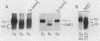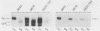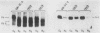Abstract
The COX5a and COX5b genes encode divergent forms of yeast cytochrome c oxidase subunit V. Although the polypeptide products of the two genes are functionally interchangeable, it is the Va subunit that is normally found in preparations of yeast mitochondria and cytochrome c oxidase. We show here that the predominance of subunit Va stems in part from the differential response of the two genes to the presence of molecular oxygen. Our results indicate that during aerobic growth, COX5a levels were high, while COX5b levels were low. Anaerobically, the pattern was reversed; COX5a levels dropped sevenfold, while those of COX5b were elevated sevenfold. Oxygen appeared to act at the level of transcription through heme, since the addition of heme restored an aerobic pattern of transcription to anaerobically grown cells and the effect of anaerobiosis on COX5 transcription was reproduced in strains containing a mutation in the heme-biosynthetic pathway (hem1). In conjunction with the oxygen-heme response, we determined that the product of the ROX1 gene, a trans-acting regulator of several yeast genes controlled by oxygen, is also involved in COX5 expression. These results, as well as our observation that COX5b expression varied significantly in certain yeast strains, indicate that the COX5 genes undergo a complex pattern of regulation. This regulation, especially the increase in COX5b levels anaerobically, may reflect an attempt to modulate the activity of a key respiratory enzyme in response to varying environmental conditions. The results presented here, as well as those from other laboratories, suggest that the induction or derepression of certain metabolic enzymes during anaerobiosis may be a common and important physiological response in yeast cells.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Basson M. E., Thorsness M., Rine J. Saccharomyces cerevisiae contains two functional genes encoding 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(15):5563–5567. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.15.5563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumsky M. G., Ko C., Trueblood C. E., Poyton R. O. Two nonidentical forms of subunit V are functional in yeast cytochrome c oxidase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2235–2239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cumsky M. G., McEwen J. E., Ko C., Poyton R. O. Nuclear genes for mitochondrial proteins. Identification and isolation of a structural gene for subunit V of yeast cytochrome c oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 25;258(22):13418–13421. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Vassarotti A., Garrett J., Geller B. L., Takeda M., Douglas M. G. The amino terminus of the yeast F1-ATPase beta-subunit precursor functions as a mitochondrial import signal. J Cell Biol. 1986 Feb;102(2):523–533. doi: 10.1083/jcb.102.2.523. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Lalonde B., Gifford P., Alani E. Distinctly regulated tandem upstream activation sites mediate catabolite repression of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):503–511. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Mason T. Heme regulates transcription of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae via an upstream activation site. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90309-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters and lacZ fusions designed to study expression of cloned genes in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:181–191. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keng T., Guarente L. Constitutive expression of the yeast HEM1 gene is actually a composite of activation and repression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9113–9117. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry C. V., Lieber R. H. Negative regulation of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae ANB1 gene by heme, as mediated by the ROX1 gene product. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4145–4148. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry C. V., Weiss J. L., Walthall D. A., Zitomer R. S. Modulator sequences mediate oxygen regulation of CYC1 and a neighboring gene in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):151–155. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowry C. V., Zitomer R. S. Oxygen regulation of anaerobic and aerobic genes mediated by a common factor in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Oct;81(19):6129–6133. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.19.6129. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers A. M., Crivellone M. D., Koerner T. J., Tzagoloff A. Characterization of the yeast HEM2 gene and transcriptional regulation of COX5 and COR1 by heme. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 15;262(35):16822–16829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A., Tatchell K. The structure of transposable yeast mating type loci. Cell. 1980 Mar;19(3):753–764. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(80)80051-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Arcangioli B., Guarente L. Yeast HAP1 activator competes with the factor RC2 for binding to the upstream activation site UAS1 of the CYC1 gene. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):9–18. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90750-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer K., Prezant T., Guarente L. Yeast HAP1 activator binds to two upstream activation sites of different sequence. Cell. 1987 Apr 10;49(1):19–27. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90751-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saltzgaber-Müller J., Schatz G. Heme is necessary for the accumulation and assembly of cytochrome c oxidase subunits in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jan 10;253(1):305–310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stinchcomb D. T., Mann C., Davis R. W. Centromeric DNA from Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jun 25;158(2):157–190. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90427-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trueblood C. E., Poyton R. O. Differential effectiveness of yeast cytochrome c oxidase subunit genes results from differences in expression not function. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Oct;7(10):3520–3526. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.10.3520. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trueblood C. E., Wright R. M., Poyton R. O. Differential regulation of the two genes encoding Saccharomyces cerevisiae cytochrome c oxidase subunit V by heme and the HAP2 and REO1 genes. Mol Cell Biol. 1988 Oct;8(10):4537–4540. doi: 10.1128/mcb.8.10.4537. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H., Adam G., Mattes E., Schanz M., Hartig A., Ruis H. Co-ordinate control of synthesis of mitochondrial and non-mitochondrial hemoproteins: a binding site for the HAP1 (CYP1) protein in the UAS region of the yeast catalase T gene (CTT1). EMBO J. 1988 Jun;7(6):1799–1804. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03011.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagorec M., Buhler J. M., Treich I., Keng T., Guarente L., Labbe-Bois R. Isolation, sequence, and regulation by oxygen of the yeast HEM13 gene coding for coproporphyrinogen oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 15;263(20):9718–9724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zagorec M., Labbe-Bois R. Negative control of yeast coproporphyrinogen oxidase synthesis by heme and oxygen. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 25;261(6):2506–2509. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]