Abstract
We have reported that protein kinase C epsilon (PKCε) expression level in epidermis dictates the susceptibility of mice to the development of squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) elicited either by repeated exposure to ultraviolet radiation (UVR) or by the DMBA-TPA tumor promotion protocol. To find clues about the mechanism by which PKCε mediates susceptibility to UVR-induced development of SCC, we found that PKCε-over-expressing transgenic mice, as compared to their wild-type littermates, when exposed to UVR, elicit enhanced phosphorylation of Stat3 at Ser727 residues. Stat3 is constitutively activated in SCC and UVR fails to induce SCC in Stat3 mutant mice. Stat3Ser727 phosphorylation is essential for Stat3 transcriptional activity (Cancer Res. 67: 1385, 2007). We now present severa novel findings including that PKCε integrates with its downstream partner ERK1/2 to phosphorylate Stat3Ser727. In these experiments, mice were either exposed to UVR (2 kJ/m2/dose) emitted by Kodacel-filtered FS-40 sun lamps or treated with TPA (5 nmol). Both UVR and TPA treatment stimulated PKCε-Stat3 interaction, Stat3Ser727 phosphorylation and Stat3-regulated gene COX-2 expression. PKCε-Stat3 interaction and Stat3Ser727 phosphorylation was also observed in SCC elicited by repeated UVR exposures of mice. PKCε-Stat3 interaction was PKCε specific. UVR or TPA-stimulated Stat3Ser727 phosphorylation accompanied interaction of PKCε with ERK1/2 in intact mouse skin in vivo. Deletion of PKCε in wild-type mice attenuated both TPA and UVR-induced expression of phosphoforms of ERK1/2 and Stat3Ser727. These results indicate that PKCε integrates with ERK1/2 to mediate both TPA and UVR-induced epidermal Stat3Ser727 phosphorylation. PKCε and Stat3 may be potential molecular targets for SCC prevention.
Keywords: PKC, Stat3, SCC, transgenic mice, ultraviolet radiation
Introduction
Skin cancer is the most common human cancer [1] and the multistage model of mouse skin carcinogenesis has been on the forefront to provide clues about the cellular, biochemical, and genetic events linked to the initiation, promotion, and progression steps of skin cancer formation [2–4]. There are two commonly used protocols to induce skin cancer in mice: (1) by the initiation (DMBA) and promotion (TPA) protocol and (2) by the complete carcinogenesis regimen involving either repeated exposure to a polycylic hydrocarbon (e.g., DMBA, benzo(a)pyrene or methylcholanthene) or ultraviolet radiation (UVR) [4]. Protein kinase C (PKC), a family of phospholipid-dependent serine/threonine (Thr) kinases, is not only the major intracellular receptor for the mouse skin tumor promoter 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate (TPA) [5–9] but also is activated by a variety of stress factors including UVR [10].
PKC represents a large family of phosphatidylserine (PS)-dependent serine/Thr kinases [6–9]. Based on structural similarities and co-factor dependence, at least 11 PKC isoforms have been classified into three subfamilies: the classical (cPKC), the novel (nPKC), and the atypical (aPKC). The cPKCs (α, βI, βII, and γ) are dependent on PS, diacylglycerol (DAG), and Ca2+. The nPKCs (δ, ε, η, and θ) retain responsiveness to DAG and PS, but do not require Ca2+ for full activation. The aPKCs (λ and σ) only require PS for their activation. At least five PKC isoforms (α, δ, ε, η, ζ) are expressed in epidermal keratinocytes [11]. PKC isoforms are differentially expressed in proliferative (basal layer) and non-proliferative compartments (spinous, granular, cornified layers), which exhibit divergence in their roles in the regulation of epidermal cell proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis. Immunocytochemical localization of PKC isoforms indicate that PKCa is found in the membranes of suprabasal cells in the spinous and granular layers. PKCε is mostly localized in the proliferative basal layers. PKCη is localized exclusively in the granular layer. PKCδ is detected throughout the epidermis [11].
PKC isozymes (α, δ ε, and η), exhibit specificities in their signals to the development of skin cancer [12–14]. PKCε, a calcium-insensitive PKC isoform, is linked to the development of squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) elicited either by the DMBA-TPA protocol [14] or by repeated exposures to UVR [10]. PKCε over-expressing transgenic mice, when treated either with TPA or exposed to UVR, elicit similar responses such as inhibition of apoptosis, promotion of cell survival, and development of SCC [10,14]. Also, PKCε over-expression sensitizes skin to both TPA and UVR for activation of Stat3 [15]. Both PKCε and Stat3 are implicated in the development of SCC [16–18]. We found that PKCε interacts with Stat3 [15].
Signal transducers and activators of transcriptions (STATs) comprise a family of seven [Stat1 (α and β splice isoforms), Stat2 and Stat3 (α and β isoforms), Stat4, Stat5a, Stat5b, and Stat6)] latent transcription factors which reside in the cytoplasm and are encoded by seven distinct genes [19–23]. Constitutively activated STATs, in particular Stat3, has been found in a number of human cancers (e.g., SCCs, head and neck, breast, ovary, prostate, lung). Since naturally occurring mutations of Stat3 have not been observed, constitutive activation of Stat3 appears to be mediated by aberrant growth factor signaling [19]. The activation of STATs (Stat1, 3, and 5) is an essential component of the mechanism in mouse skin tumor promotion by diverse tumor promoters. Tumor promoter-induced activation of STATs is mediated by EGFR [2]. Furthermore, Stat3 is constitutively activated in both skin papillomas and carcinomas [17,18]. Disruption of Stat3 activation prevents development of skin tumors elicited by DMBA initiation and TPA promotion protocol [17]. Reports by Sano et al. [18] link activated Stat3 to the development of psoriasis, keratinocyte survival, and to keratinocyte proliferation following UV irradiation. Constitutive activation of Stat3 is observed in UVB-induced human or mouse SCCs [18].
Stat1, Stat3, and Stat4 share a consensus motif between 720 and 730 in C-terminal transactivation domain in which the serine (serine 727 in Stat3) residue is the target for phosphorylation [24–29]. Evidence indicates that cooperation of both tyrosine and serine phosphorylation is necessary for full activation of Stat3 [26]. For example, over-expression of Stat3b, which lacks Ser727, acts as a dominant negative Stat3, and impairs the IL-6-induced Stat3 activation [30]. Ser727 phosphorylation of Stat3 is required for transactivation by association with CREB binding protein p300 [31]. Varinou et al. [32] showed, using a Stat 1 serine 727 to alanine knockin mutant mouse, that phosphorylation of the Stat 1 transactivation domain is required for Stat1 regulated increases in transcriptional activity. Similarly, Shen et al. [33] have shown that using knockin mouse models that Stat3Ser727 plays an essential role in post-natal survival and growth. Ser727 phosphorylation is involved in the progression of the pre-malignant lesions and possibly early events in pathogenesis of cervical cancer and is also constitutively activated in SCC [34]. We found in intact mouse skin in vivo that PKCε, which sensitizes skin to development of SCC by UVR, leads to constitutive activation of Stat3 [15]. PKCε interacts with Stat3 and phosphorylates Stat3Ser727 [15]. In a reciprocal immunoprecipitation/blotting experiments, Stat3 co-immunoprecipitated with PKCε. Co-localization of PKCε with Stat3 was also confirmed by double immunofluorescence staining [15].
