Abstract
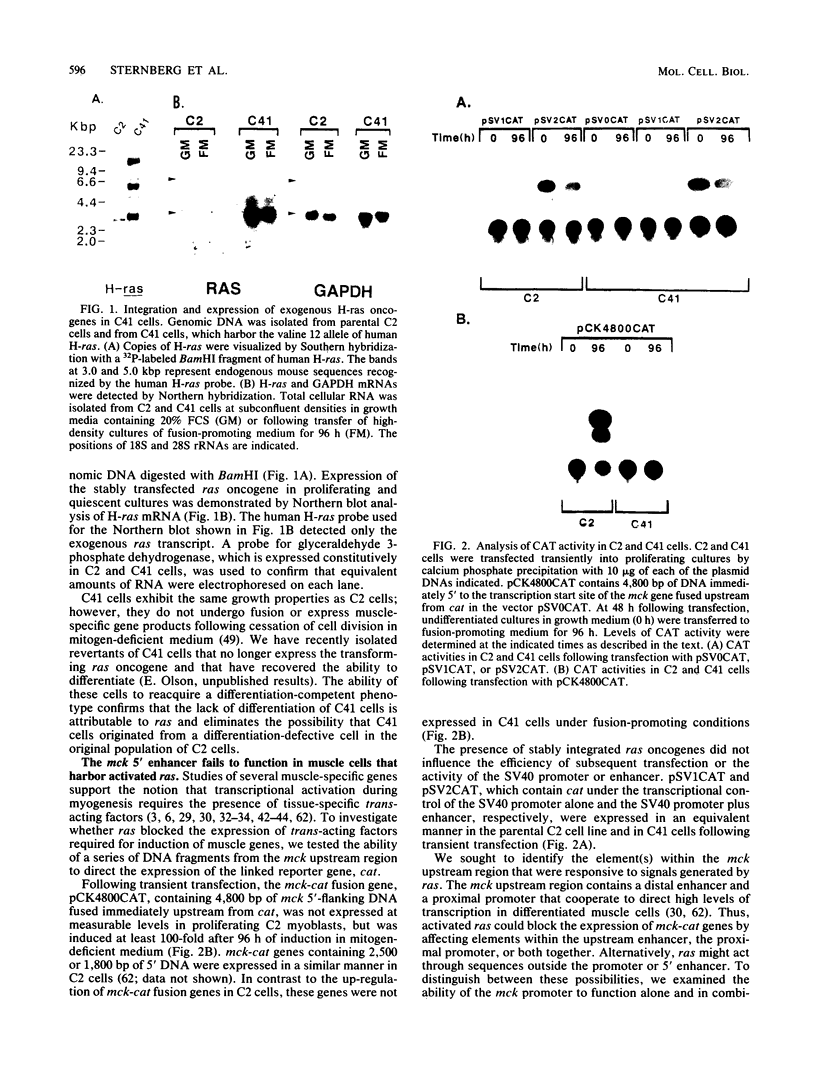
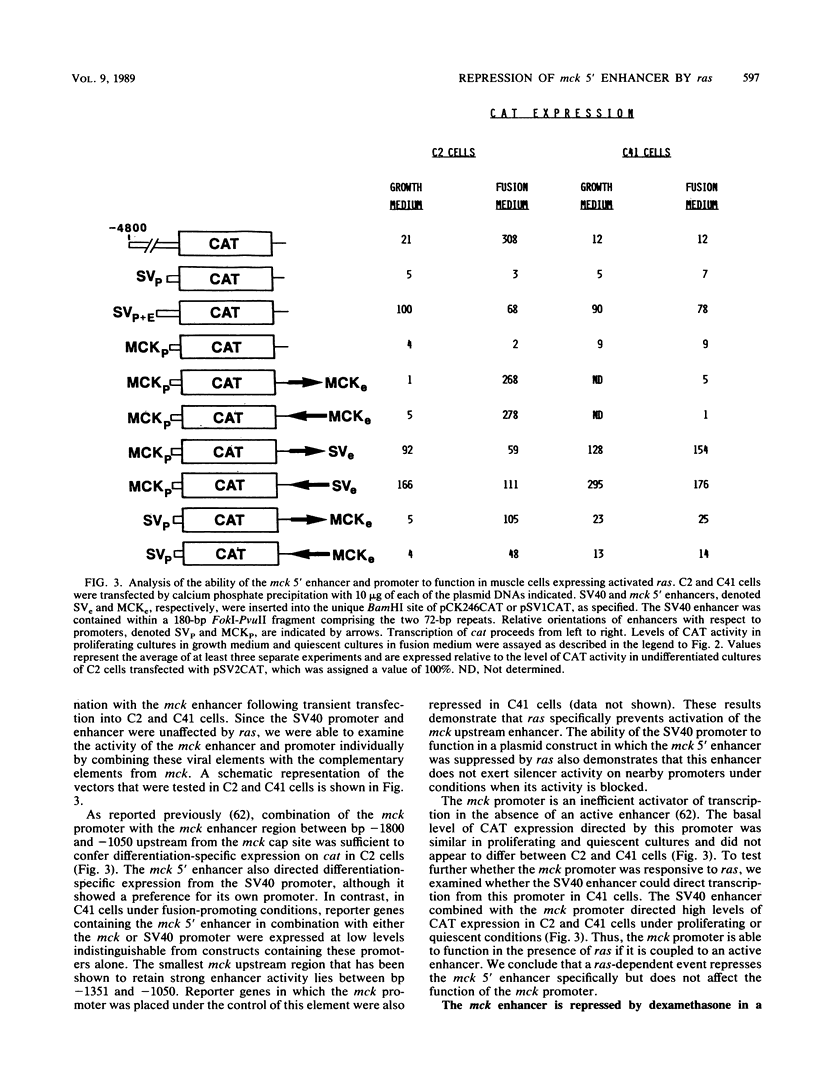
Differentiation of skeletal myoblasts is accompanied by induction of a series of tissue-specific genes whose products are required for the specialized functions of the mature muscle fiber. The program for myogenic differentiation is subject to negative control by several peptide growth factors and by the products of mutationally activated ras oncogenes, which persistently activate intracellular cascades normally triggered by specific growth factors. Previously, we reported that induction of the muscle creatine kinase (mck) gene during myogenesis was dependent on a distal upstream enhancer that cooperated with a proximal promoter to direct high levels of expression in developing muscle cells (E. A. Sternberg, G. Spizz, W. M. Perry, D. Vizard, T. Weil, and E. N. Olson, Mol. Cell. Biol. 8:2896-2909). To investigate the mechanisms whereby ras blocks the induction of muscle-specific genes, we have examined the ability of mck 5' regulatory elements to direct expression of the linked reporter gene for chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (cat) in C2 myoblasts bearing mutant N-ras and H-ras oncogenes. In this paper we report that expression of activated ras alleles abolishes activity of the mck upstream enhancer but does not affect the activity of the mck promoter. The ability of ras to repress the expression of mck-cat fusion genes that have been transfected either transiently or stably into myoblasts suggests that ras may exert its effects on muscle-specific genes through mechanisms independent of chromatin configurations or DNA methylation. These results also suggest that ras blocks establishment of the myogenic phenotype by preventing the accumulation of regulatory factors required for transcriptional induction of muscle-specific genes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Angel P., Allegretto E. A., Okino S. T., Hattori K., Boyle W. J., Hunter T., Karin M. Oncogene jun encodes a sequence-specific trans-activator similar to AP-1. Nature. 1988 Mar 10;332(6160):166–171. doi: 10.1038/332166a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bar-Sagi D., Feramisco J. R. Microinjection of the ras oncogene protein into PC12 cells induces morphological differentiation. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):841–848. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90280-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergsma D. J., Grichnik J. M., Gossett L. M., Schwartz R. J. Delimitation and characterization of cis-acting DNA sequences required for the regulated expression and transcriptional control of the chicken skeletal alpha-actin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2462–2475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau H. M., Chiu C. P., Webster C. Cytoplasmic activation of human nuclear genes in stable heterocaryons. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1171–1180. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90300-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blau H. M., Pavlath G. K., Hardeman E. C., Chiu C. P., Silberstein L., Webster S. G., Miller S. C., Webster C. Plasticity of the differentiated state. Science. 1985 Nov 15;230(4727):758–766. doi: 10.1126/science.2414846. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvagnet P. F., Strehler E. E., White G. E., Strehler-Page M. A., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Multiple positive and negative 5' regulatory elements control the cell-type-specific expression of the embryonic skeletal myosin heavy-chain gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4377–4389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown R., Marshall C. J., Pennie S. G., Hall A. Mechanism of activation of an N-ras gene in the human fibrosarcoma cell line HT1080. EMBO J. 1984 Jun;3(6):1321–1326. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01970.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caffrey J. M., Brown A. M., Schneider M. D. Mitogens and oncogenes can block the induction of specific voltage-gated ion channels. Science. 1987 May 1;236(4801):570–573. doi: 10.1126/science.2437651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caravatti M., Minty A., Robert B., Montarras D., Weydert A., Cohen A., Daubas P., Buckingham M. Regulation of muscle gene expression. The accumulation of messenger RNAs coding for muscle-specific proteins during myogenesis in a mouse cell line. J Mol Biol. 1982 Sep;160(1):59–76. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90131-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmon Y., Czosnek H., Nudel U., Shani M., Yaffe D. DNAase I sensitivity of genes expressed during myogenesis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3085–3098. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chiu R., Boyle W. J., Meek J., Smeal T., Hunter T., Karin M. The c-Fos protein interacts with c-Jun/AP-1 to stimulate transcription of AP-1 responsive genes. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):541–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90076-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clegg C. H., Linkhart T. A., Olwin B. B., Hauschka S. D. Growth factor control of skeletal muscle differentiation: commitment to terminal differentiation occurs in G1 phase and is repressed by fibroblast growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;105(2):949–956. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.2.949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crowder C. M., Merlie J. P. DNase I-hypersensitive sites surround the mouse acetylcholine receptor delta-subunit gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8405–8409. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8405. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. L., Weintraub H., Lassar A. B. Expression of a single transfected cDNA converts fibroblasts to myoblasts. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):987–1000. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90585-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devlin R. B., Emerson C. P., Jr Coordinate regulation of contractile protein synthesis during myoblast differentiation. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):599–611. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90211-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugaiczyk A., Haron J. A., Stone E. M., Dennison O. E., Rothblum K. N., Schwartz R. J. Cloning and sequencing of a deoxyribonucleic acid copy of glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase messenger ribonucleic acid isolated from chicken muscle. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1605–1613. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Gross M., Kamata T., Rosenberg M., Sweet R. W. Microinjection of the oncogene form of the human H-ras (T-24) protein results in rapid proliferation of quiescent cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90531-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Florini J. R., Roberts A. B., Ewton D. Z., Falen S. L., Flanders K. C., Sporn M. B. Transforming growth factor-beta. A very potent inhibitor of myoblast differentiation, identical to the differentiation inhibitor secreted by Buffalo rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1986 Dec 15;261(35):16509–16513. