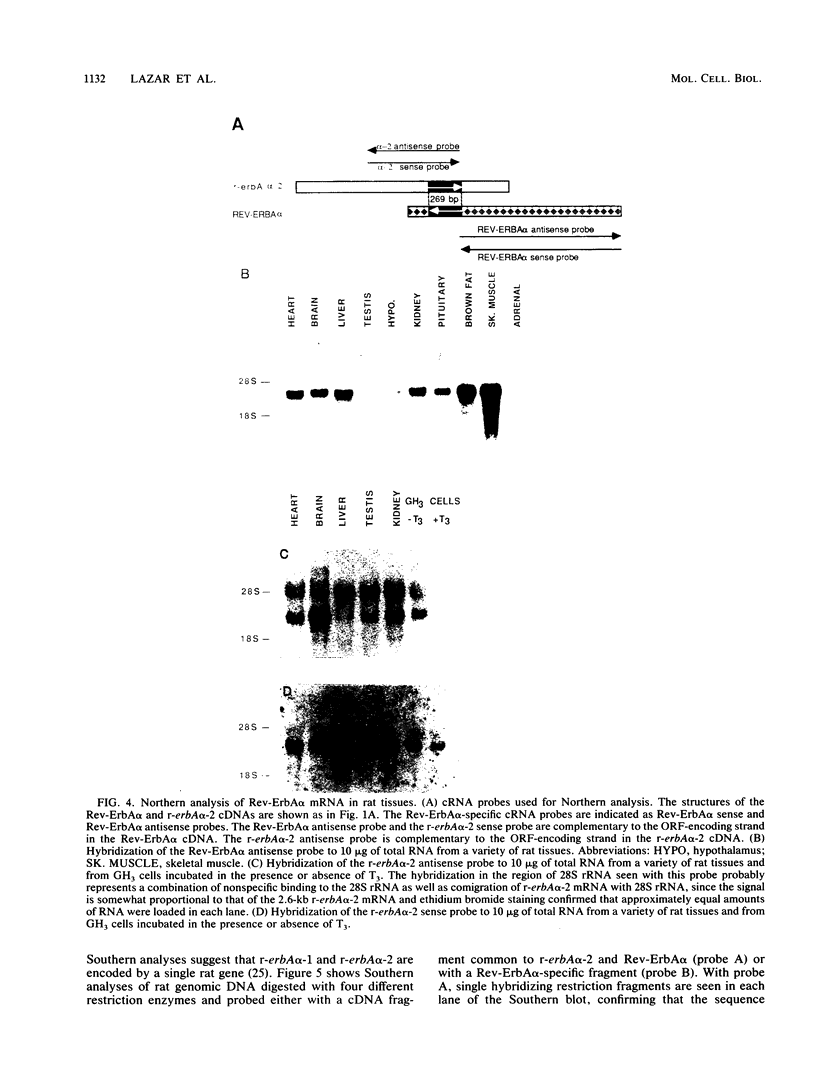
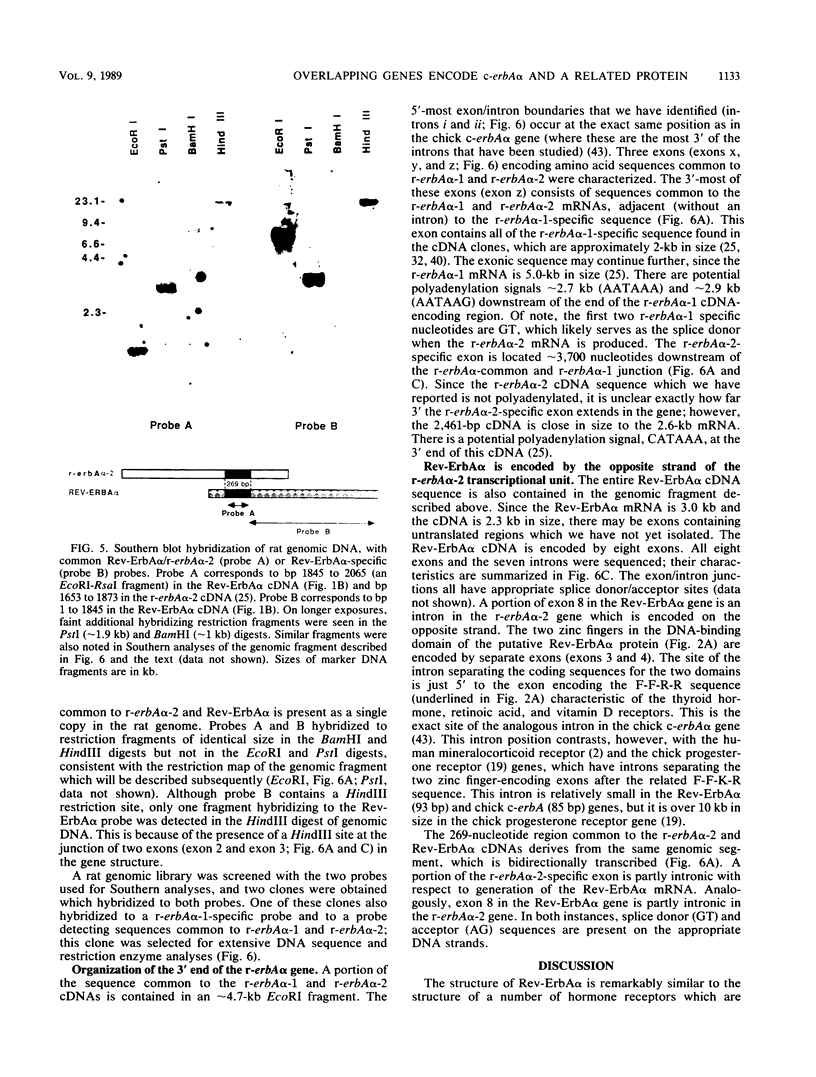
Abstract
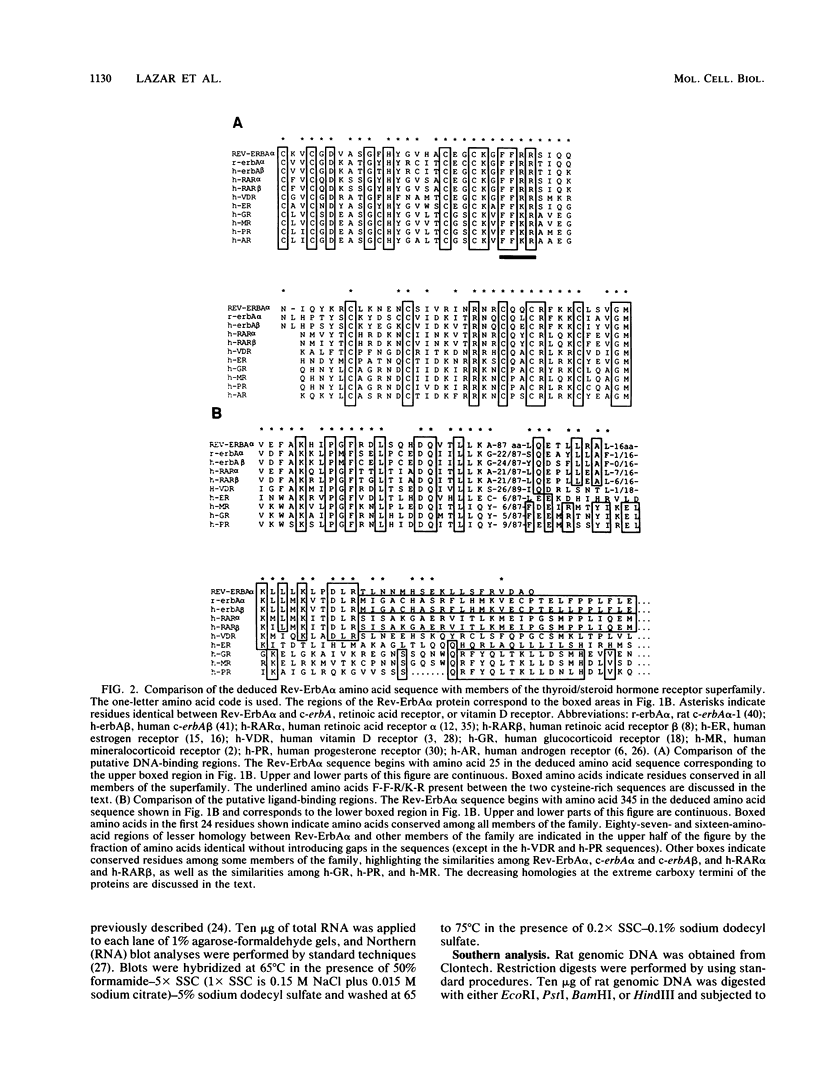
A cDNA encoding a novel member of the thyroid/steroid hormone receptor superfamily, called Rev-ErbA alpha, has been isolated from a rat GH3 cell library. Rev-ErbA alpha is an approximately 56-kilodalton protein most similar in structure to the thyroid hormone receptor (c-erbA) and the retinoic acid receptor, but it does not bind either thyroid hormone or retinoic acid. The mRNA encoding Rev-ErbA alpha is present in many tissues and is particularly abundant in skeletal muscle and brown fat. A genomic DNA fragment containing the entire Rev-ErbA alpha cDNA sequence was isolated and characterized. Remarkably, this DNA fragment also contained a portion of the c-erbA alpha gene. r-erbA alpha-1 and r-erbA alpha-2 are alternative splice products of the c-erbA alpha gene and are members of the receptor superfamily. The genes encoding Rev-ErbA alpha and r-erbA alpha-2 overlap, with their coding strands oriented opposite one another. A 269-base-pair segment of the bidirectionally transcribed region is exonic in both the Rev-ErbA alpha and r-erbA alpha-2 genes, resulting in complementary mRNAs. Thus, through alternative splicing and opposite-strand transcription, a single genomic locus codes for three different members of the thyroid/steroid hormone receptor superfamily. Potential implications of this unusual genomic arrangement are discussed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adelman J. P., Bond C. T., Douglass J., Herbert E. Two mammalian genes transcribed from opposite strands of the same DNA locus. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1514–1517. doi: 10.1126/science.3547652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arriza J. L., Weinberger C., Cerelli G., Glaser T. M., Handelin B. L., Housman D. E., Evans R. M. Cloning of human mineralocorticoid receptor complementary DNA: structural and functional kinship with the glucocorticoid receptor. Science. 1987 Jul 17;237(4812):268–275. doi: 10.1126/science.3037703. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker A. R., McDonnell D. P., Hughes M., Crisp T. M., Mangelsdorf D. J., Haussler M. R., Pike J. W., Shine J., O'Malley B. W. Cloning and expression of full-length cDNA encoding human vitamin D receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3294–3298. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3294. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benbrook D., Pfahl M. A novel thyroid hormone receptor encoded by a cDNA clone from a human testis library. Science. 1987 Nov 6;238(4828):788–791. doi: 10.1126/science.3672126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand N., Petkovich M., Krust A., Chambon P., de Thé H., Marchio A., Tiollais P., Dejean A. Identification of a second human retinoic acid receptor. Nature. 