In this communication, we have further characterized PKCε–Stat3 interaction. We now report here novel results never reported before in our previous publication [15] that: (1) both UVR and TPA treatment stimulate PKCε–Stat3 interaction and Stat3Ser727 phosphorylation, (2) PKCε–Stat3 interaction and Stat3Ser727 phosphorylation are also observed in SCC. (3) PKCε–Stat3 interaction is PKCε specific. (4) UVR or TPA-stimulated Stat3Ser727 phosphorylation accompany interaction of PKCε with ERK1/2 in intact mouse skin in vivo, and (5) deletion of PKCε attenuates both TPA and UVR-induced expression of phosphoforms of ERK1/2 and Stat3Ser727.
Materials and Methods
Generation of PKCε Transgenic Mice
PKCε transgenic mice were generated as described previously [14]. Transgenic mice were maintained by mating hemizygous transgenic mice with wild-type FVB/N mice. The mice were housed in groups of two to three in plastic bottom cages in light-, humidity-, and temperature-controlled rooms; food and water were available ad libitum. The animals were kept in a normal rhythm of 12-h light and 12-h dark periods. The transgene was detected by polymerase chain reaction analysis using genomic DNA isolated from 1 cm tail clips [14].
Generation of PKCε-Null Mice
PKCε knockout mice were generated and provided by Dr. Michael Leitges (The Biotechnology Centre of Oslo, University of Oslo, P.O. Box 1125, Blindern, N-0317, Oslo, Norway). Briefly, the ES cell line used for targeting was E14 from mouse strain 129/Ola. The embryonic stem cells were introduced into the blastocyst of C57BL/6. The germ-line chimeras were identified by the presence of agouti coat color in the F1progeny. Chimeric mice (C57Bl/6/129/Ola) were bred for 10 generations for mutant transmission to FVB/N mice for a unified genetic background.
Chemicals, Antibodies, and Assay Kits
The sources of the antibodies used in this study were: PKCε, Stat3, ß-actin, ERK1/2, phosphorylated ERK1/2 (pERK1/2), MEK1/2, phosphorylated MEK1/2 (pMEK1/2), PKCα, PKCβI, PKCβII, PKCγ, PKCδ, PKCη, PKCλ, PKCζ, PKCθ, p38, phosphorypurchased from Thermo Scientific lated p38 (p-p38), Raf-1 from Santa Cruz Biotechnologies (Santa Cruz CA); and phosphorylated Stat3Tyr705 (pStat3Tyr705) and Stat3Ser727 (pStat3Ser727; BD Biosciences, San Jose CA). COX-2 antibody was purchased from Cayman Chemical Company (Ann Arbor MI). Anti-mouse, anti-goat, and anti-rabbit secondary antibodies were purchased from Thermo Scientific (Rockford IL). TPA was purchased from Alexis Biochemicals (Farminlysate were fractionated on micrograms of cell lysate were fractionated dale NY).
UVR Treatment
The UVR source was Kodacel-filtered FS-40 sun-lamps (approximately 60% UV-B and 40% UV-A). Mice were exposed to UVR from a bank of six Kodacel-filtered sunlamps. UVR dose was routinely measured using a UVX-radiometer. Mice were used for experimentation beginning at 7–9 wk of age. The dorsal skin of the mice was shaved 3–4 days before experimentation. Mice were exposed to UVR as indicated in each experiment.
Western Blot Analysis
Mice were shaved and depilated 24 h before experimentation. Mouse skin was excised and scraped to remove subcutaneous fat. The epidermis was scraped off on a ice-cold glass plate, homogenized in lysis buffer [50 mmol/L HEPES, 150 mmol/L NaCl, 10% glycerol, 1% Triton X-100, 1.5 mmol/L MgCl2, 10 mg/ml aprotinin, 10 mg/ml leupeptin, 1 mmol/L phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF), 200 μmol/L Na3VO4, 200 μmol/L NaF, and 1 mmol/L EGTA (final pH 7.5)]. The homogenate was centrifuged at 14,000g for 30 min at 4°C. Twenty-five micrograms of cell lysate were fractionated on 10% criterion precast SDS–polyacrylamide gel (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules CA). The protein was transferred to 0.45 μm Hybond-P polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) transfer membrane (Amersham Life Sciences, Piscataway NJ). The membrane was then incubated with the indicated antibody followed by a horseradish peroxidase secondary antibody (Thermo Scientific), and the detection signal was developed with Amersham's enhanced chemiluminescence reagent and using FOTO/Analyst Luminary Work Station (Fotodyne Inc.). The Western blots were quantitated by densitometric analysis using Totallab Nonlinear Dynamic Image analysis software (Nonlinear USA, Inc., Durham, NC).
Immunoprecipitation Protocol
Epidermal lysates were prepared as for Western blot analysis. 100 μg of epidermal lysate was incubated with 10 μg of the indicated antibody. The total volume of the lysate/antibody mixture was adjusted to 1,000 μL with lysis buffer to allow for appropriate mixing and rotated at 4°C overnight. Lysate/antibody mixture was then mixed with-mixed with 50 μL of protein agarose A/G (sc-2003 Santa Cruz Biotechnology, Santa Cruz, CA) for 6 h. Lysate/antibody/protein A/G agarose mixture was then centrifuged at 8,000g for 10 min to sediment the protein A/G agarose. Pellet was washed with 0.1% tween in PBS and then sedimented at 8,000g for 10 min three times to wash any non-specific binding from the pellet. After three washes the immunoprecipite was then boiled for 5 min in 20 μL Protein Loading Buffer Blue (Cat # EC-886, National Diagnostics, Atlanta, GA). Immunoprecipitates were then treated as in Western Blot analysis above.
