Abstract
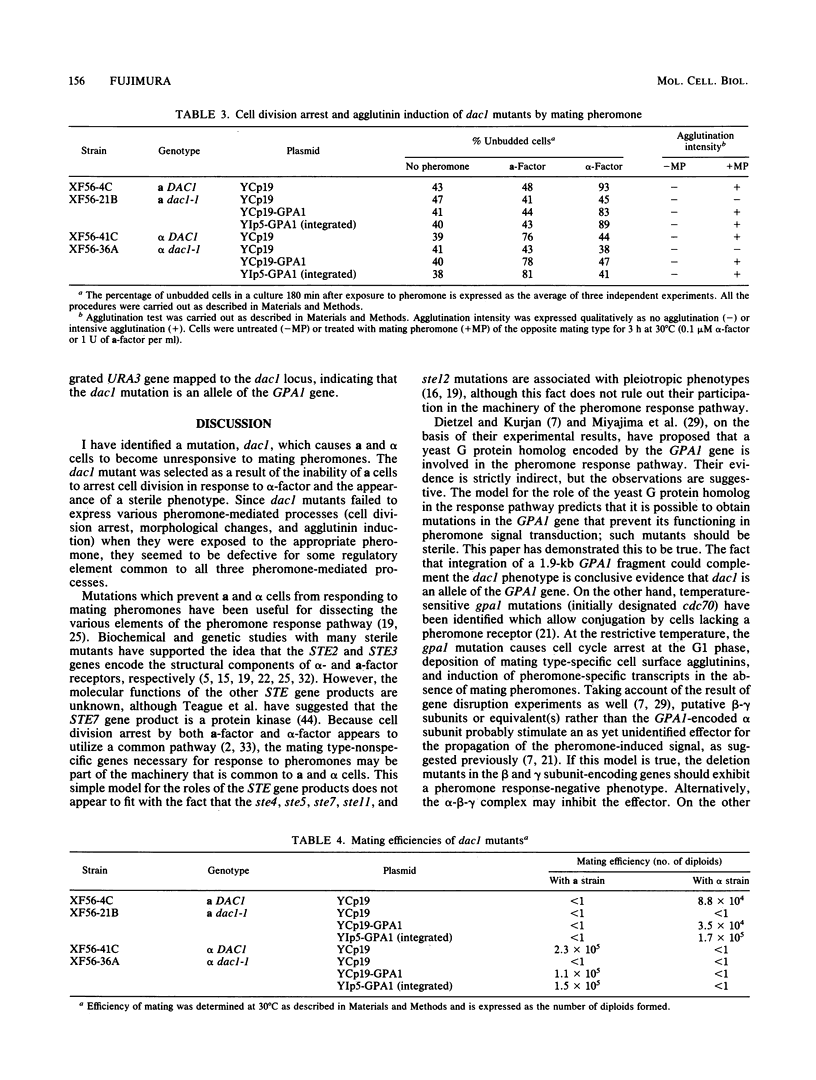
I have isolated a new type of sterile mutant of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, carrying a single mutant allele, designated dac1, which was mapped near the centromere on chromosome VIII. The dac1 mutation caused specific defects in the pheromone responsiveness of both a and alpha cells and did not seem to be associated with any pleiotropic phenotypes. Thus, in contrast to the ste4, ste5, ste7, ste11, and ste12 mutations, the dac1 mutation had no significant effect on such constitutive functions of haploid cells as pheromone production and alpha-factor destruction. The characteristics of this phenotype suggest that the DAC1 gene encodes a component of the pheromone response pathway common to both a and alpha cells. Introduction of the GPA1 gene encoding an S. cerevisiae homolog of the alpha subunit of mammalian guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory proteins (G proteins) into sterile dac1 mutants resulted in restoration of pheromone responsiveness and mating competence to both a and alpha cells. These results suggest that the dac1 mutation is an allele of the GPA1 gene and thus provide genetic evidence that the yeast G protein homolog is directly involved in the mating pheromone signal transduction pathway.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baffi R. A., Shenbagamurthi P., Terrance K., Becker J. M., Naider F., Lipke P. N. Different structure-function relationships for alpha-factor-induced morphogenesis and agglutination in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1152–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1152-1156.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bender A., Sprague G. F., Jr Yeast peptide pheromones, a-factor and alpha-factor, activate a common response mechanism in their target cells. Cell. 1986 Dec 26;47(6):929–937. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90808-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Betz R., MacKay V. L., Duntze W. a-Factor from Saccharomyces cerevisiae: partial characterization of a mating hormone produced by cells of mating type a. J Bacteriol. 1977 Nov;132(2):462–472. doi: 10.1128/jb.132.2.462-472.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkholder A. C., Hartwell L. H. The yeast alpha-factor receptor: structural properties deduced from the sequence of the STE2 gene. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Dec 9;13(23):8463–8475. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.23.8463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bücking-Throm E., Duntze W., Hartwell L. H., Manney T. R. Reversible arrest of haploid yeast cells in the initiation of DNA synthesis by a diffusible sex factor. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Jan;76(1):99–110. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90424-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan R. K., Otte C. A. Isolation and genetic analysis of Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants supersensitive to G1 arrest by a factor and alpha factor pheromones. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Jan;2(1):11–20. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzel C., Kurjan J. Pheromonal regulation and sequence of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae SST2 gene: a model for desensitization to pheromone. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4169–4177. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzel C., Kurjan J. The yeast SCG1 gene: a G alpha-like protein implicated in the a- and alpha-factor response pathway. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1001–1010. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90166-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duntze W., Stötzler D., Bücking-Throm E., Kalbitzer S. Purification and partial characterization of -factor, a mating-type specific inhibitor of cell reproduction from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Eur J Biochem. 1973 Jun;35(2):357–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1973.tb02847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fehrenbacher G., Perry K., Thorner J. Cell-cell recognition in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: regulation of mating-specific adhesion. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):893–901. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.893-901.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fields S., Herskowitz I. The yeast STE12 product is required for expression of two sets of cell-type specific genes. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):923–930. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukui Y., Kozasa T., Kaziro Y., Takeda T., Yamamoto M. Role of a ras homolog in the life cycle of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):329–336. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90767-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins: transducers of receptor-generated signals. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:615–649. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., McCaffrey G., Sprague G. F., Jr Evidence the yeast STE3 gene encodes a receptor for the peptide pheromone a factor: gene sequence and implications for the structure of the presumed receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1418–1422. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1418. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hagen D. C., Sprague G. F., Jr Induction of the yeast alpha-specific STE3 gene by the peptide pheromone a-factor. J Mol Biol. 1984 Oct 5;178(4):835–852. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90314-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartig A., Holly J., Saari G., MacKay V. L. Multiple regulation of STE2, a mating-type-specific gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2106–2114. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae unresponsive to cell division control by polypeptide mating hormone. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jun;85(3):811–822. doi: 10.1083/jcb.85.3.811. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartwell L. H. Synchronization of haploid yeast cell cycles, a prelude to conjugation. Exp Cell Res. 1973 Jan;76(1):111–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(73)90425-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahng K. Y., Ferguson J., Reed S. I. Mutations in a gene encoding the alpha subunit of a Saccharomyces cerevisiae G protein indicate a role in mating pheromone signaling. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2484–2493. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenness D. D., Burkholder A. C., Hartwell L. H. Binding of alpha-factor pheromone to yeast a cells: chemical and genetic evidence for an alpha-factor receptor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):521–529. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90186-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenness D. D., Goldman B. S., Hartwell L. H. Saccharomyces cerevisiae mutants unresponsive to alpha-factor pheromone: alpha-factor binding and extragenic suppression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Apr;7(4):1311–1319. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.4.1311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Powers S., McGill C., Fasano O., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genetic analysis of yeast RAS1 and RAS2 genes. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):437–445. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90374-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackay V., Manney T. R. Mutations affecting sexual conjugation and related processes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Genetic analysis of nonmating mutants. Genetics. 1974 Feb;76(2):273–288. doi: 10.1093/genetics/76.2.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manney T. R., Woods V. Mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae resistant to the alpha mating-type factor. Genetics. 1976 Apr;82(4):639–644. doi: 10.1093/genetics/82.4.639. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey G., Clay F. J., Kelsay K., Sprague G. F., Jr Identification and regulation of a gene required for cell fusion during mating of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2680–2690. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyajima I., Nakafuku M., Nakayama N., Brenner C., Miyajima A., Kaibuchi K., Arai K., Kaziro Y., Matsumoto K. GPA1, a haploid-specific essential gene, encodes a yeast homolog of mammalian G protein which may be involved in mating factor signal transduction. Cell. 1987 Sep 25;50(7):1011–1019. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90167-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore S. A. Comparison of dose-response curves for alpha factor-induced cell division arrest, agglutination, and projection formation of yeast cells. Implication for the mechanism of alpha factor action. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13849–13856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakafuku M., Itoh H., Nakamura S., Kaziro Y. Occurrence in Saccharomyces cerevisiae of a gene homologous to the cDNA coding for the alpha subunit of mammalian G proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(8):2140–2144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.8.2140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama N., Miyajima A., Arai K. Common signal transduction system shared by STE2 and STE3 in haploid cells of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: autocrine cell-cycle arrest results from forced expression of STE2. EMBO J. 1987 Jan;6(1):249–254. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04746.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakayama N., Miyajima A., Arai K. Nucleotide sequences of STE2 and STE3, cell type-specific sterile genes from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2643–2648. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03982.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose M. D., Price B. R., Fink G. R. Saccharomyces cerevisiae nuclear fusion requires prior activation by alpha factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3490–3497. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakai K., Yanagishima N. Mating reaction in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. II. Hormonal regulation of agglutinability of a type cells. Arch Mikrobiol. 1972;84(3):191–198. doi: 10.1007/BF00425197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salminen A., Novick P. J. A ras-like protein is required for a post-Golgi event in yeast secretion. Cell. 1987 May 22;49(4):527–538. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90455-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmitt H. D., Wagner P., Pfaff E., Gallwitz D. The ras-related YPT1 gene product in yeast: a GTP-binding protein that might be involved in microtubule organization. Cell. 1986 Nov 7;47(3):401–412. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90597-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segev N., Botstein D. The ras-like yeast YPT1 gene is itself essential for growth, sporulation, and starvation response. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2367–2377. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2367. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprague G. F., Jr, Herskowitz I. Control of yeast cell type by the mating type locus. I. Identification and control of expression of the a-specific gene BAR1. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 5;153(2):305–321. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90280-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinchcomb D. T., Mann C., Davis R. W. Centromeric DNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 25;158(2):157–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90427-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K., Stinchcomb D. T., Scherer S., Davis R. W. High-frequency transformation of yeast: autonomous replication of hybrid DNA molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1035–1039. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teague M. A., Chaleff D. T., Errede B. Nucleotide sequence of the yeast regulatory gene STE7 predicts a protein homologous to protein kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Oct;83(19):7371–7375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.19.7371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Throm E., Duntze W. Mating-Type-Dependent Inhibition of Deoxyribonucleic Acid Synthesis in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1388–1390. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1388-1390.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Uno I., Ishikawa T., Powers S., Kataoka T., Broek D., Cameron S., Broach J., Matsumoto K., Wigler M. In yeast, RAS proteins are controlling elements of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trueheart J., Boeke J. D., Fink G. R. Two genes required for cell fusion during yeast conjugation: evidence for a pheromone-induced surface protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2316–2328. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2316. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson L. E., Pringle J. R. Transient G1 arrest of S. cerevisiae cells of mating type alpha by a factor produced by cells of mating type a. Exp Cell Res. 1974 Nov;89(1):175–187. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(74)90200-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]