1988 Apr 28;332(6167):850–853. doi: 10.1038/332850a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. S., Kokontis J., Liao S. T. Molecular cloning of human and rat complementary DNA encoding androgen receptors. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):324–326. doi: 10.1126/science.3353726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M., Hollenberg S. M. Zinc fingers: gilt by association. Cell. 1988 Jan 15;52(1):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90522-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans R. M. The steroid and thyroid hormone receptor superfamily. Science. 1988 May 13;240(4854):889–895. doi: 10.1126/science.3283939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguere V., Ong E. S., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a receptor for the morphogen retinoic acid. Nature. 1987 Dec 17;330(6149):624–629. doi: 10.1038/330624a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giguère V., Yang N., Segui P., Evans R. M. Identification of a new class of steroid hormone receptors. Nature. 1988 Jan 7;331(6151):91–94. doi: 10.1038/331091a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Chambon P. A superfamily of potentially oncogenic hormone receptors. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):615–617. doi: 10.1038/324615a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green S., Walter P., Kumar V., Krust A., Bornert J. M., Argos P., Chambon P. Human oestrogen receptor cDNA: sequence, expression and homology to v-erb-A. Nature. 1986 Mar 13;320(6058):134–139. doi: 10.1038/320134a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene G. L., Gilna P., Waterfield M., Baker A., Hort Y., Shine J. Sequence and expression of human estrogen receptor complementary DNA. Science. 1986 Mar 7;231(4742):1150–1154. doi: 10.1126/science.3753802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S., Keene M. A., Fechtel K., Fristrom J. W. Gene within a gene: nested Drosophila genes encode unrelated proteins on opposite DNA strands. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):33–42. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90482-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollenberg S. M., Weinberger C., Ong E. S., Cerelli G., Oro A., Lebo R., Thompson E. B., Rosenfeld M. G., Evans R. M. Primary structure and expression of a functional human glucocorticoid receptor cDNA. Nature. 1985 Dec 19;318(6047):635–641. doi: 10.1038/318635a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huckaby C. S., Conneely O. M., Beattie W. G., Dobson A. D., Tsai M. J., O'Malley B. W. Structure of the chromosomal chicken progesterone receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(23):8380–8384. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.23.8380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumo S., Mahdavi V. Thyroid hormone receptor alpha isoforms generated by alternative splicing differentially activate myosin HC gene transcription. Nature. 