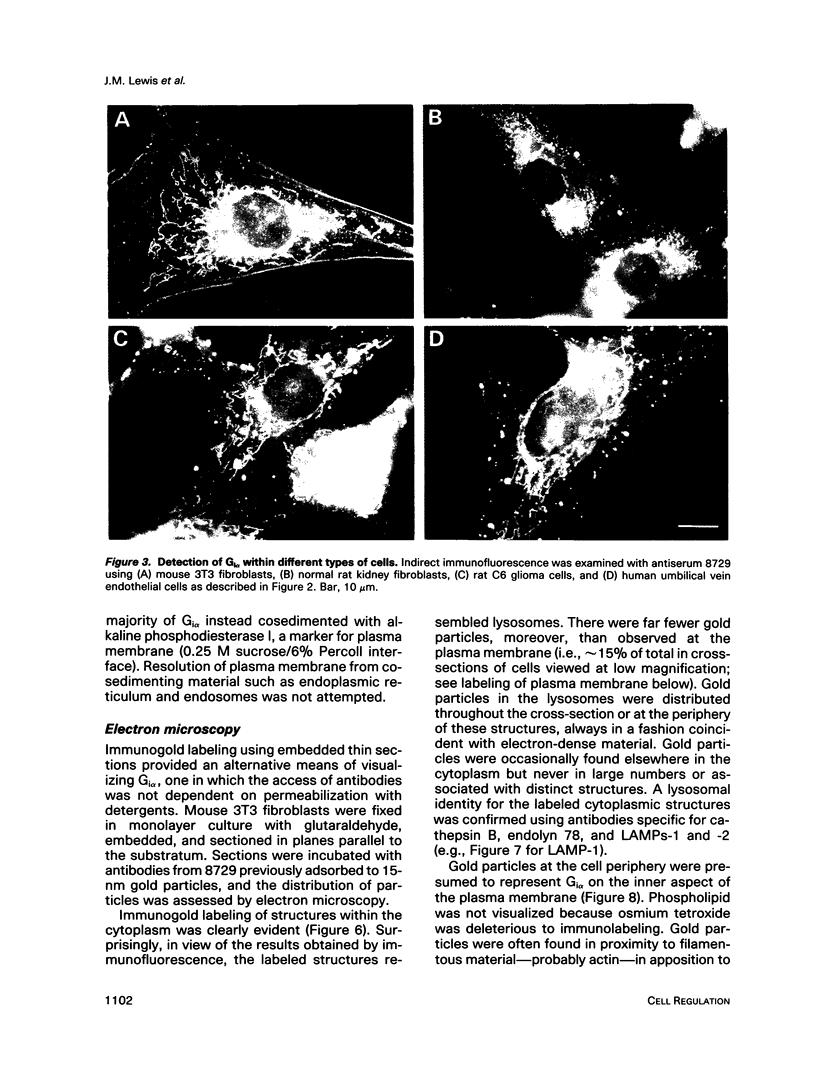
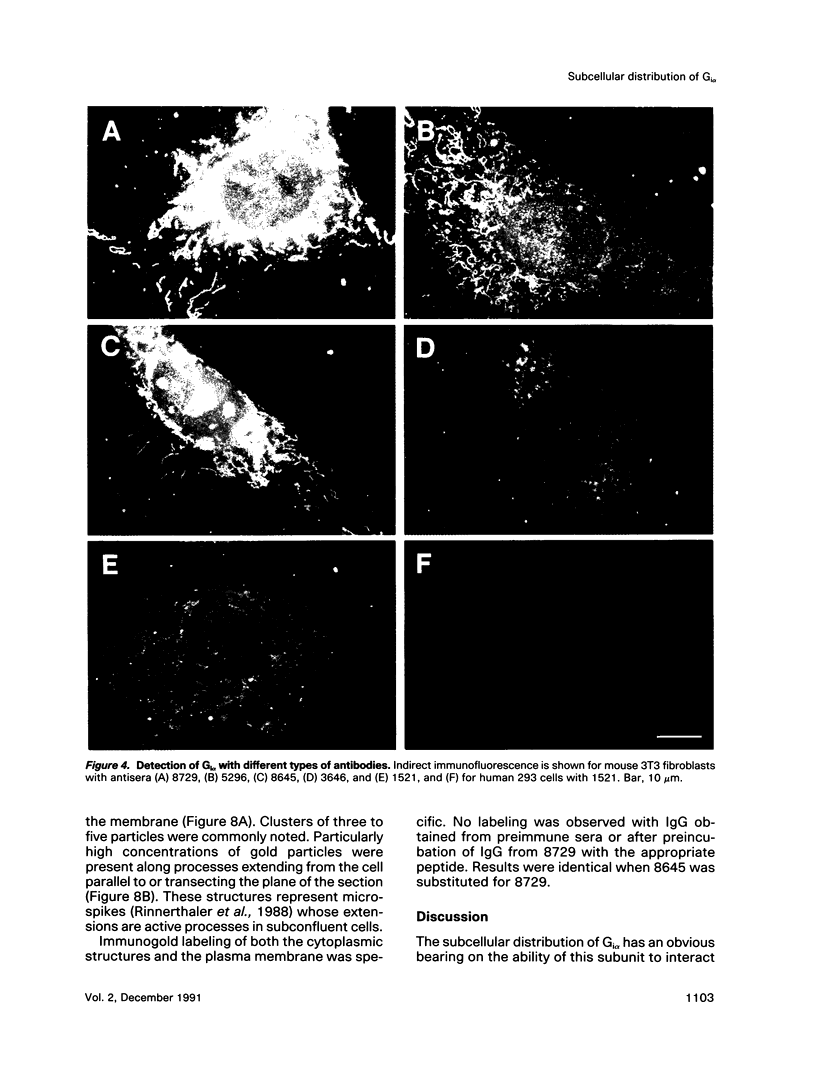
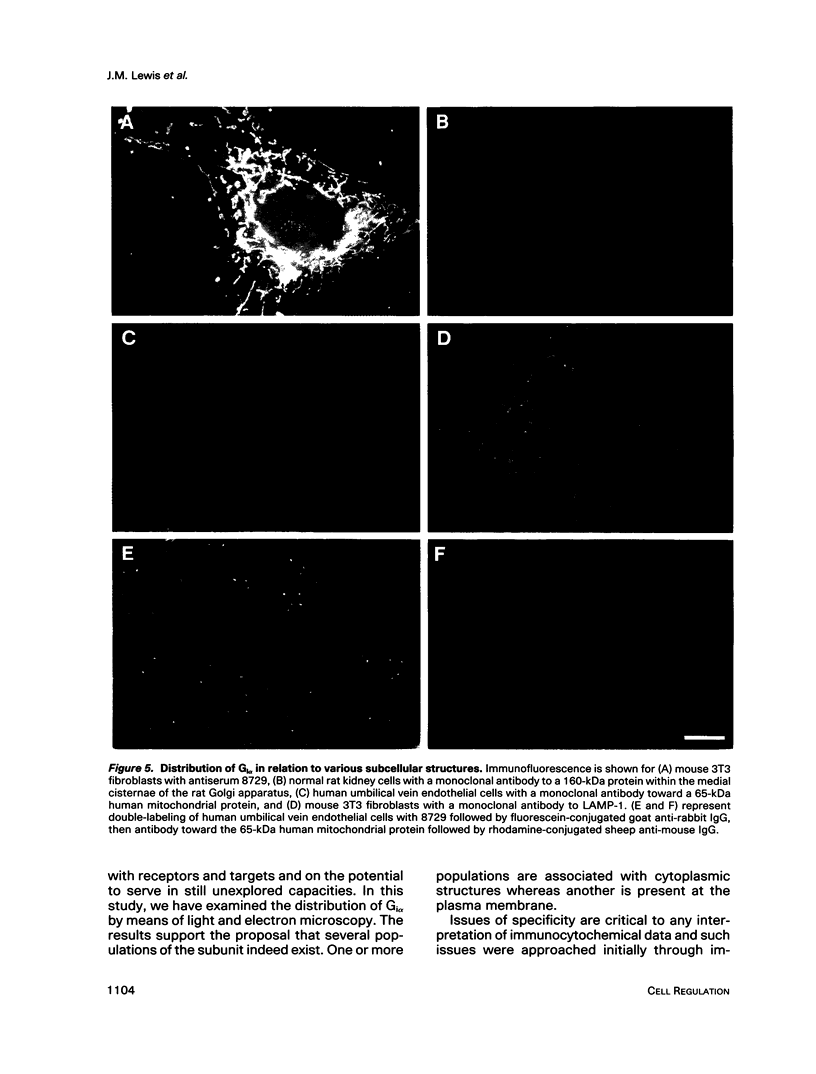
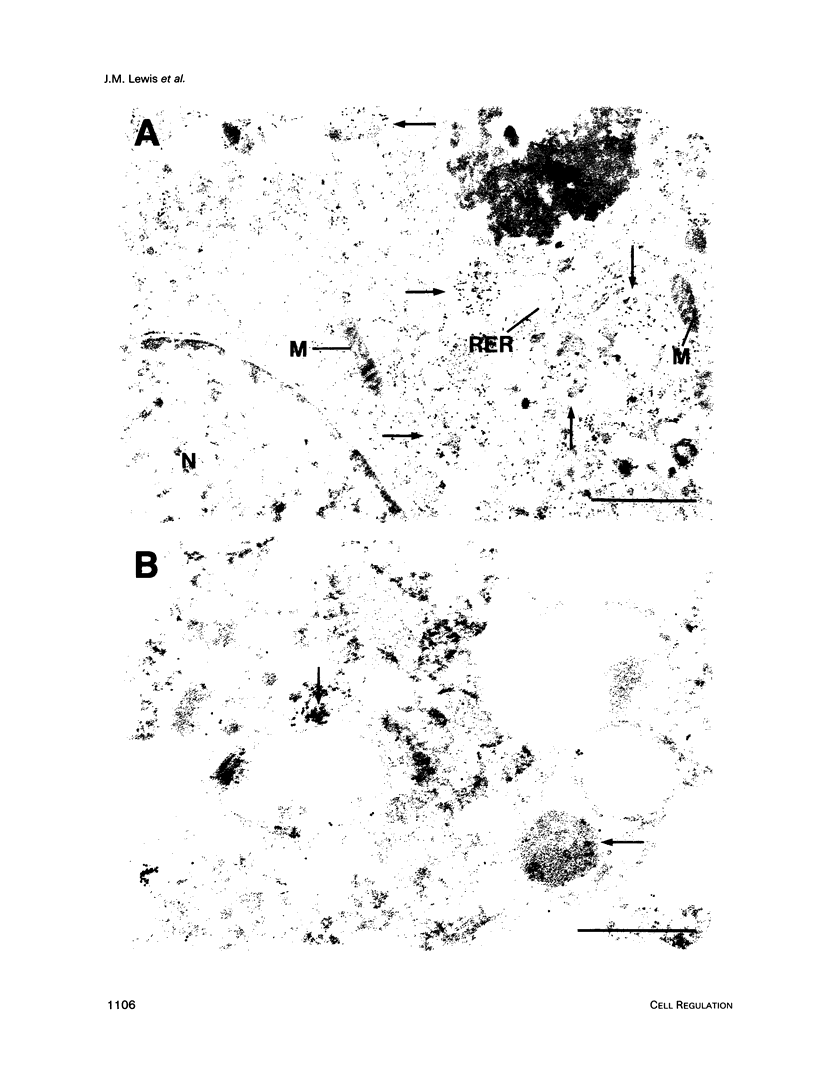
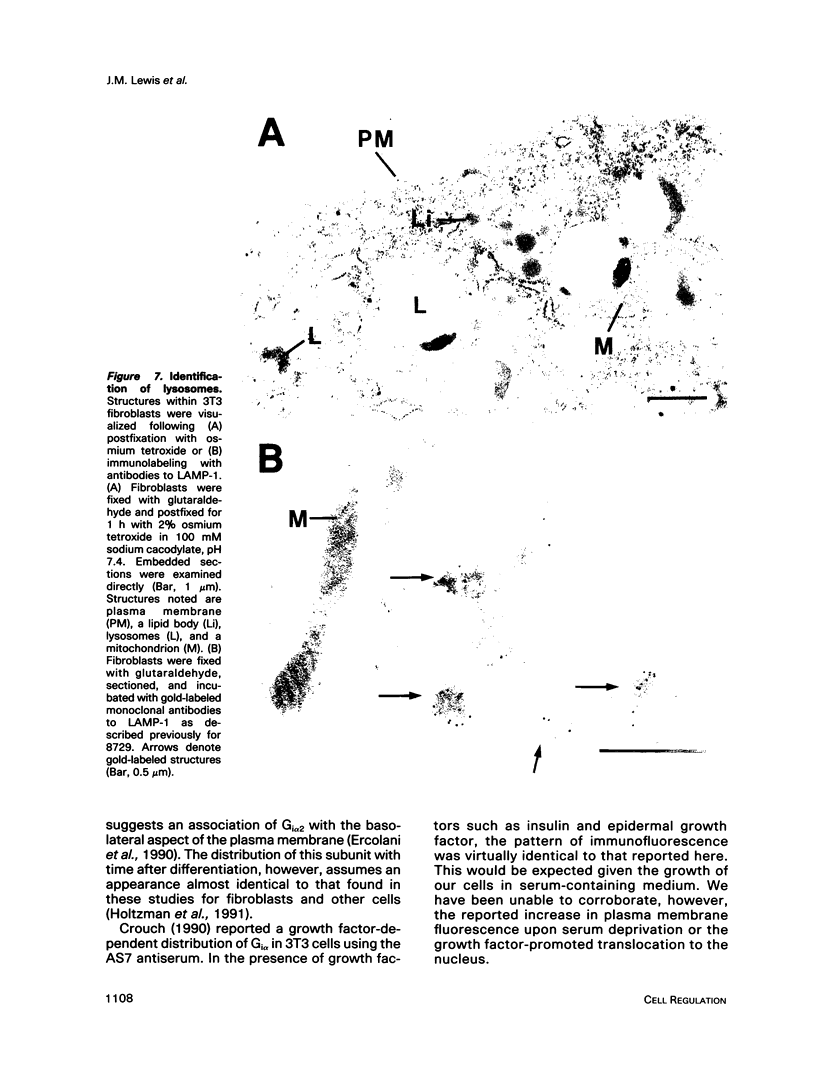
The subcellular distribution of the alpha subunit(s) of Gi has an obvious bearing on the ability of this protein to interact with receptors and targets and on its potential to serve in still unexplored capacities. In this study, we have examined the distribution of Gi alpha by means of light and electron microscopy. The cells employed were mouse 3T3 fibroblasts, normal rat kidney fibroblasts, rat C6 glioma cells, human umbilical vein endothelial cells, and human 293 kidney fibroblasts. By indirect immunofluorescence, two patterns of Gi alpha were evident. The more prominent was that associated with phase-dense, cytoplasmic structures exhibiting a tubule-like morphology. A similar distribution was noted for mitochondria, indicating attachment to a subset of microtubules. The second pattern appeared as a diffuse, particulate fluorescence associated with the plasma membrane. By immunogold labeling and electron microscopy, two populations of Gi alpha were again evident. In this instance, labeling of the plasma membrane was the more prominent. Gold particles were most often evenly distributed along the plasma membrane and were concentrated along microspikes. The second, less abundant population of Gi alpha represented the subunit (or fragments) within lysosomes. Specificity in immunolabeling was confirmed in all instances by immunotransfer blotting, the use of antibodies differing in specificities for epitopes within Gi alpha, the absence of labeling with preimmune sera, and the decrease in labeling after preincubation of antisera with appropriate peptides. These results support the proposal that several populations of Gi alpha exist: those evident within the cytoplasm by immunofluorescence, those present at the plasma membrane, and those evident within lysosomes by immunogold labeling.
