Abstract
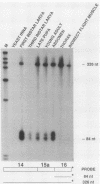
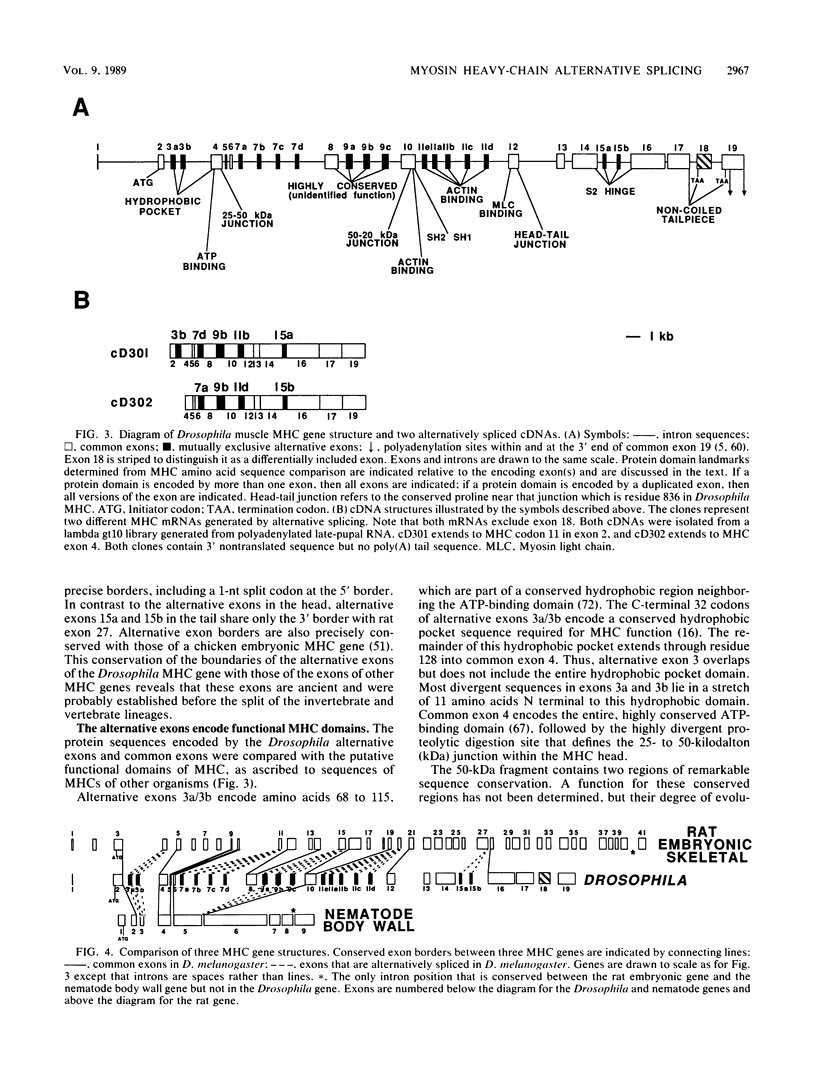
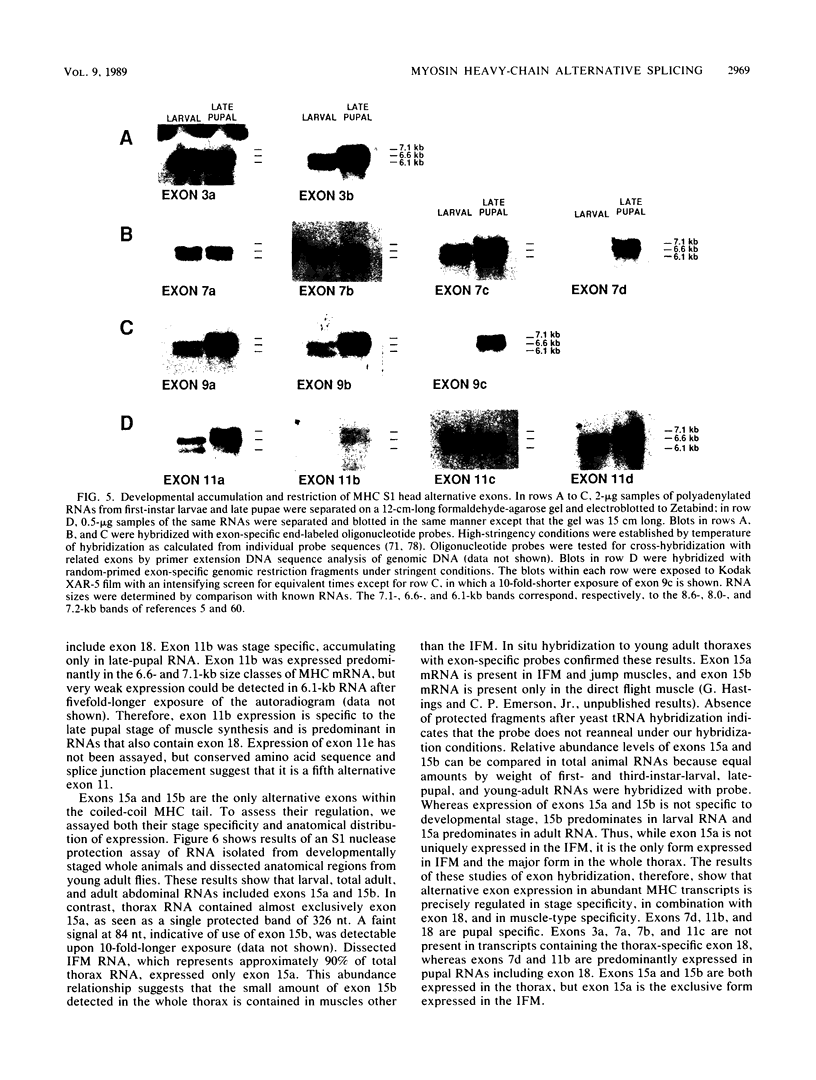
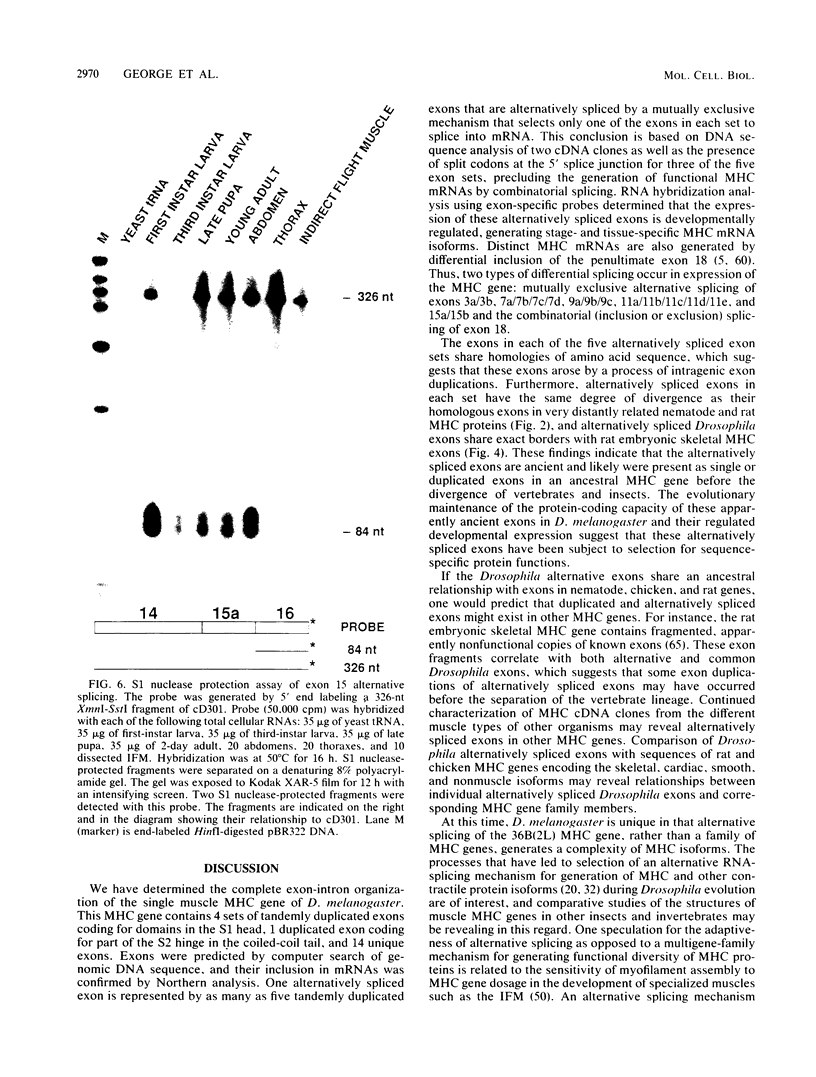
The single-copy Drosophila muscle myosin heavy-chain (MHC) gene, located at 36B(2L), has a complex exon structure that produces a diversity of larval and adult muscle MHC isoforms through regulated alternative RNA splicing. Genomic and cDNA sequence analyses revealed that this 21-kilobase MHC gene encodes these MHC isoforms in 19 exons. However, five sets of these exons, encoding portions of the S1 head and the hinge domains of the MHC protein, are tandemly repeated as two, three, four, or five divergent copies, which are individually spliced into RNA transcripts. RNA hybridization studies with exon-specific probes showed that at least 10 of the 480 possible MHC isoforms that could arise by alternative RNA splicing of these exons are expressed as MHC transcripts and that the expression of specific members of alternative exon sets is regulated, both in stage and in muscle-type specificity. This regulated expression of specific exons is of particular interest because the alternatively spliced exon sets encode discrete domains of the MHC protein that likely contribute to the specialized contractile activities of different Drosophila muscle types. The alternative exon structure of the Drosophila MHC gene and the single-copy nature of this gene in the Drosophila genome make possible transgenic experiments to test the physiological functions of specific MHC protein domains and genetic and molecular experiments to investigate the mechanisms that regulate alternative exon splicing of MHC and other muscle gene transcripts.