Expression and Purification of Recombinant PKCε and Stat3
To determine whether PKCε directly interacts with Stat3 and phosphorylates Stat3Ser727, the bacterial expression plasmid construct containing a PKCε or a GST-Stat3 fusion plasmid were transformed into the BL21 strain of Escherichia coli. At a growth density of 0.2 (A600) cells were induced with 0.1 mM isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactoside (IPTG) for 2.5 h at 37°C. The bacteria were harvested and pellets were resuspended in cold PBS and after sonication for a total of 2 min (six times for 20 sec sonication with 15-s intervals in between). Cells debris was pelleted and to the clear protein extract, protease inhibitor was added. To purify the GST-Stat3 fusion protein, the supernatant was incubated with 500 μl of 50% glutathione-Sepharose 4B (Amersham) slurry for 4–5 h at 4°C with gentle agitation. The beads were subsequently washed four times with cold PBS and GST-Stat3 fusion protein was eluted with 1 mM glutathione. Purity of recombinant protein was assessed by SDS–PAGE and coomassie brilliant blue staining.
GST Pull-Down
Approximately 25 μg of affinity purified GST-Stat3-fusion protein was incubated with approximately 50 μg of bacterial expressed PKCε protein in cold 500 μl pull down buffer [GSH agarose slurry (50%), 10 mM Tros-HCl (pH 7.5), 130 mM KCl, 1 mM MgCl2, 1 mM EDTA, protease inhibitor cocktail, 0.5–1.0% NP40] in a total volume of 1 ml. Tubes were rotated at 4°C for 2 h. The beads were then washed two times with 1 ml of pull down buffer, centrifuged at 1,000 rpm for 2 min, and rotated for 5 min at 4°C in between washes.
Results
PKCε–Stat3 Interaction and Stat3 Phosphorylation are Increased After TPA Treatment and PKCε–Stat3 Interaction is PKCε Specific
To determine the effects of TPA treatment and epidermal PKCε level on the Stat3 phosphorylation, PKCε over-expressing transgenic line 215 mice and their wildtype littermates were treated with 5 nmoles TPA and sacrificed at 1, 3, and 5 h post-TPA treatment. In both PKCε transgenic and wild-type mice, TPA treatment elicited rapid and time-dependent increase in the level of expression of phosphorylated Stat3 at both tyrosine 705 and serine 727 residues. PKCε over-expression in PKCε transgenic mice potentiated phosphorylation of Stat3 at both tyrosine 705 and serine 727 residues (Figure 1A,Bi-Bii).
Figure 1.
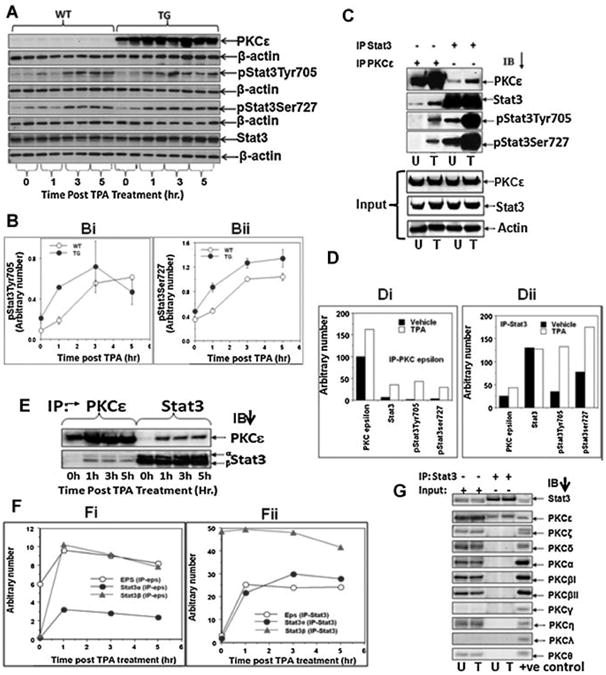
TPA-dependency and isoform specificity of PKCε-Stat3 nteraction. A: PKCε over-expressing transgenic mice (line 215) (TG) and their wildtype littermates (WT) (2 mice/group) were treated topically with 5 nmol of TPA or vehicle acetone in 0.2 ml. Mice were sacrificed at 1, 3, and 5 h post-treatment and total epidermal lysates were prepared. Epidermal protein (25 μg) was subjected to SDS-PAGE and then blotted with antibodies specific for PKCε, Stat3, pStat3Tyr705, and pStat3Ser727. Bi,ii: Quantification of Western blot A (normalized to total Stat3)(Mean ± SE). C: Total epidermal lysate prepared at 3 h post-TPA treatment (Figure 1A) was pooled. Total epidermal cell lysate (100 μg) was immunoprecipitated using Stat3 or PKCε antibody. The immunoprecipiate was then subjected to SDS-PAGE and blotted with antibodies to PKCε, Stat3, pStat3Tyr705, pStat3Ser727. Di,ii: Quantitation of Western blots shown in (C). E: Total epidermal lysates were prepared at 0,1, 3, and 5 h post-TPA treatment (A) was pooled. Total epidermal cell Iysate (100 μg) was immunoprecipitated using Stat3 or PKCε antibody and blotted for PKCε and Stat3. Fi,ii: Quantitation of Western blots shown in (E). G: Total epidermal cell lysate (100 μg) prepared from untreated and 3 h post-TPA treated transgenic mice (A) was pooled and then immunoprecipitated using Stat3 antibody. Stat3-immunoprecipitated proteins were subjected to SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted with the indicated PKC isoform (α, β, δ, ε, γ, η, ι, λ) antibody. Input is 25 mg of epidermal lysate. Positive controls were purchased from Santa Cruz Biotechnologies (Santa Cruz CA), PKCα, βI, and δ were Jurkat T-lymphocyte whole cell lysate, PKCλ and ζ were A431 epidermoid carcinoma whole cell lysate, PKCβII and μ were K562 leukemia whole cell lysate, PKCε was IMR-32 neuroblastoma whole cell lysate, PKCγ was 293T human embryonic kidney whole cell lysate, PKCη was mouse lung tissue whole cell lysate, and PKCθ was Molt4 leukemia whole cell lysate. U: vehicle treated, T: TPA treated.
To determine whether interaction between PKCε and Stat3 is TPA-dependent, reciprocal immunoprecipitation/blotting experiments were performed. In this experiment (Figure 1C–F), the same epidermal protein extracts, prepared from the previous experiment with PKCε transgenic mice(Figure 1A), were used. The epidermal protein extract was immunoprecipitated with antibodies against PKCε or Stat3. The immunoprecipitates were subjected to immunoblot analysis using antibodies against the indicated proteins. As shown in Figure 1C, Di,ii, TPA treatment increased the interaction of PKCε with Stat3, pStat3Tyr705, and pStat3Ser727. TPA-increased PKCε–Stat3 interaction was also observed in a separate repeat experiment (Figure 1E,F). The results of the reciprocal immunoprecipitation/blotting experiments illustrated in Figure 1E indicate that TPA treatment increases the interaction of PKCε with Stat3 (Figure 1F). PKCε interacts with Stat3a isoform, which has Ser727, and not with Stat3b isoform, which lacks Ser727. PKCε–Stat3 interaction and PKCε isoforms specificity was only observed in PKCε over-expressing transgenic mice. Since PKCε level is very low (see Figure 1A) in the wild-type mice, PKCε–Stat3 interaction and PKCε isoform specificity could not be detected (data not shown).
