Abstract
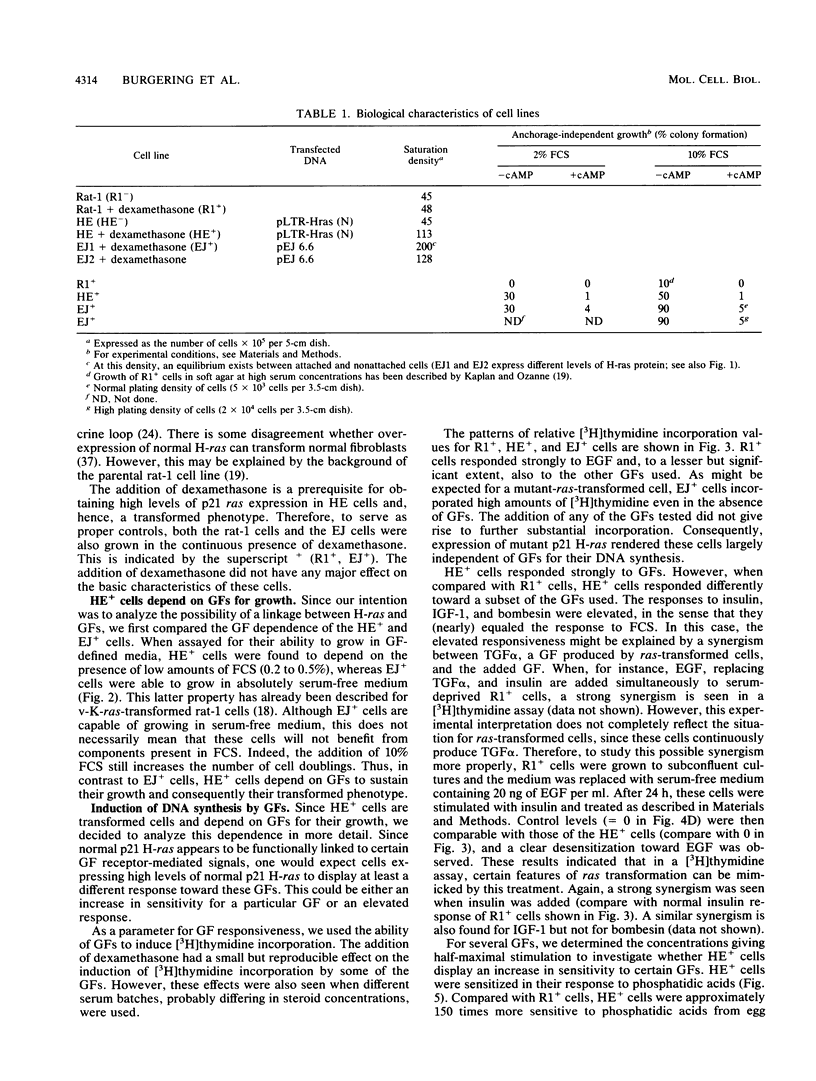
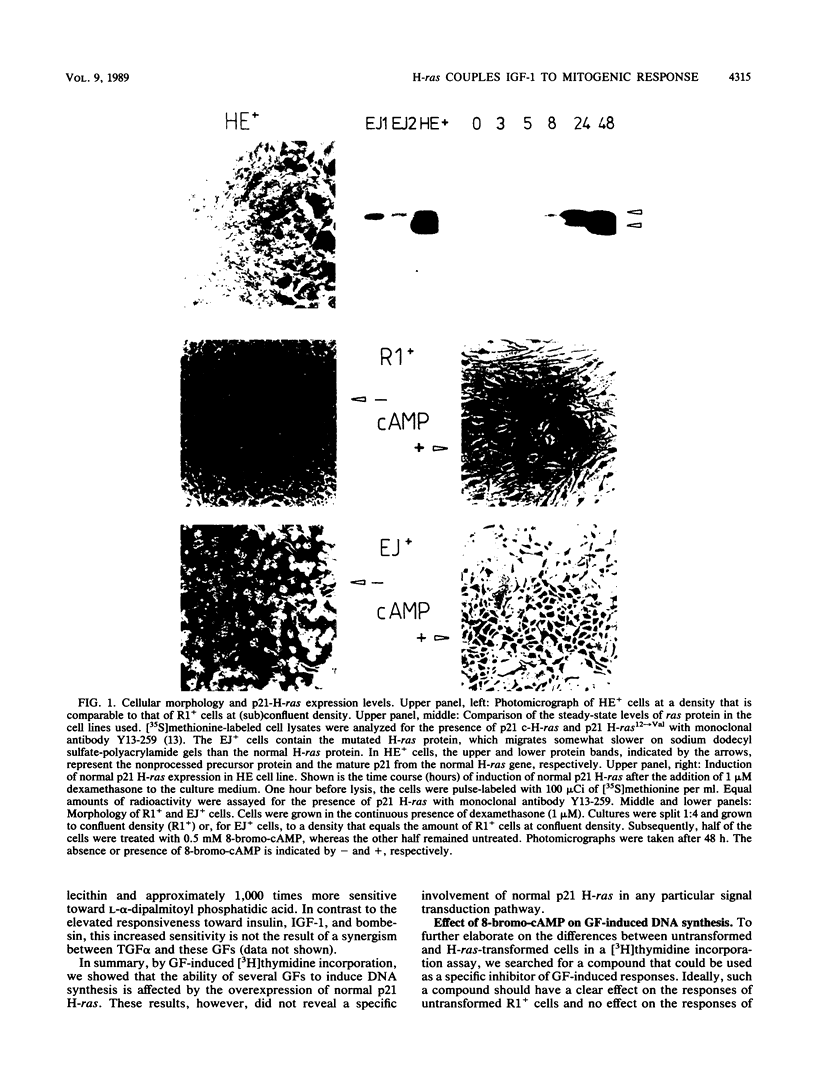
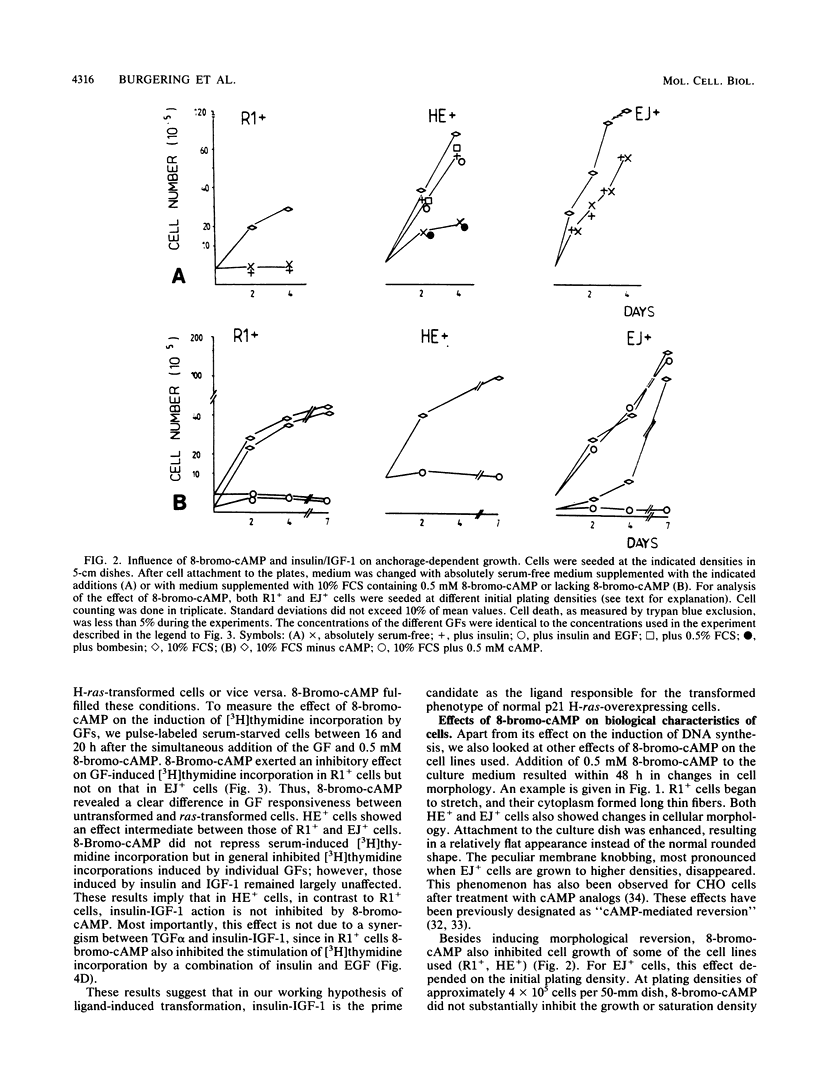
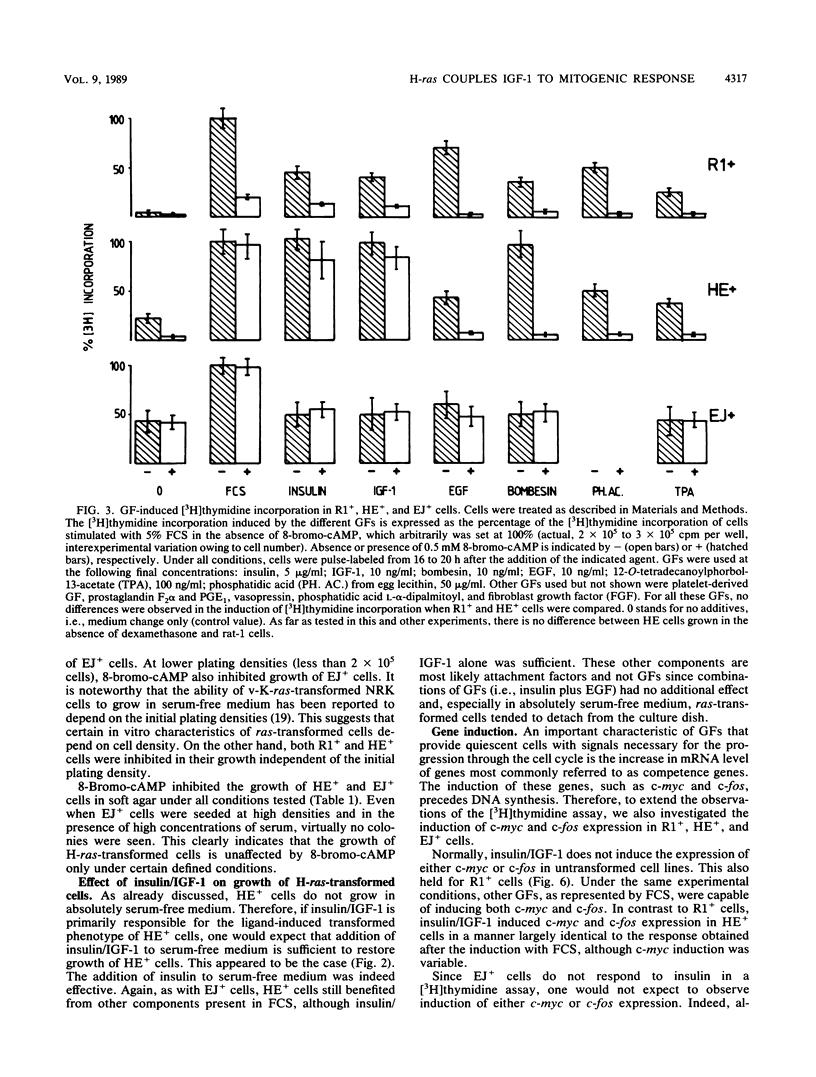
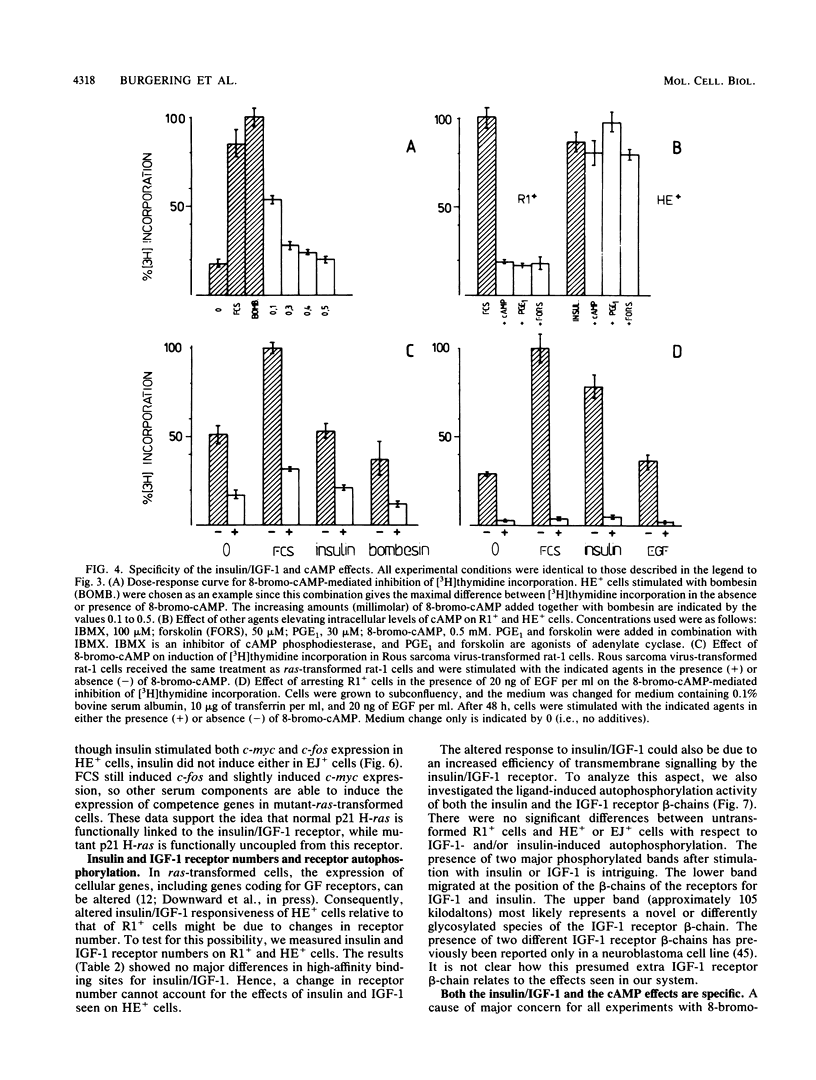
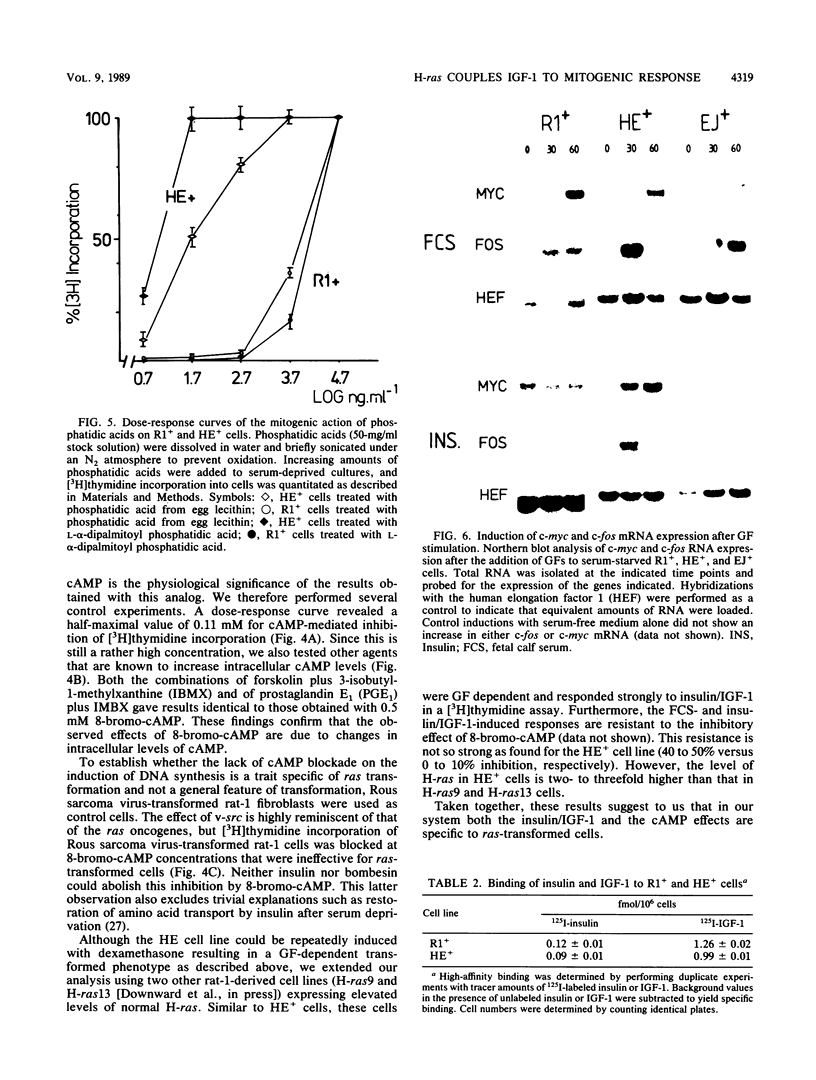
Expression of a mutant H-ras gene confers a transformed phenotype to rat-1 fibroblasts which is basically independent of exogenous growth factors (GFs). Rat-1 cells induced to express high levels of the normal H-ras gene were also found to display a transformed phenotype. In contrast to cells expressing mutant H-ras, these cells were dependent on GFs. We used this difference in GF dependence to analyze a possible involvement of exogenous GFs in H-ras function. Compared with untransformed rat-1 cells, cells overexpressing normal H-ras displayed an elevated response toward insulinlike growth factor 1 (IGF-1), insulin, and bombesin and an increased sensitivity toward phosphatidic acids. It was found that 8-bromo-cyclic AMP inhibited the responses to all GFs in rat-1 cells but had no effect on mutant-H-ras-transformed cells. In cells overexpressing normal H-ras, 8-bromo-cyclic AMP inhibited the responses to all GFs except those to insulin and IGF-1. This implies that overexpression of normal H-ras in the presence of insulin/IGF-1 is functionally similar to the expression of mutant H-ras, since mutant H-ras can circumvent this block by itself. These and other results strongly suggest a functional linkage between insulin/IGF-1 and normal p21 H-ras.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alhanaty E., Patinkin J., Tauber-Finkelstein M., Shaltiel S. Degradative inactivation of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase by a membranal proteinase is restricted to the free catalytic subunit in its native conformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3492–3495. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3492. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Feramisco J. R. Induction of membrane ruffling and fluid-phase pinocytosis in quiescent fibroblasts by ras proteins. Science. 1986 Sep 5;233(4768):1061–1068. doi: 10.1126/science.3090687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benjamin C. W., Tarpley W. G., Gorman R. R. Loss of platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated phospholipase activity in NIH-3T3 cells expressing the EJ-ras oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jan;84(2):546–550. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.2.546. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birchmeier C., Broek D., Wigler M. ras proteins can induce meiosis in Xenopus oocytes. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):615–621. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90233-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen-Pope D. F., Vogel A., Ross R. Production of platelet-derived growth factor-like molecules and reduced expression of platelet-derived growth factor receptors accompany transformation by a wide spectrum of agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2396–2400. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brands J. H., Maassen J. A., van Hemert F. J., Amons R., Möller W. The primary structure of the alpha subunit of human elongation factor 1. Structural aspects of guanine-nucleotide-binding sites. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Feb 17;155(1):167–171. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey P. J., Gilman A. G. G protein involvement in receptor-effector coupling. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 25;263(6):2577–2580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Fiore P. P., Pierce J. H., Fleming T. P., Hazan R., Ullrich A., King C. R., Schlessinger J., Aaronson S. A. Overexpression of the human EGF receptor confers an EGF-dependent transformed phenotype to NIH 3T3 cells. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):1063–1070. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90592-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Downward J., de Gunzburg J., Riehl R., Weinberg R. A. p21ras-induced responsiveness of phosphatidylinositol turnover to bradykinin is a receptor number effect. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5774–5778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farese R. V., Konda T. S., Davis J. S., Standaert M. L., Pollet R. J., Cooper D. R. Insulin rapidly increases diacylglycerol by activating de novo phosphatidic acid synthesis. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):586–589. doi: 10.1126/science.3107122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finzi E., Fleming T., Segatto O., Pennington C. Y., Bringman T. S., Derynck R., Aaronson S. A. The human transforming growth factor type alpha coding sequence is not a direct-acting oncogene when overexpressed in NIH 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Jun;84(11):3733–3737. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.11.3733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flier J. S., Mueckler M. M., Usher P., Lodish H. F. Elevated levels of glucose transport and transporter messenger RNA are induced by ras or src oncogenes. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1492–1495. doi: 10.1126/science.3103217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Davis L. J., Fleurdelys B., Scolnick E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to the p21 products of the transforming gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus and of the cellular ras gene family. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):294–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.294-304.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goshima K., Masuda A., Owaribe K. Insulin-induced formation of ruffling membranes of KB cells and its correlation with enhancement of amino acid transport. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):801–809. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaggi R., Salmons B., Muellener D., Groner B. The v-mos and H-ras oncogene expression represses glucocorticoid hormone-dependent transcription from the mouse mammary tumor virus LTR. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2609–2616. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04541.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaye M., Lyall R. M., Mudd R., Schlessinger J., Sarver N. Expression of acidic fibroblast growth factor cDNA confers growth advantage and tumorigenesis to Swiss 3T3 cells. EMBO J. 1988 Apr;7(4):963–969. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02902.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamata T., Feramisco J. R. Epidermal growth factor stimulates guanine nucleotide binding activity and phosphorylation of ras oncogene proteins. Nature. 1984 Jul 12;310(5973):147–150. doi: 10.1038/310147a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. L., Anderson M., Ozanne B. Transforming growth factor(s) production enables cells to grow in the absence of serum: an autocrine system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):485–489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan P. L., Ozanne B. Cellular responsiveness to growth factors correlates with a cell's ability to express the transformed phenotype. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):931–938. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korn L. J., Siebel C. W., McCormick F., Roth R. A. Ras p21 as a potential mediator of insulin action in Xenopus oocytes. Science. 1987 May 15;236(4803):840–843. doi: 10.1126/science.3554510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maassen J. A., Klinkhamer M. P., Odink R. J., Sips H., van der Zon G. C., Wieringa T., Krans H. M., Möller W. Improper expression of insulin receptors on fibroblasts from a leprechaun patient. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Mar 15;172(3):725–729. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13949.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maassen J. A., Krans H. M., Möller W. The effect of insulin, serum and dexamethasone on mRNA levels for the insulin receptor in the human lymphoblastoic cell line IM-9. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Aug 19;930(1):72–78. doi: 10.1016/0167-4889(87)90157-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay I. A., Malone P., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Malignant transformation of murine fibroblasts by a human c-Ha-ras-1 oncogene does not require a functional epidermal growth factor receptor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Oct;6(10):3382–3387. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.10.3382. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay I. A., Marshall C. J., Calés C., Hall A. Transformation and stimulation of DNA synthesis in NIH-3T3 cells are a titratable function of normal p21N-ras expression. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2617–2621. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04542.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Kruijer W., Tilly B. C., Verlaan I., Bierman A. J., de Laat S. W. Growth factor-like action of phosphatidic acid. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):171–173. doi: 10.1038/323171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Ui M. Phosphatidic acid may stimulate membrane receptors mediating adenylate cyclase inhibition and phospholipid breakdown in 3T3 fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1987 Apr 25;262(12):5522–5529. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien R. M., Siddle K., Houslay M. D., Hall A. Interaction of the human insulin receptor with the ras oncogene product p21. FEBS Lett. 1987 Jun 15;217(2):253–259. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(87)80673-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozanne B., Fulton R. J., Kaplan P. L. Kirsten murine sarcoma virus transformed cell lines and a spontaneously transformed rat cell-line produce transforming factors. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Oct;105(1):163–180. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041050118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parries G., Hoebel R., Racker E. Opposing effects of a ras oncogene on growth factor-stimulated phosphoinositide hydrolysis: desensitization to platelet-derived growth factor and enhanced sensitivity to bradykinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(9):2648–2652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.9.2648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I. H., Johnson G. S., Anderson W. B. Role of cyclic nucleotides in growth control. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:491–522. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.002423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pastan I., Willingham M. Cellular transformation and the 'morphologic phenotype' of transformed cells. Nature. 1978 Aug 17;274(5672):645–650. doi: 10.1038/274645a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puck T. T., Waldren C. A., Hsie A. W. Membrane dynamics in the action of dibutyryl adenosine 3':5'-cyclic monophosphate and testosterone on mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jul;69(7):1943–1947. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.7.1943. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pulciani S., Santos E., Long L. K., Sorrentino V., Barbacid M. ras gene Amplification and malignant transformation. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2836–2841. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ran W., Dean M., Levine R. A., Henkle C., Campisi J. Induction of c-fos and c-myc mRNA by epidermal growth factor or calcium ionophore is cAMP dependent. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8216–8220. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8216. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricketts M. H., Levinson A. D. High-level expression of c-H-ras1 fails to fully transform rat-1 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1460–1468. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riedel H., Schlessinger J., Ullrich A. A chimeric, ligand-binding v-erbB/EGF receptor retains transforming potential. Science. 1987 Apr 10;236(4798):197–200. doi: 10.1126/science.3494307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal A., Lindquist P. B., Bringman T. S., Goeddel D. V., Derynck R. Expression in rat fibroblasts of a human transforming growth factor-alpha cDNA results in transformation. Cell. 1986 Jul 18;46(2):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90747-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltiel A. R., Fox J. A., Sherline P., Cuatrecasas P. Insulin-stimulated hydrolysis of a novel glycolipid generates modulators of cAMP phosphodiesterase. Science. 1986 Aug 29;233(4767):967–972. doi: 10.1126/science.3016898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier P. I., Bernards R., Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Expression of class I major histocompatibility antigens switched off by highly oncogenic adenovirus 12 in transformed rat cells. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):771–775. doi: 10.1038/305771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scolnick E. M., Papageorge A. G., Shih T. Y. Guanine nucleotide-binding activity as an assay for src protein of rat-derived murine sarcoma viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5355–5359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seals J. R., Czech M. P. Evidence that insulin activates an intrinsic plasma membrane protease in generating a secondary chemical mediator. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 25;255(14):6529–6531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shemer J., Adamo M., Wilson G. L., Heffez D., Zick Y., LeRoith D. Insulin and insulin-like growth factor-I stimulate a common endogenous phosphoprotein substrate (pp185) in intact neuroblastoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 15;262(32):15476–15482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih C., Weinberg R. A. Isolation of a transforming sequence from a human bladder carcinoma cell line. Cell. 1982 May;29(1):161–169. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shih T. Y., Papageorge A. G., Stokes P. E., Weeks M. O., Scolnick E. M. Guanine nucleotide-binding and autophosphorylating activities associated with the p21src protein of Harvey murine sarcoma virus. Nature. 1980 Oct 23;287(5784):686–691. doi: 10.1038/287686a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Hare D. L., Cecchini M. A., Weinberg R. A. Construction of a novel oncogene based on synthetic sequences encoding epidermal growth factor. Science. 1987 Jan 16;235(4786):321–324. doi: 10.1126/science.3492043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Roberts A. B., Roche N. S., Sporn M. B., Weinberg R. A. Differential responsiveness of myc- and ras-transfected cells to growth factors: selective stimulation of myc-transfected cells by epidermal growth factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):870–877. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stumpo D. J., Stewart T. N., Gilman M. Z., Blackshear P. J. Identification of c-fos sequences involved in induction by insulin and phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 5;263(4):1611–1614. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet R. W., Yokoyama S., Kamata T., Feramisco J. R., Rosenberg M., Gross M. The product of ras is a GTPase and the T24 oncogenic mutant is deficient in this activity. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):273–275. doi: 10.1038/311273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanabe T., Nukada T., Nishikawa Y., Sugimoto K., Suzuki H., Takahashi H., Noda M., Haga T., Ichiyama A., Kangawa K. Primary structure of the alpha-subunit of transducin and its relationship to ras proteins. Nature. 1985 May 16;315(6016):242–245. doi: 10.1038/315242a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarpley W. G., Hopkins N. K., Gorman R. R. Reduced hormone-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity in NIH-3T3 cells expressing the EJ human bladder ras oncogene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):3703–3707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.3703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub R., Roy A., Dieter R., Koontz J. Insulin as a growth factor in rat hepatoma cells. Stimulation of proto-oncogene expression. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10893–10897. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temeles G. L., Gibbs J. B., D'Alonzo J. S., Sigal I. S., Scolnick E. M. Yeast and mammalian ras proteins have conserved biochemical properties. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):700–703. doi: 10.1038/313700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai M. H., Yu C. L., Wei F. S., Stacey D. W. The effect of GTPase activating protein upon ras is inhibited by mitogenically responsive lipids. Science. 1989 Jan 27;243(4890):522–526. doi: 10.1126/science.2536192. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Lazar E., Sporn M. B. Transformation of normal rat kidney (NRK) cells by an infectious retrovirus carrying a synthetic rat type alpha transforming growth factor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Mar;84(5):1258–1262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.5.1258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westaway D., Papkoff J., Moscovici C., Varmus H. E. Identification of a provirally activated c-Ha-ras oncogene in an avian nephroblastoma via a novel procedure: cDNA cloning of a chimaeric viral-host transcript. EMBO J. 1986 Feb;5(2):301–309. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04213.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheeler T. J., Hinkle P. C. The glucose transporter of mammalian cells. Annu Rev Physiol. 1985;47:503–517. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ph.47.030185.002443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Christensen A., Hubbert N. L., Papageorge A. G., Lowy D. R. The p21 ras C-terminus is required for transformation and membrane association. Nature. 1984 Aug 16;310(5978):583–586. doi: 10.1038/310583a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Zoelen E. J., van Oostwaard T. M., van der Saag P. T., de Laat S. W. Phenotypic transformation of normal rat kidney cells in a growth-factor-defined medium: induction by a neuroblastoma-derived transforming growth factor independently of the EGF receptor. J Cell Physiol. 1985 May;123(2):151–160. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041230202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Eb A. J., Graham F. L. Assay of transforming activity of tumor virus DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):826–839. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]