Abstract
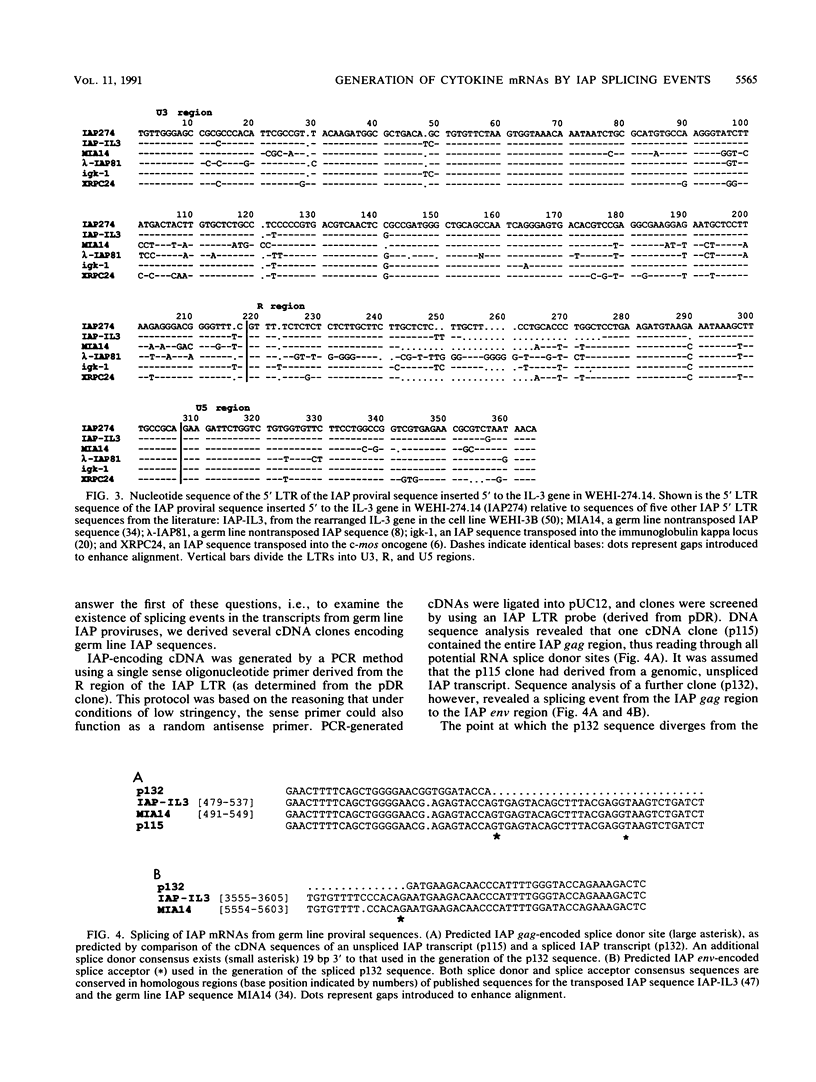
Previously we have described the derivation of three distinct classes of leukemic cell clones from a single in vivo-passaged myelomonocytic leukemia, WEHI-274, that arose in a mouse infected with the Abelson leukemia virus/Moloney leukemia virus complex (K. B. Leslie and J. W. Schrader, Mol. Cell. Biol. 9:2414-2423, 1989). The three classes of cell clones were characterized by distinct patterns of growth in vitro, the production of cytokines, and the presence of cytokine gene rearrangements. However, all three classes of WEHI-274 clones bore a common rearrangement of the c-myb gene, suggesting that all were derived from the one ancestral cell and that at least three distinct and independent autostimulatory events were involved in the progression of a single myeloid leukemic disease. In this article, we demonstrate that the autocrine growth factor production by the WEHI-274 leukemic clones resulted from cytokine gene activations mediated by the insertion of an intracisternal A-type particle (IAP) sequence 5' to the interleukin-3 (IL-3) gene, in the case of the class I clone, or 5' to the gene for granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor (GM-CSF), in the case of the class II clones. IAPs are defective murine retroviruses encoded by endogenous genetic elements which may undergo transpositions and act as endogenous mutagens. The functional IL-3 and GM-CSF mRNAs were generated by mechanisms in which the splice donor apparatus of the IAP sequence has been used in IAP gag-to-IL-3 or -GM-CSF splicing events.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Augenlicht L. H., Kobrin D., Pavlovec A., Royston M. E. Elevated expression of an endogenous retroviral long terminal repeat in a mouse colon tumor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 10;259(3):1842–1847. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baumbach W. R., Stanley E. R., Cole M. D. Induction of clonal monocyte-macrophage tumors in vivo by a mouse c-myc retrovirus: rearrangement of the CSF-1 gene as a secondary transforming event. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):664–671. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.664. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blankenstein T., Qin Z. H., Li W. Q., Diamantstein T. DNA rearrangement and constitutive expression of the interleukin 6 gene in a mouse plasmacytoma. J Exp Med. 1990 Mar 1;171(3):965–970. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.3.965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blatt C., Aberdam D., Schwartz R., Sachs L. DNA rearrangement of a homeobox gene in myeloid leukaemic cells. EMBO J. 1988 Dec 20;7(13):4283–4290. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03326.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burt D. W., Reith A. D., Brammar W. J. A retroviral provirus closely associated with the Ren-2 gene of DBA/2 mice. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8579–8593. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8579. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Canaani E., Dreazen O., Klar A., Rechavi G., Ram D., Cohen J. B., Givol D. Activation of the c-mos oncogene in a mouse plasmacytoma by insertion of an endogenous intracisternal A-particle genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(23):7118–7122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.23.7118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy R. J., Brown A. R., Gourlie B. B., Huang R. C. Nucleotide sequences of murine intracisternal A-particle gene LTRs have extensive variability within the R region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Jan 11;13(1):289–302. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.1.289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christy R. J., Huang R. C. Functional analysis of the long terminal repeats of intracisternal A-particle genes: sequences within the U3 region determine both the efficiency and direction of promoter activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1093–1102. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1093. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. B., Unger T., Rechavi G., Canaani E., Givol D. Rearrangement of the oncogene c-mos in mouse myeloma NSI and hybridomas. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):797–799. doi: 10.1038/306797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dührsen U., Stahl J., Gough N. M. In vivo transformation of factor-dependent hemopoietic cells: role of intracisternal A-particle transposition for growth factor gene activation. EMBO J. 1990 Apr;9(4):1087–1096. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08214.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falzon M., Kuff E. L. A variant binding sequence for transcription factor EBP-80 confers increased promoter activity on a retroviral long terminal repeat. J Biol Chem. 1990 Aug 5;265(22):13084–13090. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falzon M., Kuff E. L. Isolation and characterization of a protein fraction that binds to enhancer core sequences in intracisternal A-particle long terminal repeats. J Biol Chem. 1989 Dec 25;264(36):21915–21922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falzon M., Kuff E. L. Multiple protein-binding sites in an intracisternal A particle long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1988 Nov;62(11):4070–4077. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4070-4077.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feenstra A., Fewell J., Lueders K., Kuff E. In vitro methylation inhibits the promotor activity of a cloned intracisternal A-particle LTR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 27;14(10):4343–4352. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.10.4343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel W. N., Potter T. A., Rajan T. V. Effect of proviral insertion on transcription of the murine B2mb gene. J Virol. 1989 Jun;63(6):2623–2628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.63.6.2623-2628.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gattoni-Celli S., Hsiao W. L., Weinstein I. B. Rearranged c-mos locus in a MOPC 21 murine myeloma cell line and its persistence in hybridomas. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):795–796. doi: 10.1038/306795a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda T. J., Cory S., Sobieszczuk P., Holtzman D., Adams J. M. Generation of altered transcripts by retroviral insertion within the c-myb gene in two murine monocytic leukemias. J Virol. 1987 Sep;61(9):2754–2763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.9.2754-2763.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M., Metcalf D., Gough J., Grail D., Dunn A. R. Structure and expression of the mRNA for murine granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):645–653. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawley R. G., Shulman M. J., Hozumi N. Transposition of two different intracisternal A particle elements into an immunoglobulin kappa-chain gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2565–2572. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2565. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Howe C. C., Overton G. C. Expression of the intracisternal A-particle is elevated during differentiation of embryonal carcinoma cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jan;6(1):150–157. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.1.150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kongsuwan K., Allen J., Adams J. M. Expression of Hox-2.4 homeobox gene directed by proviral insertion in a myeloid leukemia. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Mar 11;17(5):1881–1892. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.5.1881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kono T., Doi T., Yamada G., Hatakeyama M., Minamoto S., Tsudo M., Miyasaka M., Miyata T., Taniguchi T. Murine interleukin 2 receptor beta chain: dysregulated gene expression in lymphoma line EL-4 caused by a promoter insertion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1806–1810. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Feenstra A., Lueders K., Smith L., Hawley R., Hozumi N., Shulman M. Intracisternal A-particle genes as movable elements in the mouse genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1992–1996. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuff E. L., Lueders K. K. The intracisternal A-particle gene family: structure and functional aspects. Adv Cancer Res. 1988;51:183–276. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60223-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laker C., Stocking C., Bergholz U., Hess N., De Lamarter J. F., Ostertag W. Autocrine stimulation after transfer of the granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor gene and autonomous growth are distinct but interdependent steps in the oncogenic pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8458–8462. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leslie K. B., Schrader J. W. Growth factor gene activation and clonal heterogeneity in an autostimulatory myeloid leukemia. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2414–2423. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2414. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lesser J., Lasneret J., Canivet M., Emanoil-Ravier R., Périès J. Simultaneous activation by 5-azacytidine of intracisternal R particles and murine intracisternal-A particle related sequences in Syrian hamster cells. Virology. 1986 Nov;155(1):249–256. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90184-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. Intracisternal A-particle genes: identification in the genome of Mus musculus and comparison of multiple isolates from a mouse gene library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3571–3575. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3571. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luria S., Horowitz M. The long terminal repeat of the intracisternal A particle as a target for transactivation by oncogene products. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):998–1003. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.998-1003.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Man Y. M., Delius H., Leader D. P. Molecular analysis of elements inserted into mouse gamma-actin processed pseudogenes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Apr 24;15(8):3291–3304. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.8.3291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietz J. A., Grossman Z., Lueders K. K., Kuff E. L. Nucleotide sequence of a complete mouse intracisternal A-particle genome: relationship to known aspects of particle assembly and function. J Virol. 1987 Oct;61(10):3020–3029. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.10.3020-3029.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mietz J. A., Kuff E. L. Tissue and strain-specific patterns of endogenous proviral hypomethylation analyzed by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2269–2273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Otsuka T., Yokota T., Lee F., Arai K. Structure of the chromosomal gene for granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor: comparison of the mouse and human genes. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2561–2568. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03971.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyatake S., Yokota T., Lee F., Arai K. Structure of the chromosomal gene for murine interleukin 3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):316–320. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peckham I., Sobel S., Comer J., Jaenisch R., Barklis E. Retrovirus activation in embryonal carcinoma cells by cellular promoters. Genes Dev. 1989 Dec;3(12B):2062–2071. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.12b.2062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rechavi G., Givol D., Canaani E. Activation of a cellular oncogene by DNA rearrangement: possible involvement of an IS-like element. Nature. 1982 Dec 16;300(5893):607–611. doi: 10.1038/300607a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Setoguchi M., Higuchi Y., Yoshida S., Nasu N., Miyazaki Y., Akizuki S., Yamamoto S. Insertional activation of N-myc by endogenous Moloney-like murine retrovirus sequences in macrophage cell lines derived from myeloma cell line-macrophage hybrids. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;9(10):4515–4522. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.10.4515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro M. B., Senapathy P. RNA splice junctions of different classes of eukaryotes: sequence statistics and functional implications in gene expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 11;15(17):7155–7174. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.17.7155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Morse H. C., 3rd, Potter M., Mushinski J. F. Two modes of c-myb activation in virus-induced mouse myeloid tumors. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):380–392. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stocking C., Löliger C., Kawai M., Suciu S., Gough N., Ostertag W. Identification of genes involved in growth autonomy of hematopoietic cells by analysis of factor-independent mutants. Cell. 1988 Jun 17;53(6):869–879. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)90329-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugita T., Totsuka T., Saito M., Yamasaki K., Taga T., Hirano T., Kishimoto T. Functional murine interleukin 6 receptor with the intracisternal A particle gene product at its cytoplasmic domain. Its possible role in plasmacytomagenesis. J Exp Med. 1990 Jun 1;171(6):2001–2009. doi: 10.1084/jem.171.6.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tohyama K., Lee K. H., Tashiro K., Kinashi T., Honjo T. Establishment of an interleukin-5-dependent subclone from an interleukin-3-dependent murine hemopoietic progenitor cell line, LyD9, and its malignant transformation by autocrine secretion of interleukin-5. EMBO J. 1990 Jun;9(6):1823–1830. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08307.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trusko S. P., Hoffman E. K., George D. L. Transcriptional activation of cKi-ras proto-oncogene resulting from retroviral promoter insertion. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Nov 25;17(22):9259–9265. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.22.9259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstein Y., Cleveland J. L., Askew D. S., Rapp U. R., Ihle J. N. Insertion and truncation of c-myb by murine leukemia virus in a myeloid cell line derived from cultures of normal hematopoietic cells. J Virol. 1987 Jul;61(7):2339–2343. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.7.2339-2343.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ymer S., Tucker W. Q., Campbell H. D., Young I. G. Nucleotide sequence of the intracisternal A-particle genome inserted 5' to the interleukin-3 gene of the leukemia cell line WEHI-3B. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5901–5918. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5901. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ymer S., Tucker W. Q., Sanderson C. J., Hapel A. J., Campbell H. D., Young I. G. Constitutive synthesis of interleukin-3 by leukaemia cell line WEHI-3B is due to retroviral insertion near the gene. Nature. 1985 Sep 19;317(6034):255–258. doi: 10.1038/317255a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ziltener H. J., Clark-Lewis I., Hood L. E., Kent S. B., Schrader J. W. Antipeptide antibodies of predetermined specificity recognize and neutralize the bioactivity of the pan-specific hemopoietin interleukin 3. J Immunol. 1987 Feb 15;138(4):1099–1104. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]