An increase in the interaction of PKCε with Stat3 upon TPA treatment is most probably a result of both increased total and mature PKCε levels. It is noteworthy that newly synthesized PKC is cytosolic. PKC undergoes covalent modification by phosphorylation and that is accompanied by allosteric activation (see Ref. [7]). TPA treatment has been reported to increase the translocation of PKCε from the cytosol to the membrane.
To determine whether PKCε, and not other PKC isoform interacts with Stat3, total epidermal lysate, prepared 3 h post-TPA treatment of PKCε over-expressing transgenic mice, was immunoprecipitated using an antibody directed to Stat3. Stat3-immunoprecipitated proteins were subjected to SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted with PKC isoform (α, βI, βII, γ, δ, ε, η, λ, ζ, θ) antibody. We observed that PKCε, and not any other PKC isoform, associated with Stat3 and PKCε–Stat3 interaction appears to be increased after TPA treatment (Figure 1G).
PKCε–Stat3 Interaction and Stat3 Phosphorylation are Increased After UVR Treatment and PKCε–Stat3 Interaction is PKCε Specific
In this experiment (Figure 2), PKCε transgenic mice (line 224) were exposed to UVR (2 kJ/m2) once and total epidermal lysate was prepared for reciprocal immunoprecipitation/blotting experiments at 1, 3, and 6 h post-UVR exposure. UVR treatment stimulated the association of PKCε with Stat3 and pStat3Ser727 and pStat3Tyr705) (Figure 2A, Bii,iii). UVR treatment also increased the basal PKCε level (input) at 3 and 6 hr post-UVR treatment (Figure 2Bi). To determine whether the interaction of PKCε and Stat3 is persistent in SCC, PKCε line 224 and wildtype littermates were exposed to UVR until appearance of SCC. Mice were then sacrificed and SCCs were excised. Total epidermal lysates were prepared and immunoprecipitated with antibody to PKCε and Stat3. The immunoprecipitated lysates were then subjected to SDS–PAGE and blotted with the indicated antibody (Figure 2C,E). We observed that the interaction of PKCε and Stat3 is still present in SCC samples from transgenc (Figure 2C,D) as well as wildtype mice. (Figure 2 E,F). To determine whether PKCε, and not other PKC isoforms, interact with Stat3 in UVR treated mous skin, we used PKCε transgenic mouse line 215. PKCε transgenic mice were exposed to UVR (2 kJ/m2) four times (Monday, Wednesday, Friday, and Monday). The mice were then sacrificed 3 h post-final UVR exposure. Total epidermal lysate was immunoprecipitated using a Stat3 antibody. Stat3-immunoprecipitated proteins were subjected to SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted with the indicated PKC isoform (α, βI, βII, γ, δ, ε, η, λ, ζ, θ) antibody (Figure 2G). We observed that PKCε, and not any other PKC isoform, immuno-precipitated with Stat3 (Figure 2G). We have previously reported lack of PKCδ-Stat3 interaction in UVR-treated PKCδ over-expressing transgenic mice [15].
Figure 2.
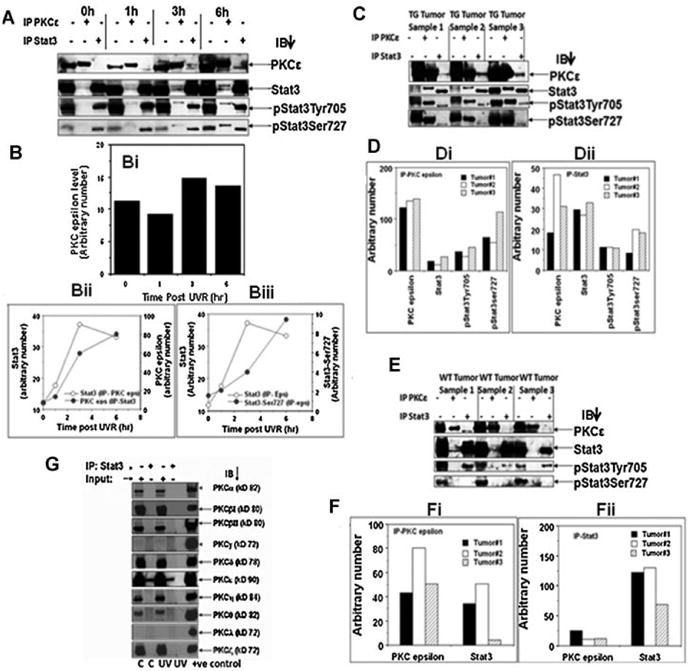
UVR-dependency and isoform specificity of PKCε– Stat3 interaction. A: PKCε transgenic mice (line 224) were exposed once to 2 kJ/m2 UVR and sacrificed 1, 3, and 6 h after UVR exposure (3 mice/group). Epidermal lysates were prepared as described in Materials and Methods Section. Epidermal lysates from three mice were pooled. Epidermal lysate (100 μg) was immunoprecipitated with either PKCε or Stat3 and immunoblotted with the indicated antibodies. B: Quantification of the Western blots shown in (A). Bi: Effect of UVR treatment on basal level of PKCε expression (input), Bii–iii: PKCε–Stat3 interaction increases following UVR treatment. C,E: PKCε transgenic mice (TG) (line 224) and wildtype littermate (WT) were exposed thrice weekly to UVR (1 kJ/m2) for development of SCC, 23 wk. Mice were then sacrificed and the SCC (TG Tumor, WT Tumor) was excised and total epidermal lysates were prepared. Total epidermal cell lysate (100 μg) was immunoprecipitated using Stat3 or PKCε antibody. Immunoprecipitated proteins were then subjected to SDS–PAGE and blotted with PKCε, Stat3, pStat3Tyr705, and pStat3Ser727. D,F: Quantification of blots shown in C (TG Tumor) and E (WT Tumor). Di: ip PKCε, (Dii) ip Stat3, (Fi) ip PKCε, (Fii) ip Stat3. G: PKCε transgenic mice (line 215) were exposed to UVR (2 kJ/m2) four times (Monday, Wednesday, Friday, and Monday). The mice were then sacrificed 3 h post-last UVR exposure. Total epidermal cell lysate (100 μg) was immunoprecipitated using Stat3 antibody. Stat3-immunoprecipitated proteins were subjected to SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted with the indicated PKC isoform (α, β, δ, ε, γ, η, ι, λ) antibody. Input is 25 μg of epidermal lysate. Positive controls for PKC isoforms as described in Figure 1. C: control (untreated) mice, UV: 3 h post-final UVR exposed mice.
