Abstract
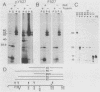
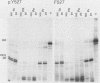
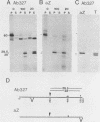
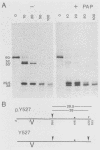
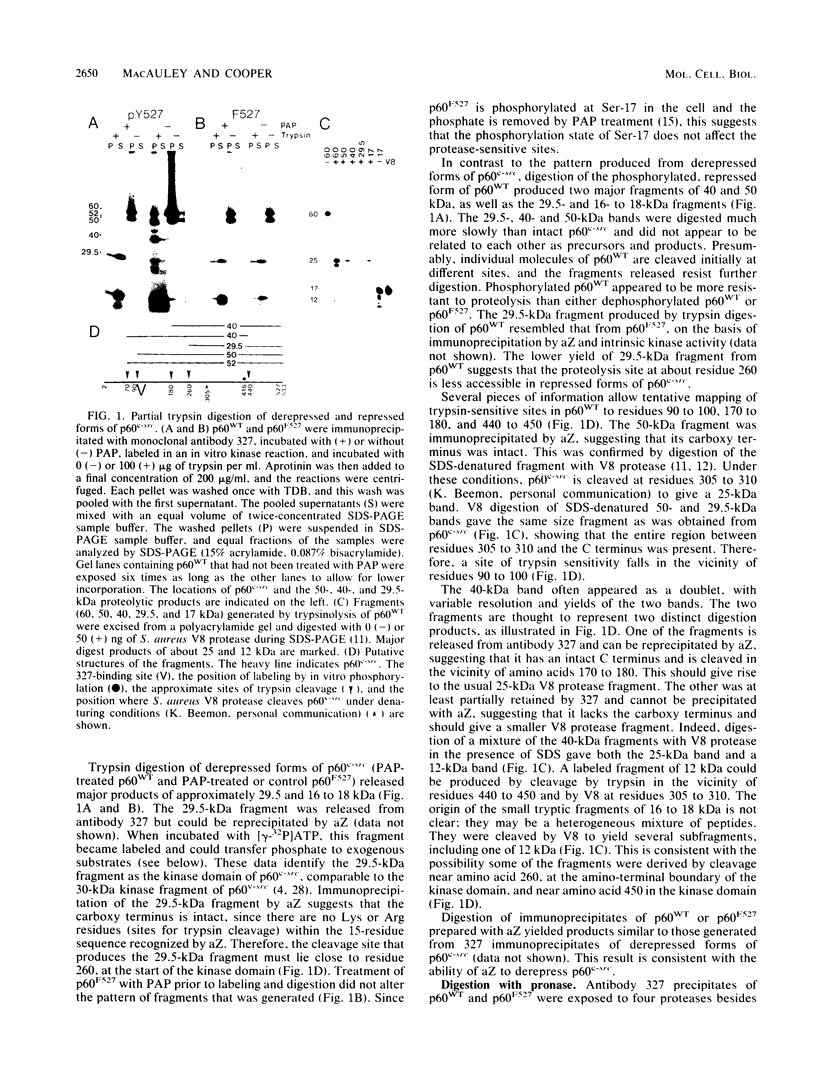
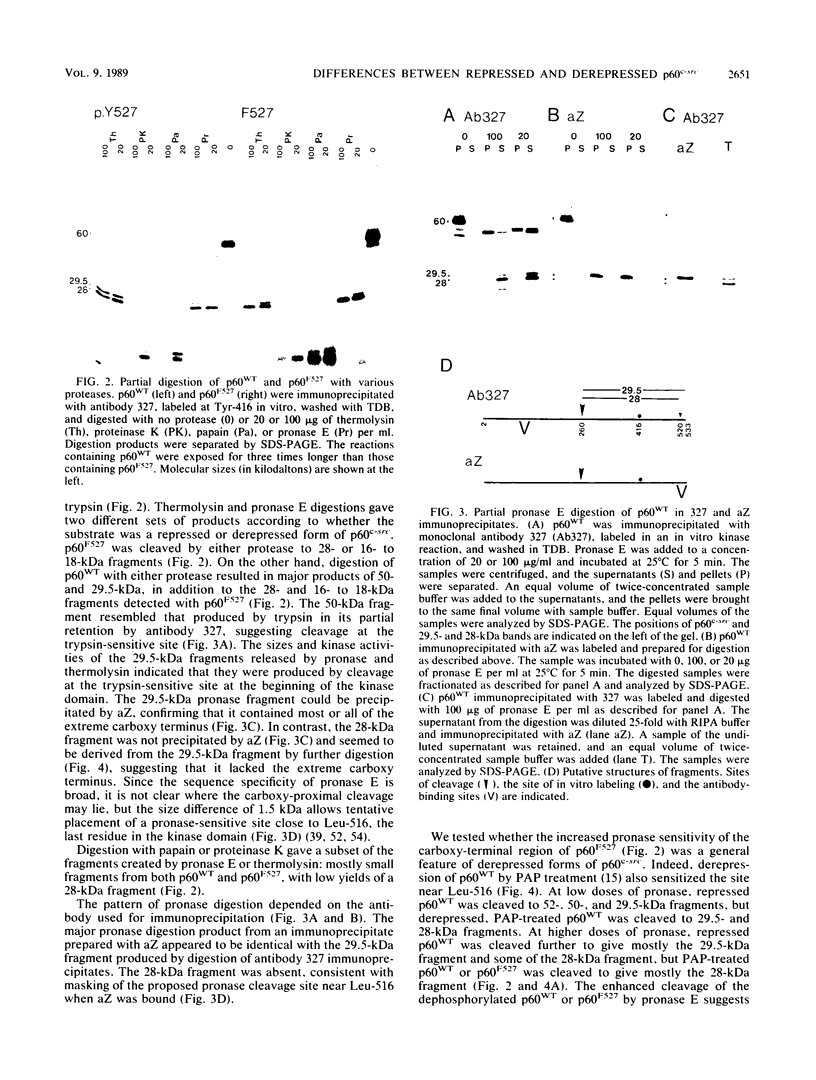
The kinase activity of p60c-src is derepressed by removal of phosphate from Tyr-527, mutation of this residue to Phe, or binding of a carboxy-terminal antibody. We have compared the structures of repressed and active p60c-src, using proteases. All forms of p60c-src are susceptible to proteolysis at the boundary between the amino-terminal region and the kinase domain, but there are several sites elsewhere that are more sensitive to trypsin digestion in repressed than in derepressed forms of p60c-src. The carboxy-terminal tail (containing Tyr-527) is more sensitive to digestion by pronase E and thermolysin when Tyr-527 is not phosphorylated. The kinase domain fragment released with trypsin has kinase activity. Relative to intact p60c-src, the kinase domain fragment shows altered substrate specificity, diminished regulation by the phosphorylated carboxy terminus, and novel phosphorylation sites. The results identify parts of p60c-src that change conformation upon kinase activation and suggest functions for the amino-terminal region.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basu M., Biswas R., Das M. 42,000-molecular weight EGF receptor has protein kinase activity. Nature. 1984 Oct 4;311(5985):477–480. doi: 10.1038/311477a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beemon K., Hunter T. Characterization of Rous sarcoma virus src gene products synthesized in vitro. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):551–566. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.551-566.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Thiele C. J., Israel M. A., Yonemoto W., Lipsich L. A., Brugge J. S. Enhancement of cellular src gene product associated tyrosyl kinase activity following polyoma virus infection and transformation. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):767–777. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90272-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brugge J. S., Darrow D. Analysis of the catalytic domain of phosphotransferase activity of two avian sarcoma virus-transforming proteins. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 10;259(7):4550–4557. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant D. L., Parsons J. T. Amino acid alterations within a highly conserved region of the Rous sarcoma virus src gene product pp60src inactivate tyrosine protein kinase activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 May;4(5):862–866. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.5.862. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryant D., Parsons J. T. Site-directed point mutation in the src gene oF rous sarcoma virus results in an inactive src gene product. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1211–1216. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1211-1216.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Eckhart W., Simon S., Kaplan P. L. Cell transformation by pp60c-src mutated in the carboxy-terminal regulatory domain. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):83–91. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90758-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright C. A., Kaplan P. L., Cooper J. A., Hunter T., Eckhart W. Altered sites of tyrosine phosphorylation in pp60c-src associated with polyomavirus middle tumor antigen. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1562–1570. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1562. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng S. H., Piwnica-Worms H., Harvey R. W., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E. The carboxy terminus of pp60c-src is a regulatory domain and is involved in complex formation with the middle-T antigen of polyomavirus. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1736–1747. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chinkers M., Brugge J. S. Characterization of structural domains of the human epidermal growth factor receptor obtained by partial proteolysis. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11534–11542. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collett M. S., Erikson E., Erikson R. L. Structural analysis of the avian sarcoma virus transforming protein: sites of phosphorylation. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):770–781. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.770-781.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Gould K. L., Cartwright C. A., Hunter T. Tyr527 is phosphorylated in pp60c-src: implications for regulation. Science. 1986 Mar 21;231(4744):1431–1434. doi: 10.1126/science.2420005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., King C. S. Dephosphorylation or antibody binding to the carboxy terminus stimulates pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4467–4477. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., MacAuley A. Potential positive and negative autoregulation of p60c-src by intermolecular autophosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jun;85(12):4232–4236. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.12.4232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Runge K. Avian pp60c-src is more active when expressed in yeast than in vertebrate fibroblasts. Oncogene Res. 1987 Sep-Oct;1(4):297–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtneidge S. A. Activation of the pp60c-src kinase by middle T antigen binding or by dephosphorylation. EMBO J. 1985 Jun;4(6):1471–1477. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03805.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis L., Clauser E., Morgan D. O., Edery M., Roth R. A., Rutter W. J. Replacement of insulin receptor tyrosine residues 1162 and 1163 compromises insulin-stimulated kinase activity and uptake of 2-deoxyglucose. Cell. 1986 Jun 6;45(5):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90786-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Kornbluth S., Hanafusa H. Enzymatically inactive p60c-src mutant with altered ATP-binding site is fully phosphorylated in its carboxy-terminal regulatory region. Cell. 1987 Sep 11;50(6):937–943. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90520-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Mayer B. J., Iba H., Laugier D., Poirier F., Calothy G., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Genetic analysis of p60v-src domains involved in the induction of different cell transformation parameters. J Virol. 1986 Dec;60(3):840–848. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.3.840-848.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato J. Y., Takeya T., Grandori C., Iba H., Levy J. B., Hanafusa H. Amino acid substitutions sufficient to convert the nontransforming p60c-src protein to a transforming protein. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4155–4160. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Yoshida M. Small deletion in src of Rous sarcoma virus modifying transformation phenotypes: identification of 207-nucleotide deletion and its smaller product with protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):985–992. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.985-992.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Johnson P. J., Shalloway D. Regulation by the autophosphorylation site in overexpressed pp60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4541–4546. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kmiecik T. E., Shalloway D. Activation and suppression of pp60c-src transforming ability by mutation of its primary sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):65–73. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90756-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laudano A. P., Buchanan J. M. Phosphorylation of tyrosine in the carboxyl-terminal tryptic peptide of pp60c-src. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):892–896. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levinson A. D., Courtneidge S. A., Bishop J. M. Structural and functional domains of the Rous sarcoma virus transforming protein (pp60src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1624–1628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. B., Iba H., Hanafusa H. Activation of the transforming potential of p60c-src by a single amino acid change. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4228–4232. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4228. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipsich L. A., Lewis A. J., Brugge J. S. Isolation of monoclonal antibodies that recognize the transforming proteins of avian sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):352–360. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.352-360.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacAuley A., Cooper J. A. The carboxy-terminal sequence of p56lck can regulate p60c-src. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Aug;8(8):3560–3564. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.8.3560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patschinsky T., Hunter T., Esch F. S., Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M. Analysis of the sequence of amino acids surrounding sites of tyrosine phosphorylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):973–977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patschinsky T., Hunter T., Sefton B. M. Phosphorylation of the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus: direct demonstration of phosphorylation of serine 17 and identification of an additional site of tyrosine phosphorylation in p60v-src of Prague Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1986 Jul;59(1):73–81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.59.1.73-81.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piwnica-Worms H., Saunders K. B., Roberts T. M., Smith A. E., Cheng S. H. Tyrosine phosphorylation regulates the biochemical and biological properties of pp60c-src. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):75–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90757-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potts W. M., Reynolds A. B., Lansing T. J., Parsons J. T. Activation of pp60c-src transforming potential by mutations altering the structure of an amino terminal domain containing residues 90-95. Oncogene Res. 1988;3(4):343–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Foulkes J. G., Baltimore D. The minimum transforming region of v-abl is the segment encoding protein-tyrosine kinase. J Virol. 1985 Apr;54(1):114–122. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.1.114-122.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raibaud O., Goldberg M. E. Characterization of two complementary polypeptide chains obtained by proteolysis of rabbit muscle phosphorylase. Biochemistry. 1973 Dec 4;12(25):5154–5161. doi: 10.1021/bi00749a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raymond V. W., Parsons J. T. Identification of an amino terminal domain required for the transforming activity of the Rous sarcoma virus src protein. Virology. 1987 Oct;160(2):400–410. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90011-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds A. B., Vila J., Lansing T. J., Potts W. M., Weber M. J., Parsons J. T. Activation of the oncogenic potential of the avian cellular src protein by specific structural alteration of the carboxy terminus. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2359–2364. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02512.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen O. M., Herrera R., Olowe Y., Petruzzelli L. M., Cobb M. H. Phosphorylation activates the insulin receptor tyrosine protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3237–3240. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth C. W., Richert N. D., Pastan I., Gottesman M. M. Cyclic AMP treatment of Rous sarcoma virus-transformed Chinese hamster ovary cells increases phosphorylation of pp60src and increases pp60src kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1983 Sep 10;258(17):10768–10773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowski I., Stone J. C., Pawson T. A noncatalytic domain conserved among cytoplasmic protein-tyrosine kinases modifies the kinase function and transforming activity of Fujinami sarcoma virus P130gag-fps. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4396–4408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schuh S. M., Brugge J. S. Investigation of factors that influence phosphorylation of pp60c-src on tyrosine 527. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2465–2471. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2465. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smart J. E., Oppermann H., Czernilofsky A. P., Purchio A. F., Erikson R. L., Bishop J. M. Characterization of sites for tyrosine phosphorylation in the transforming protein of Rous sarcoma virus (pp60v-src) and its normal cellular homologue (pp60c-src). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6013–6017. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder M. A., Bishop J. M. A mutation at the major phosphotyrosine in pp60v-src alters oncogenic potential. Virology. 1984 Jul 30;136(2):375–386. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90174-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprang S. R., Acharya K. R., Goldsmith E. J., Stuart D. I., Varvill K., Fletterick R. J., Madsen N. B., Johnson L. N. Structural changes in glycogen phosphorylase induced by phosphorylation. Nature. 1988 Nov 17;336(6196):215–221. doi: 10.1038/336215a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sprang S., Fletterick R. J. The structure of glycogen phosphorylase alpha at 2.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 1979 Jul 5;131(3):523–551. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90006-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoker A. W., Kellie S., Wyke J. A. Intracellular localization and processing of pp60v-src proteins expressed by two distinct temperature-sensitive mutants of Rous sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):876–883. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.876-883.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tornqvist H. E., Pierce M. W., Frackelton A. R., Nemenoff R. A., Avruch J. Identification of insulin receptor tyrosine residues autophosphorylated in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10212–10219. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber I. T., Johnson L. N., Wilson K. S., Yeates D. G., Wild D. L., Jenkins J. A. Crystallographic studies on the activity of glycogen phosphorylase b. Nature. 1978 Aug 3;274(5670):433–437. doi: 10.1038/274433a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinmaster G., Zoller M. J., Smith M., Hinze E., Pawson T. Mutagenesis of Fujinami sarcoma virus: evidence that tyrosine phosphorylation of P130gag-fps modulates its biological activity. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):559–568. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90386-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkerson V. W., Bryant D. L., Parsons J. T. Rous sarcoma virus variants that encode src proteins with an altered carboxy terminus are defective for cellular transformation. J Virol. 1985 Aug;55(2):314–321. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.2.314-321.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaciuk P., Cannella M. T., Shalloway D. Comparison of the effects of carboxyl terminal truncation and point mutations on pp60c-src activities. Oncogene Res. 1988 Sep;3(2):207–212. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaciuk P., Shalloway D. Features of the pp60v-src carboxyl terminus that are required for transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2807–2819. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]