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Sigal I. S., Poe M., Scolnick E. M. Intrinsic GTPase activity distinguishes normal and oncogenic ras p21 molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5704–5708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Weseman J., Moran J. S., Lindstrom J. Effect of fibroblast growth factor on the division and fusion of bovine myoblasts. J Cell Biol. 1976 Aug;70(2 Pt 1):395–405. doi: 10.1083/jcb.70.2.395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett L. A., Zhang W., Olson E. N. Dexamethasone-dependent inhibition of differentiation of C2 myoblasts bearing steroid-inducible N-ras oncogenes. J Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;106(6):2127–2137. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.6.2127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hölttä E., Sistonen L., Alitalo K. The mechanisms of ornithine decarboxylase deregulation in c-Ha-ras oncogene-transformed NIH 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1988 Mar 25;263(9):4500–4507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imler J. L., Schatz C., Wasylyk C., Chatton B., Wasylyk B. A Harvey-ras responsive transcription element is also responsive to a tumour-promoter and to serum. Nature. 1988 Mar 17;332(6161):275–278. doi: 10.1038/332275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes J. B., Chamberlain J. S., Buskin J. N., Johnson J. E., Hauschka S. D. Transcriptional regulation of the muscle creatine kinase gene and regulated expression in transfected mouse myoblasts. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Aug;6(8):2855–2864. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.8.2855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaynes J. B., Johnson J. E., Buskin J. N., Gartside C. L., Hauschka S. D. The muscle creatine kinase gene is regulated by multiple upstream elements, including a muscle-specific enhancer. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):62–70. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N. C. Gene expression. Negative regulation of enhancers. Nature. 1986 May 15;321(6067):202–203. doi: 10.1038/321202a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klarsfeld A., Daubas P., Bourachot B., Changeux J. P. A 5'-flanking region of the chicken acetylcholine receptor alpha-subunit gene confers tissue specificity and developmental control of expression in transfected cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):951–955. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny S. F., Emerson C. P., Jr Complex regulation of the muscle-specific contractile protein (troponin I) gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Sep;7(9):3065–3075. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.9.3065. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konieczny S. F., Emerson C. P., Jr Differentiation, not determination, regulates muscle gene activation: transfection of troponin I genes into multipotential and muscle lineages of 10T1/2 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Sep;5(9):2423–2432. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.9.2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop B., Olson E., Glaser L. Control by fibroblast growth factor of differentiation in the BC3H1 muscle cell line. J Cell Biol. 1985 May;100(5):1540–1547. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.5.1540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lathrop B., Thomas K., Glaser L. Control of myogenic differentiation by fibroblast growth factor is mediated by position in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. J Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;101(6):2194–2198. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.6.2194. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Massagué J., Cheifetz S., Endo T., Nadal-Ginard B. Type beta transforming growth factor is an inhibitor of myogenic differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8206–8210. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller S. C., Ito H., Blau H. M., Torti F. M. Tumor necrosis factor inhibits human myogenesis in vitro. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jun;8(6):2295–2301. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.6.2295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Blau H., Kedes L. Two-level regulation of cardiac actin gene transcription: muscle-specific modulating factors can accumulate before gene activation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2137–2148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Minty A., Kedes L. Upstream regions of the human cardiac actin gene that modulate its transcription in muscle cells: presence of an evolutionarily conserved repeated motif. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):2125–2136. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.2125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miwa T., Kedes L. Duplicated CArG box domains have positive and mutually dependent regulatory roles in expression of the human alpha-cardiac actin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2803–2813. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulcahy L. S., Smith M. R., Stacey D. W. Requirement for ras proto-oncogene function during serum-stimulated growth of NIH 3T3 cells. Nature. 1985 Jan 17;313(5999):241–243. doi: 10.1038/313241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadal-Ginard B. Commitment, fusion and biochemical differentiation of a myogenic cell line in the absence of DNA synthesis. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):855–864. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90270-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Caldwell K. L., Gordon J. I., Glaser L. Regulation of creatine phosphokinase expression during differentiation of BC3H1 cells. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2644–2652. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Spizz G., Tainsky M. A. The oncogenic forms of N-ras or H-ras prevent skeletal myoblast differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jun;7(6):2104–2111. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.6.2104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson E. N., Sternberg E., Hu J. S., Spizz G., Wilcox C. Regulation of myogenic differentiation by type beta transforming growth factor. J Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;103(5):1799–1805. doi: 10.1083/jcb.103.5.1799. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen R. D., Ostrowski M. C. Rapid and selective alterations in the expression of cellular genes accompany conditional transcription of Ha-v-ras in NIH 3T3 cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2512–2520. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parada L. F., Tabin C. J., Shih C., Weinberg R. A. Human EJ bladder carcinoma oncogene is homologue of Harvey sarcoma virus ras gene. Nature. 1982 Jun 10;297(5866):474–478. doi: 10.1038/297474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne P. A., Olson E. N., Hsiau P., Roberts R., Perryman M. B., Schneider M. D. An activated c-Ha-ras allele blocks the induction of muscle-specific genes whose expression is contingent on mitogen withdrawal. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):8956–8960. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.8956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sassone-Corsi P., Lamph W. W., Kamps M., Verma I. M. fos-associated cellular p39 is related to nuclear transcription factor AP-1. Cell. 1988 Aug 12;54(4):553–560. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90077-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. D., Olson E. N. Control of myogenic differentiation by cellular oncogenes. Mol Neurobiol. 1988 Spring;2(1):1–39. doi: 10.1007/BF02935631. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider M. D., Perryman M. B., Payne P. A., Spizz G., Roberts R., Olson E. N. Autonomous expression of c-myc in BC3H1 cells partially inhibits but does not prevent myogenic differentiation. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):1973–1977. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seiler-Tuyns A., Eldridge J. D., Paterson B. M. Expression and regulation of chicken actin genes introduced into mouse myogenic and nonmyogenic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):2980–2984. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.2980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizz G., Hu J. S., Olson E. N. Inhibition of myogenic differentiation by fibroblast growth factor or type beta transforming growth factor does not require persistent c-myc expression. Dev Biol. 1987 Oct;123(2):500–507. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90408-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizz G., Roman D., Strauss A., Olson E. N. Serum and fibroblast growth factor inhibit myogenic differentiation through a mechanism dependent on protein synthesis and independent of cell proliferation. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jul 15;261(20):9483–9488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Watson T., Kung H. F., Curran T. Microinjection of transforming ras protein induces c-fos expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jan;7(1):523–527. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.1.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberg E. A., Spizz G., Perry W. M., Vizard D., Weil T., Olson E. N. Identification of upstream and intragenic regulatory elements that confer cell-type-restricted and differentiation-specific expression on the muscle creatine kinase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jul;8(7):2896–2909. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.7.2896. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sweet R. W., Yokoyama S., Kamata T., Feramisco J. R., Rosenberg M., Gross M. The product of ras is a GTPase and the T24 oncogenic mutant is deficient in this activity. Nature. 1984 Sep 20;311(5983):273–275. doi: 10.1038/311273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakelam M. J., Davies S. A., Houslay M. D., McKay I., Marshall C. J., Hall A. Normal p21N-ras couples bombesin and other growth factor receptors to inositol phosphate production. Nature. 1986 Sep 11;323(6084):173–176. doi: 10.1038/323173a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster K. A., Muscat G. E., Kedes L. Adenovirus E1A products suppress myogenic differentiation and inhibit transcription from muscle-specific promoters. Nature. 1988 Apr 7;332(6164):553–557. doi: 10.1038/332553a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E., Aronoff J. The suppression of myogenic functions in heterokaryons formed by fusing chick myocytes to diploid rat fibroblasts. Cell Differ. 1983 May;12(5):299–306. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(83)90026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright W. E. Expression of differentiated functions in heterokaryons between skeletal myocytes, adrenal cells, fibroblasts and glial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Mar;151(1):55–69. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yaffe D., Saxel O. Serial passaging and differentiation of myogenic cells isolated from dystrophic mouse muscle. Nature. 1977 Dec 22;270(5639):725–727. doi: 10.1038/270725a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yisraeli J., Adelstein R. S., Melloul D., Nudel U., Yaffe D., Cedar H. Muscle-specific activation of a methylated chimeric actin gene. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):409–416. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90661-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