PKCε and Stat3 Co-Immunoprecipitate With ERK1/2
The results (Figures 1 and 2) presented clearly indicate that PKCε interacts with Stat3. However, it is unknown whether PKCε integrates with other protein kinase cascade to phosphorylate Stat3Ser727. To determine whether PKCε-downstream protein kinase ERK1/2 is involved in the interaction of PKCε and Stat3, the same epidermal lysate prepared for the experiment described in Figure 2 was used. Total epidermal lysates were immunoprecipitated with antibodies to PKCε or Stat3, and were subjected to SDS–PAGE and immunoblotted with the indicated antibody. As shown in Figure 3A, PKCε and Stat3 co-immunoprecipitated with both pERK1/2 and total ERK1/2. PKCε-ERK1/2 interaction was increased following UVR treatment (Figure 3A,B). Similar results were obtained in a reciprocal/immunoprecipitation experiment (Figure 3C,D). To examine whether the interaction of PKCε and Stat3 with ERK1/2 was present in UVR-induced SCCs, PKCε line 224 mice were exposed to UVR thrice weekly for 23 wk. Mice were then sacrificed and SCCs were excised. Total epidermal lysates were prepared and immunoprecipitated with antibody to PKCε and Stat3 and blotted with ERK1/2 (Figure 3E). We observed that PKCε and Stat3 interacts with ERK1/2 in all UVR-induced SCC (Figure 3E,F).
Figure 3.
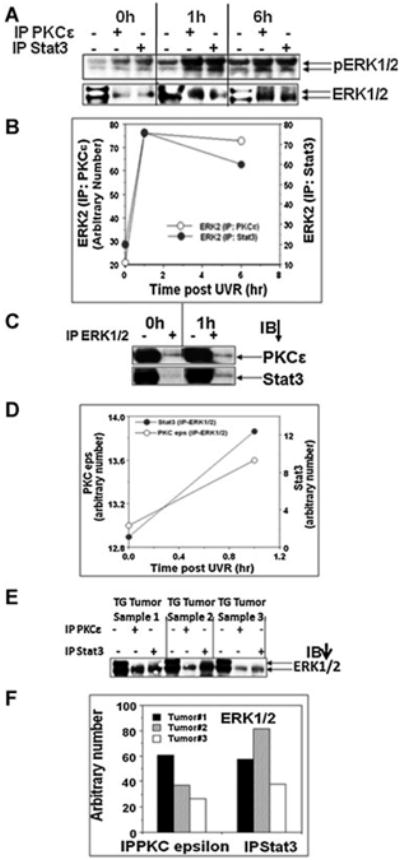
PKCε and Stat3 co-immunoprecipitate with ERK1/2. Same epidermal lysate, prepared for experiment described in Figure 2, was used. A: Epidermal lysate (100 μg) was immunoprecipitated with either PKCε or Stat3 and immunoblotted with phospho and total ERK1/2 antibodies. Input was 25 μg epidermal protein. B: Quantification of the Western blot in (A). C: Epidermal lysate (100 μg) was immunoprecipitated with ERK1/2 and immunoblotted with PKCε and Stat3. Input was 25 μg epidermal protein. D: Quantification of the Western blot in C. E: PKCε line 224 and wildtype littermates were exposed thrice weekly to UVR (1 kJ/m2) for 23 wk. Mice were then sacrificed and the SCC was excised and total epidermal lysate was prepared. Total epidermal cell lysate (100 μg) was immunoprecipitated using Stat3 or PKCε antibody and blotted for ERK1/2. Input was 25 μg epidermal protein. F: Quantification of the Western blot in (E).
PKCε Deletion in Mice Attenuated Both UVR- and TPA-Induced Phosphorylation of MAPKs and Stat3Ser727
In these experiments (Figure 4), PKCε KO, PKCε Heterzygous (Het) mice and their wild-type littermates were exposed to UVR (2 kJ/m2 four times) or PKCε KO mice and their wild-type littermates treated topically once with 5 nmol TPA. Total epidermal lysate, prepared at 2 and 3 h after TPA or UVR treatment respectively, and subjected to SDS–PAGE. PKCε deletion suppressed both UVR (Figure 4A,B) - and TPA (Figure 4C,D)-induced phosphorylation of Stat3Ser727 and ERK1/2. The results of the inability of UVR treatment to stimulate phosphorylation of Stat3Ser727 in PKCε KO mice are in accord with our previous findings [15]. PKCε deletion also suppressed COX-2 protein expression level in UVR and TPA treated mouse epidermis (Figure 4A–D). Interestingly, in the chronically UVR treated mouse skin but not in TPA treated skin, there was a suppression in Raf-1 and MEK1/2 phosphorylation suggesting a different pathway for activation of Stat3ser727 phosphorylation (Figure 4A–D).
Figure 4.
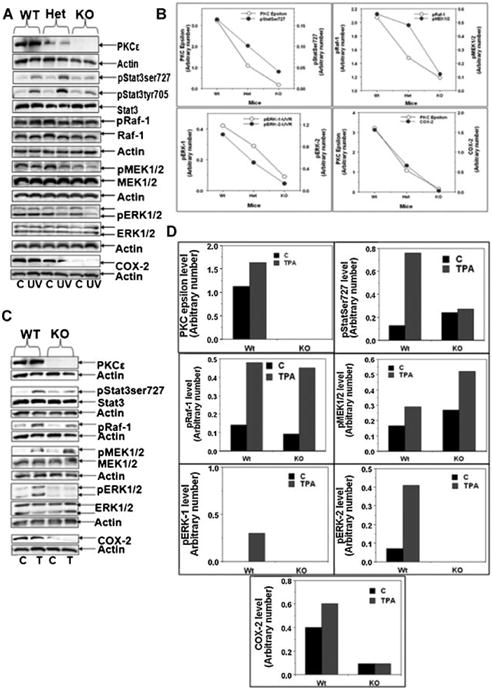
PKCε deletion in mice attenuated both UVR- and TPA-induced phsophorylation of ERK1/2 and Stat3Ser727. A: The indicated mice (three per group) were exposed to UVR (2 kJ/m2) four times (Monday, Wednesday, Friday, and Monday). Mice were sacrificed 3 h post-final UVR exposure. Epidermal lysate was then prepared and subjected to SDS/PAGE and blotted with the indicated antibody. Shown are the representative results of three replicates. B: Quantification of (A) Western: pStat3 was normalized to total Stat3 while other proteins were normalized to β-actin. C: Indicated mice (three per group) were treated once with 5 nmol of TPA in 0.2 ml acetone. Total epidermal cell lysate, prepared 2 h after TPA treatment. Total epidermal lysate was then subjected to SDS/PAGE and blotted with the indicated antibody; results are representative of three replicates. D: Quantification of (C) Western blots: pStat3 was normalized to total Stat3 while other proteins were normalized to β-actin.
