Abstract
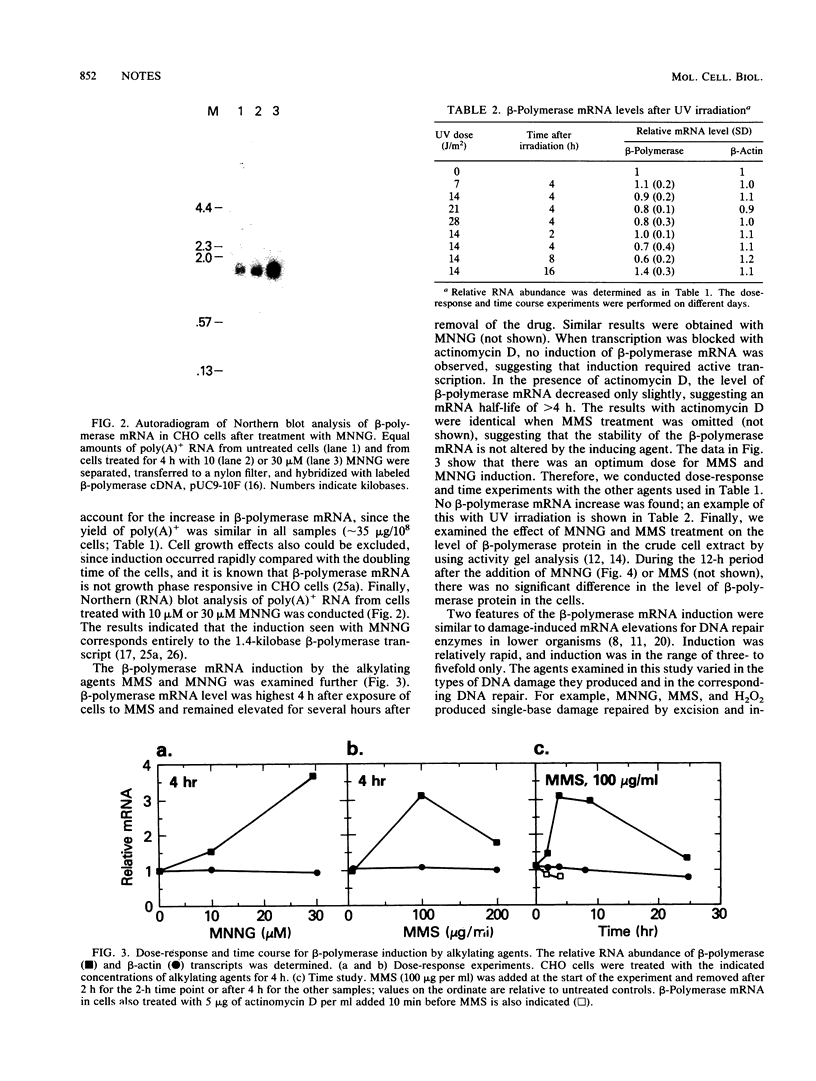
Only a few of the genes involved in DNA repair in mammalian cells have been isolated, and induction of a DNA repair gene in response to DNA damage has not yet been established. DNA polymerase beta (beta-polymerase) appears to have a synthetic role in DNA repair after certain types of DNA damage. Here we show that the level of beta-polymerase mRNA is increased in CHO cells after treatment with several DNA-damaging agents.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cleaver J. E. Structure of repaired sites in human DNA synthesized in the presence of inhibitors of DNA polymerases alpha and beta in human fibroblasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Apr 15;739(3):301–311. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(83)90105-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobianchi F., SenGupta D. N., Zmudzka B. Z., Wilson S. H. Structure of rodent helix-destabilizing protein revealed by cDNA cloning. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3536–3543. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresler S. L., Lieberman M. W. Identification of DNA polymerases involved in DNA excision repair in diploid human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1983 Aug 25;258(16):9990–9994. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. H., Linn S. Excision repair of pyrimidine dimers from simian virus 40 minichromosomes in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10252–10259. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr, Dobson P. P., Kinsella T. J. Analysis of the effect of DNA alkylation on alkaline elution. Carcinogenesis. 1986 Jun;7(6):927–932. doi: 10.1093/carcin/7.6.927. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr, Mitchell J. B. Induction of B2 RNA polymerase III transcription by heat shock: enrichment for heat shock induced sequences in rodent cells by hybridization subtraction. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jul 25;14(14):5793–5811. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.14.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fornace A. J., Jr Recombination of parent and daughter strand DNA after UV-irradiation in mammalian cells. Nature. 1983 Aug 11;304(5926):552–554. doi: 10.1038/304552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. L., Barker D. G., Johnston L. H. Induction of yeast DNA ligase genes in exponential and stationary phase cultures in response to DNA damaging agents. Curr Genet. 1986;11(2):107–112. doi: 10.1007/BF00378201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston L. H., White J. H., Johnson A. L., Lucchini G., Plevani P. The yeast DNA polymerase I transcript is regulated in both the mitotic cell cycle and in meiosis and is also induced after DNA damage. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Jul 10;15(13):5017–5030. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.13.5017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karawya E., Swack J. A., Wilson S. H. Improved conditions for activity gel analysis of DNA polymerase catalytic polypeptides. Anal Biochem. 1983 Dec;135(2):318–325. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90689-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller M. R., Chinault D. N. The roles of DNA polymerases alpha, beta, and gamma in DNA repair synthesis induced in hamster and human cells by different DNA damaging agents. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10204–10209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell J. B., Karawya E., Kinsella T. J., Wilson S. H. Measurement of DNA polymerase beta in skin fibroblast cell lines from patients with ataxia telangiectasia. Mutat Res. 1985 Nov;146(3):295–300. doi: 10.1016/0167-8817(85)90071-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosbaugh D. W., Linn S. Excision repair and DNA synthesis with a combination of HeLa DNA polymerase beta and DNase V. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):108–118. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roberts J. J., Pascoe J. M., Plant J. E., Sturrock J. E., Crathorn A. R. Quantitative aspects of the repair of alkylated DNA in cultured mammalian cells. I. The effect on HeLa and Chinese hamster cell survival of alkylation of cellular macromolecules. Chem Biol Interact. 1971 Feb;3(1):29–47. doi: 10.1016/0009-2797(71)90024-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SenGupta D. N., Zmudzka B. Z., Kumar P., Cobianchi F., Skowronski J., Wilson S. H. Sequence of human DNA polymerase beta mRNA obtained through cDNA cloning. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Apr 14;136(1):341–347. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90916-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Okumoto D. S. Nature of DNA repair synthesis resistant to inhibitors of polymerase alpha in human cells. Biochemistry. 1984 Mar 27;23(7):1383–1391. doi: 10.1021/bi00302a008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sołtyk A., Siedlecki J. A., Pietrzykowska I., Zmudzka B. Reactions of calf thymus DNA polymerases alpha and beta with native DNA damaged by thymine starvation or by methyl methanesulphonate treatment with Escherichia coli cells. FEBS Lett. 1981 Mar 23;125(2):227–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(81)80725-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker G. C. Mutagenesis and inducible responses to deoxyribonucleic acid damage in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1984 Mar;48(1):60–93. doi: 10.1128/mr.48.1.60-93.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. S., Eichler D. C., Korn D. Effect of Mn2+ on the in vitro activity of human deoxyribonucleic acid polymerase beta. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 1;16(22):4927–4934. doi: 10.1021/bi00641a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang T. S., Korn D. Reactivity of KB cell deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases alpha and beta with nicked and gapped deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1980 Apr 29;19(9):1782–1790. doi: 10.1021/bi00550a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widen S. G., Kedar P., Wilson S. H. Human beta-polymerase gene. Structure of the 5'-flanking region and active promoter. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 15;263(32):16992–16998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson S., Abbotts J., Widen S. Progress toward molecular biology of DNA polymerase beta. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Feb 28;949(2):149–157. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90078-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada K., Hanaoka F., Yamada M. Effects of aphidicolin and/or 2',3'-dideoxythymidine on DNA repair induced in HeLa cells by four types of DNA-damaging agents. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10412–10417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi M., Hirose F., Hayashi Y., Nishimoto Y., Matsukage A. Murine DNA polymerase beta gene: mapping of transcription initiation sites and the nucleotide sequence of the putative promoter region. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 May;7(5):2012–2018. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.5.2012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zmudzka B. Z., Fornace A., Collins J., Wilson S. H. Characterization of DNA polymerase beta mRNA: cell-cycle and growth response in cultured human cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Oct 25;16(20):9587–9596. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.20.9587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zmudzka B. Z., SenGupta D., Matsukage A., Cobianchi F., Kumar P., Wilson S. H. Structure of rat DNA polymerase beta revealed by partial amino acid sequencing and cDNA cloning. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(14):5106–5110. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.14.5106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]