Abstract
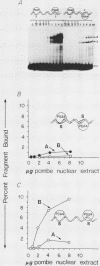
When the DNA-binding site for the Saccharomyces cerevisiae transcription activator GAL4 is placed upstream of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe ADH1 TATA box, transcription of the ADH1 gene is activated in S. pombe in vivo by an endogenous transcription factor. In vitro studies show that this S. pombe protein, PGA4, binds specifically to DNA containing a GAL4 site and that when two GAL4 sites are present, this protein binds cooperatively. Cooperating binding of PGA4 to DNA is favored if the GAL4 sites are separated by an integral number of turns of the DNA helix.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Giniger E., Ptashne M. Cooperative DNA binding of the yeast transcriptional activator GAL4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jan;85(2):382–386. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.2.382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harshman K. D., Moye-Rowley W. S., Parker C. S. Transcriptional activation by the SV40 AP-1 recognition element in yeast is mediated by a factor similar to AP-1 that is distinct from GCN4. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90393-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horikoshi M., Carey M. F., Kakidani H., Roeder R. G. Mechanism of action of a yeast activator: direct effect of GAL4 derivatives on mammalian TFIID-promoter interactions. Cell. 1988 Aug 26;54(5):665–669. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(88)80011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston M. A model fungal gene regulatory mechanism: the GAL genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Dec;51(4):458–476. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.4.458-476.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones R. H., Moreno S., Nurse P., Jones N. C. Expression of the SV40 promoter in fission yeast: identification and characterization of an AP-1-like factor. Cell. 1988 May 20;53(4):659–667. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90581-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonardo J. M., Bhairi S. M., Dickson R. C. Identification of upstream activator sequences that regulate induction of the beta-galactosidase gene in Kluyveromyces lactis. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4369–4376. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma J., Ptashne M. Deletion analysis of GAL4 defines two transcriptional activating segments. Cell. 1987 Mar 13;48(5):847–853. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90081-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruden D. M., Ma J., Ptashne M. No strict alignment is required between a transcriptional activator binding site and the "TATA box" of a yeast gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4262–4266. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4262. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P. R. Evolutionary divergence of the mRNA transcription initiation mechanism in yeast. Nature. 1983 Jan 13;301(5896):167–169. doi: 10.1038/301167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P. R., Hall B. D. The primary structure of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene from the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):143–149. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruzzi M., Breunig K. D., Ficca A. G., Hollenberg C. P. Positive regulation of the beta-galactosidase gene from Kluyveromyces lactis is mediated by an upstream activation site that shows homology to the GAL upstream activation site of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Mar;7(3):991–997. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.3.991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh H., Sen R., Baltimore D., Sharp P. A. A nuclear factor that binds to a conserved sequence motif in transcriptional control elements of immunoglobulin genes. Nature. 1986 Jan 9;319(6049):154–158. doi: 10.1038/319154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struhl K. Promoters, activator proteins, and the mechanism of transcriptional initiation in yeast. Cell. 1987 May 8;49(3):295–297. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thireos G., Penn M. D., Greer H. 5' untranslated sequences are required for the translational control of a yeast regulatory gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5096–5100. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5096. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Adachi Y., Hiraoka Y., Yanagida M. Identification of the pleiotropic cell division cycle gene NDA2 as one of two different alpha-tubulin genes in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):233–242. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90319-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Topol J., Ruden D. M., Parker C. S. Sequences required for in vitro transcriptional activation of a Drosophila hsp 70 gene. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):527–537. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90110-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster N., Jin J. R., Green S., Hollis M., Chambon P. The yeast UASG is a transcriptional enhancer in human HeLa cells in the presence of the GAL4 trans-activator. Cell. 1988 Jan 29;52(2):169–178. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90505-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]