PKCε May Also Directly Interact With Stat3 to Phosphorylate Stat3Ser727
We also investigated whether PKCε directly interacts with Stat3 to phosphorylate Stat3Ser727. In an immunocomplex kinase assay, purified bacterially expressed recombinant PKCε phosphorylated purified recombinant GST-Stat3 at Ser727. The result of the immunocomplex kinase assay is shown in Figure 5. These results indicate that PKCε phosphorylates Stat3 at Ser727. Omission of any components of the immunocomplex kinase assay resulted in no Stat3ser727 phosphorylation. This result indicates that Stat3 may also be a direct substrate for PKCε.
Figure 5.
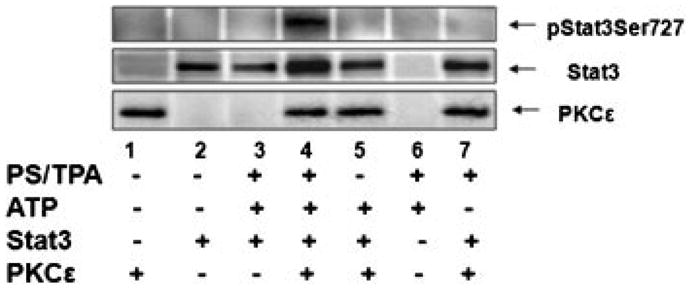
Bacterially expressed PKCε directly interacts with Stat3 and phosphorylates Stat3Ser727. In in vitro immunocomplex kinase assays, purified PKCε phosphorylates Stat3 at serine 727 residue. Recombinant PKCε and GST-Stat3 were used in an immunocom-plex kinase assay. Stat3-fusion protein was incubated with approximately 20 μg of bacterial cell lysate (a source of PKCε) in cold pull down buffer in a total volume of 1 ml. Lane 1 and 2 are expression level of PKCε and GST-Stat3 respectively. Lane 3: Bacterial extract without plasmid + GST-Stat3 bacterial extract + complete kinase assay components, Lane 4:PKCε + GST-Stat3 + complete kinase assay components Lane 5: PKCε + GST-Stat3 + kinase assay without lipid (PS + TPA) Lane 6: Complete kinase assay without proteins (PKCε + GST-Stat3) Lane 7: PKCε + GST-Stat3 + kinase assay without ATP.
Discussion
We have previously reported that PKCε, a Ca+2-independent PKC isoform, plays a key role in development of SCC elicited either by the DMBA-TPA protocol [14] or repeated UVR exposures [10]. The mechanisms by which PKCε may mediate susceptibility to SCC induction constitute PKCε-mediated both anti-apoptotic and survival signals [15]. We also found that PKCε-mediated cell survival signal may involve PKCε interaction with Stat3. PKCε interacts with Stat3 and phosphorylates Stat3Ser727, which is essential for its maximal transcriptional activity of Stat3 [15]. Overwhelming evidence presented by Dr. DiGiovanni and his associates links Stat3 activation to the induction of skin cancer [17,18]. We now present that PKCε-Stat3 interaction is specific for PKCε and is enhanced both by TPA and UVR treatment. PKCε may integrate with mitogen activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascade to phosphorylate Stat3Ser727.
PKCε and not any other PKC isoform (α, βI, βII, γ, δ, ε, η, λ, ζ, θ) mediated TPA- or UVR-induced Stat3Ser727 phosphorylation (Figures 1G and 2G). This conclusion is supported by the findings: (1) PKCε and not other PKC isoform co-immunoprecipitated with Stat3 and (2) PKCε deletion suppressed TPA- or UVR-mediated Stat3Ser727 phosphorylation. We have also shown that, using either immunopurified PKCε [15] or recombinant PKCε (Figure 5), PKCε phosphorylated Stat3 in an immunocomplex kinase assay. These results indicate that PKCε is a Stat3ser727 kinase.
The interaction of PKCε with Stat3 was enhanced by both TPA and UVR treatments (Figures 1C,E, and 2A). These results indicate that TPA and UVR-induced mature and catalytically-competent PKCε mediate Stat3Ser727 phosphorylation. The generally accepted paradigm for the activation of PKC consists of two major biological events [35–37]. The initial event is a well-ordered sequential covalent modifications on the PKCs by phosphorylation, and that is accompanied by the allosteric activation mediated by two lipid signals. Priming phosphorylation on the activation loop residue Thr by phospholipid-dependent kinase 1 (PDK1) initiates autophosphorylation on the turn motif Thr residue, and hydrophobic motif Ser residue. Most PKC in unstimulated cells is in the triple-phosphorylated mature form. The mature, phosphorylated species is released to the cytosol and the pseudosubstrate gains access to the active site, thus maintaining the enzyme in an autoinhibited state [35–37]. The mature PKC positions near the membrane for rapid access to DAG. The translocation of the mature enzyme from the cytosolic soluble fraction to particulate plasma membrane fraction is mediated by the binding of lipid second messenger. Subsequent association with the membrane allows the phosphorylated PKC to carry out phosphorylation of target substrates. The initial phosphorylation reaction, and the final membrane tethering is a common theme for most PKC isoforms. But several variations in PKC translocation mechanisms have been noticed. UVR-induced generation of lipid second messenger DAG is possibly involved in PKCε translocation to membrane.
PKCε appears to integrate with ERK1/2 in intact mouse skin in vivo to mediate TPA and UVR-induced Stat3Ser727 phosphorylation (Figure 3). This conclusion is supported by the findings that: (1) both PKCε and Stat3 co-immunopreciptaed with ERK1/2 and (2) PKCε deletion in mice attenuated both UVR- and TPA-induced phosphorylation of ERK1/2 (Figure 4). PKCε appears to integrate with Raf-1, MEK1/2 in addition to ERK1/2 in UVR-induced Stat3Ser727 phosphorylation. PKCε deletion suppressed both TPA-induced Stat3ser727 and ERK1/2 phosphorylation but, neither Raf-1 nor MEK1/2 phosphorylation. This observation is not surprising considering that TPA is a direct activator of PKC's while UVR is thought to signal through reactive oxygen/nitrogen species to activate PKC's [38,39]. TPA is also known to signal through other molecules, such as Ras, which may also play an important role in the activation of Raf-1 and MEK1/2 [40]. It is also notable that, depending upon cellular context, Stat3 has been shown to be a substrate for other protein kinases [41–43]. We have recently reported, using specific PKCε siRNA, that PKCε mediates Stat3Ser727 phosphorylation, Stat3-regulated gene expression, and cell invasion in various human cancer cell lines through integration with MAPK cascade (RAF-1, MEK1/2, and ERK1/2) [43].
