Abstract
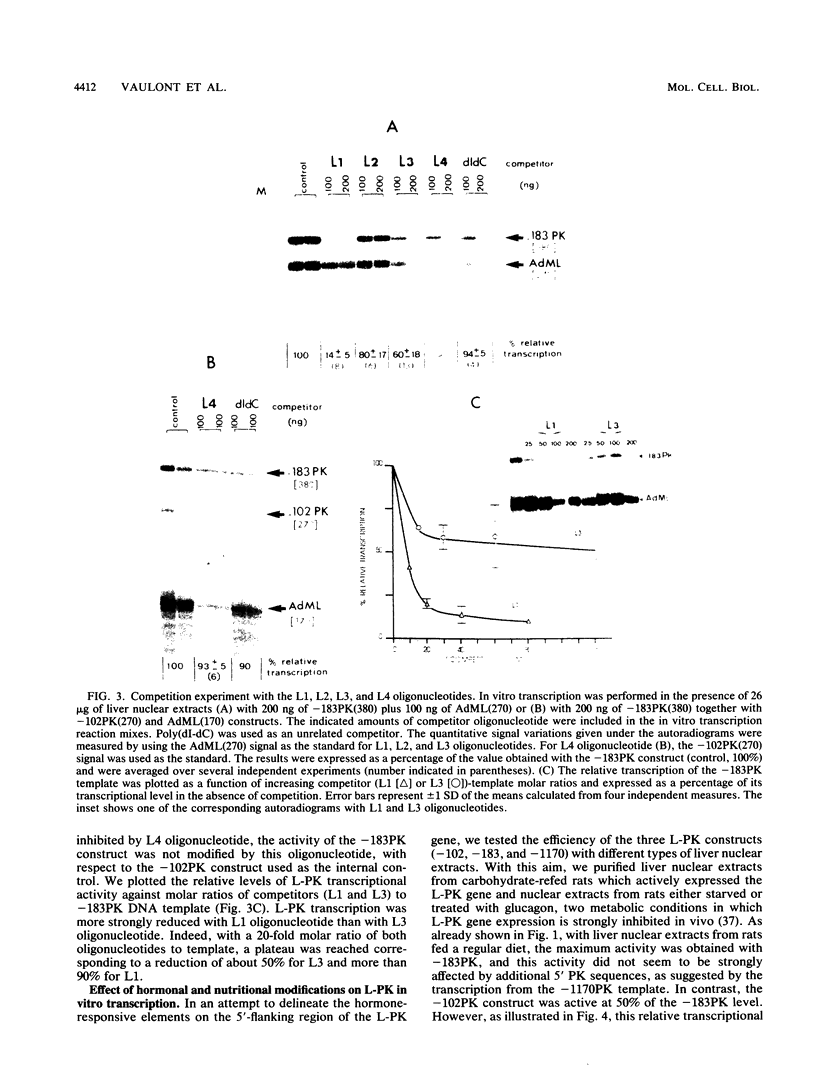
A DNA fragment spanning nucleotides -183 to -4 with respect to the cap site of the rat L-type pyruvate kinase (L-PK) gene contains at least four binding sites for putative transcriptional factors: hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 (HNF1), liver factor A1 (LF-A1), nuclear factor 1 (NF1), and major late transcription factor (MLTF). This fragment was used to direct transcription of a reporter sequence (a G-free cassette) in cell extracts. This L-PK promoter was active in liver nuclear extracts, but not in extracts from nonhepatic tissues. A reduction of 50% of the activity was obtained with a deleted L-PK promoter containing only the HNF1-binding site. In contrast, deletion of the HNF1-binding site inactivated the promoter by more than 90%. These results were confirmed by titration experiments with synthetic oligonucleotides. Titration of HNF1 resulted in an 85% decrease of transcriptional activity, while titration of LF-A1 resulted in only a 40% decrease. The influence of NF1 and MLTF seemed to be marginal in this system. The proximal 5'-flanking sequence of the L-PK gene therefore appears to function in vitro as an efficient liver-specific promoter which requires the binding of the liver factor HNF1 and which is also stimulated by the binding of another liver-specific factor, LF-A1.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baumhueter S., Courtois G., Crabtree G. R. A variant nuclear protein in dedifferentiated hepatoma cells binds to the same functional sequences in the beta fibrinogen gene promoter as HNF-1. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2485–2493. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03095.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bazett-Jones D. P., Yeckel M., Gottesfeld J. M. Nuclear extracts from globin-synthesizing cells enhance globin transcription in vitro. 1985 Oct 31-Nov 6Nature. 317(6040):824–828. doi: 10.1038/317824a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bodner M., Karin M. A pituitary-specific trans-acting factor can stimulate transcription from the growth hormone promoter in extracts of nonexpressing cells. Cell. 1987 Jul 17;50(2):267–275. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90222-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Z. D., Barron E. A., Carillo A. J., Sharp Z. D. Reconstitution of cell-type-specific transcription of the rat prolactin gene in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3402–3408. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3402. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Blumenfeld M., Yaniv M. A liver-specific factor essential for albumin transcription differs between differentiated and dedifferentiated rat hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):957–974. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Morgan J. G., Crabtree G. R., Sharp P. A. The adenovirus major late transcription factor activates the rat gamma-fibrinogen promoter. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):684–688. doi: 10.1126/science.3672119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cognet M., Lone Y. C., Vaulont S., Kahn A., Marie J. Structure of the rat L-type pyruvate kinase gene. J Mol Biol. 1987 Jul 5;196(1):11–25. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90507-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corthésy B., Hipskind R., Theulaz I., Wahli W. Estrogen-dependent in vitro transcription from the vitellogenin promoter in liver nuclear extracts. Science. 1988 Mar 4;239(4844):1137–1139. doi: 10.1126/science.2830672. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Grayson D. R., Darnell J. E., Jr Multiple hepatocyte-enriched nuclear factors function in the regulation of transthyretin and alpha 1-antitrypsin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Apr;9(4):1415–1425. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.4.1415. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Baumhueter S., Crabtree G. R. Purified hepatocyte nuclear factor 1 interacts with a family of hepatocyte-specific promoters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(21):7937–7941. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.21.7937. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Courtois G., Morgan J. G., Campbell L. A., Fourel G., Crabtree G. R. Interaction of a liver-specific nuclear factor with the fibrinogen and alpha 1-antitrypsin promoters. Science. 1987 Oct 30;238(4827):688–692. doi: 10.1126/science.3499668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Döbbeling U., Ross K., Klein-Hitpass L., Morley C., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. A cell-specific activator in the Xenopus A2 vitellogenin gene: promoter elements functioning with rat liver nuclear extracts. EMBO J. 1988 Aug;7(8):2495–2501. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03096.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gil G., Smith J. R., Goldstein J. L., Slaughter C. A., Orth K., Brown M. S., Osborne T. F. Multiple genes encode nuclear factor 1-like proteins that bind to the promoter for 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8963–8967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst R. S., Friedman N., Darnell J. E., Jr, Babiss L. E. Positive and negative regulatory elements in the mouse albumin enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1553–1557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kugler W., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. Tissue-specificity of liver gene expression: a common liver-specific promoter element. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Apr 25;16(8):3165–3174. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.8.3165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Y., Shen R. F., Tsai S. Y., Woo S. L. Multiple hepatic trans-acting factors are required for in vitro transcription of the human alpha-1-antitrypsin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4362–4369. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Schibler U. A glycosylated liver-specific transcription factor stimulates transcription of the albumin gene. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1179–1187. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maire P., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The role of cis-acting promoter elements in tissue-specific albumin gene expression. Science. 1989 Apr 21;244(4902):343–346. doi: 10.1126/science.2711183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meisterernst M., Gander I., Rogge L., Winnacker E. L. A quantitative analysis of nuclear factor I/DNA interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 May 25;16(10):4419–4435. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.10.4419. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaci P., Nicosia A., Cortese R. Two different liver-specific factors stimulate in vitro transcription from the human alpha 1-antitrypsin promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2075–2087. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03047.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncollin V., Miyamoto N. G., Zheng X. M., Egly J. M. Purification of a factor specific for the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2577–2584. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan J. G., Courtois G., Fourel G., Chodosh L. A., Campbell L., Evans E., Crabtree G. R. Sp1, a CAAT-binding factor, and the adenovirus major late promoter transcription factor interact with functional regions of the gamma-fibrinogen promoter. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2628–2637. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2628. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakagawa J., von der Ahe D., Pearson D., Hemmings B. A., Shibahara S., Nagamine Y. Transcriptional regulation of a plasminogen activator gene by cyclic AMP in a homologous cell-free system. Involvement of cyclic AMP-dependent protein kinase in transcriptional control. J Biol Chem. 1988 Feb 15;263(5):2460–2468. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikolaev L. G., Glotov B. O., Belyavsky A. V., Grachev S. A., Levin A. V. Identification of sequence-specific DNA-binding factors by label transfer: application to the adenovirus-2 major late promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Jan 25;16(2):519–535. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.2.519. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paonessa G., Gounari F., Frank R., Cortese R. Purification of a NF1-like DNA-binding protein from rat liver and cloning of the corresponding cDNA. EMBO J. 1988 Oct;7(10):3115–3123. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03178.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phan-Dinh-Tuy F., Henry J., Boucheix C., Perrot J. Y., Rosenfeld C., Kahn A. Protein kinases in human leukemic cells. Am J Hematol. 1985 Jul;19(3):209–218. doi: 10.1002/ajh.2830190302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryffel G. U., Kugler W., Wagner U., Kaling M. Liver cell specific gene transcription in vitro: the promoter elements HP1 and TATA box are necessary and sufficient to generate a liver-specific promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Feb 11;17(3):939–953. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.3.939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B., Cohen R. B., Garfinkel S., Thompson J. A. DNA affinity labeling of adenovirus type 2 upstream promoter sequence-binding factors identifies two distinct proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):105–113. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Gelfand D. H., Stoffel S., Scharf S. J., Higuchi R., Horn G. T., Mullis K. B., Erlich H. A. Primer-directed enzymatic amplification of DNA with a thermostable DNA polymerase. Science. 1988 Jan 29;239(4839):487–491. doi: 10.1126/science.2448875. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santoro C., Mermod N., Andrews P. C., Tjian R. A family of human CCAAT-box-binding proteins active in transcription and DNA replication: cloning and expression of multiple cDNAs. Nature. 1988 Jul 21;334(6179):218–224. doi: 10.1038/334218a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription by human RNA polymerase II: analysis by a rapid and quantitative in vitro assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4394–4398. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schorpp M., Kugler W., Wagner U., Ryffel G. U. Hepatocyte-specific promoter element HP1 of the Xenopus albumin gene interacts with transcriptional factors of mammalian hepatocytes. J Mol Biol. 1988 Jul 20;202(2):307–320. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90460-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaulont S., Munnich A., Decaux J. F., Kahn A. Transcriptional and post-transcriptional regulation of L-type pyruvate kinase gene expression in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jun 15;261(17):7621–7625. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K. K., Gonzalez G. A., Biggs W. H., 3rd, Montminy M. R. Phosphorylation-induced binding and transcriptional efficacy of nuclear factor CREB. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):494–498. doi: 10.1038/334494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]