1988 Aug 11;334(6182):539–542. doi: 10.1038/334539a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim S. K., Wold B. J. Stable reduction of thymidine kinase activity in cells expressing high levels of anti-sense RNA. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):129–138. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80108-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindy M. S., McCormack J. E., Buckler A. J., Levine R. A., Sonenshein G. E. Independent regulation of transcription of the two strands of the c-myc gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Aug;7(8):2857–2862. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.8.2857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig R. J., Warne R. L., Brent G. A., Harney J. W., Larsen P. R., Moore D. D. Isolation of a cDNA clone encoding a biologically active thyroid hormone receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Jul;85(14):5031–5035. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.14.5031. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar M. A., Chin W. W. Regulation of two c-erbA messenger ribonucleic acids in rat GH3 cells by thyroid hormone. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Jun;2(6):479–484. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-6-479. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazar M. A., Hodin R. A., Darling D. S., Chin W. W. Identification of a rat c-erbA alpha-related protein which binds deoxyribonucleic acid but does not bind thyroid hormone. Mol Endocrinol. 1988 Oct;2(10):893–901. doi: 10.1210/mend-2-10-893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubahn D. B., Joseph D. R., Sullivan P. M., Willard H. F., French F. S., Wilson E. M. Cloning of human androgen receptor complementary DNA and localization to the X chromosome. Science. 1988 Apr 15;240(4850):327–330. doi: 10.1126/science.3353727. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell D. P., Mangelsdorf D. J., Pike J. W., Haussler M. R., O'Malley B. W. Molecular cloning of complementary DNA encoding the avian receptor for vitamin D. Science. 1987 Mar 6;235(4793):1214–1217. doi: 10.1126/science.3029866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Misrahi M., Atger M., d'Auriol L., Loosfelt H., Meriel C., Fridlansky F., Guiochon-Mantel A., Galibert F., Milgrom E. Complete amino acid sequence of the human progesterone receptor deduced from cloned cDNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1987 Mar 13;143(2):740–748. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(87)91416-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitsuhashi T., Tennyson G. E., Nikodem V. M. Alternative splicing generates messages encoding rat c-erbA proteins that do not bind thyroid hormone. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):5804–5808. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.5804. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray M. B., Zilz N. D., McCreary N. L., MacDonald M. J., Towle H. C. Isolation and characterization of rat cDNA clones for two distinct thyroid hormone receptors. J Biol Chem. 1988 Sep 5;263(25):12770–12777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai A., Seino S., Sakurai A., Szilak I., Bell G. I., DeGroot L. J. Characterization of a thyroid hormone receptor expressed in human kidney and other tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2781–2785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nepveu A., Marcu K. B. Intragenic pausing and anti-sense transcription within the murine c-myc locus. EMBO J. 1986 Nov;5(11):2859–2865. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04580.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petkovich M., Brand N. J., Krust A., Chambon P. A human retinoic acid receptor which belongs to the family of nuclear receptors. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):444–450. doi: 10.1038/330444a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. Retinoic acid receptor. Towards a biochemistry of morphogenesis. Nature. 1987 Dec 3;330(6147):420–421. doi: 10.1038/330420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sap J., Muñoz A., Damm K., Goldberg Y., Ghysdael J., Leutz A., Beug H., Vennström B. The c-erb-A protein is a high-affinity receptor for thyroid hormone. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):635–640. doi: 10.1038/324635a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spencer C. A., Gietz R. D., Hodgetts R. B. Overlapping transcription units in the dopa decarboxylase region of Drosophila. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):279–281. doi: 10.1038/322279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. C., Weinberger C., Lebo R., Evans R. M. Identification of a novel thyroid hormone receptor expressed in the mammalian central nervous system. Science. 1987 Sep 25;237(4822):1610–1614. doi: 10.1126/science.3629259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinberger C., Thompson C. C., Ong E. S., Lebo R., Gruol D. J., Evans R. M. The c-erb-A gene encodes a thyroid hormone receptor. Nature. 1986 Dec 18;324(6098):641–646. doi: 10.1038/324641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams T., Fried M. A mouse locus at which transcription from both DNA strands produces mRNAs complementary at their 3' ends. Nature. 1986 Jul 17;322(6076):275–279. doi: 10.1038/322275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahraoui A., Cuny G. Nucleotide sequence of the chicken proto-oncogene c-erbA corresponding to domain 1 of v-erbA. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Jul 1;166(1):63–69. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13484.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]