Abstract
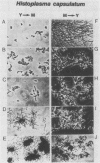
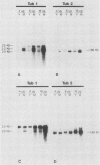
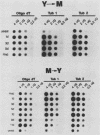
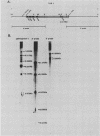
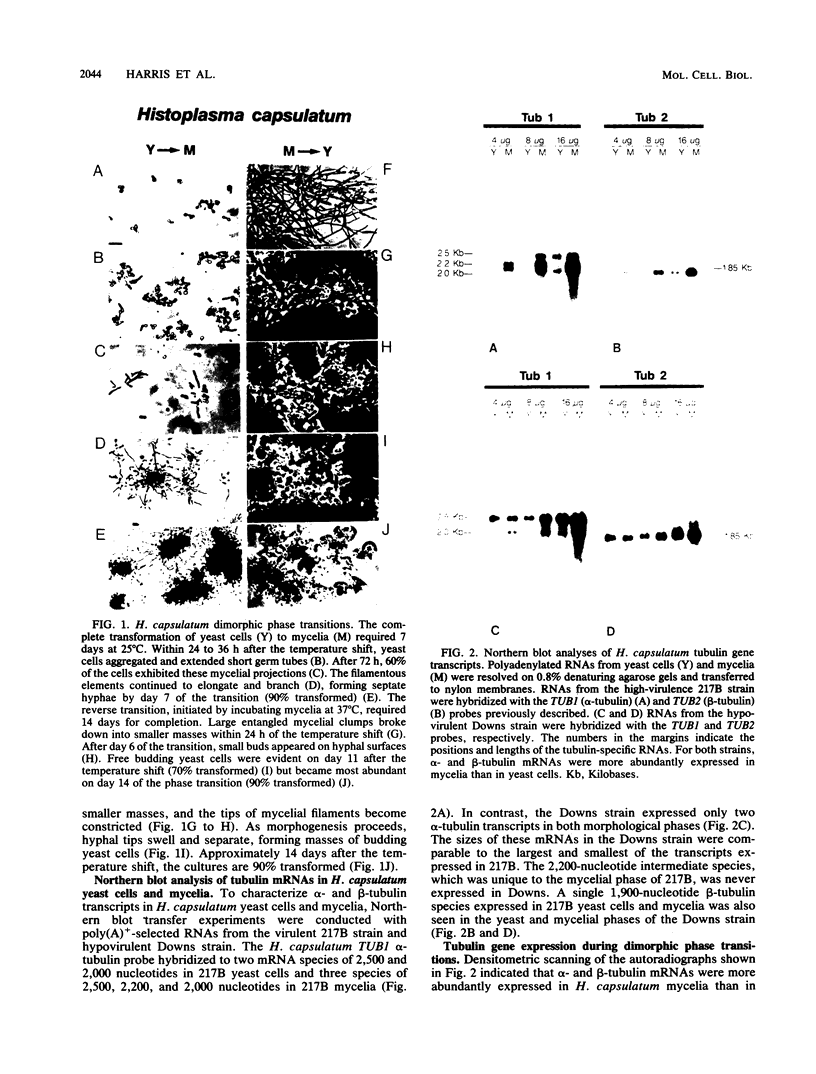
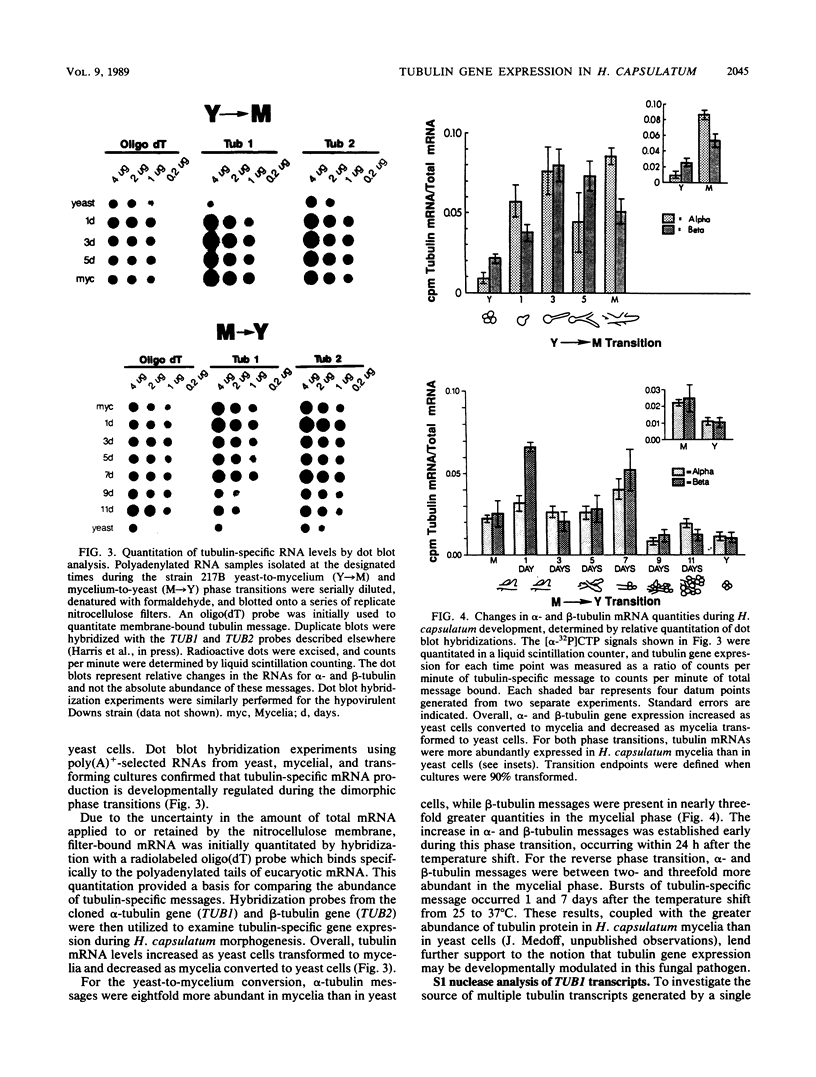
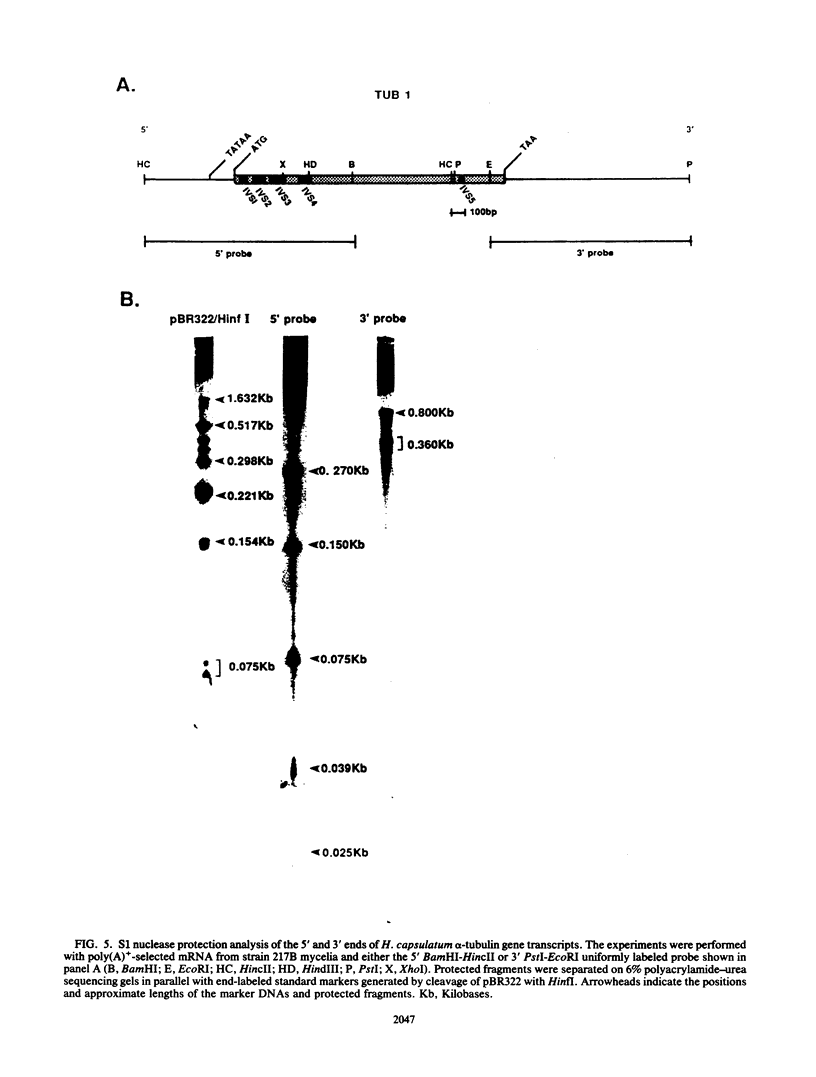
Recent investigations have confirmed the presence of one alpha-tubulin gene (TUB1) and one beta-tubulin gene (TUB2) in the dimorphic fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. In the present study, Northern blot (RNA blot) analyses revealed multiple alpha-tubulin transcripts and a single beta-tubulin transcript in the yeast and mycelial phases of the high-virulence 217B strain and low-virulence Downs strain. S1 nuclease protection assays demonstrated one initiation start site and two major stop sites for the TUB1 transcripts, suggesting that variations in 3' processing generate the alpha-tubulin messages of 2.5 and 2.0 kilobases. Dot blot hybridization experiments indicated that tubulin gene expression is developmentally regulated during the dimorphic phase transitions. alpha- and beta-tubulin mRNAs increased six- to eightfold during the yeast-to-mycelium conversion and decreased two- to threefold during the reverse transition. These changes in tubulin mRNA content coincided with major morphological events associated with H. capsulatum development. Western blots (immunoblots) of H. capsulatum yeast-specific proteins resolved by two-dimensional gel electrophoresis demonstrated a single alpha- and a single beta-tubulin isoform. Multiple tubulin polypeptides expressed in mycelia are probably products of posttranslational modifications.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Argaraña C. E., Barra H. S., Caputto R. Release of [14C]tyrosine from tubulinyl-[14C]tyrosine by brain extract. Separation of a carboxypeptidase from tubulin-tyrosine ligase. Mol Cell Biochem. 1978 Feb 24;19(1):17–21. doi: 10.1007/BF00231230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baker E. J., Schloss J. A., Rosenbaum J. L. Rapid changes in tubulin RNA synthesis and stability induced by deflagellation in Chlamydomonas. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2074–2081. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ben-Ze'ev A., Farmer S. R., Penman S. Mechanisms of regulating tubulin synthesis in cultured mammalian cells. Cell. 1979 Jun;17(2):319–325. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church G. M., Gilbert W. Genomic sequencing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):1991–1995. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eipper B. A. Rat brain microtubule protein: purification and determination of covalently bound phosphate and carbohydrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2283–2287. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Forgue S. T., Dahl J. L. Rat brain tubulin: subunit heterogeneity and phosphorylation. J Neurochem. 1979 Mar;32(3):1015–1025. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1979.tb04588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gay D. A., Yen T. J., Lau J. T., Cleveland D. W. Sequences that confer beta-tubulin autoregulation through modulated mRNA stability reside within exon 1 of a beta-tubulin mRNA. Cell. 1987 Aug 28;50(5):671–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90325-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green L. L., Dove W. F. Tubulin proteins and RNA during the myxamoeba-flagellate transformation of Physarum polycephalum. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Sep;4(9):1706–1711. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.9.1706. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harley C. B. Hybridization of oligo(dT) to RNA on nitrocellulose. Gene Anal Tech. 1987 Mar-Apr;4(2):17–22. doi: 10.1016/0735-0651(87)90013-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kafatos F. C., Jones C. W., Efstratiadis A. Determination of nucleic acid sequence homologies and relative concentrations by a dot hybridization procedure. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1541–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keath E. J., Kelekar A., Cole M. D. Transcriptional activation of the translocated c-myc oncogene in mouse plasmacytomas: similar RNA levels in tumor and proliferating normal cells. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):521–528. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90382-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller L. R., Schloss J. A., Silflow C. D., Rosenbaum J. L. Transcription of alpha- and beta-tubulin genes in vitro in isolated Chlamydomonas reinhardi nuclei. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):1138–1143. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.1138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maresca B., Lambowitz A. M., Kumar V. B., Grant G. A., Kobayashi G. S., Medoff G. Role of cysteine in regulating morphogenesis and mitochondrial activity in the dimorphic fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4596–4600. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4596. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maresca B., Medoff G., Schlessinger D., Kobayashi G. S. Regulation of dimorphism in the pathogenic fungus Histoplasma capsulatum. Nature. 1977 Mar 31;266(5601):447–448. doi: 10.1038/266447a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medoff J., Jacobson E., Medoff G. Regulation of dimorphism in Histoplasma capsulatum by cyclic adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate. J Bacteriol. 1981 Mar;145(3):1452–1455. doi: 10.1128/jb.145.3.1452-1455.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mertins P., Gallwitz D. A single intronless action gene in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe: nucleotide sequence and transcripts formed in homologous and heterologous yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Sep 25;15(18):7369–7379. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.18.7369. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ono M., Cole M. D., White A. T., Huang R. C. Sequence organization of cloned intracisternal A particle genes. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):465–473. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90483-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rave N., Crkvenjakov R., Boedtker H. Identification of procollagen mRNAs transferred to diazobenzyloxymethyl paper from formaldehyde agarose gels. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Aug 10;6(11):3559–3567. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.11.3559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schedl T., Burland T. G., Gull K., Dove W. F. Cell cycle regulation of tubulin RNA level, tubulin protein synthesis, and assembly of microtubules in Physarum. J Cell Biol. 1984 Jul;99(1 Pt 1):155–165. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.1.155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen-Ong G. L., Keath E. J., Piccoli S. P., Cole M. D. Novel myc oncogene RNA from abortive immunoglobulin-gene recombination in mouse plasmacytomas. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):443–452. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90137-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White B. A., Bancroft F. C. Cytoplasmic dot hybridization. Simple analysis of relative mRNA levels in multiple small cell or tissue samples. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8569–8572. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]