Abstract
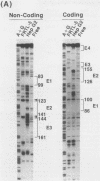
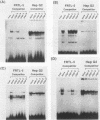
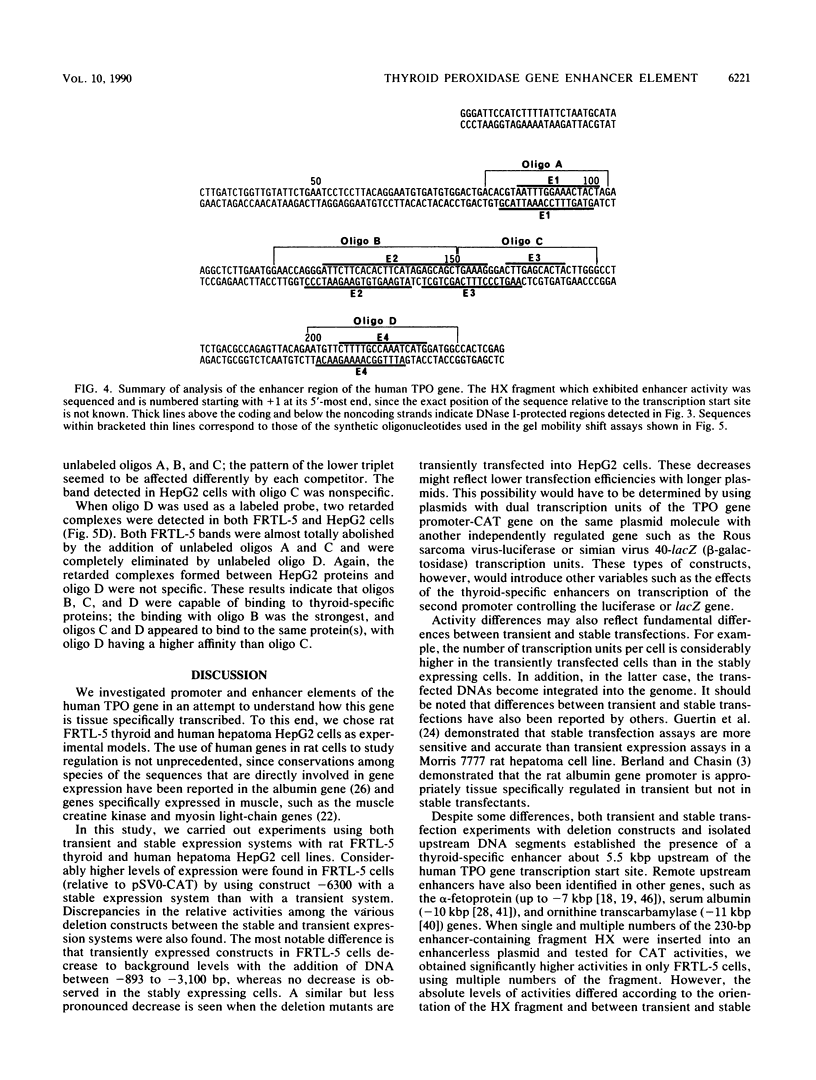
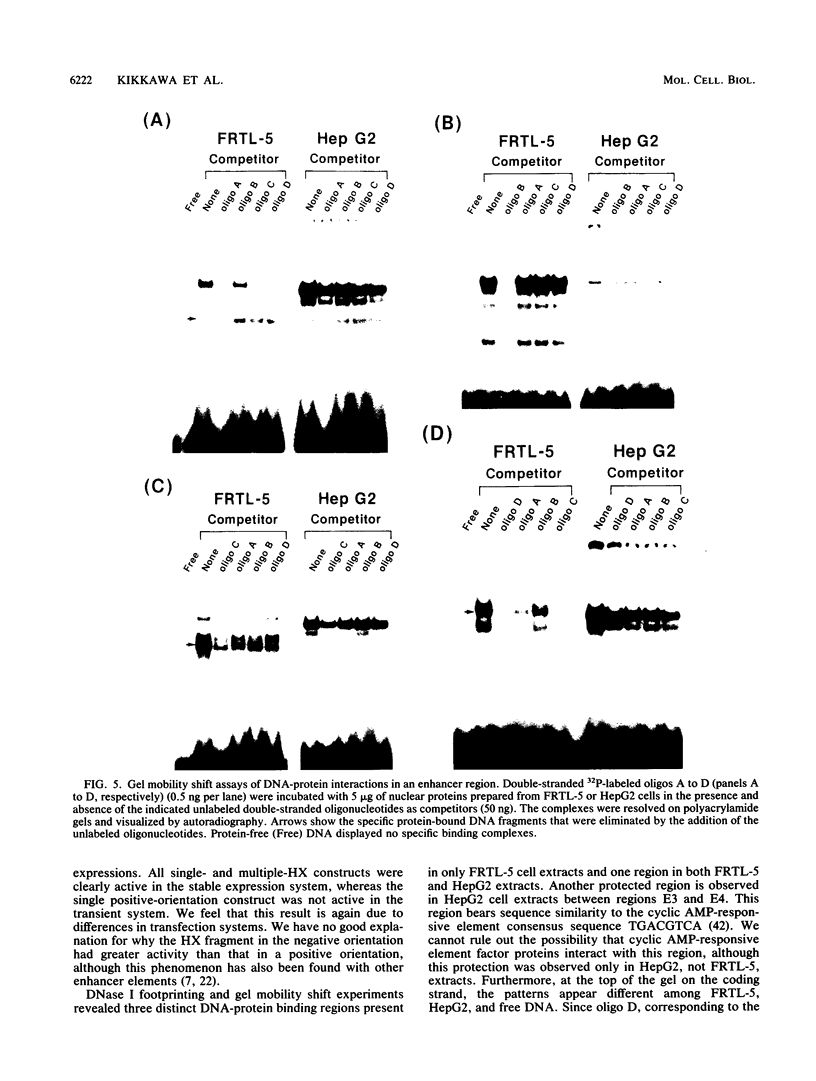
A 6.3-kbp segment of DNA, upstream of the human thyroid peroxidase gene, and various deletions thereof were linked to a promoterless bacterial chloramphenicol acetyltransferase reporter gene. These constructs were analyzed by transfection and expression in rat FRTL-5 thyroid cells and in human hepatoma HepG2 cells to localize sequences that are important for thyroid cell-specific expression of the thyroid peroxidase gene. A thyroid-specific enhancer element, capable of activating enhancerless simian virus 40 promoter expression in FRTL-5 cells, was localized to a 230-bp region approximately 5.5 kbp upstream of the human thyroid peroxidase gene transcription start site. DNase I footprinting, using nuclear extracts prepared from FRTL-5 cells, revealed three regions within the 230-bp fragment; none of these regions were protected by nuclear extracts from HepG2 cells. Gel mobility shift assays, using double-stranded oligonucleotides corresponding to the three protected regions, further confirmed the existence of factors in FRTL-5 cells, but not HepG2 cells, able to specifically bind to the enhancer sequences. These results suggest the presence of three cis-acting DNA elements in the human thyroid peroxidase gene enhancer that interact with thyroid-specific trans-acting factors.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abramowicz M. J., Vassart G., Christophe D. Thyroid peroxidase gene promoter confers TSH responsiveness to heterologous reporter genes in transfection experiments. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Feb 14;166(3):1257–1264. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91001-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ambesi-Impiombato F. S., Parks L. A., Coon H. G. Culture of hormone-dependent functional epithelial cells from rat thyroids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3455–3459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berland R., Chasin L. A. The rat albumin gene promoter is appropriately regulated in transient but not in stable transfections. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Dec 23;16(24):11573–11590. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.24.11573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cereghini S., Blumenfeld M., Yaniv M. A liver-specific factor essential for albumin transcription differs between differentiated and dedifferentiated rat hepatoma cells. Genes Dev. 1988 Aug;2(8):957–974. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.8.957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C. A., Okayama H. Calcium phosphate-mediated gene transfer: a highly efficient transfection system for stably transforming cells with plasmid DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 Jul-Aug;6(7):632–638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Civitareale D., Lonigro R., Sinclair A. J., Di Lauro R. A thyroid-specific nuclear protein essential for tissue-specific expression of the thyroglobulin promoter. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2537–2542. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08391.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comb M., Birnberg N. C., Seasholtz A., Herbert E., Goodman H. M. A cyclic AMP- and phorbol ester-inducible DNA element. 1986 Sep 25-Oct 1Nature. 323(6086):353–356. doi: 10.1038/323353a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Costa R. H., Lai E., Grayson D. R., Darnell J. E., Jr The cell-specific enhancer of the mouse transthyretin (prealbumin) gene binds a common factor at one site and a liver-specific factor(s) at two other sites. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Jan;8(1):81–90. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.1.81. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degroot L. J., Niepomniszcze H. Biosynthesis of thyroid hormone: basic and clinical aspects. Metabolism. 1977 Jun;26(6):665–718. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(77)90088-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derwahl M., Seto P., Rapoport B. Complete nucleotide sequence of the cDNA for thyroid peroxidase in FRTL5 rat thyroid cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Oct 25;17(20):8380–8380. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.20.8380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foti D., Gestautas J., Rapoport B. Studies on the functional activity of the promoter for the human thyroid peroxidase gene. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Apr 16;168(1):281–287. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91705-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godbout R., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M. Fine-structure mapping of the three mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene enhancers. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Mar;8(3):1169–1178. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.3.1169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godbout R., Ingram R., Tilghman S. M. Multiple regulatory elements in the intergenic region between the alpha-fetoprotein and albumin genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;6(2):477–487. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorski K., Carneiro M., Schibler U. Tissue-specific in vitro transcription from the mouse albumin promoter. Cell. 1986 Dec 5;47(5):767–776. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90519-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossett L. A., Kelvin D. J., Sternberg E. A., Olson E. N. A new myocyte-specific enhancer-binding factor that recognizes a conserved element associated with multiple muscle-specific genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;9(11):5022–5033. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.11.5022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guertin M., LaRue H., Bernier D., Wrange O., Chevrette M., Gingras M. C., Bélanger L. Enhancer and promoter elements directing activation and glucocorticoid repression of the alpha 1-fetoprotein gene in hepatocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;8(4):1398–1407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.4.1398. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen C., Javaux F., Juvenal G., Vassart G., Christophe D. cAMP-dependent binding of a trans-acting factor to the thyroglobulin promoter. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Apr 28;160(2):722–731. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92493-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heard J. M., Herbomel P., Ott M. O., Mottura-Rollier A., Weiss M., Yaniv M. Determinants of rat albumin promoter tissue specificity analyzed by an improved transient expression system. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2425–2434. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbomel P., Bourachot B., Yaniv M. Two distinct enhancers with different cell specificities coexist in the regulatory region of polyoma. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(3 Pt 2):653–662. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90472-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst R. S., Friedman N., Darnell J. E., Jr, Babiss L. E. Positive and negative regulatory elements in the mouse albumin enhancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Mar;86(5):1553–1557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.5.1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horlick R. A., Benfield P. A. The upstream muscle-specific enhancer of the rat muscle creatine kinase gene is composed of multiple elements. Mol Cell Biol. 1989 Jun;9(6):2396–2413. doi: 10.1128/mcb.9.6.2396. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isozaki O., Kohn L. D., Kozak C. A., Kimura S. Thyroid peroxidase: rat cDNA sequence, chromosomal localization in mouse, and regulation of gene expression by comparison to thyroglobulin in rat FRTL-5 cells. Mol Endocrinol. 1989 Nov;3(11):1681–1692. doi: 10.1210/mend-3-11-1681. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Haslinger A., Heguy A., Dietlin T., Cooke T. Metal-responsive elements act as positive modulators of human metallothionein-IIA enhancer activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):606–613. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Hong Y. S., Kotani T., Ohtaki S., Kikkawa F. Structure of the human thyroid peroxidase gene: comparison and relationship to the human myeloperoxidase gene. Biochemistry. 1989 May 16;28(10):4481–4489. doi: 10.1021/bi00436a054. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Kotani T., McBride O. W., Umeki K., Hirai K., Nakayama T., Ohtaki S. Human thyroid peroxidase: complete cDNA and protein sequence, chromosome mapping, and identification of two alternately spliced mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(16):5555–5559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.16.5555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latimer J. J., Berger F. G., Baumann H. Highly conserved upstream regions of the alpha 1-antitrypsin gene in two mouse species govern liver-specific expression by different mechanisms. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Feb;10(2):760–769. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.2.760. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee N. T., Nayfeh S. N., Chae C. B. Induction of nuclear protein factors specific for hormone-responsive region during activation of thyroglobulin gene by thyrotropin in rat thyroid FRTL-5 cells. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 5;264(13):7523–7530. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Libert F., Ruel J., Ludgate M., Swillens S., Alexander N., Vassart G., Dinsart C. Complete nucleotide sequence of the human thyroperoxidase-microsomal antigen cDNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6735–6735. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6735. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopata M. A., Cleveland D. W., Sollner-Webb B. High level transient expression of a chloramphenicol acetyl transferase gene by DEAE-dextran mediated DNA transfection coupled with a dimethyl sulfoxide or glycerol shock treatment. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jul 25;12(14):5707–5717. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.14.5707. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson R. P., Chazenbalk G. D., Gestautas J., Seto P., Filetti S., DeGroot L. J., Rapoport B. Molecular cloning of the complementary deoxyribonucleic acid for human thyroid peroxidase. Mol Endocrinol. 1987 Nov;1(11):856–861. doi: 10.1210/mend-1-11-856. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami T., Nishiyori A., Takiguchi M., Mori M. Promoter and 11-kilobase upstream enhancer elements responsible for hepatoma cell-specific expression of the rat ornithine transcarbamylase gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1180–1191. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1180. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkert C. A., Ornitz D. M., Brinster R. L., Palmiter R. D. An albumin enhancer located 10 kb upstream functions along with its promoter to direct efficient, liver-specific expression in transgenic mice. Genes Dev. 1987 May;1(3):268–276. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.3.268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roesler W. J., Vandenbark G. R., Hanson R. W. Cyclic AMP and the induction of eukaryotic gene transcription. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 5;263(19):9063–9066. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Widen S. G., Papaconstantinou J. Liver-specific expression of the mouse alpha-fetoprotein gene is mediated by cis-acting DNA elements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(21):8196–8200. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.21.8196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanagida A., Sogawa K., Yasumoto K. I., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. A novel cis-acting DNA element required for a high level of inducible expression of the rat P-450c gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1470–1475. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1470. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Wet J. R., Wood K. V., DeLuca M., Helinski D. R., Subramani S. Firefly luciferase gene: structure and expression in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Feb;7(2):725–737. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]