Full text
PDF










Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asano T., Nagahama M., Kato K. Subcellular distribution of GTP-binding proteins, Go and Gi2, in rat cerebral cortex. J Biochem. 1990 May;107(5):694–698. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Audigier Y., Nigam S. K., Blobel G. Identification of a G protein in rough endoplasmic reticulum of canine pancreas. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16352–16357. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch W. E. Biochemistry of interorganelle transport. A new frontier in enzymology emerges from versatile in vitro model systems. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):16965–16968. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnbaumer L. G proteins in signal transduction. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 1990;30:675–705. doi: 10.1146/annurev.pa.30.040190.003331. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Bickford K., Bohl B. P. Subcellular localization and quantitation of the major neutrophil pertussis toxin substrate, Gn. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):1927–1936. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.1927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Katada T., Northup J. K., Ui M., Gilman A. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3560–3567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brass L. F., Woolkalis M. J., Manning D. R. Interactions in platelets between G proteins and the agonists that stimulate phospholipase C and inhibit adenylyl cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 15;263(11):5348–5355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buss J. E., Mumby S. M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G., Sefton B. M. Myristoylated alpha subunits of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7493–7497. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson K. E., Brass L. F., Manning D. R. Thrombin and phorbol esters cause the selective phosphorylation of a G protein other than Gi in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1989 Aug 5;264(22):13298–13305. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson K. E., Woolkalis M. J., Newhouse M. G., Manning D. R. Fractionation of the beta subunit common to guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins with the cytoskeleton. Mol Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;30(5):463–468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Connolly T., Gilmore R. The signal recognition particle receptor mediates the GTP-dependent displacement of SRP from the signal sequence of the nascent polypeptide. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):599–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90129-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crouch M. F. Growth factor-induced cell division is paralleled by translocation of Gi alpha to the nucleus. FASEB J. 1991 Feb;5(2):200–206. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.5.2.1900794. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croze E., Ivanov I. E., Kreibich G., Adesnik M., Sabatini D. D., Rosenfeld M. G. Endolyn-78, a membrane glycoprotein present in morphologically diverse components of the endosomal and lysosomal compartments: implications for lysosome biogenesis. J Cell Biol. 1989 May;108(5):1597–1613. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.5.1597. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Lean A., Stadel J. M., Lefkowitz R. J. A ternary complex model explains the agonist-specific binding properties of the adenylate cyclase-coupled beta-adrenergic receptor. J Biol Chem. 1980 Aug 10;255(15):7108–7117. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ercolani L., Stow J. L., Boyle J. F., Holtzman E. J., Lin H., Grove J. R., Ausiello D. A. Membrane localization of the pertussis toxin-sensitive G-protein subunits alpha i-2 and alpha i-3 and expression of a metallothionein-alpha i-2 fusion gene in LLC-PK1 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jun;87(12):4635–4639. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.12.4635. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falloon J., Malech H., Milligan G., Unson C., Kahn R., Goldsmith P., Spiegel A. Detection of the major pertussis toxin substrate of human leukocytes with antisera raised against synthetic peptides. FEBS Lett. 1986 Dec 15;209(2):352–356. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(86)81141-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freissmuth M., Casey P. J., Gilman A. G. G proteins control diverse pathways of transmembrane signaling. FASEB J. 1989 Aug;3(10):2125–2131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garty N. B., Galiani D., Aharonheim A., Ho Y. K., Phillips D. M., Dekel N., Salomon Y. G-proteins in mammalian gametes: an immunocytochemical study. J Cell Sci. 1988 Sep;91(Pt 1):21–31. doi: 10.1242/jcs.91.1.21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassner M., Jones J., Kligman I., Woolkalis M. J., Gerton G. L., Kopf G. S. Immunocytochemical and biochemical characterization of guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins in mammalian spermatozoa. Dev Biol. 1991 Aug;146(2):438–450. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(91)90245-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein S., Korczack L. B. Status of mitochondria in living human fibroblasts during growth and senescence in vitro: use of the laser dye rhodamine 123. J Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;91(2 Pt 1):392–398. doi: 10.1083/jcb.91.2.392. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomperts B. D., Tatham P. E. GTP-binding proteins in the control of exocytosis. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 2):983–992. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonatas J. O., Mezitis S. G., Stieber A., Fleischer B., Gonatas N. K. MG-160. A novel sialoglycoprotein of the medial cisternae of the Golgi apparatus [published eeratum appears in J Biol Chem 1989 Mar 5;264(7):4264]. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):646–653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heine U. I., Burmester J. K., Flanders K. C., Danielpour D., Munoz E. F., Roberts A. B., Sporn M. B. Localization of transforming growth factor-beta 1 in mitochondria of murine heart and liver. Cell Regul. 1991 Jun;2(6):467–477. doi: 10.1091/mbc.2.6.467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heuser J. Changes in lysosome shape and distribution correlated with changes in cytoplasmic pH. J Cell Biol. 1989 Mar;108(3):855–864. doi: 10.1083/jcb.108.3.855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinton D. R., Blanks J. C., Fong H. K., Casey P. J., Hildebrandt E., Simons M. I. Novel localization of a G protein, Gz-alpha, in neurons of brain and retina. J Neurosci. 1990 Aug;10(8):2763–2770. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.10-08-02763.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D., Nuñez G., Milliman C., Schreiber R. D., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):334–336. doi: 10.1038/348334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtzman E. J., Soper B. W., Stow J. L., Ausiello D. A., Ercolani L. Regulation of the G-protein alpha i-2 subunit gene in LLC-PK1 renal cells and isolation of porcine genomic clones encoding the gene promoter. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jan 25;266(3):1763–1771. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huff R. M., Axton J. M., Neer E. J. Physical and immunological characterization of a guanine nucleotide-binding protein purified from bovine cerebral cortex. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10864–10871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Insel P. A., Koachman A. M. Cytochalasin B enhances hormone and cholera toxin-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation in S49 lymphoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9717–9723. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaffe E. A., Nachman R. L., Becker C. G., Minick C. R. Culture of human endothelial cells derived from umbilical veins. Identification by morphologic and immunologic criteria. J Clin Invest. 1973 Nov;52(11):2745–2756. doi: 10.1172/JCI107470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jesaitis A. J., Tolley J. O., Bokoch G. M., Allen R. A. Regulation of chemoattractant receptor interaction with transducing proteins by organizational control in the plasma membrane of human neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):2783–2790. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.2783. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones D. T., Reed R. R. Molecular cloning of five GTP-binding protein cDNA species from rat olfactory neuroepithelium. J Biol Chem. 1987 Oct 15;262(29):14241–14249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones T. L., Simonds W. F., Merendino J. J., Jr, Brann M. R., Spiegel A. M. Myristoylation of an inhibitory GTP-binding protein alpha subunit is essential for its membrane attachment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):568–572. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Bokoch G. M., Smigel M. D., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Subunit dissociation and the inhibition of adenylate cyclase in S49 lymphoma cyc- and wild type membranes. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3586–3595. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Oinuma M., Ui M. Mechanisms for inhibition of the catalytic activity of adenylate cyclase by the guanine nucleotide-binding proteins serving as the substrate of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1986 Apr 15;261(11):5215–5221. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy M. S., Insel P. A. Inhibitors of microtubule assembly enhance beta-adrenergic and prostaglandin E1-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation in S49 lymphoma cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 Jul;16(1):215–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Law S. F., Manning D., Reisine T. Identification of the subunits of GTP-binding proteins coupled to somatostatin receptors. J Biol Chem. 1991 Sep 25;266(27):17885–17897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C., Chen L. B. Dynamic behavior of endoplasmic reticulum in living cells. Cell. 1988 Jul 1;54(1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90177-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerea C. L., Somers D. E., Hurley J. B., Klock I. B., Bunt-Milam A. H. Identification of specific transducin alpha subunits in retinal rod and cone photoreceptors. Science. 1986 Oct 3;234(4772):77–80. doi: 10.1126/science.3529395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linder M. E., Ewald D. A., Miller R. J., Gilman A. G. Purification and characterization of Go alpha and three types of Gi alpha after expression in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8243–8251. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melançon P., Glick B. S., Malhotra V., Weidman P. J., Serafini T., Gleason M. L., Orci L., Rothman J. E. Involvement of GTP-binding "G" proteins in transport through the Golgi stack. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1053–1062. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90591-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mumby S. M., Heukeroth R. O., Gordon J. I., Gilman A. G. G-protein alpha-subunit expression, myristoylation, and membrane association in COS cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Jan;87(2):728–732. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.2.728. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neubig R. R., Gantzos R. D., Brasier R. S. Agonist and antagonist binding to alpha 2-adrenergic receptors in purified membranes from human platelets. Implications of receptor-inhibitory nucleotide-binding protein stoichiometry. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Nov;28(5):475–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phaire-Washington L., Silverstein S. C., Wang E. Phorbol myristate acetate stimulates microtubule and 10-nm filament extension and lysosome redistribution in mouse macrophages. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):641–655. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.641. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Péraldi S., Nguyen Than Dao B., Brabet P., Homburger V., Rouot B., Toutant M., Bouille C., Assenmacher I., Bockaert J., Gabrion J. Apical localization of the alpha subunit of GTP-binding protein Go in choroidal and ciliated ependymocytes. J Neurosci. 1989 Mar;9(3):806–814. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.09-03-00806.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rinnerthaler G., Geiger B., Small J. V. Contact formation during fibroblast locomotion: involvement of membrane ruffles and microtubules. J Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;106(3):747–760. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.3.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross E. M., Gilman A. G. Biochemical properties of hormone-sensitive adenylate cyclase. Annu Rev Biochem. 1980;49:533–564. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.002533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotrosen D., Gallin J. I., Spiegel A. M., Malech H. L. Subcellular localization of Gi alpha in human neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1988 Aug 5;263(22):10958–10964. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scherer N. M., Toro M. J., Entman M. L., Birnbaumer L. G-protein distribution in canine cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum and sarcolemma: comparison to rabbit skeletal muscle membranes and to brain and erythrocyte G-proteins. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1987 Dec;259(2):431–440. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(87)90509-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schroer T. A., Kelly R. B. In vitro translocation of organelles along microtubules. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):729–730. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90329-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sibley D. R., Benovic J. L., Caron M. G., Lefkowitz R. J. Regulation of transmembrane signaling by receptor phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):913–922. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90700-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slot J. W., Geuze H. J. A new method of preparing gold probes for multiple-labeling cytochemistry. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Jul;38(1):87–93. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C. The purified alpha subunits of Go and Gi from bovine brain require beta gamma for association with phospholipid vesicles. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):631–637. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Storrie B., Madden E. A. Isolation of subcellular organelles. Methods Enzymol. 1990;182:203–225. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)82018-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strittmatter S. M., Valenzuela D., Kennedy T. E., Neer E. J., Fishman M. C. G0 is a major growth cone protein subject to regulation by GAP-43. Nature. 1990 Apr 26;344(6269):836–841. doi: 10.1038/344836a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan S. J., Daukas G., Zigmond S. H. Asymmetric distribution of the chemotactic peptide receptor on polymorphonuclear leukocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1461–1467. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1461. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson J., Bushnell A., Silverstein S. C. Tubular lysosome morphology and distribution within macrophages depend on the integrity of cytoplasmic microtubules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1921–1925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor S. J., Chae H. Z., Rhee S. G., Exton J. H. Activation of the beta 1 isozyme of phospholipase C by alpha subunits of the Gq class of G proteins. Nature. 1991 Apr 11;350(6318):516–518. doi: 10.1038/350516a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldo G. L., Northup J. K., Perkins J. P., Harden T. K. Characterization of an altered membrane form of the beta-adrenergic receptor produced during agonist-induced desensitization. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13900–13908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang N., Yan K., Rasenick M. M. Tubulin binds specifically to the signal-transducing proteins, Gs alpha and Gi alpha 1. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jan 25;265(3):1239–1242. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilde M. W., Carlson K. E., Manning D. R., Zigmond S. H. Chemoattractant-stimulated GTPase activity is decreased on membranes from polymorphonuclear leukocytes incubated in chemoattractant. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jan 5;264(1):190–196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. G., Woolkalis M. J., Poncz M., Manning D. R., Gewirtz A. M., Brass L. F. Identification of the pertussis toxin-sensitive G proteins in platelets, megakaryocytes, and human erythroleukemia cells. Blood. 1990 Aug 15;76(4):721–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolkalis M. J., Nakada M. T., Manning D. R. Alterations in components of adenylate cyclase associated with transformation of chicken embryo fibroblasts by Rous sarcoma virus. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3408–3413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]