Abstract
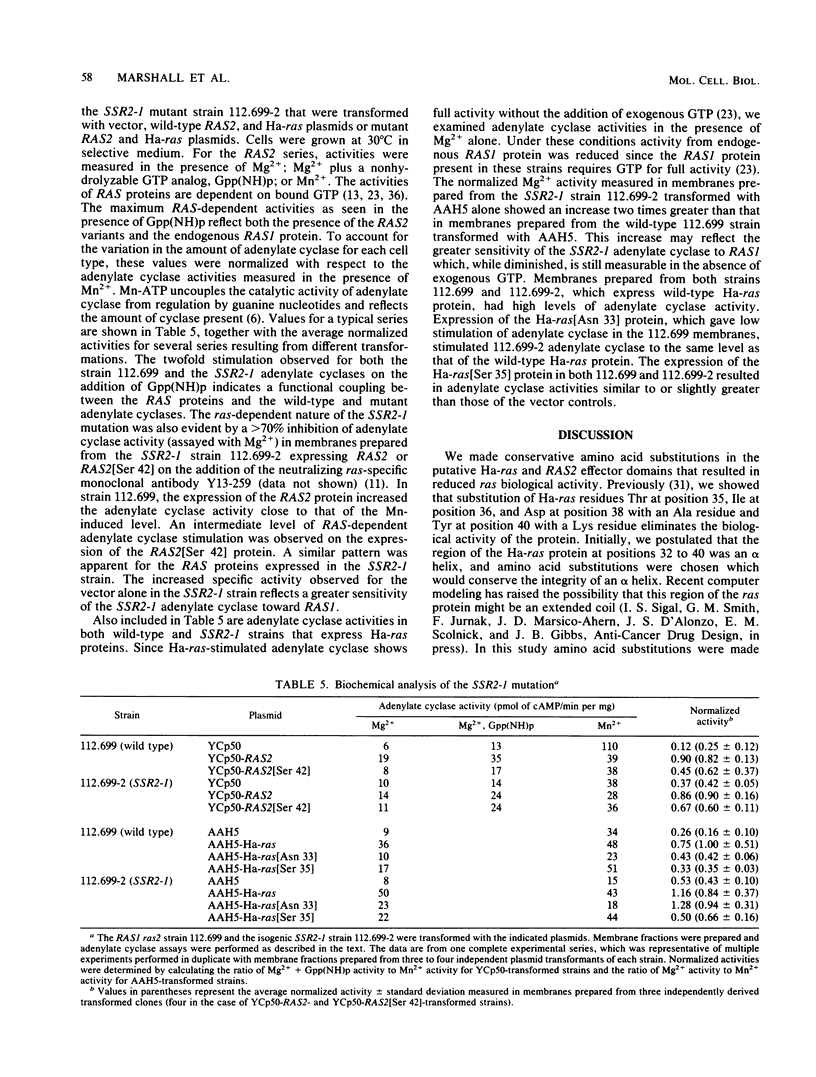
Conservative amino acid substitutions were introduced into the proposed effector regions of both mammalian Ha-ras (residues 32 to 40) and Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAS2 (residues 39 to 47) proteins. The RAS2[Ser 42] protein had reduced biological function in the yeast S. cerevisiae. A S. cerevisiae strain with a second-site suppressor mutation, SSR2-1, was isolated which could grow on nonfermentable carbon sources when the endogenous RAS2 protein was replaced by the RAS2[Ser 42] protein. The SSR2-1 mutation was mapped to the structural gene for adenylate cyclase (CYR1), and the gene containing SSR2-1 was cloned and sequenced. SSR2-1 corresponded to a point mutation that would create an amino acid substitution of a tyrosine residue for an aspartate residue at position 1547. The SSR2-1 gene encodes an adenylate cyclase that is dependent on ras proteins for activity, but is stimulated by Ha-ras and RAS2 mutant proteins that are unable to stimulate wild-type adenylate cyclase.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahnn J., March P. E., Takiff H. E., Inouye M. A GTP-binding protein of Escherichia coli has homology to yeast RAS proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):8849–8853. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.8849. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutelet F., Petitjean A., Hilger F. Yeast cdc35 mutants are defective in adenylate cyclase and are allelic with cyr1 mutants while CAS1, a new gene, is involved in the regulation of adenylate cyclase. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2635–2641. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03981.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breviario D., Hinnebusch A., Cannon J., Tatchell K., Dhar R. Carbon source regulation of RAS1 expression in Saccharomyces cerevisiae and the phenotypes of ras2- cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4152–4156. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4152. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broek D., Samiy N., Fasano O., Fujiyama A., Tamanoi F., Northup J., Wigler M. Differential activation of yeast adenylate cyclase by wild-type and mutant RAS proteins. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):763–769. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cannon J. F., Gibbs J. B., Tatchell K. Suppressors of the ras2 mutation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics. 1986 Jun;113(2):247–264. doi: 10.1093/genetics/113.2.247. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casperson G. F., Walker N., Brasier A. R., Bourne H. R. A guanine nucleotide-sensitive adenylate cyclase in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 10;258(13):7911–7914. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Seeburg P. H. Supercoil sequencing: a fast and simple method for sequencing plasmid DNA. DNA. 1985 Apr;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Vendittis E., Vitelli A., Zahn R., Fasano O. Suppression of defective RAS1 and RAS2 functions in yeast by an adenylate cyclase activated by a single amino acid change. EMBO J. 1986 Dec 20;5(13):3657–3663. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04696.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeFeo-Jones D., Tatchell K., Robinson L. C., Sigal I. S., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. M. Mammalian and yeast ras gene products: biological function in their heterologous systems. Science. 1985 Apr 12;228(4696):179–184. doi: 10.1126/science.3883495. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Findlay J. B., Pappin D. J. The opsin family of proteins. Biochem J. 1986 Sep 15;238(3):625–642. doi: 10.1042/bj2380625. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraenkel D. G. On ras gene function in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(14):4740–4744. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.14.4740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Davis L. J., Fleurdelys B., Scolnick E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to the p21 products of the transforming gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus and of the cellular ras gene family. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):294–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.294-304.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallwitz D., Donath C., Sander C. A yeast gene encoding a protein homologous to the human c-has/bas proto-oncogene product. Nature. 1983 Dec 15;306(5944):704–707. doi: 10.1038/306704a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Schaber M. D., Marshall M. S., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S. Identification of guanine nucleotides bound to ras-encoded proteins in growing yeast cells. J Biol Chem. 1987 Aug 5;262(22):10426–10429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbs J. B., Sigal I. S., Poe M., Scolnick E. M. Intrinsic GTPase activity distinguishes normal and oncogenic ras p21 molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5704–5708. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. M. Are guanine nucleotide binding proteins a distinct class of regulatory proteins? FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 28;164(1):1–8. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80006-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito H., Fukuda Y., Murata K., Kimura A. Transformation of intact yeast cells treated with alkali cations. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):163–168. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.163-168.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Broek D., Wigler M. DNA sequence and characterization of the S. cerevisiae gene encoding adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):493–505. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90179-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kataoka T., Powers S., Cameron S., Fasano O., Goldfarb M., Broach J., Wigler M. Functional homology of mammalian and yeast RAS genes. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):19–26. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90304-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madaule P., Axel R., Myers A. M. Characterization of two members of the rho gene family from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Feb;84(3):779–783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.3.779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marshall M. S., Gibbs J. B., Scolnick E. M., Sigal I. S. Regulatory function of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae RAS C-terminus. Mol Cell Biol. 1987 Jul;7(7):2309–2315. doi: 10.1128/mcb.7.7.2309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumoto K., Uno I., Oshima Y., Ishikawa T. Isolation and characterization of yeast mutants deficient in adenylate cyclase and cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(7):2355–2359. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.7.2355. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGrath J. P., Capon D. J., Goeddel D. V., Levinson A. D. Comparative biochemical properties of normal and activated human ras p21 protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 23;310(5979):644–649. doi: 10.1038/310644a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orr-Weaver T. L., Szostak J. W., Rothstein R. J. Yeast transformation: a model system for the study of recombination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6354–6358. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers S., Kataoka T., Fasano O., Goldfarb M., Strathern J., Broach J., Wigler M. Genes in S. cerevisiae encoding proteins with domains homologous to the mammalian ras proteins. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):607–612. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90340-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rothstein R. J. One-step gene disruption in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:202–211. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01015-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B., D'Alonzo J. S., Scolnick E. M. Identification of effector residues and a neutralizing epitope of Ha-ras-encoded p21. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4725–4729. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sigal I. S., Gibbs J. B., D'Alonzo J. S., Temeles G. L., Wolanski B. S., Socher S. H., Scolnick E. M. Mutant ras-encoded proteins with altered nucleotide binding exert dominant biological effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Feb;83(4):952–956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.4.952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K., Chaleff D. T., DeFeo-Jones D., Scolnick E. M. Requirement of either of a pair of ras-related genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for spore viability. Nature. 1984 Jun 7;309(5968):523–527. doi: 10.1038/309523a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temeles G. L., Gibbs J. B., D'Alonzo J. S., Sigal I. S., Scolnick E. M. Yeast and mammalian ras proteins have conserved biochemical properties. Nature. 1985 Feb 21;313(6004):700–703. doi: 10.1038/313700a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toda T., Uno I., Ishikawa T., Powers S., Kataoka T., Broek D., Cameron S., Broach J., Matsumoto K., Wigler M. In yeast, RAS proteins are controlling elements of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):27–36. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volkert F. C., Broach J. R. Site-specific recombination promotes plasmid amplification in yeast. Cell. 1986 Aug 15;46(4):541–550. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90879-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willumsen B. M., Papageorge A. G., Kung H. F., Bekesi E., Robins T., Johnsen M., Vass W. C., Lowy D. R. Mutational analysis of a ras catalytic domain. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;6(7):2646–2654. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.7.2646. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]