Full text
PDF











Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Amara S. G., Jonas V., Rosenfeld M. G., Ong E. S., Evans R. M. Alternative RNA processing in calcitonin gene expression generates mRNAs encoding different polypeptide products. Nature. 1982 Jul 15;298(5871):240–244. doi: 10.1038/298240a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aviv H., Leder P. Purification of biologically active globin messenger RNA by chromatography on oligothymidylic acid-cellulose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Jun;69(6):1408–1412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.6.1408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Sharp P. A. Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell. 1977 Nov;12(3):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90272-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein S. I., Hansen C. J., Becker K. D., Wassenberg D. R., 2nd, Roche E. S., Donady J. J., Emerson C. P., Jr Alternative RNA splicing generates transcripts encoding a thorax-specific isoform of Drosophila melanogaster myosin heavy chain. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2511–2519. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein S. I., Mogami K., Donady J. J., Emerson C. P., Jr Drosophila muscle myosin heavy chain encoded by a single gene in a cluster of muscle mutations. 1983 Mar 31-Apr 6Nature. 302(5907):393–397. doi: 10.1038/302393a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitbart R. E., Nguyen H. T., Medford R. M., Destree A. T., Mahdavi V., Nadal-Ginard B. Intricate combinatorial patterns of exon splicing generate multiple regulated troponin T isoforms from a single gene. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):67–82. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90062-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler-Browne G. S., Whalen R. G. Myosin isozyme transitions occurring during the postnatal development of the rat soleus muscle. Dev Biol. 1984 Apr;102(2):324–334. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90197-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caplan A. I., Fiszman M. Y., Eppenberger H. M. Molecular and cell isoforms during development. Science. 1983 Sep 2;221(4614):921–927. doi: 10.1126/science.6348946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J., Davidson N. Rates of formation and thermal stabilities of RNA:DNA and DNA:DNA duplexes at high concentrations of formamide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1539–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dibb N. J., Brown D. M., Karn J., Moerman D. G., Bolten S. L., Waterston R. H. Sequence analysis of mutations that affect the synthesis, assembly and enzymatic activity of the unc-54 myosin heavy chain of Caenorhabditis elegans. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jun 25;183(4):543–551. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90170-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodgson J. B., Engel J. D. The nucleotide sequence of the adult chicken alpha-globin genes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4623–4629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emerson C. P., Jr, Bernstein S. I. Molecular genetics of myosin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1987;56:695–726. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.56.070187.003403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkenthal S., Graham M., Wilkinson J. The indirect flight muscle of Drosophila accumulates a unique myosin alkali light chain isoform. Dev Biol. 1987 May;121(1):263–272. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90158-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Falkenthal S., Parker V. P., Davidson N. Developmental variations in the splicing pattern of transcripts from the Drosophila gene encoding myosin alkali light chain result in different carboxyl-terminal amino acid sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):449–453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fyrberg E. A., Mahaffey J. W., Bond B. J., Davidson N. Transcripts of the six Drosophila actin genes accumulate in a stage- and tissue-specific manner. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):115–123. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90340-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier J., Osguthorpe D. J., Robson B. Analysis of the accuracy and implications of simple methods for predicting the secondary structure of globular proteins. J Mol Biol. 1978 Mar 25;120(1):97–120. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90297-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler U., Hoffman B. J. A simple and very efficient method for generating cDNA libraries. Gene. 1983 Nov;25(2-3):263–269. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90230-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrington W. F., Rodgers M. E. Myosin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:35–73. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.000343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hastings K. E., Bucher E. A., Emerson C. P., Jr Generation of troponin T isoforms by alternative RNA splicing in avian skeletal muscle. Conserved and divergent features in birds and mammals. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13699–13703. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helfman D. M., Cheley S., Kuismanen E., Finn L. A., Yamawaki-Kataoka Y. Nonmuscle and muscle tropomyosin isoforms are expressed from a single gene by alternative RNA splicing and polyadenylation. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3582–3595. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynes T. R., Block S. M., White B. T., Spudich J. A. Movement of myosin fragments in vitro: domains involved in force production. Cell. 1987 Mar 27;48(6):953–963. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90704-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karlik C. C., Fyrberg E. A. Two Drosophila melanogaster tropomyosin genes: structural and functional aspects. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jun;6(6):1965–1973. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.6.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L. Protein structural domains in the Caenorhabditis elegans unc-54 myosin heavy chain gene are not separated by introns. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4253–4257. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiehart D. P., Lutz M. S., Chan D., Ketchum A. S., Laymon R. A., Nguyen B., Goldstein L. S. Identification of the gene for fly non-muscle myosin heavy chain: Drosophila myosin heavy chains are encoded by a gene family. EMBO J. 1989 Mar;8(3):913–922. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03452.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- King C. R., Piatigorsky J. Alternative RNA splicing of the murine alpha A-crystallin gene: protein-coding information within an intron. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):707–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90056-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laski F. A., Rio D. C., Rubin G. M. Tissue specificity of Drosophila P element transposition is regulated at the level of mRNA splicing. Cell. 1986 Jan 17;44(1):7–19. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90480-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinwand L. A., Saez L., McNally E., Nadal-Ginard B. Isolation and characterization of human myosin heavy chain genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(12):3716–3720. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.12.3716. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linzer D. I., Nathans D. Growth-related changes in specific mRNAs of cultured mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4271–4275. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacLeod A. R., Karn J., Brenner S. Molecular analysis of the unc-54 myosin heavy-chain gene of Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1981 Jun 4;291(5814):386–390. doi: 10.1038/291386a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavi V., Periasamy M., Nadal-Ginard B. Molecular characterization of two myosin heavy chain genes expressed in the adult heart. Nature. 1982 Jun 24;297(5868):659–664. doi: 10.1038/297659a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maniatis T., Hardison R. C., Lacy E., Lauer J., O'Connell C., Quon D., Sim G. K., Efstratiadis A. The isolation of structural genes from libraries of eucaryotic DNA. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):687–701. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90036-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D. Structural implications of the myosin amino acid sequence. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1984;13:167–189. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.13.060184.001123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medford R. M., Nguyen H. T., Destree A. T., Summers E., Nadal-Ginard B. A novel mechanism of alternative RNA splicing for the developmentally regulated generation of troponin T isoforms from a single gene. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):409–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90496-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. M., 3rd, Ortiz I., Berliner G. C., Epstein H. F. Differential localization of two myosins within nematode thick filaments. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):477–490. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90381-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller D. M., Stockdale F. E., Karn J. Immunological identification of the genes encoding the four myosin heavy chain isoforms of Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(8):2305–2309. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.8.2305. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mitchell E. J., Jakes R., Kendrick-Jones J. Localisation of light chain and actin binding sites on myosin. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Nov 17;161(1):25–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb10120.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mogami K., O'Donnell P. T., Bernstein S. I., Wright T. R., Emerson C. P., Jr Mutations of the Drosophila myosin heavy-chain gene: effects on transcription, myosin accumulation, and muscle function. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Mar;83(5):1393–1397. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.5.1393. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina M. I., Kropp K. E., Gulick J., Robbins J. The sequence of an embryonic myosin heavy chain gene and isolation of its corresponding cDNA. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 15;262(14):6478–6488. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mount S. M. A catalogue of splice junction sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Jan 22;10(2):459–472. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.2.459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabeshima Y., Fujii-Kuriyama Y., Muramatsu M., Ogata K. Alternative transcription and two modes of splicing results in two myosin light chains from one gene. Nature. 1984 Mar 22;308(5957):333–338. doi: 10.1038/308333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson-White S. H., Emerson C. P., Jr A novel hybrid alpha-tropomyosin in fibroblasts is produced by alternative splicing of transcripts from the skeletal muscle alpha-tropomyosin gene. J Biol Chem. 1987 Nov 25;262(33):15998–16010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Periasamy M., Wieczorek D. F., Nadal-Ginard B. Characterization of a developmentally regulated perinatal myosin heavy-chain gene expressed in skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13573–13578. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Periasamy M., Wydro R. M., Strehler-Page M. A., Strehler E. E., Nadal-Ginard B. Characterization of cDNA and genomic sequences corresponding to an embryonic myosin heavy chain. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 15;260(29):15856–15862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pringle J. W. The contractile mechanism of insect fibrillar muscle. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1967;17:1–60. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(67)90003-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins J., Freyer G. A., Chisholm D., Gilliam T. C. Isolation of multiple genomic sequences coding for chicken myosin heavy chain protein. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):549–556. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozek C. E., Davidson N. Differential processing of RNA transcribed from the single-copy Drosophila myosin heavy chain gene produces four mRNAs that encode two polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Apr;83(7):2128–2132. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.7.2128. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rozek C. E., Davidson N. Drosophila has one myosin heavy-chain gene with three developmentally regulated transcripts. Cell. 1983 Jan;32(1):23–34. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90493-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin G. M., Spradling A. C. Genetic transformation of Drosophila with transposable element vectors. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):348–353. doi: 10.1126/science.6289436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. Splicing of messenger RNA precursors. Science. 1987 Feb 13;235(4790):766–771. doi: 10.1126/science.3544217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stockdale F. E., Miller J. B. The cellular basis of myosin heavy chain isoform expression during development of avian skeletal muscles. Dev Biol. 1987 Sep;123(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(87)90420-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strehler E. E., Strehler-Page M. A., Perriard J. C., Periasamy M., Nadal-Ginard B. Complete nucleotide and encoded amino acid sequence of a mammalian myosin heavy chain gene. Evidence against intron-dependent evolution of the rod. J Mol Biol. 1986 Aug 5;190(3):291–317. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90003-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutoh K. Mapping of actin-binding sites on the heavy chain of myosin subfragment 1. Biochemistry. 1983 Mar 29;22(7):1579–1585. doi: 10.1021/bi00276a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tong S. W., Elzinga M. The sequence of the NH2-terminal 204-residue fragment of the heavy chain of rabbit skeletal muscle myosin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):13100–13110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toyoshima Y. Y., Kron S. J., McNally E. M., Niebling K. R., Toyoshima C., Spudich J. A. Myosin subfragment-1 is sufficient to move actin filaments in vitro. Nature. 1987 Aug 6;328(6130):536–539. doi: 10.1038/328536a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno H., Harrington W. F. Local melting in the subfragment-2 region of myosin in activated muscle and its correlation with contractile force. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 5;190(1):69–82. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueno H., Harrington W. F. Temperature-dependence of local melting in the myosin subfragment-2 region of the rigor cross-bridge. J Mol Biol. 1986 Jul 5;190(1):59–68. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90075-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wallace R. B., Schold M., Johnson M. J., Dembek P., Itakura K. Oligonucleotide directed mutagenesis of the human beta-globin gene: a general method for producing specific point mutations in cloned DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Aug 11;9(15):3647–3656. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.15.3647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warrick H. M., Spudich J. A. Myosin structure and function in cell motility. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1987;3:379–421. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.03.110187.002115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wassenberg D. R., 2nd, Kronert W. A., O'Donnell P. T., Bernstein S. I. Analysis of the 5' end of the Drosophila muscle myosin heavy chain gene. Alternatively spliced transcripts initiate at a single site and intron locations are conserved compared to myosin genes of other organisms. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10741–10747. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells J. A., Yount R. G. Chemical modification of myosin by active-site trapping of metal-nucleotides with thiol crosslinking reagents. Methods Enzymol. 1982;85(Pt B):93–116. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(82)85013-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weydert A., Daubas P., Caravatti M., Minty A., Bugaisky G., Cohen A., Robert B., Buckingham M. Sequential accumulation of mRNAs encoding different myosin heavy chain isoforms during skeletal muscle development in vivo detected with a recombinant plasmid identified as coding for an adult fast myosin heavy chain from mouse skeletal muscle. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13867–13874. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wieczorek D. F., Periasamy M., Butler-Browne G. S., Whalen R. G., Nadal-Ginard B. Co-expression of multiple myosin heavy chain genes, in addition to a tissue-specific one, in extraocular musculature. J Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;101(2):618–629. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.2.618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wydro R. M., Nguyen H. T., Gubits R. M., Nadal-Ginard B. Characterization of sarcomeric myosin heavy chain genes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):670–678. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoller M. J., Smith M. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Oct 25;10(20):6487–6500. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.20.6487. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]