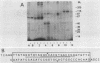
Abstract
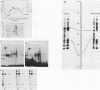
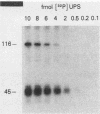
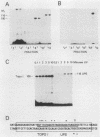
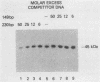
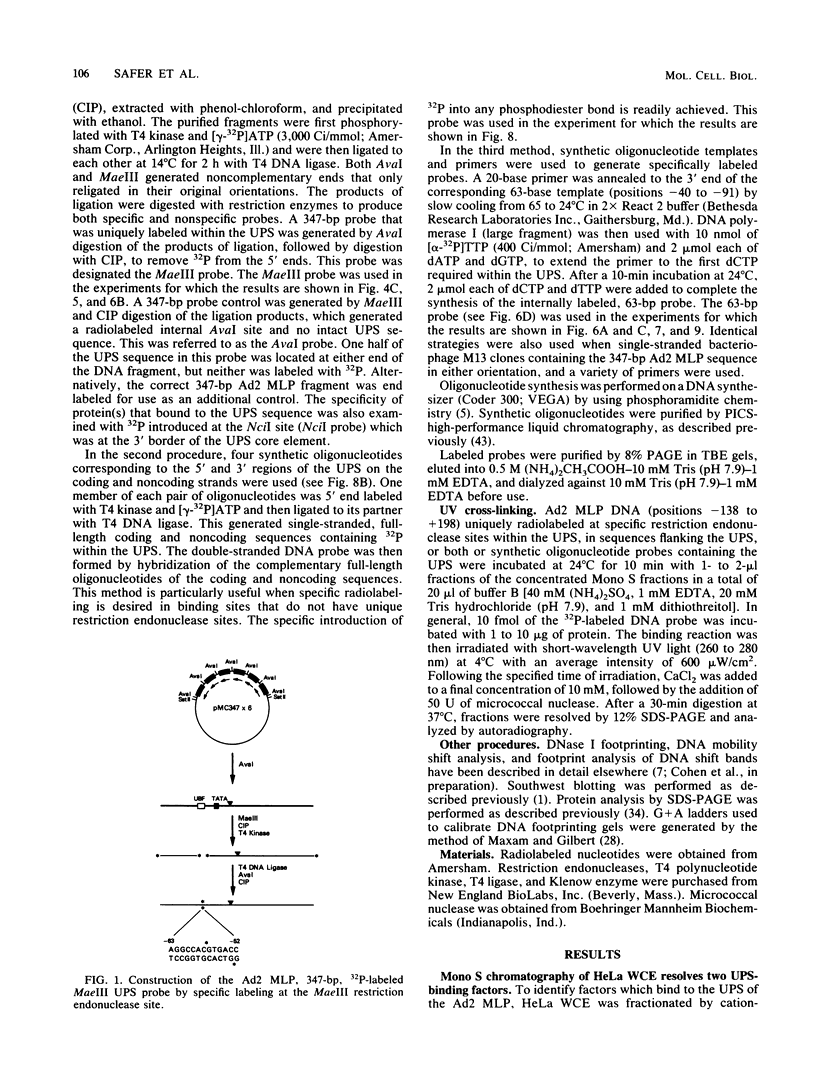
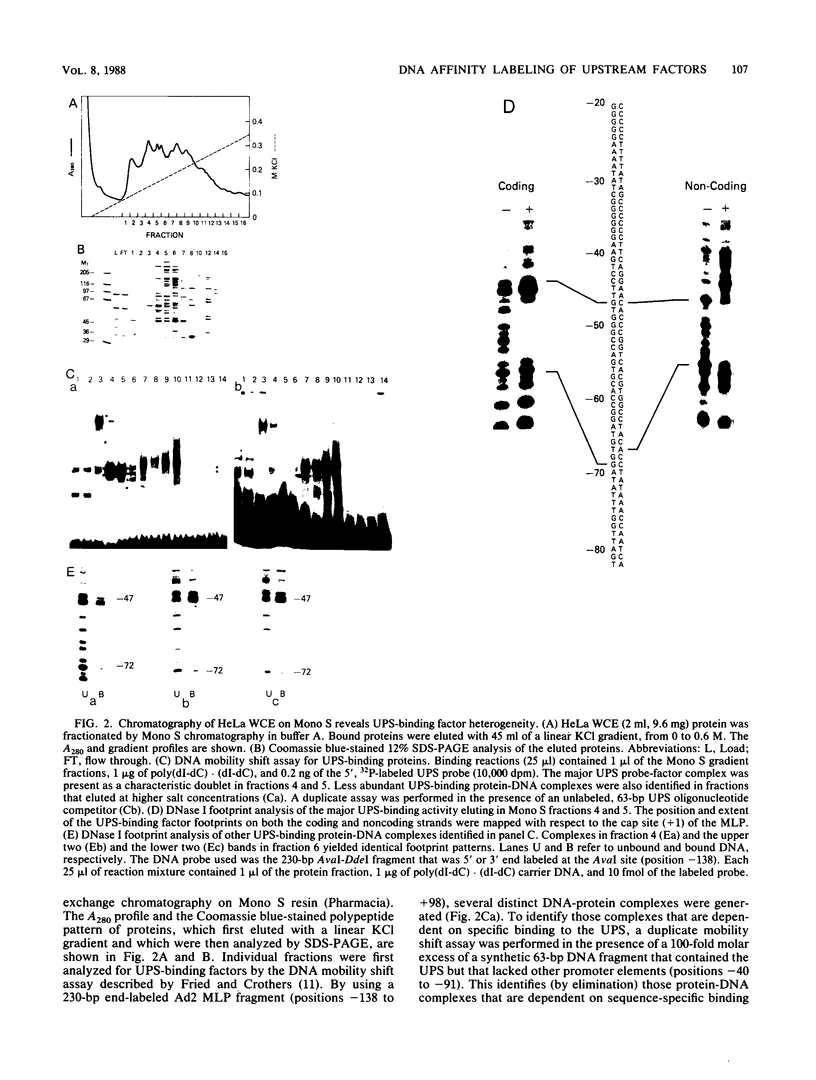
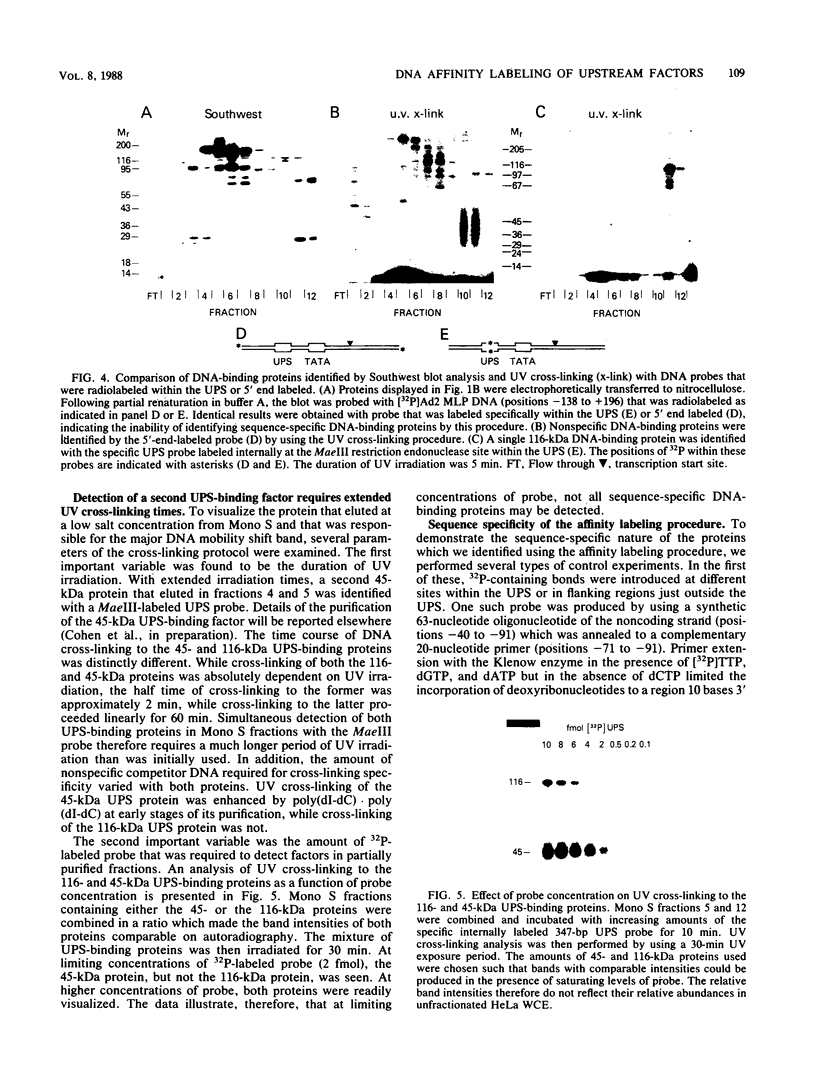
A rapid affinity labeling procedure with enhanced specificity was developed to identify DNA-binding proteins. 32P was first introduced at unique phosphodiester bonds within the DNA recognition sequence. UV light-dependent cross-linking of pyrimidines to amino acid residues in direct contact at the binding site, followed by micrococcal nuclease digestion, resulted in the transfer of 32P to only those specific protein(s) which recognized the binding sequence. This method was applied to the detection and characterization of proteins that bound to the upstream promoter sequence (-50 to -66) of the human adenovirus type 2 major late promoter. We detected two distinct proteins with molecular weights of 45,000 and 116,000 that interacted with this promoter element. The two proteins differed significantly in their chromatographic and cross-linking behaviors.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bowen B., Steinberg J., Laemmli U. K., Weintraub H. The detection of DNA-binding proteins by protein blotting. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):1–20. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach R., Chambon P. Organization and expression of eucaryotic split genes coding for proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:349–383. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brent R., Ptashne M. A eukaryotic transcriptional activator bearing the DNA specificity of a prokaryotic repressor. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(3 Pt 2):729–736. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carthew R. W., Chodosh L. A., Sharp P. A. An RNA polymerase II transcription factor binds to an upstream element in the adenovirus major late promoter. Cell. 1985 Dec;43(2 Pt 1):439–448. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caruthers M. H. Gene synthesis machines: DNA chemistry and its uses. Science. 1985 Oct 18;230(4723):281–285. doi: 10.1126/science.3863253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chodosh L. A., Carthew R. W., Sharp P. A. A single polypeptide possesses the binding and transcription activities of the adenovirus major late transcription factor. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Dec;6(12):4723–4733. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.12.4723. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. B., Sheffery M., Kim C. G. Partial purification of a nuclear protein that binds to the CCAAT box of the mouse alpha 1-globin gene. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Mar;6(3):821–832. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diffley J. F., Stillman B. Purification of a cellular, double-stranded DNA-binding protein required for initiation of adenovirus DNA replication by using a rapid filter-binding assay. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 May;6(5):1363–1373. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.5.1363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dignam J. D., Lebovitz R. M., Roeder R. G. Accurate transcription initiation by RNA polymerase II in a soluble extract from isolated mammalian nuclei. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 11;11(5):1475–1489. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.5.1475. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Control of eukaryotic messenger RNA synthesis by sequence-specific DNA-binding proteins. 1985 Aug 29-Sep 4Nature. 316(6031):774–778. doi: 10.1038/316774a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fried M., Crothers D. M. Equilibria and kinetics of lac repressor-operator interactions by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 11;9(23):6505–6525. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.23.6505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galas D. J., Schmitz A. DNAse footprinting: a simple method for the detection of protein-DNA binding specificity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Sep;5(9):3157–3170. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.9.3157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gidoni D., Dynan W. S., Tjian R. Multiple specific contacts between a mammalian transcription factor and its cognate promoters. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):409–413. doi: 10.1038/312409a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hen R., Sassone-Corsi P., Corden J., Gaub M. P., Chambon P. Sequences upstream from the T-A-T-A box are required in vivo and in vitro for efficient transcription from the adenovirus serotype 2 major late promoter. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Dec;79(23):7132–7136. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.23.7132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hillel Z., Wu C. W. Photochemical cross-linking studies on the interaction of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase with T7 DNA. Biochemistry. 1978 Jul 25;17(15):2954–2961. doi: 10.1021/bi00608a003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockensmith J. W., Kubasek W. L., Vorachek W. R., von Hippel P. H. Laser cross-linking of nucleic acids to proteins. Methodology and first applications to the phage T4 DNA replication system. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 15;261(8):3512–3518. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. L., Manley J. L. DNA sequence required for initiation of transcription in vitro from the major late promoter of adenovirus 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Feb;78(2):820–824. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.2.820. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones K. A., Kadonaga J. T., Rosenfeld P. J., Kelly T. J., Tjian R. A cellular DNA-binding protein that activates eukaryotic transcription and DNA replication. Cell. 1987 Jan 16;48(1):79–89. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90358-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jove R., Manley J. L. In vitro transcription from the adenovirus 2 major late promoter utilizing templates truncated at promoter-proximal sites. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8513–8521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jump D. B., Smulson M. Purification and characterization of the major nonhistone protein acceptor for poly(adenosine diphosphate ribose) in HeLa cell nuclei. Biochemistry. 1980 Mar 4;19(5):1024–1030. doi: 10.1021/bi00546a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadonaga J. T., Tjian R. Affinity purification of sequence-specific DNA binding proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Aug;83(16):5889–5893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.16.5889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameshita I., Matsuda Z., Taniguchi T., Shizuta Y. Poly (ADP-Ribose) synthetase. Separation and identification of three proteolytic fragments as the substrate-binding domain, the DNA-binding domain, and the automodification domain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):4770–4776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keegan L., Gill G., Ptashne M. Separation of DNA binding from the transcription-activating function of a eukaryotic regulatory protein. Science. 1986 Feb 14;231(4739):699–704. doi: 10.1126/science.3080805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin S. Y., Riggs A. D. Photochemical attachment of lac repressor to bromodeoxyuridine-substituted lac operator by ultraviolet radiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Mar;71(3):947–951. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.3.947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manley J. L., Fire A., Cano A., Sharp P. A., Gefter M. L. DNA-dependent transcription of adenovirus genes in a soluble whole-cell extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3855–3859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3855. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martinson H. G., Shetlar M. D., McCarthy B. J. Histone-histone interactions within chromatin. Crosslinking studies using ultraviolet light. Biochemistry. 1976 May 4;15(9):2002–2007. doi: 10.1021/bi00654a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S., Tjian R. Transcriptional selectivity of viral genes in mammalian cells. Cell. 1986 Sep 12;46(6):795–805. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90061-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moncollin V., Miyamoto N. G., Zheng X. M., Egly J. M. Purification of a factor specific for the upstream element of the adenovirus-2 major late promoter. EMBO J. 1986 Oct;5(10):2577–2584. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04537.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogata R., Gilbert W. Contacts between the lac repressor and the thymines in the lac operator. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4973–4976. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker C. S., Topol J. A Drosophila RNA polymerase II transcription factor contains a promoter-region-specific DNA-binding activity. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):357–369. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90229-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinberg D., Horikoshi M., Roeder R. G. Factors involved in specific transcription in mammalian RNA polymerase II. Functional analysis of initiation factors IIA and IID and identification of a new factor operating at sequences downstream of the initiation site. J Biol Chem. 1987 Mar 5;262(7):3322–3330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safer B., Yang L., Tolunay H. E., Anderson W. F. Isolation of stable preinitiation, initiation, and elongation complexes from RNA polymerase II-directed transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2632–2636. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2632. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawadogo M., Roeder R. G. Interaction of a gene-specific transcription factor with the adenovirus major late promoter upstream of the TATA box region. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shenk T. Transcriptional control regions: nucleotide sequence requirements for initiation by RNA polymerase II and III. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;93:25–46. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68123-3_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi X. P., Lee R., Weinmann R. Protein factor(s) binding independently to two different regions of the adenovirus 2 major late promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 May 12;14(9):3729–3744. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.9.3729. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slattery E., Dignam J. D., Matsui T., Roeder R. G. Purification and analysis of a factor which suppresses nick-induced transcription by RNA polymerase II and its identity with poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5955–5959. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vosberg H. P. DNA topoisomerases: enzymes that control DNA conformation. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;114:19–102. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70227-3_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiederrecht G., Shuey D. J., Kibbe W. A., Parker C. S. The Saccharomyces and Drosophila heat shock transcription factors are identical in size and DNA binding properties. Cell. 1987 Feb 13;48(3):507–515. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90201-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu C. An exonuclease protection assay reveals heat-shock element and TATA box DNA-binding proteins in crude nuclear extracts. Nature. 1985 Sep 5;317(6032):84–87. doi: 10.1038/317084a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yu Y. T., Manley J. L. Generation and functional analyses for base-substitution mutants of the adenovirus 2 major late promoter. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Dec 21;12(24):9309–9321. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.24.9309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]