Both TPA and the tumor promotion component of UVR carcinogenesis, involve clonal expansion of initiated cells as the result of aberrant expression of genes altered during tumor initiation [44,45]. TPA and UVR have been reported to alter the expression of genes regulating inflammation, cell growth, and differentiation. Specific examples include up-regulation of the expression of p21 (WAF1/C1P1), p53, AP-1, Stat3 activation, ornithine decarboxylase, cyclo-oxygenase-2 (COX2), cytokines, and growth factors [46–50]. Our results indicate that the development SCC, either by TPA promotion or UVR, involves PKCε activation and its interaction with Stat3, as a common converging point.
In summary, PKCε–Stat3 interaction, which leads to expression of survival and anti-apoptotic genes, appears to be the key mechanism for the development of SCC [15]. Evidence employing gene deletion experiments indicates that PKCε may integrate with ERK1/2 in both TPA- and UVR-induced phosphorylation of Stat3ser727. Also, purified PKCε phosphorylates purified Stat3 in vitro in an immunocomplex kinase assay. Taken together, the results indicate that PKCε directly or indirectly phosphorylates Stat3Ser727, which is essential for Stat3 activation [15]. PKCε and its protein partner Stat3 constitute important components of signal transduction pathway to mouse skin carcinogenesis. PKCε and Stat3 may be important molecular targets for the prevention and treatment of skin cancer.
Acknowledgments
The PKCε KO mice were generated and kindly provided by Dr. Michael Leitges, The Biotechnology Centre of Oslo, University of Oslo, P.O. Box 1125, Blindern, N-0317, Oslo, Norway. We are also thankful to Dr. Herbert Manoharan for his help in an experiment focused on determining the direct interaction of PKCε with Stat3. This work was supported by NIH Grants CA35368, CA102431, and Molecular and Environmental Toxicology Center pre-doctoral training grant T32ES007015, for Jordan M Sand.
Abbreviations
- PKC
protein kinase C
- SCC
squamous cell carcinoma
- UVR
ultraviolet radiation
- TPA
12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate
- DMBA
7, 12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene
- DAG
diacylglycerol
- STAT
signal transducers and activators of transcription
- MAPK
mitogen activated protein kinase
References
- 1.Jemal A, Murray T, Ward E, et al. Cancer statistics, 2005. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005;55:10–30. doi: 10.3322/canjclin.55.1.10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Chan KS, Carbajal S, Kiguchi K, Clifford J, Sano S, DiGio-vanni J. Epidermal growth factor receptor-mediated activation of Stat3 during multistage skin carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004;64:2382–2389. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.can-03-3197. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Cataisson C, Ohman R, Patel G, et al. Inducible cutaneous inflammation reveals a protumorigenic role for keratinocyte CXCR2 in skin carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2009;69:319–328. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-2490. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Li Y, Wheeler DL, Ananthaswamy HN, Verma AK, Oberley TD. Differential tumor biology effects of double-initiation in a mouse skin chemical carcinogenesis model comparing wild type versus protein kinase Cepsilon overexpression mice. Toxicol Pathol. 2007;35:942–951. doi: 10.1080/01926230701748164. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Griner EM, Kazanietz MG. Protein kinase C and other diacylglycerol effectors in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2007;7:281–294. doi: 10.1038/nrc2110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mellor H, Parker PJ. The extended protein kinase C super-family. Biochem J. 1998;332:281–292. doi: 10.1042/bj3320281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Newton AC. Protein kinase C: Structural and spatial regulation by phosphorylation, cofactors, and macromolecular interactions. Chem Rev. 2001;101:2353–2364. doi: 10.1021/cr0002801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mochly-Rosen D, Kauvar LM. Modulating protein kinase C signal transduction. Adv Pharmacol. 1998;44:91–145. doi: 10.1016/s1054-3589(08)60126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Angel JM, Caballero M, DiGiovanni J. Identification of novel genetic loci contributing to 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate skin tumor promotion susceptibility in DBA/2 and C57BL/6 mice. Cancer Res. 2003;63:2747–2751. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Wheeler DL, Martin KE, Ness KJ, et al. Protein kinase C epsilon is an endogenous photosensitizer that enhances ultraviolet radiation-induced cutaneous damage and development of squamous cell carcinomas. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7756–7765. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1881. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Breitkreutz D, Braiman-Wiksman L, Daum N, Denning MF, Tennenbaum T. Protein kinase C family: On the crossroads of cell signaling in skin and tumor epithelium. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2007;133:793–808. doi: 10.1007/s00432-007-0280-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Cataisson C, Pearson AJ, Tsien MZ, et al. CXCR2 ligands and G-CSF mediate PKCalpha-induced intraepidermal inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2006;116:2757–2766. doi: 10.1172/JCI27514. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Chida K, Hara T, Hirai T, et al. Disruption of protein kinase Ceta results in impairment of wound healing and enhancement of tumor formation in mouse skin carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2003;63:2404–2408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Reddig PJ, Dreckschmidt NE, Zou J, Bourguignon SE, Oberley TD, Verma AK. Transgenic mice overexpressing protein kinase C epsilon in their epidermis exhibit reduced papilloma burden but enhanced carcinoma formation after tumor promotion. Cancer Res. 2000;60:595–602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Aziz MH, Manoharan HT, Verma AK. Protein kinase C epsilon, which sensitizes skin to sun's UV radiation-induced cutaneous damage and development of squamous cell carcinomas, associates with Stat3. Cancer Res. 2007;67:1385–1394. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-3350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Chan KS, Sano S, Kiguchi K, et al. Disruption of Stat3 reveals a critical role in both the initiation and the promotion stages of epithelial carcinogenesis. J Clin Invest. 2004;114:720–728. doi: 10.1172/JCI21032. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Sano S, Chan KS, Carbajal S, et al. Stat3 links activated keratinocytes and immunocytes required for development of psoriasis in a novel transgenic mouse model. Nat Med. 2005;11:43–49. doi: 10.1038/nm1162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Sano S, Chan KS, Kira M, et al. Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 is a key regulator of keratinocyte survival and proliferation following UV irradiation. Cancer Res. 2005;65:5720–5729. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-4359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Klampfer L. Signal transducers and activators of transcription (STATs): Novel targets of chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic drugs. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2006;6:107–121. doi: 10.2174/156800906776056491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Hodge DR, Hurt EM, Farrar WL. The role of IL-6 and STAT3 in inflammation and cancer. Eur J Cancer. 2005;41:2502–2512. doi: 10.1016/j.ejca.2005.08.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Kortylewski M, Jove R, Yu H. Targeting STAT3 affects melanoma on multiple fronts. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2005;24:315–327. doi: 10.1007/s10555-005-1580-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Nikitakis NG, Siavash H, Sauk JJ. Targeting the STAT pathway in head and neck cancer: Recent advances and future prospects. Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 2004;4:637–651. doi: 10.2174/1568009043332736. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Vinkemeier U. Getting the message across, STAT! Design principles of a molecular signaling circuit. J Cell Biol. 2004;167:197–201. doi: 10.1083/jcb.200407163. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Decker T, Kovarik P. Serine phosphorylation of STATs. Oncogene. 2000;19:2628–2637. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203481. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zhang JJ, Vinkemeier U, Gu W, Chakravarti D, Horvath CM, Darnell JE., Jr Two contact regions between Stat1 and CBP/p300 in interferon gamma signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1996;93:15092–15096. doi: 10.1073/pnas.93.26.15092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Akira S. Roles of STAT3 defined by tissue-specific gene targeting. Oncogene. 2000;19:2607–2611. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203478. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Aznar S, Valeron PF, del Rincon SV, Perez LF, Perona R, Lacal JC. Simultaneous tyrosine and serine phosphorylation of STAT3 transcription factor is involved in Rho A GTPase oncogenic transformation. Mol Biol Cell. 2001;12:3282–3294. doi: 10.1091/mbc.12.10.3282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Li L, Shaw PE. A STAT3 dimer formed by inter-chain disulphide bridging during oxidative stress. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004;322:1005–1011. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.08.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ng J, Cantrell D. STAT3 is a serine kinase target in T lymphocytes.Interleukin 2 and T cell antigen receptor signals converge upon serine 727. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:24542–24549. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.39.24542. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Caldenhoven E, van Dijk TB, Solari R, et al. STAT3beta, a splice variant of transcription factor STAT3, is a dominant negative regulator of transcription. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:13221–13227. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.22.13221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Schuringa JJ, Schepers H, Vellenga E, Kruijer W. Ser727-dependent transcriptional activation by association of p300 with STAT3 upon IL-6 stimulation. FEBS Lett. 2001;495:71–76. doi: 10.1016/s0014-5793(01)02354-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Varinou L, Ramsauer K, Karaghiosoff M, et al. Phosphorylation of the Stat1 transactivation domain is required for full-fledged IFN-gamma-dependent innate immunity. Immunity. 2003;19:793–802. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(03)00322-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Shen Y, Schlessinger K, Zhu X, et al. Essential role of STAT3 in postnatal survival and growth revealed by mice lacking STAT3 serine 727 phosphorylation. Mol Cell Biol. 2004;24:407–419. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.1.407-419.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Yang SF, Yuan SS, Yeh YT, et al. The role of p-STAT3 (ser727) revealed by its association with Ki-67 in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. Gynecol Oncol. 2005;98:446–452. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2005.05.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Parker PJ, Murray-Rust J. PKC at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2004;117:131–132. doi: 10.1242/jcs.00982. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Parekh DB, Ziegler W, Parker PJ. Multiple pathways control protein kinase C phosphorylation. EMBO J. 2004;19:496–503. doi: 10.1093/emboj/19.4.496. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Flint AJ, Paladini RD, Koshland DE., Jr Autophosphorylation of protein kinase C at three separated regions of its primary sequence. Science. 1990;249:408–411. doi: 10.1126/science.2377895. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Gopalakrishna R, Jaken S. Protein kinase C signaling and oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 2000;28:1349–1361. doi: 10.1016/s0891-5849(00)00221-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Bossi O, Gartsbein M, Leitges M, Kuroki T, Grossman S, Tennenbaum T. UV irradiation increases ROS production via PKCdelta signaling in primary murine fibroblasts. J Cell Biochem. 2008;105:194–207. doi: 10.1002/jcb.21817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bruder JT, Heidecker G, Rapp UR. Serum-, TPA-, and Ras-induced expression from Ap-1/Ets-driven promoters requires Raf-1 kinase. Genes Dev. 1992;6:545–556. doi: 10.1101/gad.6.4.545. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Jain N, Zhang T, Kee WH, Li W, Cao X. Protein kinase C delta associates with and phosphorylates Stat3 in an interleukin-6-dependent manner. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:24392–24400. doi: 10.1074/jbc.274.34.24392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Zhang Y, Cho YY, Petersen BL, Bode AM, Zhu F, Dong Z. Ataxia telangiectasia mutated proteins, MAPKs, and RSK2 are involved in the phosphorylation of STAT3. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:12650–12659. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M210368200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Aziz MH, Hafeez BB, Sand JM, et al. Protein kinase Cvarepsilon mediates Stat3Ser727 phosphorylation Stat3-regulated gene expression cell invasion in various human cancer cell lines through integration with MAPK cascade (RAF-1, MEK1/2, ERK1/2) Oncogene. 2010;29:3100–3109. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.63. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ikuta S, Edamatsu H, Li M, Hu L, Kataoka T. Crucial role of phospholipase C epsilon in skin inflammation induced by tumor-promoting phorbol ester. Cancer Res. 2008;68:64–72. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-3245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Melnikova VO, Ananthaswamy HN. Cellular and molecular events leading to the development of skin cancer. Mutat Res. 2005;571:91–106. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2004.11.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Lee JY, Kim HS, Kim JY, Sohn J. Nuclear translocation of p21(WAF1/CIP1) protein prior to its cytosolic degradation by UV enhances DNA repair and survival. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;390:1361–1366. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.10.160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Brash DE. Roles of the transcription factor p53 in keratinocyte carcinomas. Br J Dermatol. 2006;154:8–10. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2006.07230.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Hopper BD, Przybyszewski J, Chen HW, Hammer KD, Birt DF. Effect of ultraviolet B radiation on activator protein 1 constituent proteins and modulation by dietary energy restriction in SKH-1 mouse skin. Mol Carcinog. 2009;48:843–852. doi: 10.1002/mc.20529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Kim DJ, Angel JM, Sano S, DiGiovanni J. Constitutive activation and targeted disruption of signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (Stat3) in mouse epidermis reveal its critical role in UVB-induced skin carcinogenesis. Oncogene. 2009;28:950–960. doi: 10.1038/onc.2008.453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Fernau NS, Fugmann D, Leyendecker M, et al. Role of HuR and p38-MAP kinase in ultraviolet B-induced post-transcriptional regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in the human keratinocyte cell line HaCaT. J Biol Chem. 2009;5:3896–3904. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.081430. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


