Abstract
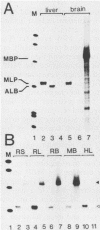
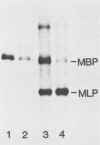
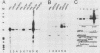
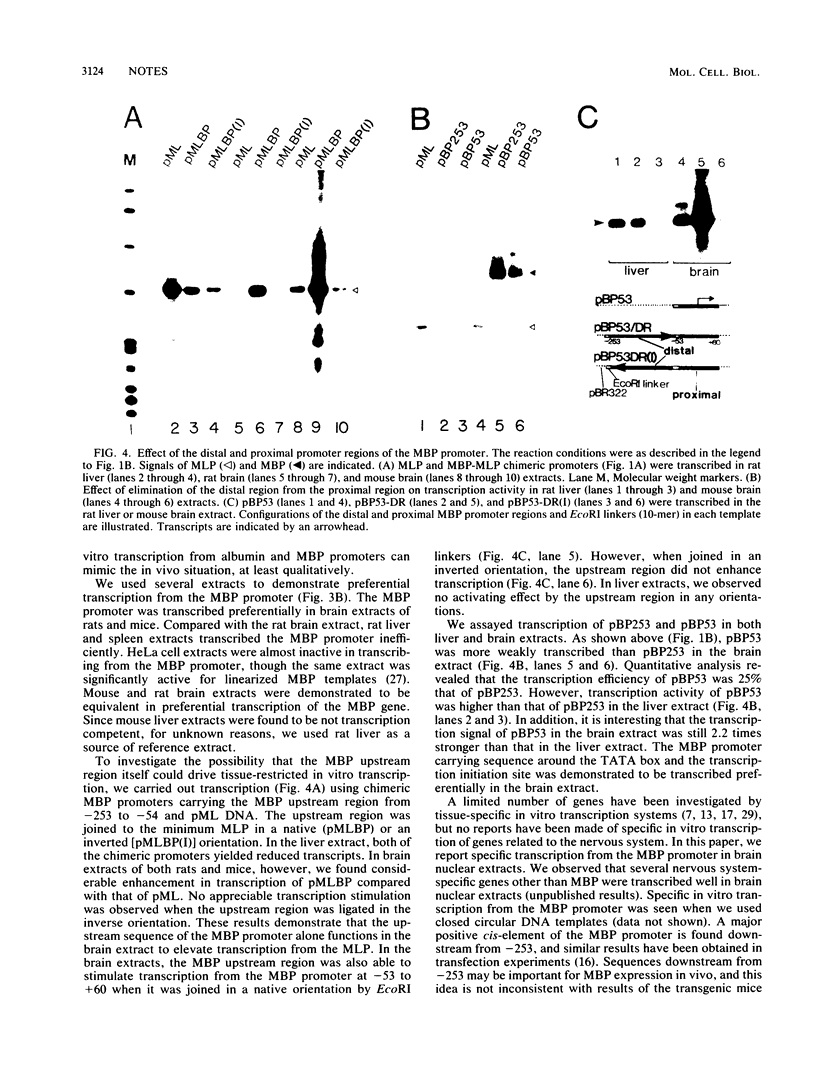
The mouse myelin basic protein promoter was transcribed in brain nuclear extracts. The distal promoter region from -253 to -54 directed preferential transcription in brain extracts, whereas the same region repressed transcription activity in liver extracts. Stimulation of transcription was observed when the distal region was located only in a native orientation. The proximal region downstream from -53 alone still directed preferential transcription. It is suggested that cooperative function by the two promoter regions may be required for higher specificity.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker C. C., Ziff E. B. Promoters and heterogeneous 5' termini of the messenger RNAs of adenovirus serotype 2. J Mol Biol. 1981 Jun 25;149(2):189–221. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90298-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouvagnet P. F., Strehler E. E., White G. E., Strehler-Page M. A., Nadal-Ginard B., Mahdavi V. Multiple positive and negative 5' regulatory elements control the cell-type-specific expression of the embryonic skeletal myosin heavy-chain gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4377–4389. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen W., Struhl K. Saturation mutagenesis of a yeast his3 "TATA element": genetic evidence for a specific TATA-binding protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Apr;85(8):2691–2695. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.8.2691. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colantuoni V., Pirozzi A., Blance C., Cortese R. Negative control of liver-specific gene expression: cloned human retinol-binding protein gene is repressed in HeLa cells. EMBO J. 1987 Mar;6(3):631–636. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb04801.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dierich A., Gaub M. P., LePennec J. P., Astinotti D., Chambon P. Cell-specificity of the chicken ovalbumin and conalbumin promoters. EMBO J. 1987 Aug;6(8):2305–2312. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02505.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grass D. S., Manley J. L. Effects of the adenovirus 2 late promoter on simian virus 40 transcription and replication. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):129–137. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.129-137.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirose S., Tsuda M., Suzuki Y. Enhanced transcription of fibroin gene in vitro on covalently closed circular templates. J Biol Chem. 1985 Sep 5;260(19):10557–10562. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikenaka K., Furuichi T., Iwasaki Y., Moriguchi A., Okano H., Mikoshiba K. Myelin proteolipid protein gene structure and its regulation of expression in normal and jimpy mutant mice. J Mol Biol. 1988 Feb 20;199(4):587–596. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90303-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuki M., Sato M., Kimura M., Yokoyama M., Kobayashi K., Nomura T. Conversion of normal behavior to shiverer by myelin basic protein antisense cDNA in transgenic mice. Science. 1988 Jul 29;241(4865):593–595. doi: 10.1126/science.2456614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtsteiner S., Wuarin J., Schibler U. The interplay of DNA-binding proteins on the promoter of the mouse albumin gene. Cell. 1987 Dec 24;51(6):963–973. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90583-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthieu J. M., Omlin F. X. Murine leukodystrophies as tools to study myelinogenesis in normal and pathological conditions. Neuropediatrics. 1984 Sep;15 (Suppl):37–52. doi: 10.1055/s-2008-1052381. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikoshiba K., Takamatsu K., Tsukada Y. Peripheral nervous system of shiverer mutant mice: developmental change of myelin components and immunohistochemical demonstration of the absence of MBP and presence of P2 protein. Brain Res. 1983 Mar;283(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0165-3806(83)90082-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miura M., Tamura T., Aoyama A., Mikoshiba K. The promoter elements of the mouse myelin basic protein gene function efficiently in NG108-15 neuronal/glial cells. Gene. 1989 Jan 30;75(1):31–38. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90380-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monaci P., Nicosia A., Cortese R. Two different liver-specific factors stimulate in vitro transcription from the human alpha 1-antitrypsin promoter. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2075–2087. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03047.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabel G. J., Gorka C., Baltimore D. T-cell-specific expression of interleukin 2: evidence for a negative regulatory site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(9):2934–2938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.9.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson J. A., Reynolds-Kohler C., Smith B. A. Negative and positive regulation by a short segment in the 5'-flanking region of the human cytomegalovirus major immediate-early gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Nov;7(11):4125–4129. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.11.4125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. T. Biochemistry of myelin. Adv Neurol. 1981;31:93–121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano H., Miura M., Moriguchi A., Ikenaka K., Tsukada Y., Mikoshiba K. Inefficient transcription of the myelin basic protein gene possibly causes hypomyelination in myelin-deficient mutant mice. J Neurochem. 1987 Feb;48(2):470–476. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1987.tb04116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okano H., Tamura T., Miura M., Aoyama A., Ikenaka K., Oshimura M., Mikoshiba K. Gene organization and transcription of duplicated MBP genes of myelin deficient (shi(mld)) mutant mouse. EMBO J. 1988 Jan;7(1):77–83. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb02785.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Readhead C., Popko B., Takahashi N., Shine H. D., Saavedra R. A., Sidman R. L., Hood L. Expression of a myelin basic protein gene in transgenic shiverer mice: correction of the dysmyelinating phenotype. Cell. 1987 Feb 27;48(4):703–712. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90248-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roach A., Takahashi N., Pravtcheva D., Ruddle F., Hood L. Chromosomal mapping of mouse myelin basic protein gene and structure and transcription of the partially deleted gene in shiverer mutant mice. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):149–155. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80110-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi N., Roach A., Teplow D. B., Prusiner S. B., Hood L. Cloning and characterization of the myelin basic protein gene from mouse: one gene can encode both 14 kd and 18.5 kd MBPs by alternate use of exons. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):139–148. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80109-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura T., Miura M., Ikenaka K., Mikoshiba K. Analysis of transcription control elements of the mouse myelin basic protein gene in HeLa cell extracts: demonstration of a strong NFI-binding motif in the upstream region. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11441–11459. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theill L. E., Wiborg O., Vuust J. Cell-specific expression of the human gastrin gene: evidence for a control element located downstream of the TATA box. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;7(12):4329–4336. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.12.4329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuda M., Suzuki Y. Faithful transcription initiation of fibroin gene in a homologous cell-free system reveals an enhancing effect of 5' flanking sequence far upstream. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):175–182. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90371-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Ferra F., Engh H., Hudson L., Kamholz J., Puckett C., Molineaux S., Lazzarini R. A. Alternative splicing accounts for the four forms of myelin basic protein. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):721–727. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90245-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]